Ammeter

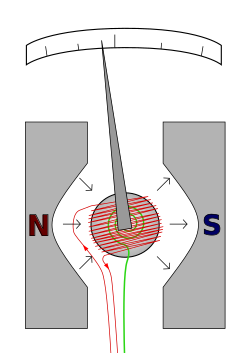
Spring providing restoring force
This illustration is conceptual; in a practical meter, the iron core is stationary, and front and rear spiral springs carry current to the coil, which is supported on a rectangular bobbin. Furthermore, the poles of the permanent magnet are arcs of a circle.



An ammeter is a measuring instrument used to measure the current in a circuit. Electric currents are measured in amperes (A), hence the name. Instruments used to measure smaller currents, in the milliampere or microampere range, are designated as milliammeters or microammeters. Early ammeters were laboratory instruments which relied on the Earth's magnetic field for operation. By the late 19th century, improved instruments were designed which could be mounted in any position and allowed accurate measurements in electric power systems.
History
The relation between electric current, magnetic fields and physical forces was first noted by Hans Christian Ørsted who, in 1820, observed a compass needle was deflected from pointing North when a current flowed in an adjacent wire. The tangent galvanometer was used to measure currents using this effect, where the restoring force returning the pointer to the zero position was provided by the Earth's magnetic field. This made these instruments usable only when aligned with the Earth's field. Sensitivity of the instrument was increased by using additional turns of wire to multiply the effect – the instruments were called "multipliers".[1]
Types
Moving-coil
The D'Arsonval galvanometer is a moving coil ammeter. It uses magnetic deflection, where current passing through a coil placed in the magnetic field of a permanent magnet causes the coil to move. The modern form of this instrument was developed by Edward Weston, and uses two spiral springs to provide the restoring force. The uniform air gap between the iron core and the permanent magnet poles make the deflection of the meter linearly proportional to current. These meters have linear scales. Basic meter movements can have full-scale deflection for currents from about 25 microamperes to 10 milliamperes.[2]
Because the magnetic field is polarised, the meter needle acts in opposite directions for each direction of current. A DC ammeter is thus sensitive to which way round it is connected; most are marked with a positive terminal, but some have centre-zero mechanisms[note 1] and can display currents in either direction. A moving coil meter indicates the average (mean) of a varying current through it,[note 2] which is zero for AC. For this reason moving-coil meters are only usable directly for DC, not AC.
This type of meter movement is extremely common for both ammeters and other meters derived from them, such as voltmeters and ohmmeters.
Moving magnet
Moving magnet ammeters operate on essentially the same principle as moving coil, except that the coil is mounted in the meter case, and a permanent magnet moves the needle. Moving magnet Ammeters are able to carry larger currents than moving coil instruments, often several tens of Amperes, because the coil can be made of thicker wire and the current does not have to be carried by the hairsprings. Indeed, some Ammeters of this type do not have hairsprings at all, instead using a fixed permanent magnet to provide the restoring force.
Electrodynamic
An electrodynamic movement uses an electromagnet instead of the permanent magnet of the d'Arsonval movement. This instrument can respond to both alternating and direct current[2] and also indicates true RMS for AC. See Wattmeter for an alternative use for this instrument.
Moving-iron
Moving iron ammeters use a piece of iron which moves when acted upon by the electromagnetic force of a fixed coil of wire. The moving-iron meter was invented by Austrian engineer Friedrich Drexler in 1884.[3] This type of meter responds to both direct and alternating currents (as opposed to the moving-coil ammeter, which works on direct current only). The iron element consists of a moving vane attached to a pointer, and a fixed vane, surrounded by a coil. As alternating or direct current flows through the coil and induces a magnetic field in both vanes, the vanes repel each other and the moving vane deflects against the restoring force provided by fine helical springs.[2] The deflection of a moving iron meter is proportional to the square of the current. Consequently, such meters would normally have a non linear scale, but the iron parts are usually modified in shape to make the scale fairly linear over most of its range. Moving iron instruments indicate the RMS value of any AC waveform applied. Moving iron ammeters are commonly used to measure current in industrial frequency AC circuits.
Hot-wire
In a hot-wire ammeter, a current passes through a wire which expands as it heats. Although these instruments have slow response time and low accuracy, they were sometimes used in measuring radio-frequency current.[2] These also measure true RMS for an applied AC current.
Digital
In much the same way as the analogue ammeter formed the basis for a wide variety of derived meters, including voltmeters, the basic mechanism for a digital meter is a digital voltmeter mechanism, and other types of meter are built around this.
Digital ammeter designs use a shunt resistor to produce a calibrated voltage proportional to the current flowing. This voltage is then measured by a digital voltmeter, through use of an analog to digital converter (ADC); the digital display is calibrated to display the current through the shunt. Such instruments are often calibrated to indicate the RMS value for a sine wave only, but many designs will indicate true RMS within limitations of the wave crest factor.
Integrating

There is also a range of devices referred to as integrating ammeters.[4][5] In these ammeters the current is summed over time, giving as a result the product of current and time; which is proportional to the electrical charge transferred with that current. These can be used for metering energy (the charge needs to be multiplied by the voltage to give energy) or for estimating the charge of a battery or capacitor.
Picoammeter
A picoammeter, or pico ammeter, measures very low electric current, usually from the picoampere range at the lower end to the milliampere range at the upper end. Picoammeters are used for sensitive measurements where the current being measured is below the theoretical limits of sensitivity of other devices, such as Multimeters.
Most picoammeters use a "virtual short" technique and have several different measurement ranges that must be switched between to cover multiple decades of measurement. Other modern picoammeters use log compression and a "current sink" method that eliminates range switching and associated voltage spikes.[6] Special design and usage considerations must be observed in order to reduce leakage current which may swamp measurements such as special insulators and driven shields, triaxial cable is often used for probe connections.
Application
The majority of ammeters are either connected in series with the circuit carrying the current to be measured (for small fractional amperes), or have their shunt resistors connected similarly in series. In either case, the current passes through the meter or (mostly) through its shunt. Ammeters must not be connected directly across a voltage source since their internal resistance is very low and excess current would flow. Ammeters are designed for a low voltage drop across their terminals, much less than one volt; the extra circuit losses produced by the ammeter are called its "burden" on the measured circuit.
Ordinary Weston-type meter movements can measure only milliamperes at most, because the springs and practical coils can carry only limited currents. To measure larger currents, a resistor called a shunt is placed in parallel with the meter. The resistances of shunts is in the integer to fractional milliohm range. Nearly all of the current flows through the shunt, and only a small fraction flows through the meter. This allows the meter to measure large currents. Traditionally, the meter used with a shunt has a full-scale deflection (FSD) of 50 mV, so shunts are typically designed to produce a voltage drop of 50 mV when carrying their full rated current.

To make a multi-range ammeter, a selector switch can be used to connect one of a number of shunts across the meter. It must be a make-before-break switch to avoid damaging current surges through the meter movement when switching ranges.
A better arrangement is the Ayrton shunt or universal shunt, invented by William E. Ayrton, which does not require a make-before-break switch. It also avoids any inaccuracy because of contact resistance. In the figure, assuming for example, a movement with a full-scale voltage of 50 mV and desired current ranges of 10 mA, 100 mA, and 1 A, the resistance values would be: R1=4.5 ohms, R2=0.45 ohm, R3=0.05 ohm. And if the movement resistance is 1000 ohms, for example, R1 must be adjusted to 4.525 ohms.
Switched shunts are rarely used for currents above 10 amperes.
Zero-center ammeters are used for applications requiring current to be measured with both polarities, common in scientific and industrial equipment. Zero-center ammeters are also commonly placed in series with a battery. In this application, the charging of the battery deflects the needle to one side of the scale (commonly, the right side) and the discharging of the battery deflects the needle to the other side. A special type of zero-center ammeter for testing high currents in cars and trucks has a pivoted bar magnet that moves the pointer, and a fixed bar magnet to keep the pointer centered with no current. The magnetic field around the wire carrying current to be measured deflects the moving magnet.
Since the ammeter shunt has a very low resistance, mistakenly wiring the ammeter in parallel with a voltage source will cause a short circuit, at best blowing a fuse, possibly damaging the instrument and wiring, and exposing an observer to injury.
In AC circuits, a current transformer converts the magnetic field around a conductor into a small AC current, typically either 1 A or 5 A at full rated current, that can be easily read by a meter. In a similar way, accurate AC/DC non-contact ammeters have been constructed using Hall effect magnetic field sensors. A portable hand-held clamp-on ammeter is a common tool for maintenance of industrial and commercial electrical equipment, which is temporarily clipped over a wire to measure current. Some recent types have a parallel pair of magnetically soft probes that are placed on either side of the conductor.
See also
- Clamp meter
- Class of accuracy in electrical measurements
- Electric circuit
- Electrical measurements
- Electronics
- List of electronics topics
- Measurement category
- Multimeter
- Ohmmeter
- Rheoscope
- Voltmeter
Notes
References
- ^ L. A. Geddes, Looking back: how measuring electric current has improved through the ages, IEEE Potentials, Feb/Mar 1996, pages 40-42
- ^ a b c d Frank Spitzer and Barry Howarth, Principles of Modern Instrumentation, Holt, Rinehart and Winston, New York, 1972, ISBN 0-03-080208-3 chapter 11
- ^ "Fragebogen aus der Personenmappe Friedrich Drexler (1858 - 1945)". Technisches Museum Wien. Retrieved 2013-07-10.
- ^ http://www-project.slac.stanford.edu/lc/local/notes/dr/Wiggler/Wigrad_BK.pdf
- ^ http://dit.upc.es/lpdntt/biblio/BREUS/LEE97a.pdf
- ^ Ix Innovations, LLC. "PocketPico Ammeter Theory of Operation" (PDF). Retrieved 2014-07-11.
External links
- DC Metering Circuits chapter from Lessons In Electric Circuits Vol 1 DC free ebook and Lessons In Electric Circuits series.
