Economy of the Czech Republic
Parts of this article (those related to Infobox economy) need to be updated. (January 2024) |
 Business district in Prague | |
| Currency | Czech koruna (CZK) |
|---|---|
| Calendar year | |
Trade organisations | EU, WTO (via EU membership) and OECD |
Country group | |
| Statistics | |
| Population | |
| GDP | |
| GDP rank | |
GDP growth |
|
GDP per capita | |
GDP per capita rank | |
GDP by sector |
|
| 2.25% (since 6 February 2020)[6] | |
Population below poverty line | |
Labour force | |
Labour force by occupation |
|
| Unemployment | |
Average gross salary | CZK 37,929 / €1,464 monthly (Q1, 2022)[17] |
| CZK 30,626 / €1,182 monthly (Q1, 2022)[18] | |
Main industries |
|
| External | |
| Exports | $161.2 billion (2016)[19] |
Export goods |
|
Main export partners | |
| Imports | $140.3 billion (2016)[19] |
Import goods |
|
Main import partners | |
FDI stock | |
Gross external debt | |
| −17 % of GDP (2020)[25] | |
| Public finances | |
| Revenues | 42.1% of GDP (2019)[26] |
| Expenses | 41.9% of GDP (2019)[26] |
| |
| $151.69 billion (January 2018 est.; 17th)[29] | |
All values, unless otherwise stated, are in US dollars. | |
The economy of the Czech Republic is a developed export-oriented social market economy based in services, manufacturing, and innovation that maintains a high-income welfare state and the European social model.[30] The Czech Republic participates in the European Single Market as a member of the European Union, and is therefore a part of the economy of the European Union. It uses its own currency, the Czech koruna, instead of the euro. It is a member of the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD). The Czech Republic ranks 12th in inequality-adjusted human development and 24th in World Bank Human Capital Index, ahead of countries such as the United States, the United Kingdom or France. It was described by The Guardian as "one of Europe’s most flourishing economies".[31]
The industry sector accounts for 37% of the economy, while services account for 61% and agriculture for 2%. The principal industries are high tech engineering, electronics and machine-building,[32] steel production, transportation equipment (automotive, rail and aerospace industry), chemicals, advanced materials and pharmaceuticals. The major services are research and development, ICT and software development, nanotechnology and life sciences.[32] Its main agricultural products are cereals, vegetable oils and hops.
As of 2022, the Czech GDP per capita at purchasing power parity is $46,811 and $28,077 at nominal value.[4] As of September 2021, the unemployment rate in the Czech Republic was the lowest in the EU at 2.6%,[33] and the poverty rate is the second lowest of OECD members, following Denmark.[34] The Czech Republic ranks 21st in the Index of Economic Freedom (ranked behind Chile),[35] 24th in the Global Innovation Index (ranked behind Australia),[36] 32nd in the Global Competitiveness Report,[37] 41st in the ease of doing business index and 25th in the Global Enabling Trade Report (ranked behind Canada).[38] The largest trading partner for both export and import is Germany, followed by other members of the EU. The Czech Republic has a highly diverse economy that ranks 7th in the 2019 Economic Complexity Index.[39]
History
Pre–1989
The Czech lands were among the first industrialized countries in continental Europe during the German Confederation era. The Czech industrial tradition dates back to the 19th century, when the Lands of the Bohemian Crown were the economic and industrial heartland of the Austrian Empire and later the Austrian side of Austria-Hungary. The Czech lands produced a majority (about 70%) of all industrial goods in the Empire, some of which were almost monopolistic. The Czechoslovak crown was introduced in April 1919. Introduced at a 1:1 ratio to the Austro-Hungarian currency, it became one of the most stable currencies in Europe. The First Republic became one of the 10 most developed countries of the world (behind the U.S., Canada, Australia, Switzerland, Argentina, Britain, France, Sweden and Belgium).[40]
The consequences of the 1938 Munich Agreement and subsequent occupation were disastrous for the economy. After the occupation and forced subordination of the economy to German economic interests, the crown was officially pegged to the mark at a ratio of 1:10, even though the unofficial exchange rate was 1 to 6-7 and Germans immediately started buying Czech goods in large quantities.[41]
In accordance with Stalin's development policy of planned interdependence, all the economies of the socialist countries were tightly linked to that of the Soviet Union. Czechoslovakia was the most prosperous country in the Eastern Bloc, however it continued to lag further behind the rest of the developed world. With the disintegration of the communist economic alliance in 1991, Czech manufacturers lost their traditional markets among former communist countries in the east.
Today, this heritage is both an asset and a liability. The Czech Republic has a well-educated population and a densely developed infrastructure.[42]



1989–1995
The "Velvet Revolution" in 1989, offered a chance for profound and sustained political and economic reform. Signs of economic resurgence began to appear in the wake of the shock therapy that the International Monetary Fund (IMF) labelled the "big bang" of January 1991. Since then, consistent liberalization and astute economic management has led to the removal of 95% of all price controls, low unemployment, a positive balance of payments position, a stable exchange rate, a shift of exports from former communist economic bloc markets to Western Europe, and relatively low foreign debt. Inflation has been higher than in some other countries – mostly in the 10% range[citation needed] – and the government has run consistent modest budget deficits.[citation needed]
Two government priorities have been strict fiscal policies and creating a good climate for incoming investment in the republic. Following a series of currency devaluations, the crown has remained stable in relation to the US dollar.[citation needed] The Czech crown became fully convertible for most business purposes in late 1995.
In order to stimulate the economy and attract foreign partners, the government has revamped the legal and administrative structure governing investment. With the breakup of the Soviet Union, the country, till that point highly dependent on exports to the USSR, had to make a radical shift in economic outlook: away from the East, and towards the West. This necessitated the restructuring of existing banking and telecommunications facilities, as well as adjusting commercial laws and practices to fit Western standards. Further minimizing reliance on a single major partner, successive Czech governments have welcomed U.S. investment (amongst others) as a counterbalance to the strong economic influence of Western European partners, especially of their powerful neighbour, Germany. Although foreign direct investment (FDI) runs in uneven cycles, with a 12.9% share of total FDI between 1990 and March 1998, the U.S. was the third-largest foreign investor in the Czech economy, behind Germany and the Netherlands.
Progress toward creating a stable investment climate was recognized when the Czech Republic became the first post-communist country to receive an investment-grade credit rating by international credit institutions.[citation needed]
The country boasts a flourishing consumer production sector and has privatized most state-owned heavy industries through the voucher privatization system. Under the system, every citizen was given the opportunity to buy, for a moderate price, a book of vouchers that represents potential shares in any state-owned company. The voucher holders could then invest their vouchers, increasing the capital base of the chosen company, and creating a nation of citizen share-holders. This is in contrast to Russian privatization, which consisted of sales of communal assets to private companies rather than share-transfer to citizens. The effect of this policy has been dramatic. Under communism, state ownership of businesses was estimated to be 97%.[citation needed] Privatization through restitution of real estate to the former owners was largely completed in 1992. By 1998, more than 80% of enterprises were in private hands. Now completed,[citation needed] the program has made Czechs, who own shares of each of the Czech companies, one of the highest per-capita share owners in the world.[citation needed]
1995–2000

The country's economic transformation was far from complete. Political and financial crises in 1997, shattered the Czech Republic's image as one of the most stable and prosperous of post-Communist states. Delays in enterprise restructuring and failure to develop a well-functioning capital market played major roles in Czech economic troubles, which culminated in a currency crisis in May. The formerly pegged currency was forced into a floating system as investors sold their Korunas faster than the government could buy them. This followed a worldwide trend to divest from developing countries that year. Investors also worried the republic's economic transformation was far from complete. Another complicating factor was the current account deficit, which reached nearly 8% of GDP.
In response to the crisis, two austerity packages were introduced later in the spring (called vernacularly "The Packages"), which cut government spending by 2.5% of GDP. Growth dropped to 0.3% in 1997, −2.3% in 1998, and −0.5% in 1999. The government established a restructuring agency in 1999 and launched a revitalization program – to spur the sale of firms to foreign companies. Key priorities included accelerating legislative convergence with EU norms, restructuring enterprises, and privatising banks and utilities. The economy, fueled by increased export growth and investment, was expected to recover by 2000.
2000–2005
Growth in 2000–05 was supported by exports to the EU, primarily to Germany, and a strong recovery of foreign and domestic investment. Domestic demand is playing an ever more important role in underpinning growth as interest rates drop and the availability of credit cards and mortgages increases. Current account deficits of around 5% of GDP are beginning to decline as demand for Czech products in the European Union increases. Inflation is under control. Recent accession to the EU gives further impetus and direction to structural reform. In early 2004 the government passed increases in the Value Added Tax (VAT) and tightened eligibility for social benefits with the intention to bring the public finance gap down to 4% of GDP by 2006, but more difficult pension and healthcare reforms will have to wait until after the next elections. Privatization of the state-owned telecommunications firm Český Telecom took place in 2005. Intensified restructuring among large enterprises, improvements in the financial sector, and effective use of available EU funds should strengthen output growth.
2005–2010
Growth continued in the first years of the EU membership. The credit portion of the Financial crisis of 2007–2010 did not affect the Czech Republic much, mostly due to its stable banking sector which has learned its lessons during a smaller crisis in the late 1990s and became much more cautious. As a fraction of the GDP, the Czech public debt is among the smallest ones in Central and Eastern Europe. Moreover, unlike many other post-communist countries, an overwhelming majority of the household debt – over 99% – is denominated in the local Czech currency. That's why the country wasn't affected by the shrunken money supply in the U.S. dollars.
However, as a large exporter, the economy was sensitive to the decrease of the demand in Germany and other trading partners. In the middle of 2009, the annual drop of the GDP for 2009 was estimated around 3% or 4.3%,[43] a relatively modest decrease. The impact of the economic crisis may have been limited by the existence of the national currency that temporarily weakened in H1 of 2009, simplifying the life of the exporters.
2010–2015

From the financial crisis of 2007–2010, Czech Republic is in stagnation or decreasing of GDP. Some commenters and economists criticising fiscally conservative policy of Petr Nečas' right-wing government, especially criticising ex-minister of finance, Miroslav Kalousek. Miroslav Kalousek in a 2008 interview, as minister of finance in the center-right government of Mirek Topolánek, said "Czech Republic will not suffer by financial crisis".[44] In September 2008, Miroslav Kalousek formed state budget with projection of 5% GDP increase in 2009. In 2009 and 2010, Czech Republic suffered strong economical crisis and GDP decreased by 4,5%. From 2009 to 2012, Czech Republic suffered highest state budget deficits in history of independent Czech Republic. From 2008 to 2012, the public debt of Czech Republic increased by 18,9%. Most decrease of industrial output was in construction industry (-25% in 2009, -15,5% in 2013). From 4Q 2009 to 1Q 2013, GDP decreased by 7,8%.
In 2012, Czech government increased VAT. Basic VAT was increased from 20% in 2012 to 21% in 2013 and reduced VAT increased from 14% to 15% in 2013. Small enterprises sales decreased by 21% from 2012 to 2013 as result of increasing VAT.[45] Patria.cz predicting sales stagnation and mild increase in 2013. Another problem is foreign trade. The Czech Republic is considered an export economy (the Czech Republic has strong machinery and automobile industries), however in 2013, foreign trade rapidly decreased which led to many other problems and increase of state budget deficit. In 2013, Czech National Bank, central bank, implemented controversial monetary step. To increase export and employment, CNB wilfully deflated Czech Crown (CZK), which inflation increased from 0.2% in November 2013, to 1.3% in 1Q 2014.
In 2014, GDP in the Czech Republic increased by 2% and is predicted to increase by 2.7% in 2015. In 2015, Czech Republic's economy grew by 4,2% and it's the fastest growing economy in the European Union.[46] On 29 May 2015, it was announced that growth of the Czech economy has increased from calculated 3,9% to 4,2%.[47]
2015–present

In August 2015, Czech GDP growth was 4.4%, making the Czech economy the highest growing in Europe.[49] On 9 November 2015, unemployment in the Czech Republic was at 5.9%, the lowest number since February 2009.[50] Dividends worth CZK 289 billion were paid to the foreign owners of Czech companies in 2016.[51]
European Union
Since its accession to the European Union in 2004, the Czech Republic has adopted the Economic and Monetary Union of the European Union and it is bound by the Treaty of Accession 2003 to adopt the Euro currency in the future.
The Czech Republic also receives €24.2bn between 2014 and 2020 from the European Structural and Investment Funds,[52][53] however, this sum does not outweigh the amount of capital outflow of profits of foreign owned firms from the Czech Republic into other EU members, at which the funds are aimed to compensate for.[54]
Public policy

This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (August 2017) |
As of 2016, the Czech Republic has the second lowest poverty rate of OECD members only behind Denmark.[34] The Czech healthcare system ranks 13th in the 2016 Euro health consumer index.[55]
Energy
The Czech Republic is a long-term net-exporter of electricity.[56] 97% -98% of oil used in the Czech Republic is imported.[57]
The government's 2015 energy policy designates nuclear power as main source of energy and its share is projected to rise to between 46% and 58% by 2040. Coal-powered energy is planned to fall to 21%, while renewables would rise to 25% and gas range from 5 to 15%.[58]
The updated energy strategy of 2019 envisions a gradual phase out of coal power share in total electricity generation from 2015's 46.2% down to 15.5% by 2040. The strategy sees nuclear energy as a non-carbon source of energy to be used during a slow transition to renewables in order to minimize the use of carbon-emitting fossil fuels that cause climate change. The increase in the share of nuclear, renewables and natural gas is to fill in the energy demand created by the impending gradual shutdowns of coal power stations.[59] This 2015-approved energy strategy expects construction of an additional nuclear reactor in the Temelín Nuclear Power Station and another one in the Dukovany Nuclear Power Station with the possibility of further expansion to two reactors in each power station. The older station of the two, Dukovany, is to be expanded before Temelín.[60] As of 2019, the financing models and contractor selection for the planned reactors are being negotiated by the government.[61]

| Energy source | 2015 | 2040 |
|---|---|---|
| Coal | 46.2% | 15.5% |
| Nuclear | 31.5% | 43.2% |
| Natural gas | 4.8% | 8.2% |
| Renewables | 10.1% | 20.2% |
Statistical indicators
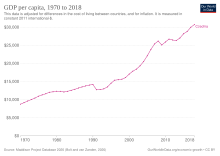





Development of main indicators
The following table shows the main economic indicators in 1980–2017. Inflation under 2% is in green.[62]
| Year | GDP (in Bil. US$ PPP) |
GDP per capita (in US$ PPP) |
GDP growth (real) |
Inflation rate (in Percent) |
Unemployment (in Percent) |
Government debt (in % of GDP) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2015 | ||||||
| 2016 | ||||||
| 2017 | ||||||
| 2018 est. | ||||||
| 2019 est. | ||||||
| 2020 est. |
Background
From the CIA World Factbook 2017 GDP (pp.): $353.9 billion (2016) GDP (nom.): $195.3 billion (2016) GDP Growth: 2.6% (2016) GDP per capita (pp.): $33,500 (2016) GDP per capita (nom.): $18,487 (2016) GDP by sector: Agriculture: 2.5% Industry: 37.5% Services: 60% (2016) Inflation: 0.7% (2016) Labour Force: 5.427 million (2017) Unemployment: 2,3% (September 2018)[63]
Industrial production growth rate: 3.5% (2016)
Household income or consumption by percentage share: (2015)
- lowest 10%: 4.1%
- highest 10%: 21.7%
Public Debt: 34.2% GDP (2018)
Trade and finance
Exports: $136.1 billion Export goods: machinery and transport equipment, raw materials, fuel, chemicals (2018)
Imports: $122.8 billion Import goods: machinery and transport equipment, raw materials and fuels, chemicals (2018) Current Account balance: $2.216 billion (2018) Export partners: Germany 32.4%, Slovakia 8.4%, Poland 5.8%, UK 5.2%, France 5.2%, Italy 4.3%, Austria 4.2% (2016) Import partners: Germany 30.6%, Poland 9.6%, China 7.5%, Slovakia 6.3%, Netherlands 5.3%, Italy 4.1% (2016) Reserves: $85.73 billion (31 December 2016) Foreign Direct Investment: $139.6 billion (31 December 2016) Czech Investment Abroad: $43.09 billion (31 December 2016) External debt: $138 billion (31 December 2016) Value of Publicly Traded Shares: $44.5 billion (31 December 2016)
Exchange rates:
- koruny (Kč) per US$1 – 21.82 Kč (September 2018), 18.75 (December 2010),[64] 18.277 (2007), 23.957 (2005), 25.7 (2004), 28.2 (2003), 32.7 (2002), 38.0 (2001), 38.6 (2001), 34.6 (1999), 32.3 (1998), 31.7 (1997), 27.1 (1996), 26.5 (1995)
- koruny (Kč) per EUR€1 – 27.33 (May 2015), 25.06 (December 2010)[64]
IT and Telecommunications
Households with access to fixed and mobile telephone access[65]
- landline telephone – 25% (2009)
- according to the Czech Statistical Office:[66] 55,2% (2005); 31,1% (2008); 27,6% (2009); 24,2% (2010); 23,4% (2011); 21,8% (2012)
- mobile telephone – 94% (2009)
- according to the Czech Statistical Office:[66] 81,2% (2005); 92,4% (2008); 94,6% (2009); 95,6% (2010); 96,2% (2011); 97,0% (2012)
Individuals with mobile telephone access
- according to the Czech Statistical Office:[67] 75,8% (2005); 90,6% (2009); 93,9% (2011); 96,0% (2012); 96,0% (2013)
Broadband penetration rate[65]
- fixed broadband – 19.1% (2010)
- mobile broadband – 3.5% (2010)
Individuals using computer and internet[65]
- computer – 67% (2009)
- according to the Czech Statistical Office:[68] 42,0% (2005); 59,2% (2009); 64,1% (2010); 67,1% (2011); 69,5% (2012); 70,2% (2013)
- internet – 80.9% (2019)
- according to the Czech Statistical Office:[69] 32,1% (2005); 55,9% (2009); 61,8% (2010); 65,5% (2011); 69,5% (2012); 70,4% (2013)
International rankings
Society and quality of life

- 27th in Human Development Index (2019)
- 13th in inequality-adjusted Human Development Index (2019)
- 7th in Henley Passport Index (2019)[70]
- 24th in Human Capital Index (2018)[71]
- 16th in Quality of Nationality Index (Henley & Partners, 2018)
- 27th in Legatum Prosperity Index (2019)
- 22th in Social Progress Index (2019)
Macroeconomics
- 41st in Ease of doing business index (2019)
- 7th in Economic Complexity Index (2018)
- 26th in Global Competitiveness Report (2022)
- 25th in Global Enabling Trade Report (2016)
- 24th in Global Innovation Index (2019)[72]
- 21th in Index of Economic Freedom (2018)
See also
- List of Czech regions by GDP
- Czech National Bank
- CzechInvest and CzechStartups.org
- International rankings of the Czech Republic
- Prague Stock Exchange
- Tourism in the Czech Republic
- Transport in the Czech Republic
Resources
- Statistická ročenka České republiky (Statistical Yearbook of the Czech Republic) by the Czech Statistical Office. The current line is published annually since 1957. Recent yearbooks can be read online (in Czech and English).
- Czechoslovakia published its first statistical yearbook in 1920. Historically used names: Statistická příručka Republiky československé, Statistická ročenka Protektorátu Čechy a Morava (during the occupation) and Statistická ročenka Československé socialistické republiky.
- Statistics about the Czech lands in Austria-Hungary were collected by Zemský statistický úřad Království českého (Provincial Statistical Office of the Czech Kingdom) founded in 1897. Two detailed books (in Czech and German) were published in 1909 and 1913.
- Benacek, Vladimir: economics of alliances and (dis)integration, an alternative interpretation of transition illustrated on Czech economic history (June 2002) - 25 p.
- Horvath, Julius: the Czech currency crisis of 1997 - En: Dabrovski, Marek: currency crises in emerging markets - New York: Springer, 2003 - p. 221-234
- OECD: economic surveys, Czech republic, 1991-2018 (OECD iLibrary)
- Zidek, Libor: from central planning to the market, the transformation of the Czech economy 1989-2004 Budapest: CEU press, 2017
References
- ^ "World Economic Outlook Database, April 2019". IMF.org. International Monetary Fund. Retrieved 29 September 2019.
- ^ "World Bank Country and Lending Groups". datahelpdesk.worldbank.org. World Bank. Retrieved 29 September 2019.
- ^ "Population".
- ^ a b c d e f g h i "World Economic Outlook Database, October 2020". IMF.org. International Monetary Fund. Retrieved 18 November 2021.
- ^ "Czechia". The World Factbook (2024 ed.). Central Intelligence Agency. Retrieved 14 February 2017. (Archived 2017 edition.)
- ^ Česká národní banka překvapila, zvýšila úrokové sazby. Koruna obratem zpevnila pod 25 za euro. ČT24. 06.02.2020.
- ^ "Vic než Milion Čechů žije pod hranicí chudoby. Potvrzují to data Českého statistického úřadu". info.cz. 18 March 2021. Retrieved 26 September 2021.
- ^ "People at risk of poverty or social exclusion" (PDF). ec.europa.eu. EAPN CR & EU, 2020. Archived (PDF) from the original on 10 October 2022. Retrieved 3 July 2020.
- ^ "Gini coefficient of equivalised disposable income - EU-SILC survey". ec.europa.eu. Eurostat. Retrieved 3 July 2020.
- ^ "Human Development Index (HDI)". hdr.undp.org. HDRO (Human Development Report Office) United Nations Development Programme. Retrieved 11 October 2022.
- ^ "Inequality-adjusted HDI (IHDI)". hdr.undp.org. UNDP. Retrieved 11 October 2022.
- ^ "Labor force, total - Czech Republic". data.worldbank.org. World Bank. Retrieved 18 November 2021.
- ^ "Employment rate by sex, age group 20-64". ec.europa.eu/eurostat. Eurostat. Retrieved 18 June 2019.
- ^ LABOR FORCE - BY OCCUPATION. The World Factbook.
- ^ "Unemployment by sex and age - monthly average". appsso.eurostat.ec.europa.eu. Eurostat. Retrieved 18 November 2021.
- ^ "Unemployment rate by age group". data.oecd.org. OECD. Retrieved 7 September 2020.
- ^ Average wages - 1st quarter of 2022. Czech Statistical Office.
- ^ "Výpočet čisté mzdy v roce 2021 vypocet.cz".
- ^ a b "Czech Republic exports, imports and trade balance By Country 2016".
- ^ Vyvážené zboží míří z 84 procent do EU. Do Ruska jde minimum. (Czech) ČT24. 13. 9. 2016.
- ^ "Export Partners of Czech Republic". CIA World Factbook. 2012. Archived from the original on 13 June 2007. Retrieved 24 July 2013.
- ^ Podíl dovozu ze zemí EU 28 na celkovém dovozu (%). Czech Statistical Office. 20.02.2017.
- ^ "Import Partners of Czech Republic". CIA World Factbook. 2012. Archived from the original on 13 June 2007. Retrieved 24 July 2013.
- ^ a b c d "Czechia". The World Factbook (2024 ed.). Central Intelligence Agency. Retrieved 24 April 2019. (Archived 2019 edition.)
- ^ "International investment position statistics - Statistics Explained". ec.europa.eu.
- ^ a b c d e f "GDP, government deficit/surplus and debt in the EU (in national currencies)" (PDF). ec.europa.eu. Eurostat. Archived (PDF) from the original on 10 October 2022. Retrieved 28 April 2020.
- ^ "Sovereigns rating list". Standard & Poor's. Retrieved 15 January 2012.
- ^ "Scope affirms Czech Republic's AA ratings; Outlook revised to Negative". Scope Ratings. Retrieved 9 July 2022.
- ^ "ČNB".
- ^ Christian Aspalter, Kim Jinsoo, Park Sojeung. Analysing the Welfare State in Poland, the Czech Republic, Hungary and Slovenia: An Ideal-Typical Perspective. Published on 10 March 2009. DOI: 10.1111/j.1467-9515.2009.00654.x
- ^ Robert Tait. Czech democracy ‘under threat’ from rising debt crisis. The Guardian. 6 January 2019.
- ^ a b Market Information: Sectors and Products Archived 23 September 2017 at the Wayback Machine. Businessinfo.cz
- ^ "Unemployment rates, seasonally adjusted, March 2018 (%)".
- ^ a b Federica Cocco. Israel and the US have the highest poverty rates in the developed world. Financial Times. Published on 19 October 2016.
- ^ "2022 Index of Economic Freedom Country Rankings".
- ^ "Global Innovation Index | Tracking Innovation through the COVID-19 Crisis". Archived from the original on 23 September 2016.
- ^ "The Global Competitiveness Report 2018". Retrieved 17 October 2018.
- ^ "Enabling Trade rankings".
- ^ Economic Complexity Rankings (ECI) Archived 14 March 2018 at the Wayback Machine. The Atlas of Economic Complexity. Access date 3 October 2017.
- ^ "Náš účet za komunismus". 18 October 2012. Retrieved 3 March 2015.
- ^ "History of Czechoslovak currency". zlate-mince.cz (in Czech). Retrieved 17 July 2014.
- ^ Petr Pabian (2009). "Europeanisation of higher education governance in the post-communist context: The case of the Czech Republic". European Integration and the Governance of Higher Education and Research: 257–278.
- ^ "Earth Times: show/278536,czech-economy-to-shrink-by-43-per-cent-in-2009.html". Retrieved 3 March 2015.
- ^ "Miroslav Kalousek: Moná vás zklamu: krize nám nehrozí". Hospodáøské noviny. 6 October 2008. Retrieved 3 March 2015.
- ^ "Služby - vývoj tržeb ve službách v ČR, 2015". Retrieved 3 March 2015.
- ^ "Česká ekonomika roste nejrychleji v celé EU". ČT24. Retrieved 9 June 2015.
- ^ "Tvorba a užití HDP - 1. čtvrtletí 2015, Rychlejší růst české ekonomiky potvrzen (in Czech)". Czech Statistical Office. Retrieved 29 May 2015.
- ^ "Figure 1.9 Share of ICT sector in total value added, 2013". doi:10.1787/888933224163.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ "Czechs Power EU's Fastest GDP Growth as Romania, Hungary Stumble". Bloomberg Business. Retrieved 14 August 2015.
- ^ "Nezaměstnanost v říjnu opět klesla, lidí bez práce je nejméně od února 2009" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 9 November 2015.
- ^ "Czech foreign owned companies take second biggest dividend yield in 2017:report". Radio Prague. 7 March 2018.
- ^ European Structural and Investment Funds: Country factsheet - Czech Republic. http://ec.europa.eu/. Published on 19/05/2016.
- ^ "DotaceEU - EU funds in the CZ".
- ^ Germany’s troubled relations with the Visegrad states show the limits to its power. The Economist. 14 June 2018.
- ^ "Euro Health Consumer Index 2016" (PDF). Health Consumer Powerhouse. Archived from the original (PDF) on 14 October 2017. Retrieved 8 April 2017.
- ^ Češi loni spotřebovali rekordní množství elektřiny. Země ale zůstává i významným exportérem energie. ČT24. 21. 2. 2019.
- ^ Zásobování České republiky ropou Archived 23 October 2018 at the Wayback Machine (in Czech).
- ^ Jo Harper. Czech Republic weighs nuclear options. Deutsche Welle. 17.04.2018.
- ^ a b Nový jaderný blok v Dukovanech by měl stát maximálně 200 miliard korun, věří Drábová. ČT24. 15. 6. 2019
- ^ Nejlepší reference na stavbu nových reaktorů v Česku mají Korejci, tvrdí Drábová (in Czech). 14. 10. 2018. aktualne.cz.
- ^ Nové jaderné zdroje budou financovány dceřinými firmami skupiny ČEZ, rozhodla vláda (in Czech). ČT24.
- ^ "Report for Selected Countries and Subjects". www.imf.org. Retrieved 15 September 2018.
- ^ Unemployment rates, seasonally adjusted, July 2016. Eurostat. 31 August 2016.
- ^ a b "CEE Basic Data - Key economic indicators and forecasts". Retrieved 3 March 2015.
- ^ a b c IT and telecommunications in Central and Eastern Europe Archived 11 October 2013 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ a b "Obsah nenalezen | ČSÚ".
- ^ "Obsah nenalezen | ČSÚ".
- ^ "Obsah nenalezen | ČSÚ".
- ^ "Persons and ICT".Page 4, Table C2
- ^ "Henley Passport Index" (PDF). www.henleypassportindex.com. Archived (PDF) from the original on 12 January 2019. Retrieved 8 January 2019.
- ^ WORLD DEVELOPMENT REPORT 2019. The World Bank.
- ^ "Global Innovation Index 2019" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 10 October 2022.
External links
- OECD Economic Survey of the Czech Republic
- Czech economic indicators Latest indicators collected by Czech national bank
- OECD's Czech Republic country Web site
- Doing business in Czech Republic at the Wayback Machine (archived 30 May 2008)
- Current economic data
- Economy: Development and potential at the Wayback Machine (archived 11 June 2008)
- Maldonado, Carlos Gustavo: República checa, transición del socialismo de Estado a la economía de mercado - En: economía de posguerra, blog de historia económica global
- Economy of the Czech Republic – Annual Trends
- World Bank Summary Trade Statistics Czech Republic


