Bernard Morin
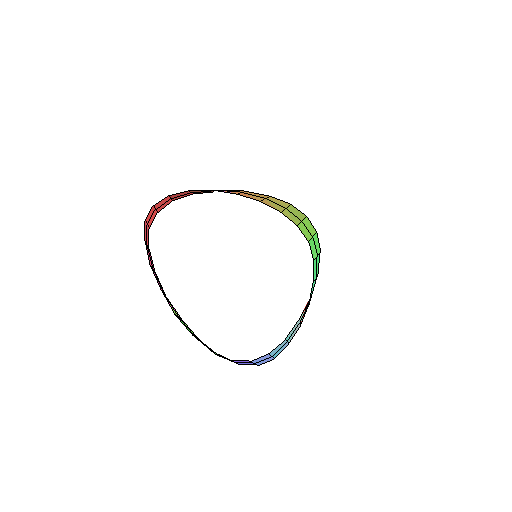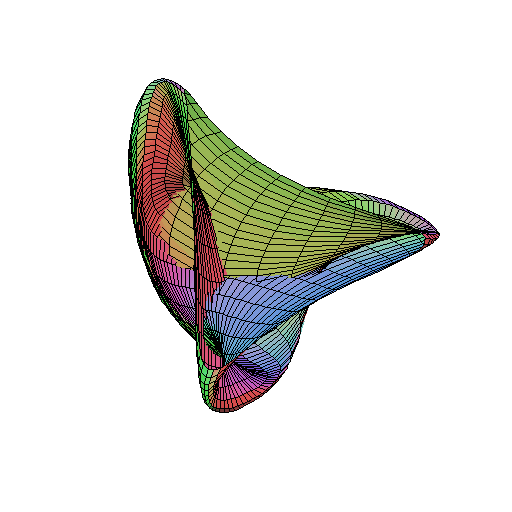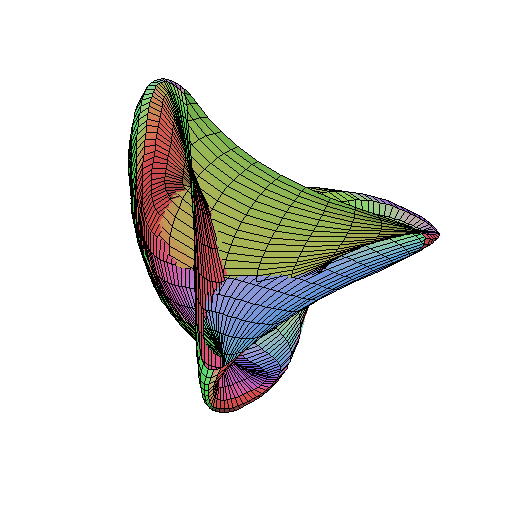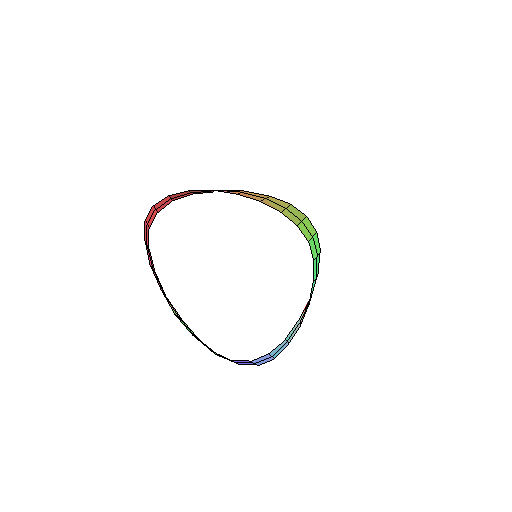
Bernard Morin is a French mathematician, specifically a topologist, born in 1931, who is now retired. He has been blind since age 6 due to glaucoma, but his blindness did not prevent him from having a successful career in mathematics.
Morin was a member of the group that first exhibited an eversion of the sphere, i.e. a homotopy (topological metamorphosis) which starts with a sphere and ends with the same sphere but turned inside-out. (See Smale's paradox.) He also discovered the Morin surface, which is a half-way model for the sphere eversion, and used it to prove a lower bound on the number of steps needed to turn a sphere inside out.
He discovered the first parametrization of Boy's surface (earlier used as a half-way model) in 1978. His graduate student François Apéry later discovered (in 1986) another parametrization of Boy's surface, which conforms to the general method for parametrizing non-orientable surfaces.[1]
Morin worked at the Institute for Advanced Study in Princeton. Most of his career, though, he spent at the University of Strasbourg.
- Morin's surface.
References
- ^ Weisstein, Eric W. "Boy Surface." From MathWorld--A Wolfram Web Resource. http://mathworld.wolfram.com/BoySurface.html
- George K. Francis & Bernard Morin (1980) "Arnold Shapiro’s Eversion of the Sphere", Mathematical Intelligencer 2(4):200–3.
External links
- Photos of Morin with stereolithography models of sphere eversion.
- The World of Blind Mathematicians, PDF file at the American Mathematical Society's website.
