Chandigarh Capital Region
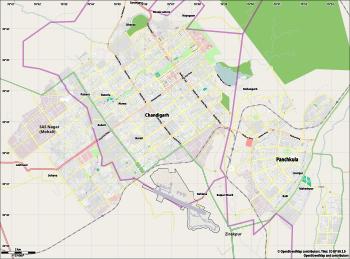
Chandigarh Capital Region (CCR) or Chandigarh Metropolitan Region (CMR) is an area, which includes the union territory city of Chandigarh, and its neighboring cities of Mohali, Kharar, Zirakpur, New Chandigarh (in Punjab) and Panchkula (in Haryana). Chandigarh Administration, Greater Mohali Area Development Authority (GMADA) and Haryana Urban Development Authority (HUDA) are different authorities responsible for development of this region.[1]
The economy of the region is interdependent as the area is continuously inhabited, though falling under different states. There is a lot of movement of people and goods daily to and from suburbs, like most of the people working in Chandigarh live in a suburb like Zirakpur. The local industry is on the outskirts like Derabassi, Lalru and Baddi.
History
The Indian Ministry of Home Affairs asked the Chandigarh Administration in October 2011 to "coordinate with the Punjab and Haryana governments for working out the modalities" of a Regional Planning Board (RPB) for the Chandigarh Capital Region (CCR). The intention was to harmonize and improve facilities across the region and coordinate local administrations. Responsibilities of the RPB would include disaster management, health planning, biomedical waste and traffic management.[2][3]
The 'Master Plan 2031' submitted to the UT administrator in January 2013 included a proposal for a "inter-state regional plan for the Chandigarh Capital Region".[4] However the final plan confined itself to the UT boundary, and did not mention the proposed "Chandigarh Capital Region".[5] Instead, the plan expected responsibilities for the region to be coordinated between Punjab, Haryana and Chandigarh UT, and that the Chandigarh plan "with the GMADA Plan 2056 and the Haryana Development Plan should together arrive at a metropolitan plan".[6]
As of May 2019[update] the Chandigarh capital region along the lines of the National Capital Region remains an un-implemented concept.[7]
Definition
The cities, towns and areas that would be part of the Chandigarh Capital region have a total population of 1,758,653 and their city-wise populations are:
| Rank | City | Union territory / State | Population (2011)[8] |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Chandigarh | Chandigarh | 1,055,450 |
| 2 | Mohali | Punjab | 176,152 |
| 3 | Panchkula | Haryana | 210,175 |
| 4 | Kharar | Punjab | 221,323 |
| 5 | New Chandigarh | Punjab | |
| 6 | Zirakpur | Punjab | 95,553 |
Overall Chandigarh ( UT ), Mohali District (Punjab) and Panchkula District ( Haryana ) are part of the CCR
Derabassi, Lalru, Banur and Kurali in Mohali district. Kalka, Pinjore, Barwala and Raipur Rani in the Panchkula district can be considered another town in Chandigarh Capital Region
In future, it can be expanded up to BBN ( Baddi-Brotiwala-Nalagarh) Area in Himachal Pradesh and Roopnagar City in Punjab.
Industry
Chandigarh IT Park is a technology park located within Chandigarh, with presence of companies like IDS Infotech, Airtel, Tech Mahindra and Infosys.
Mohali IT City is the infrastructure to facilitate information technology in the city. It spreads over 1700 acres developed by GMADA situated near Chandigarh International Airport. Infosys is given 50 Acres of land to develop state of art campus.
Quark has 40 Acres campus in Mohali for Quark software Inc. and other IT Companies like Emerson and Infosys.
Mahindra-Swaraj Tractors, Mohali
Godrej - Godrej & Boyce Mfg Co Ltd, Mohali
Semi-Conductor Laboratory ( SCL), Mohali
Punwire,Puncom, , Verka and Sun Pharma also have Plants in Mohali
Dera Bassi - Lalru is another belt with mostly medium industry, this place has many spinning mills including the Nahar group. Bhushan Steel also has a presence here.
Panchkula IT Park is the state of art infrastructure to facilitate information technology in the city. It spreads over 74 acres developed by HSIIDC situated in sector 22. Bharat Electronics Limited or B.E.L has a factory in Panchkula.
Hindustan Machine Tools has a tractor factory in Pinjore, while Associated Cement Companies has a cement factory in Pinjore.
SML-ISUZU has Bus & Truck Plant near Ropar City.
This region is the zonal headquarters for a large number of banks, their offices are mainly in the "Bank Square" in sector 17 Chandigarh. This area also houses the regional office (usually covering Punjab, Northern Haryana, Himachal Pradesh and Jammu and Kashmir) for a lot of FMCG companies.
Healthcare Infrastructure
The prominent hospitals in the region are
- Post Graduate Institute of Medical Education and Research PGIMER, Sector 12, Chandigarh
- Govt Medical Superspeciality Hospital (GMSH), Sector 16, Chandigarh
- Govt Medical College and Hospital (GMCH), Sector 32, Chandigarh
- Dr. B.R. Ambedkar State Institute of Medical Sciences, Sector 56, Mohali
- Max Hospital, Sector 56, Mohali
- Fortis Hospital, Sector 62, Mohali
- General Hospital, Sector 6, Panchkula
- Command Hospital, Chandimandir Cantonment
- Alchemist Hospital, Sector 21, Panchkula
- Paras Hospital, HSIIDC Park, Sector 22, Panchkula
Educational Institutes
Schools
- Yadavindra Public School, Mohali
- St. John's High School, Chandigarh
- Government Model Senior Secondary School, Sector 16, Chandigarh
- Shivalik Public School, Chandigarh
- VHS
- Bhavan Vidyalaya, Chandigarh
- Strawberry Fields School, Chandigarh
- Carmel Convent School, Chandigarh
- St Soldier’s School, Panchkula
Colleges and Universities
- IIT Ropar
- IISER Mohali
- NIPER Mohali
- ISB Mohali
- INST Mohali
- National Agro Biotechnology Institute Mohali
- C-DAC Mohali
- National Institute of Electronics & Information Technology,Ropar
- National Institute of Electronics & Information Technology,Chandigarh
- P.U. Chandigarh
- Punjab Engineering College, Chandigarh
- Chandigarh College of Engineering & Technology
- PGI Chandigarh
- IMTECH Chandigarh
- CSIO Chandigarh
- TBRL-DRDO Chandigarh
- GMCH, Chandigarh
- NIFT Panchkula
- Chandigarh University
- Plaksha University
- Amity University, Mohali
- Army Institute of Law
- NIIFT Mohali
Sports
Punjab Cricket Association IS Bindra Stadium, Mohali
Maharaja Yadavindra Singh International Cricket Stadium, New Chandigarh
International Hockey Stadium, Mohali
GMADA Sports Complex, Sec-78, Mohali
Sports Complex, Sector 7, Chandigarh
Chandigarh Lawn tennis Association, CLTA Stadium, Sector 10, Chandigarh
Cricket Stadium Sector 16, Chandigarh
Hockey Stadium and Sports Complex, Sector-42, Chandigarh
Golf Course, Sector 6, Chandigarh
Tau Devi Lal Cricket Stadium, Sector 3 Panchkula
Golf Course, Sector 3 Panchkula
Sports Authority of India stadium, Dayalpura, Zirakpur
Transport
- Road transport
- Rail transport
- Air transport
Chandigarh International Airport is located near Aerocity in Mohali. It has both domestic and international flights.
External links
References
- ^ "Beware! Change in city's status will ruin its uniqueness". The Tribune. 23 July 2018. Retrieved 3 January 2019.
- ^ "Decks cleared for Chandigarh Capital Region". The Times of India. Archived from the original on 7 October 2011.
- ^ "Chandigarh Capital Region gets nod". Daily Post India. Chandigarh. 24 January 2012. Archived from the original on 8 April 2013.
- ^ "Chandigarh Capital Region included in Master Plan '31". The Times of India. Archived from the original on 11 April 2013.
- ^ "Chandigarh Master Plan 2031, Preamble" (PDF). Chandigarh Administration. p. 9.
- ^ "Chandigarh Master Plan 2031, Regional Context" (PDF). Chandigarh Administration. p. 23.
- ^ Yadav, Deepak (5 May 2015). "First steps to make Tricity one". The Times of India.
- ^ "India: Major Agglomerations". .citypopulation.de. Retrieved 14 December 2014.
