Demographic estimates of the flight and expulsion of Germans
 |
| Flight and expulsion of Germans during and after World War II |
|---|
| (demographic estimates) |
| Background |
| Wartime flight and evacuation |
| Post-war flight and expulsion |
| Later emigration |
| Other themes |
Demographic estimates of the flight and expulsion of Germans have been derived by either the compilation of registered dead and missing persons or by a comparison of pre-war and post-war population data. Estimates of the number of displaced Germans vary in the range of 12.0–16.5 million. The death toll attributable to the flight and expulsions was estimated at 2.2 million by the West German government in 1958 using the population balance method. German records which became public in 1987 have caused some historians in Germany to put the actual total at about 500,000 based on the listing of confirmed deaths. The German Historical Museum puts the figure at 600,000 victims and says that the official figure of 2 million did not stand up to later review.[1] However, the German Red Cross still maintains that the total death toll of the expulsions is 2,251,500 persons.
Difficulty of developing accurate estimates[edit]
Due to a lack of accurate records listing confirmed deaths, estimates of German population transfers from 1945–1950 and associated deaths depended upon a population balance methodology. West German government official figures derived during the 1950s using the population balance method put the death toll at about 2 million. Recently some German historians believe the death toll is closer to 500,000 based on recently disclosed documentation that listed only confirmed deaths. The wide range of estimates stems from a number of factors. First, the ethnic German population in 1939 was by no means certain because bilingual persons were of dubious German ethnic identity. Second, Civilian losses were overstated because German military casualties in 1945 were poorly documented. Third, After the war it was difficult to gather reliable population data; post war census data in Central and Eastern Europe did not breakout the ethnic German population and during the Cold War there was a lack of cooperation between West Germany and communist bloc countries in the effort to locate persons reported missing. Persons reported missing may have been living in Eastern Europe after having been assimilated into the local population. Estimates of total populations expelled and deaths often include figures from the evacuation, because these people were not allowed to return, thus making it difficult to arrive at an accurate and undisputed estimate of population movements and deaths due solely to the expulsions. Some of the differences may arise from political bias, as the expulsion of Germans was widely utilized as political weapon during the Cold War.
There are also disputes over the definition of "expulsion", which may cover the flight and evacuation during the war as well as forced labor and internment before expulsion and deaths due to malnutrition and disease in the post war era. The estimated losses include civilians killed in battle during the flight and evacuation in the final months of the war as well as direct intentional actions of violent soldiers, militias and senseless killings by opportunistic mobs and individuals in the immediate aftermath of the war. Other deaths occurred in post war internment camps and the deportation to the USSR for forced labor. The privations of a forced migration in a postwar environment characterized by crime, chaos, famine, disease, and cold winter conditions added to the death toll. West German sources give only rough estimates to attribute the proportions of these deaths to specific causes.
Population balance method versus counts of confirmed deaths[edit]
The West German government during the cold war conducted investigations of the wartime flight and expulsions. The Schieder commission published a series of reports that documented the expulsions based on eyewitness accounts. Schieder chronicled the flight and expulsions, but did not provide background on the wartime crimes of Nazi Germany in Central and Eastern Europe that motivated the Allies to expel the Germans after the war. Schieder in 1953 estimated that 2 million persons perished in Poland, a figure that continues to endure in Germany.[2] Schieder's estimate of the casualties was superseded by a separate demographic analysis of prepared by the Federal Statistical Office of Germany, in 1958 they estimated losses at 2.225 million.[3] The German Church Search Service working with the German Red Cross attempted to trace and identify those who perished in the expulsions. The investigation of the Church Search Service was only partially successful, by 1965 they were able to confirm about 500,000 deaths but could not clarify the fates of 1.9 million persons that were listed as "unsolved". The findings of the Church Search Service were not published until 1987.[4][5][6] Another report was issued by the German Federal Archives that identified 600,000 civilian expulsion deaths due to crimes against international law. This report was not published until 1989.[7]
Ingo Haar who is currently on the faculty of the University of Vienna said on 14 November 2006 in Deutschlandfunk that about 500,000 to 600,000 victims are realistic, based on a German governmental studies initiated in the 1960s.[8] Haar said these numbers were compiled from actually reported deaths, while higher figures of about two million deaths were estimated with the population balance method in a German governmental study of 1958.[8] Haar said the higher estimates must be seen in the historical context of the 1950s, when the government of West Germany needed high numbers for political reasons.[8] During the Cold War West Germany wanted to revert to prewar borders in Central Europe. Military historian Rüdiger Overmans said on 6 December 2006 in Deutschlandfunk that only the about 500,000 registered deaths could be counted, and that the unaccounted cases calculated with the population balance method need be confirmed by further research.[9] However, on 29 November 2006 State Secretary in the German Federal Ministry of the Interior, Christoph Bergner, reaffirmed the position of the German government that 2 million civilians perished in the flight and expulsion from Central and Eastern Europe.[10] The German Red Cross in 2005 maintained that death toll in the expulsions is 2,251,500 persons.[11]
Demographics[edit]

Expulsion area[edit]
The Federal Expellee Law (BVFG[12]) defines the expulsion area (einheitliches Vertreibungsgebiet; i.e. uniform territory of expulsion) as the former eastern territories of Germany (lost by the First or Second World War), the former Austria-Hungary, Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, and Poland.[13]
According to a 1967 report by the West German Federal Ministry for Expellees, in 1950 there were 14,447,000 persons affected by the expulsions, 11,730,000 had fled or were expelled, and 2,717,000 still remained in their homelands. By 1966 the sum total of German expellees and their offspring had increased to 14,600,000 persons.[14] The higher figure of 14 million expellees is often cited by historians.[15][16][17][18][19]

Between 1944 and 1950, roughly 12 million ethnic Germans had fled or were expelled from east-central Europe. From 1951 to 1982 an additional 1.1 million persons of German ancestry emigrated from East-Central Europe to Germany.[20] In the eyes of German law there were a total of 16 million expellees in 1982 (see schedule below) if one also includes Germans resettled in Poland during the war by the Nazis, children born to expellees and persons who immigrated as Aussiedler to Germany from eastern Europe after 1950.[20][21][22]
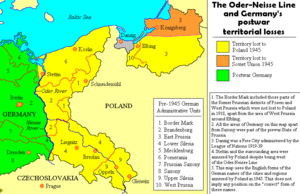
Germans fled, were evacuated, or were expelled as a result of actions of Nazi Germany, the Red Army, civilian militias, and/or the organized efforts of governments of the reconstituted states of Eastern Europe. Between 1944 and 1950, at least 12 million had fled or had been expelled and resettled to post-war Germany, almost all (11.5 million) from the territories of post-war Poland and Czechoslovakia.[23] About three million persons of German ancestry remained in the expulsion areas, but gradually emigrated westward in the Cold War era or have been assimilated into the local populations.[24] The areas from which the Germans fled or were expelled were subsequently repopulated by nationals of the states to which that territory now belonged, many of whom were Poles who fled or were expelled from the former Polish territories in the USSR. 148 000 of Polish citizens declared German nationality in 2011.[25]
The German Federal Expellee Law (BVFG) classifies the following as expellees (Vertriebene):
- Those German citizens or ethnic Germans who resided in the expulsion area prior to 31 December 1937 but fled or had been expelled (termed: Heimatvertriebene, i.e. homeland expellees;[26] BVFG § 1 (1)).
- German citizens or foreigners of German ethnicity who fled Nazi Germany, or any area it annexed or occupied, due to factual or impending Nazi persecution on political, racist or religious grounds (BVFG § 1 (1) No. 1).
- Ethnic Germans of originally foreign citizenship who were resettled during the war by the Nazis in eastern and western Europe and then fled or had been expelled are defined as expellees of the sub-group of Umsiedler by the West German Federal Expellee Law;[27] BVFG § 1 (1) No. 2);
- German citizens (expatriates) from pre-war western Europe and abroad who resettled in postwar Germany as a consequence of the Second World War (BVFG § 1 (1)). Western European democracies did not denaturalise their citizens of German ethnicity, so they were not systematically expelled, but German expatriates often had to quit as enemy aliens.
- Refugees and emigrants either originally of foreign citizenship but of German ethnicity, or who themselves or whose ancestors had involuntarily lost German citizenship, coming from the above-mentioned uniform territory of expulsion or from Albania, Bulgaria, China, Romania, the Soviet Union, or Yugoslavia, and arriving only after the end of general expulsions (usually by 1950) but not later as 31 December 1992 are also considered expellees under German law (termed: Aussiedler, about: emigrant of German ethnicity or descent; BVFG § 1 (2) No. 3).
- Expellees' spouses of whichever ethnicity or citizenship, and children born to expellees living in postwar Germany and abroad are classified as expellees too.[28]
Those ethnic Germans who emigrated from eastern Europe after 1 January 1993 are no longer classified as expellees under German law, but can apply for immigration and naturalisation under the special terms for Spätaussiedler (ethnic German "late emigrant").[12] Nazi German occupational functionaries and other German expatriates, who had relocated to German-annexed or German-occupied foreign territory during the war, are not considered expellees by German law unless they showed circumstances (such as marrying a resident of the respective area) indicating the intention to permanently settle abroad also for the time after the war (BVFG § 1 (4)).
Treated separately are refugees and expellees who had neither German citizenship nor German ethnicity but had fled or been expelled from their former domiciles and were stranded in West Germany or West Berlin before 1951, amounting to 130,000 in 1951, and only less than 3,000 in 2011. They were classified as displaced persons by the international refugee organizations until 1950, when West German authorities granted them the special status of heimatloser Ausländer (i.e. homeless foreigner, comprising either foreign citizens unable or unwilling to repatriate, or stateless persons with nowhere to go). They were covered under preferential naturalization rules, distinct from other legal aliens or stateless persons.[29]
Flight, expulsion and accounting for expellees up to 1950[30]
| Description | Population |
|---|---|
| Flight of civilians & returned POWs during 1945 | 4,500,000 |
| Official deportations 1946–50 | 4,500,000 |
| Returned POWs 1946–1950 | 2,600,000 |
| Total | 11,600,000 |
Expellees as defined by German law[31]
| Category of expellees (pre-war origin) | 1950 | 1982 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 – Pre-war Eastern Europe and Oder–Neisse region | 11,890,000 | 15,150,000 |
| 2 – Pre-war Soviet Union | 100,000 | 250,000 |
| 3 – Germans from west of Oder Neisse Resettled during war | 460,000 | 500,000 |
| 4 – Pre-war Western Europe and abroad | 235,000 | 240,000 |
| 5 – Germans settled in Western Europe during war | 65,000 | 80,000 |
| Total | 12,750,000 | 16,220,000 |
1—Pre-war eastern Europe ethnic Germans who resided in eastern Europe prior to the war.
1950–Oder–Neisse region (pre-war Germany): 6,980,000; Poland: 690,000; Danzig: 290,000; Czechoslovakia: 3,000,000; Hungary: 210,000; Romania: 250,000; Yugoslavia: 300,000; and Baltic States: 170,000.
1982–Oder–Neisse region (pre-war Germany): 8,850,000; Poland: 1,000,000; Danzig: 357,000; Czechoslovakia: 3,521,000; Hungary: 279,000; Romania: 498,000; Yugoslavia: 445,000; and Baltic States: 200,000.
2—Pre-war Soviet Union – ethnic Germans from the USSR who were resettled in German-annexed or occupied Poland during the war. 1950 (100,000); 1982 (250,000). During the war the Nazis resettled 370,000 ethnic Germans from the USSR in Poland; the Soviets returned 280,000 to the USSR after the war.
3—Germans from west of Oder Neisse resettled during war. This category includes only those German nationals living west of the Oder–Neisse line in 1939 who were resettled in occupied eastern Europe by Nazi Germany. In all 560,000 were resettled in Eastern Europe (530,000 in the postwar territory of Poland and 30,000 in Czechoslovakia). They are considered expellees in the eyes of German law. In 1950 460,000 were counted as expellees, and by 1982 the number had increased to 500,000. According to the German law defining expellees (BVFG § 1 (4)), Nazi German occupational functionaries and other German expatriates who had relocated to German-annexed or German-occupied foreign territory during the war were not considered expellees unless they showed circumstances (such as marrying a resident of the respective area) indicating the intention to permanently settle abroad after the war.[32] Section BVFG § 1 (5) of the German law excludes those persons as expellees who were implicated in Nazi war crimes and violations of human rights.[33]
An additional 1,320,000 Germans were settled in Poland and Czechoslovakia during war, including 410,000 German nationals living in the pre-war German Oder–Neisse region and 910,000 ethnic Germans from east-central Europe (166,000 from eastern Poland; 127,000 from the Baltic states; 212,000 from Romania; 35,000 from Yugoslavia; and 370,000 from the USSR in 1939 borders). These persons are included above with the first two categories of expellees, 1- Pre-war Eastern Europe and Oder–Neisse region and 2- Pre-war Soviet Union.[34]
3—Pre-war Western Europe and abroad - Ethnic Germans from pre-war Western Europe and abroad who resided in postwar Germany.[35]
4—Resettled in western Europe during war - During the war the Nazis resettled German nationals in western Europe. After the war those who returned to postwar Germany were considered expellees.[35]
Expellees' place of residence[36]
| Place of residence | 1950 | 1982 |
|---|---|---|
| West Germany | 8,100,000 | 11,000,000 |
| East Germany | 4,100,000 | 4,070,000 |
| Austria | 430,000 | 400,000 |
| Other countries | 120,000 | 750,000 |
| Total | 12,750,000 | 16,220,000 |
Post-war Germany and Austria[edit]

On 29 October 1946, the Allied Occupation Zones in Germany already held 9.5 million refugees and expellees: 3.6 million in the British zone, 3.1 million in the U.S. zone, 2.7 million in the Soviet zone, 100,000 in Berlin and 60,000 in the French zone.[37]
These numbers subsequently increased, with two million additional expellees counted in West Germany in 1950 for a total of 7.9 million[38] (16.3% of the population).[37][39] By origin, the West German expellee population consisted of about 5.5 million people from post-war Poland, primarily the former German East/new Polish West, two million from the former Sudetenland, and the rest primarily from Southeast Europe, the Baltic states and Russia.[40]

According to estimates made in West Germany, in the Soviet zone the number rose to 4.2 million by 1948 (24.2% of the population) and 4.4 million[38] by 1950,[39][41] when the Soviet zone became East Germany.
Thus, a total of 12.3 million Heimatvertriebene constituted 18% of the population in the two German states created from the Allied occupation zones (the Federal Republic of Germany and German Democratic Republic) in 1950, while another 500,000 expellees found refuge in Austria and other countries.[39] Because of their influx, the population of the post-war German territory had risen by 9.3 million (16%) from 1939 to 1950 despite wartime population losses.[38]
After the war, the area west of the new eastern border of Germany was crowded with expellees, some of them living in camps, some looking for relatives, some just stranded. Between 16.5%[42] and 19.3%[21] of the total population were expellees in the Western occupation zones and 24.2% in the Soviet occupation zone.[42] Expellees made up 45% of the population in Schleswig-Holstein and 40% in Mecklenburg-Vorpommern; similar percentages existed along the eastern border all the way to Bavaria, while in the westernmost German regions the numbers were significantly lower, especially in the French zone of occupation. Of the expellees initially stranded in East Germany, many migrated to West Germany, making up a disproportionally high number of post-war inner-German East-West migrants (close to one million of a three million total between 1949, when the West and East German states were created, and 1961, when the inner-German border was closed).[43]
German naturalisation of foreign ethnic German refugees and expellees[edit]
Ethnic German refugees and expellees of foreign or no citizenship, residing within the German borders as they stood in 1937, were granted German citizenship by the West German constitution (Grundgesetz), Art. 116 (1) when this came into force in 1949. Expellees arriving later in the Federal Republic of Germany were almost all granted German citizenship as well, but their detailed legal treatment varied, depending on their or their ancestors' citizenship. Aussiedler (see above) who themselves or whose ancestors had been German citizens before 1945 were mostly legally considered as being German citizens, regardless of any other citizenships they may have held. According to the Nationality Law of the German Empire and States (Reichs- und Staatsangehörigkeitsgesetz; RuStAG) of 1913, valid until 1999, loss of German citizenship was only valid if one applied for it (RuStAG § 21 (1)), and the competent German authority issued a denaturalisation deed (Entlassungsurkunde, RuStAG § 23 (1)), and the person to be denaturalised emigrated from German territory within a year after starting the procedure (RuStAG § 24 (1)).
West German jurisdiction maintained that until a treaty with all of Germany on the seizures of territories (concluded finally as the German–Polish Border Treaty (1990)) should legalise their de facto status, the eastern territories of Germany annexed to other nations in 1945 and the Saar Protectorate were legally German territory for this purpose. Alternatively for German citizens living abroad – in West German definition outside of the German borders of 1937 – the unilateral voluntary adoption of a foreign citizenship would entail one's denaturalisation as a German (RuStAG § 25 (1)).
However, the conditions of voluntarity, issuance of the deed, and leaving German territory (if applicable), were usually not fulfilled for German citizens authoritatively naturalised by the Eastern European states they happened to live in after 1945. Their children gained German citizenship by jus sanguinis (RuStAG § 4). Those Aussiedler of foreign citizenship but descending from ancestors holding German citizenship before 1918 (regardless of ethnicity) were granted German citizenship by the Federal Expellee Law (BVFG § 6 (2)), while those Aussiedler without such German descent but of German ethnicity (to be evidenced by German culture, language, traditions, etc.) received German citizenship also (see BVFG § 1 (1) No. 1).
Religious demographics[edit]
The West German researcher Gerhard Reichling published a study that estimated the prewar German population at 18,267,000 in Eastern Europe (including the USSR), of whom 2,020,000 were dead in the expulsions and forced labor in the USSR. In addition, he estimated military and civilian war dead in the area of the expulsions at 1,250,000, but did not provide details for this figure. Reichling provided a breakout of the ethnic German population by religion which included German-speaking Jews with other religions and beliefs. He did not give a separate total for German Jews included in his figure for "others", nor he did enumerate Jewish dead in his figures of wartime and postwar losses. Kurt Horstmann of the Federal Statistical Office of Germany wrote the foreword to the study endorsing the work of Reichling, an employee of the Federal Statistical Office who was involved in the study of German expulsion statistics since 1953.[44]
Religion of German refugees from the East according to Reichling
Religion of Germans from the East, according to Gerhard Reichling[45]
| Description | Prewar German population | Protestant | Roman Catholic | Other |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Former eastern territories of Germany | 9,575,000 | 6,411,000 | 2,862,000 | 302,000 |
| Danzig | 380,000 | 215,000 | 147,000 | 18,000 |
| Poland | 1,200,000 | 736,000 | 457,000 | 7,000 |
| Czechoslovakia | 3,544,000 | 166,000 | 3,231,000 | 147,000 |
| Baltic States | 250,000 | 239,000 | 8,000 | 3,000 |
| USSR | 1,400,000 | 1,119,000 | 254,000 | 27,000 |
| Hungary | 600,000 | 94,000 | 492,000 | 14,000 |
| Romania | 782,000 | 437,000 | 330,000 | 15,000 |
| Yugoslavia | 536,000 | 108,000 | 415,000 | 13,000 |
| Total | 18,267,000 | 9,525,000 | 8,196,000 | 546,000 |
Reichling defines "others" as follows: "The term 'other' includes other creeds (Jewish communities and groups, other peoples and world religions, freethinkers and enlightenment associations) and those without a creed or no report of religious belief".[46]
German-speaking Jews in Eastern Europe prior to the war
A. Former eastern territories of Germany – Based on the May 1939 census in the eastern regions of Germany there were according to Nazi antisemitic terminology – full Jews 27,526; one-half Jewish 6,371; and one-quarter Jewish 4,464.[47][48][49] Ingo Haar maintains that 27,533 Jews in the former eastern territories of Germany, most of whom perished in the Holocaust, were included with the dead expellees in West German figures.[50]
B. Czechoslovakia - Polish demographer Piotr Eberhardt estimated that there were 75,000 German-speaking Jews in the Czech lands in 1930; he did not give a figure for Slovakia.[51] Based on the May 1939 census in the Sudetenland there were – using Nazi terminology – full Jews 2,363; one-half Jewish 2,183; and one-quarter Jewish 1,396.[47] 2,035 Jews in the Sudetenland were included with the German population in the West German figures used to calculate expulsion losses.[52]
C. Hungary - Eberhardt estimated that there were 10,000 German-speaking Jews in Hungary in 1930.[53]
D. Poland - According to the December 1931 census of Poland there were 7,000 German-speaking Jews in Poland.[54]
C. Yugoslavia - The Schieder commission report for Yugoslavia put the number of German-speaking Jews at 10,026 in 1931.[55]
German historians Hans Henning Hahn and Eva Hahn have raised the issue of the German minority in Eastern Europe and the Holocaust. They point out that German historians of the expulsions have hardly covered the fate of the German-speaking Jews in the Holocaust. There were many Jews in Eastern Europe who spoke German as a primary language and identified with the German nationality prior to the war, and many others spoke German as a second language. In Czechoslovakia there 46,000 Jews that identified with the German nationality in 1930.
Many Jews fled Czechoslovakia in 1939 prior to the beginning of the war; most of those who remained perished in the Holocaust. The Hahns mentioned that many of the Jewish victims in Czechoslovakia have German-sounding names. According to the Hahns a wartime estimate by a Nazi researcher put the number of Jews outside of Czech lands at 6.8 million, of whom 4% spoke German.[56]
Germans remaining in Central Europe in 1950[edit]
| Country | Per West Germany | Per Reichling | Per Eberhardt |
|---|---|---|---|
| Poland (including annexed land) | 1,536,000 | 1,700,000 | 170,000 |
| Czechoslovakia | 250,000 | 300,000 | 165,000 |
| Hungary | 270,000 | 270,000 | 22,500 |
| Romania | 400,000 | 400,000 | 343,900 |
| Baltic (Memel/Klaipėda) | 15,000 | 18,000 | 0 |
| Yugoslavia | 82,000 | 82,000 | 0 |
| Total | 2,553,000 | 2,770,000 | 701,400 |
The table summarizes the estimates for ethnic Germans remaining in eastern Europe in 1950. The West German government in 1958 made an estimate that is often cited in historical literature.[57] In 1985, Gerhard Reichling, a researcher employed by the West German government, provided his own estimate of Germans remaining in east Europe in 1950, plus an additional 1,312,000 living in the USSR. Reichling detailed 1,410,000 persons who emigrated from 1951 to 1982 who were also considered expellees under West German law; Poland: 894,000; Czechoslovakia: 160,000; Hungary: 30,000; Romania: 144,000; Yugoslavia: 80,000; and USSR: 102,000.[58] In 2003, Eberhardt made his estimates for remaining Germans in 1950 that are significantly lower than those made in Germany.[59]
Method of counting confirmed deaths[edit]
Studies of this kind try to count individual deaths, by various means. Sources may include registry death records, police and military records, church files of missing and killed persons, or reports of eyewitnesses .
Research by German Church Search Service[edit]
A. The work and findings of the German Church Search Service
Already at the end of the war in August 1945 efforts were being made in Germany to trace those civilians who were dead or missing in Central and Eastern Europe. A Suchdienst (search service) was set up by the German Roman Catholic and Protestant Churches working with the German Red Cross. In 1950 the West German government provided funding for these efforts and in 1953 they set up a unified body of the Suchdienst (search service) to coordinate these various efforts, organize a complete system of records, clarify the fates of the missing and prepare a final report. The German Red Cross sent 2.8 million questionnaires to survivors in order to obtain relevant information on the fates of the dead and missing. Information was compiled from the records of the local communities in Central and Eastern Europe (Soll-Listen) and eyewitness accounts of the expellees. The work of the Suchdienst (search service) was only partially successful. They were able to survey the records (Soll-Listen) local communities that encompassed 8.6 million persons, only one half of all Germans in the territory of the expulsions. The work of the Suchdienst (search service) was hampered during the Cold War by the Communist Bloc governments in Central and Eastern Europe who did not extend full cooperation for these West German efforts to trace missing persons.[11] In 1965 the conclusions and final report was issued by the Suchdienst (search service) of the German churches which was able to confirm 473,013 civilian deaths, there were an additional 1,905,991 cases of persons whose fate could not be determined by 1965. This report remained confidential until the end of the Cold War. The West German government authorized its release in 1986 and summary of the findings was published in 1987 by the German scholar de:Gert von Pistohlkors.[60] The German Search Service is currently located in Munich Germany, they continue to investigate the fates of those persons missing in the war, in 2005 they maintained that their research put losses at 2,251,500 persons in the expulsions and deportations. They did not provide details of the figure.[11][61]
Summary of the Population Surveyed by Search Service Investigation [62][5][6]
| Description | Amount |
|---|---|
| Total Cases Investigated by Search Service 1953-1965 | 17,625,742 |
| Military deaths | (450,809) |
| Natural deaths | (296,084) |
| Relocated before expulsion | (340,826) |
| Born after expulsion | (135,876) |
| Resettled before expulsion | (203,061) |
| Total population before flight & expulsion | 16,199,086 |
Summary of Results of the Search Service Investigation As of Dec. 31, 1965 [5][6][63]
| Description | Amount |
|---|---|
| Confirmed alive | 12,848,497 |
| Natural deaths after expulsion | 971,585 |
| Confirmed deaths in expulsion | 473,013 (see Schedule below) |
| Unsolved cases | 1,905,991 |
| Total population before flight & expulsion | 16,199,086 |
Details of the 1,905,991 Unsolved Cases - Deported 68,416; Interned 17,704; Missing 768,010; Deaths 179,810; No Information provided (ohne jeden Hinweis) 872,051. Rüdiger Overmans maintains that the 872,051 cases with no information provided are “Karteileichen” (“card corpses”) of persons who could not be traced because insufficient information was provided and therefore of doubtful validity. He considers this to be the most important consideration in the analysis of the 1.9 million unsolved cases.[5]
Summary of the German Church Search Service Figures in 1965[64][62][5][6]
| Description | Total | Poland | Baltic States (resettled in Poland during war) | Resettled in Poland during war (from USSR and Romania) | Sudetenland | SE Europe
(Hungary, Romania, Yugoslavia & Slovakia) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total 1945 population before flight & expulsion | 16,199,086 | 11,038,826 | 145,615 | 365,622 | 3,160,216 | 1,488,807 |
| Confirmed deaths: | ||||||
| Violent deaths | 58,256 | 44,603 | 383 | 747 | 5,596 | 6,927 |
| Suicides | 14,356 | 10,330 | 157 | 84 | 3,411 | 374 |
| Deported (forced labor, USSR) | 49,542 | 32,947 | 1,566 | 6,465 | 705 | 7,859 |
| In internment camps | 80,522 | 27,847 | 952 | 1,037 | 6,615 | 44,071 |
| During the wartime flight | 93,283 | 86,860 | 2,394 | 738 | 629 | 2,662 |
| In the course of the expulsions | 63,876 | 57,814 | 3,510 | 561 | 1,481 | 510 |
| Cause undetermined | 112,612 | 106,991 | 64 | 3,116 | 379 | 2,062 |
| Other, misc. | 566 | - | 38 | 141 | 73 | 314 |
| Total confirmed deaths | 473,013 | 367,392 | 9,064 | 12,889 | 18,889 | 64,779 |
| Total unsolved cases | 1,905,991 | 1,404,993 | 19,374 | 73,794 | 287,169 | 120,661 |
The authors of the Search Service report used the wartime administrative regions set up by Nazi Germany in Poland and Czechoslovakia as a basis to breakout the population rather than the pre war administrative regions and boundaries. Rudiger Overmans used the description "Poland" to summarize the figures for the region east of the Oder–Neisse line, which included the Former eastern territories of Germany, Danzig, pre war Poland, and the Memel Territory[5] The population surveyed in pre war Poland included Polish citizens on the Volksliste who were of dubious German ancestry.[65] The losses in Poland included deaths in the wartime flight, as well as post war deaths in the Soviet Kaliningrad region and in post war Poland. Confirmed deaths in Poland include 17,209 refugees in Denmark and about 15,000 in Polish internment camps.[66] Figures for the Sudetenland include the Protectorate of Bohemia and Moravia but do not include Slovakia and Český Těšín – Trans-Olza. The figures for Czechoslovakia in the 1937 borders (including Slovakia and Trans-Olza) are: population in 1945 - 3,397,446; confirmed dead 21,332 and unsolved cases 307,616[67] There was no breakout of the figures showing the age and sex of the population surveyed and the date of the reported deaths or persons missing.
B. Academic commentary on the figures of the Suchdienst (search service)
Dr. Rüdiger Overmans presented a summary of the Suchdienst (search service) data at a 1994 historical symposium in Poland. Overmans believes that the figures of the Church Service are unreliable and should be treated with caution. He made the following observations regarding the Church Service data:[5]
- Non-Germans are included in the total population surveyed.
- Military deaths are included in the figures. Total military deaths are understated by more than one-half because there was no coordination with the military search service.
- The figures for expellees in the GDR are not reliable. The number of surviving persons, natural deaths and births after the war in the GDR are understated.
- The figures of persons deported to the USSR are understated.
- The reports given by eyewitnesses surveyed are not reliable in all cases.
- Overmans maintains there are more arguments for the lower figure of 500,000 rather than the higher figure of 2.3 million, he believes that since there are only 473,000 confirmed deaths, new research is needed to determine the fate of the 1.9 million reported missing.
The German historian Ingo Haar maintains that the figure of 473,000 confirmed dead provides realistic view of the total losses due to the flight and expulsions. Haar points out that 473,000 confirmed dead as well as the 1.9 million unresolved cases from the Search Service were used by the West German government when compiling the 1958 demographic analysis Die deutschen Vertreibungsverluste at which put losses 2.225 million. Haar maintains that West German government pressured the Statistisches Bundesamt to match the figures of the Search Service in the 1958 demographic analysis even though their figures included unresolved cases which lacked adequate support. After its completion, the German church numbers were archived and not released to the general public - according to Ingo Haar, this was due to a fear that they were "too low" and would lead to "politically undesirable conclusions".[68][69]
The German historians Hans Henning Hahn and Eva Hahn have published a detailed study of the flight and expulsions that is sharply critical of German accounts of the cold war era. The Hahn's believe that the official German figure of 2 million deaths is an historical myth that lacks foundation. They point out that the figure of 473,013 confirmed deaths includes 80,522 in the post war internment camps, they maintain that most deaths occurred in the flight and evacuation during the war[66]
1974 German Federal Archive Report[edit]
On 28 May 1974, the West German Federal Archive (Bundesarchiv) issued a report following a directive of the Federal Ministry of the Interior to "compile and evaluate information available in the Federal Archives and elsewhere regarding crimes and brutalities committed against Germans in the course of the expulsion".[70] In particular, the report was to identify deaths due to crimes against international law: the 1958 report of the Federal Office for Statistics listed as "post-war losses" two million people whose fate remained unaccounted for in the population balance, but who according to the 1974 report were "not exclusively victims of crimes against international law".[71] The report defined the term "expulsion" (Vertreibung) "according to its prevailing interpretation", i.e. the "whole uprooting process".[72] Sources used for the report were:
- about 10,000 eyewitness accounts (Erlebnisberichte), compiled primarily during the "documentation of the expulsion of Germans from East Central Europe", conducted on initiative of the Federal Ministry for Expellees between 1950 and 1953, which since 1955 were stored in the Federal Archive.[73] To this stock added eyewitness accounts from the Secret State Archive (GStA) in Dahlem, from the Main State Archive in Düsseldorf, from the collection of the State Commissioner for Refugee Affairs in Stuttgart and from the collection of the Bavarian Ministry of the Interior, as well as further eyewitness accounts sent to the Federal Archive directly.[73]
- about 18,000 reports about the fate of municipalities (Gemeindeschicksalsberichte), collected since 1952 in the course of the abovementioned "documentation",[73] and from 1954 to 1959 by the Federal Archive itself.[74] These reports were laid out as standardized questionaries about distinct municipalities and covered 85.2% of the municipalities in the former eastern territories of Germany, the majority of those municipalities in the area of pre-war Poland which were previously home to a German population, and other such municipalities in former Sudetenland and southeastern Europe.[74]
- about 12,100 so-called "soul lists" (Seelenlisten) compiled between 1952 and 1956 listing the former German inhabitants of rural and small urban communities east of the Oder-Neisse line, in part noting deaths and their causes.[75]
- information from the archives of German dioceses.[75]
The final report included deaths confirmed by at least two independent sources.[76] Deaths reported by one source only were rejected unless they met certain reliability criteria laid out in a catalogue adopted from Schieder et al. (1958): Dokumentation der Vertreibung der Deutschen aus Ost-Mittewleuropa Vol. I/1, page IIIf.[76] The report states that the sources hint at the magnitude of crimes, but are not sufficient for a thorough statistic.[77] Of only a faction of the sources it is said that they detail names and number of victims, others would merely point to crime scenes but do not elaborate on numbers and details.[77] Especially the extent of crimes in larger municipalities and, with few exceptions, in camps and prisons is not replicable with the sources given according to the report.[77]
In the areas east of the Oder-Neisse line, the reviewers identified 3,250 crime scenes in the sources.[77] For 630 of those, the number of victims could not be established, while 23,200 people were identified who died at the other 2,620 scenes.[77] To estimate a total number of casualties, the 1974 report relied on a data set retrieved from the 1964 Church Search Service report compiling the most complete of the "soul lists".[78] For 455 rural communities of East Prussia and 432 rural communities of Pomerania, these lists reported 1,731 and 1,278 people killed, respectively, which is about 1% of their 1939 population (152,124 and 137,709 inhabitants, respectively).[78] To the number of these identified deaths added the number of 4,000 missing, some of whom may also be unconfirmed deaths.[78] The 1974 report then relates the 1% confirmed deaths as a minimum value to the 1939 population of the former eastern territories of Germany set at 9.6 million people, thus receiving a number of at least 96,000 people killed in that area during the expulsion.[78] Similarly it was estimated that at least 19,000 people were killed during the expulsions from the area of pre-war Poland, which was calculated as 1% of 1,9 million Germans living there in 1944.[79] On the premise that in the area of pre-war Poland, 20% more people were overrun by the advancing Red Army than in areas occupied later on, the number was adjusted to above 20,000, resulting in a total of at least 120,000 people killed east of the Oder and Neisse rivers.[79] Furthermore, it was estimated that 200,000 people were incarcerated in Polish-run and 110,000 in Soviet-run camps and prisons in that area with death rates between 20% and 50%.[80] Therefore, it was estimated that at least 100,000 people died in these camps and prisons.[81] Another 200,000 people died as a result of deportation to the USSR, based on German Red Cross estimates.[81] From addition of these values, the report found that east of the Oder and Neisse rivers, at least 400,000 people died during the expulsions.[81]
Of the abovementioned sources, 2,000 were concerned with Czechoslovakia (including Sudetenland).[82] Of those, only a faction included reliable numbers of killed Germans adding to about 6,000 confirmed deaths.[82] The report cites an estimate by Kurt W. Böhme (1965): Gesucht wird..., p. 264, according to whom 350.000 Germans were interned in camps, about 100,000 of whom died.[83] From the sources, the 1974 report says that the numbers of the interned are likely to be higher, and refers to another study by A. Bohmann (1959): Das Sudetendeutschtum in Zahlen, p. 199, presenting an estimate of up to one million internees.[83] The report further states that from Czechoslovakia, relatively few Germans were deportated to the USSR.[83]
For Yugoslavia, the report says that their sources confirm that about 7,200 Germans were killed outside of camps.[84] The researchers suspected that the numbers given in the sources are in part inflated, but also referred to sources reporting other killings without quantifying the victims.[84] Adding to those numbers the victims of executions of camp inmates, the report estimates that between 15,000 and 20,000 Germans died a "violent death".[84] The report thereby refers to sources about 49 large camps, where of an estimated total of 67,000 deaths about 8,000 were due to violence, and the rest primarily due to starvation, disease and maltreatment.[84] For many small camps and prisons, as well as for Yugoslav German POWs shot in captivity by partisans, the report lacked detailed sources.[85] Regarding the numbers of Yugoslav Germans deported to the USSR, the report refers to Theodor Schieder et al. (1958): Dokumentation der Vertreibung vol. V, p. 97E, citing the numbers of 27,000 to 30,000 deportees and the respective death toll of 4,500 people given there.[86] The report postulates that at least 80,000 Yugoslav Germans died during the expulsions.[86]
The report concludes that
- no distinct group of Germans was preferred as target, instead the remaining German population was targeted as a whole[87]
- the perpetrators were identified as members of the Red Army, the NKVD, Polish militia and security forces, Czechoslovak people's guard and liberation army and Yugoslav partisans[87]
- the sources used for the report were insufficient to calculate a comprehensive balance, especially for the situation in larger communities and camps the available sources were too fragmentary for an overview[87]
- the sources differed in their accounts of number of inmates and deaths in camps[87]
- the total numbers of deaths given in the report are "rough estimates".[87]
Expulsion Deaths Listed by German Federal Archives 1974
| Description | Total Deaths | Oder-Neisse region, Poland | Czechoslovakia | Yugoslavia |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Violent deaths during war 1945 | 138,000 | 100,000 | 30,000 | 8,000 |
| Deported to USSR | 205,000 | 200,000 | - | 5,000 |
| Forced labor N. East Prussia | 40,000 | 40,000 | - | - |
| In post-war internment camps | 227,000 | 60,000 | 100,000 | 67,000 |
| Total | 610,000 | 400,000 | 130,000 | 80,000 |
Source: German Federal Archive, Spieler, Silke Vertreibung und Vertreibungsverbrechen 1945-1948. Bericht des Bundesarchivs vom 28. Mai 1974. Archivalien und ausgewählte Erlebnisberichte. Bonn 1989 Pages 53–54 The authors maintain that these figures cover only those deaths caused violent acts and inhumanities(Unmenschlichkeiten) and do not include post war deaths due to malnutrition and disease. Also not included are those persons who were raped or suffered mistreatment and did not die immediately. No figures were given for Romania and Hungary.
Rüdiger Overmans believes that the 1974 report is not definitive and that new research is needed to determine total deaths due to the expulsions. Overmans made the following observations regarding the German Federal Archives Report:[5]
- Some deaths may have gone unreported in the Archives study because there were no eye witnesses to the events.
- The German Federal Archives Report is not comparable to the other studies because the USSR, Hungary, Romania and deaths in the air war were not surveyed.
- Overmans maintains there are more arguments for the lower figures of 500,000 to 600,000 rather than the higher figures of over 2.0 million
The German historian Ingo Haar believes a realistic view of the total deaths due to the expulsions is in the range of 500,000 to 600,000. Harr maintains that these figures include post war deaths due to malnutrition and disease and that the higher figures of over 2.0 million have been overstated by the German government for political reasons.[68][69]
Since the fall of the USSR the Soviet archives have been accessible to researchers. The Russian scholar Pavel Polian in 2001 published an account of the deportations during the Soviet era, Against Their Will, Polian's study detailed the Soviet statistics on the employment of German civilian labor during the Stalin era. The research by Polian put the number of deported Germans at 271,672 and deaths at about 66,000.[88] During the Cold war the German Red Cross made rough estimates of those deported at about 400,000 persons of whom about 200,000 perished, these figures were used by the German Federal Archives to compile their 1974 report on deportations to the USSR.[89] The recent disclosures by Polian contradict the figures in the German Federal Archives report of 1974.
In 1995, a joint German and Czech commission of historians revised the number of civilian deaths in Czechoslovakia to between 15,000 and 30,000 persons[90] During the Cold war German historians made rough estimates of about 350,000 persons interned in Czechoslovakia of whom 100,000 perished, these estimates were used by the German Federal Archives[89] They also estimated 30,000 persons killed during the Prague uprising and in post- war Czechoslovakia. The recent report by the joint German and Czech commission of historians contradict the figures in the German Federal Archives report of 1974.
The German historians Hans Henning Hahn and Eva Hahn have published a detailed study of the flight and expulsions that put the number of dead in Polish internment camps at 15,000 based on information recently published in Poland.[91] These recent disclosures contradict the figures in the German Federal Archives report of 1974 that put the figure at 60,000. However, the Polish historians Witold Sienkiewicz and Grzegorz Hryciuk maintain that the internment "resulted in numerous deaths, which cannot be accurately determined because of lack of statistics or falsification. Periodically, they could be 10% of inmates. Those interned are estimated at 200-250,000 Germans and the local population, and deaths might range from 15,000 to 60,000 persons." [92]
Method of using population balance[edit]
Estimates for the population losses in the Expulsions that appear in historical literature are ultimately derived from reports published by the German government. The methodology behind these figures is a computation of the estimated population deficit.
Early estimates compiled in the 1950s[edit]
In 1950 West German Government made a preliminary estimate of 3.0 million dead and missing whose fate needed to be clarified.[93] In 1953 the German scholar Gotthold Rhode made a demographic estimate of 3,140,000 total ethnic German dead in Central and Eastern Europe from 1939 to 1950. Rhode's figures were for total population losses, including the military dead which he did not break out.[94] Bruno Gleitze estimated in 1953 800,000 civilian deaths (for Germany within 1937 borders only) among only "Eastern Germans" in the area of the expulsion[95] These early estimates were superseded by subsequent publication in 1958 of the demographic study by the West German government statistical office.
The Schieder commission[edit]
From 1954 to 1961 Schieder commission issued five reports on the flight and expulsions, they estimated a death toll of about 2.3 million civilians.[96] The head of the Commission was Dr. Theodor Schieder a rehabilitated former member of the Nazi party. In 1952 Schieder was chosen by the West German government to head the Commission that would document the fate of the Germans from East-Central Europe. The Schieder commission has been criticized because it covered the flight and expulsions but did not provide background on the wartime crimes of Germany in East-Central Europe that triggered the post war expulsions[97][98][99] The death toll estimated by the Schieder commission was superseded by subsequent publication in 1958 of the demographic study by the West German government statistical office.
Flight and Expulsion Deaths-Estimates by Schieder commission
| Description | Civilian Death Toll |
|---|---|
| Oder-Neisse region | 2,000,000[100] |
| Hungary | 6,000[101] |
| Czechoslovakia | 225,600[102] |
| Romania | 40,000[103] |
| Yugoslavia | 69,000[104] |
| Total | 2,340,600 |
Notes
- Figure of 2 million for Oder-Neisse region includes about 1.6 million in the Former eastern territories of Germany, 217,000 in the borders of pre war Poland and 100,000 in Danzig.[105]
- Figure of 2 million for Oder-Neisse region includes 75,000 to 100,000 civilian deaths prior to May 1945 during military campaign.[106]
- Figure of 2 million for Oder-Neisse region includes 100,000 to 125,000 civilian deaths in the Forced labor of Germans in the Soviet Union.[106]
- Figure of 2 million for Oder-Neisse region does not include deaths among the over 800,000 Germans Resettled in Poland during the war.[100]
- Figure of 2 million for Oder-Neisse region does not include an additional 500,000 military and 50,000 civilian air raid dead[107]
- Figure of 6,000 deaths for Hungary are due to the Forced labor of Germans in the Soviet Union[101]
- Figure of 40,000 deaths for Romania includes 10,000 in the Forced labor of Germans in the Soviet Union and 30,000 deaths in the Oder-Neisse region among the 160,000 Germans of Romania resettled in Poland during the war.[108]
- Figure of 69,000 for Yugoslavia includes 2,631 during wartime flight; 5,777 executed by Soviet and Yugoslav forces; 5,683 deportation deaths (including 4,500 to 5,000 in the Forced labor of Germans in the Soviet Union); 48,027 in Yugoslav internment camps; 187 in prisons and 6,273 missing.[109]
West German Government Demographic Study of 1958[edit]
Based on a 1954 directive of the West German government the Federal Statistical Office of Germany (Statistisches Bundesamt) was responsible for analyzing the figures relating to the population losses due to the expulsions and issuing a final report. In 1958 they issued a report Die deutschen Vertreibungsverluste (The German Expulsion Casualties), estimating "Unsolved Cases (postwar losses)" of 2.225 million German civilians in all of Central and Eastern Europe. The figures listed in the table below are from this report. The Statistisches Bundesamt noted in the introduction that since the conclusion of their study data had been published in East Germany putting the number of expellees living in East Germany at 127,000 more than the figures listed below in the Die deutschen Vertreibungsverluste.[110] In November 1958 the Statistisches Bundesamt published revised figures that put losses for Germany in 1937 borders at 1,212,100 persons, 127,000 less than the Die deutschen Vertreibungsverluste.[111]
Die deutschen Vertreibungsverluste, using prewar population figures, wartime estimates and postwar figures from both German states and in Central and Eastern Europe, concluded that 3,325,000 people died in the war and expulsions, and estimated that 1,100,000 of these were war dead, including 11,500 civilians killed by Allied Strategic Bombing (up until 1/31/1945), thus reducing the number of civilian deaths in the flight during the war and the subsequent expulsions to 2.225 million.[112] The report also listed a total of approximately 12.0 million who were actually expelled. The summary table in the West German government statistical office report uses a description giving total "post war losses" of 2.225 million persons, however the detailed analysis in the text lists 169,000 civilian deaths during the flight and evacuation during the war (128,000 pre-war Germany, 35,000 Czechoslovakia and 4,000 Hungary).[113] The figures in the report also include losses during the Forced labor of Germans in the Soviet Union.
Die deutschen Vertreibungsverluste (The German Expulsion Casualties)
| Description | German Population 1939 | War Deaths | Population growth 1939-50 | Remained in East Europe & USSR 1950 | Expelled by 1950 | Unsolved Cases (post war losses)[114] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Germany 1937 borders (Eastern Provinces) | 9,575,200 | 667,500 | 546,000 | 1,134,000 | 6,981,000 | 1,338,700 |
| Poland 1939 borders | 1,371,000 | 108,000 | 46,000 | 436,000 | 688,000 | 185,000 |
| Free City of Danzig | 380,000 | 22,000 | 22,000 | 4,000 | 290,800 | 83,200 |
| Czechoslovakia | 3,477,000 | 180,000 | 235,000 | 258,700 | 3,000,400 | 272,900 |
| Baltic States | 249,500 | 15,000 | 5,700 | 19,300 | 169,500 | 51,400 |
| Yugoslavia | 536,800 | 40,000 | 23,500 | 87,000 | 297,500 | 135,800 |
| Hungary | 623,000 | 32,000 | 17,000 | 338,000 | 213,000 | 57,000 |
| Romania | 786,000 | 35,000 | 41,000 | 438,000 | 253,000 | 101,000 |
| Total | 16,998,500 | 1,099,500 | 936,200 | 2,717,000 | 11,893,200 | 2,225,000 |
Source:
Die deutschen Vertreibungsverluste. Bevölkerungsbilanzen für die deutschen Vertreibungsgebiete 1939/50.Herausgeber: Statistisches Bundesamt - Wiesbaden. - Stuttgart: Kohlhammer Verlag, 1958 [115]
Notes
- English language sources published during the cold war dealing with the expulsions put the death toll at 2 to 3 million based on the West German government statistical analysis of the 1950s.[116][117][118][119][120][121][122][123][124][125]
- In 2006 The German government reaffirmed its belief that 2 million civilians perished in the flight and expulsion from Central and Eastern Europe. They maintain that the figure is correct because it includes additional post war deaths from malnutrition and disease of those civilians subject to the expulsions.[126] On 29 November 2006 State Secretary in the German Federal Ministry of the Interior, Christoph Bergner, outlined the stance of the respective governmental institutions in Deutschlandfunk saying that the numbers presented by the German government and others are not contradictory to the numbers cited by Haar, and that the below 600,000 estimate comprises the deaths directly caused by atrocities during the expulsion measures and thus only includes people who on the spot were raped, beaten, or else brought to death, while the above two millions estimate also includes people who on their way to post-war Germany have died of epidemics, hunger, cold, air raids and the like.[10]
- The German historian Ingo Haar believes that civilian losses in the expulsions have been overstated in Germany for decades for political reasons. Haar argues that during the Cold War the West German government put political pressure on the Statistisches Bundesamt to push the figures upward to agree to the unreliable Church Service figure of 2.3 million dead and missing. Harr disputes the statements of the German government and maintains that the lower estimates of 500–600,000 deaths already include post war deaths due to malnutrition and disease. He also maintains that the figures for the population of prewar Germany include 27,000 Jewish victims of the Holocaust. Harr points out that these issues were raised with the West German government, but the inflated numbers continued to be used when the demographic report was published in 1958 in order to agree with the previous findings of the Schieder commission and the Church Search Service.[68][69][127][128]
- The German scholar Dr. Rüdiger Overmans believes that the statistical foundations of the 1958 West German government demographic report to be questionable and cannot be regarded as definitive. Overmans made the following observations on figures of the 1958 demographic report.[129]
- 1-The report is not mathematically consistent, because it was not properly proof read.
- 2-The figures of Germans were overstated by including persons who were of doubtful German ethnic identity. Persons who became assimilated into the local population in Central and Eastern Europe are included in those persons reported as missing.
- 3-The figure given by the Statistisches Bundesamt for the total German population effected by the expulsions is 16.5 million which is higher than the Church Search Service figure of 16.2 million persons. The two figures are not directly comparable because the Church Search Service figure includes 700,000 Soviet Germans not included in the Statistisches Bundesamt study, which means that the figure for the total population used to compute losses by the Statistisches Bundesamt is inflated by 1.0 million persons.
- 4-Military losses are understated thus inflating civilian losses.
- 5-The number of surviving expellees in the GDR is understated thus inflating losses. .
- 6-Overmans maintains that there are more arguments for a lower figure of 500,000 rather than the higher figures of over 2.0 million. He believes that the previous studies by the German government should be subject to critical revision and new research is needed to establish the actual number of expulsion deaths.
- In his 2000 study of German military casualties Dr. Rüdiger Overmans found 344,000 additional military deaths of Germans from the Former eastern territories of Germany and conscripted ethnic Germans from Central and Eastern Europe. Overmans believes this will reduce the number of civilians previously listed as missing in the expulsions.[130]
- The Polish scholar Piotr Eberhardt found that; Generally speaking, the German estimates…are not only highly arbitrary, but also clearly tendentious in presentation of the German losses He maintains that the German government figures from 1958 overstated the total number of the ethnic Germans living in Poland prior to war as well as the total civilian deaths due to the expulsions. For example, Eberhardt points out that the total number of Germans in Poland is given as equal 1,371,000. According to the Polish census of 1931 there were altogether only 741,000 Germans on the entire territory of Poland.[131]
- The German historians Hans Henning Hahn and Eva Hahn have published a detailed study of the flight and expulsions that is sharply critical of German accounts of the cold war era. The Hahn's believe that the official German figure of 2 million deaths is an historical myth that lacks foundation.[132] The Hahns pointed out that the official 1958 figure of 273,000 deaths for Czechoslovakia was prepared by Alfred Bohmann an ex-Nazi party member who had served in the wartime SS, Bohmann was a journalist for an ultra-nationalist Sudeten-Deutsch newspaper in post war West Germany.[133] The Hahn's maintain that the figures for the total ethnic German population in Central and Eastern Europe also include German speaking Jews killed in the Holocaust[134]
- The organizations of the ethnic German Expellees from Yugoslavia have traced the fate of the civilians who perished in the expulsions. In 1991-1995 the results of their research were published in a four volume study that listed the names and cause of death for each person. The study identified 57,841 civilians confirmed as dead and 889 listed as missing.[135] This contradicts the 1958 study that estimated losses at 136,000.
- In 1996 a joint Czech-German Historical commission found that the demographic estimate by the German government of 270,000 civilian deaths due to the expulsions from Czechoslovakia was based on faulty data. They estimated total deaths of 15,000-30,000[136][137]
Study by Gerhard Reichling[edit]
Population Balance Estimated by Gerhard Reichling 1986
| Description | PreWar German Population | Remained in East Europe & USSR 1950 | Expelled by 1950 | Total Deaths | In Expulsion | In USSR(forced labor) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Former eastern territories of Germany | 9,575,000 | 1,440,000 | 6,980,000 | 870,000 | 730,000 | 140,000 |
| -Resettled in Central and Eastern Europe during war | - | 10,000 | 460,000 | 108,000 | 88,000 | 20,000 |
| Danzig | 380,000 | 50,000 | 290,000 | 40,000 | 35,000 | 5,000 |
| Poland | 1,200,000 | 342,000 | 690,000 | 174,000 | 134,000 | 40,000 |
| Czechoslovakia | 3,544,000 | 306,000 | 3,000,000 | 220,000 | 216,000 | 4,000 |
| Baltic States | 250,000 | 24,000 | 170,000 | 33,000 | 25,000 | 8,000 |
| USSR | 1,400,000 | 1,240,000 | 100,000 | 310,000 | - | 310,000 |
| Hungary | 600,000 | 270,000 | 210,000 | 84,000 | 74,000 | 10,000 |
| Romania | 782,000 | 406,000 | 250,000 | 75,000 | 42,000 | 33,000 |
| Yugoslavia | 536,000 | 82,000 | 300,000 | 106,000 | 96,000 | 10,000 |
| Total | 18,267,000 | 4,170,000 | 12,450,000 | 2,020,000 | 1,440,000 | 580,000 |
Source for figures-Dr. Gerhard Reichning, Die deutschen Vertriebenen in Zahlen, Teil 1, Bonn 1995. Page 36
- A 1986 study by Dr. Gerhard Reichling "Die deutschen Vertriebenen in Zahlen" (the German expellees in figures) concluded 2,020,000 ethnic Germans perished after the war including 1,440,000 as a result of the expulsions and 580,000 deaths due to deportation as forced laborers in the Soviet Union. The figures were rough estimates made by Reichling and not based on an actual enumeration of the dead. Dr. Kurt Horstmann of the Federal Statistical Office of Germany wrote the foreword to the study, endorsing the work of Reichling. Reichling was an employee of the Federal Statistical Office who was involved in the study of German expulsion statistics since 1953.[138]
- The German historians Hans Henning Hahn and Eva Hahn have provided an analysis of the work by Reichling. They remark that his work basically a new variant of the information that had been published previously. They refer to his study as "old wine in new bottles" that "magically" comes up with the official figure of 2 million expulsion deaths. They outline his career as an official in the West German civil service that focused on the fate of the expellees in post war Germany. The authors mention that Reichling does not clearly explain to readers that the Nazi racial policy of resettlement and deportation during the war was the underlying cause of the subsequent expulsion of the Germans after the war.[139]
Federation of Expellees' estimates[edit]
The German foundation Centre Against Expulsions of the Federation of Expellees has compiled the following data from various sources.[140]
| Time period | Number of expellees (incl. deaths) |
Group expelled | Expelled by | Expelled, deported, fled from |
To | Deaths* |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aug 1941 - Jun 1942 | 900,000 | Russian-Germans | Soviet Union | Ukraine, Volga Republic, Caucasus, etc. | Siberia, Central Asia, etc. | 210,000 |
| Oct 1944 - Mar 1948 | 200,000 | Germans | Yugoslavia | Yugoslavia | Germany, Austria | 62,500 |
| Jan/Feb 1945 | 75,000 | Germans | Soviet Union, Romanians | Romania | USSR | 11,000 |
| 1944 - 1948 | 2,209,000 | Germans | Poland, Soviet Union | East Germany, East Prussia | West Germany, Middle Germany | 299,000 |
| 1945 - 1948 | 5,820,000 | Germans | Poland | former East Germany, Pomerania, East Brandenburg, Silesia | West Germany, Middle Germany | 914,000 |
| 1945 - 1948 | 367,000 | Germans | Poland | Free State of Danzig | West Germany, Middle Germany | 83,000 |
| 1945 - 1948 | 3,159,000 | Germans | Czechoslovakia | Czechoslovakia | West Germany, Middle Germany, Austria | 238,000 |
| 1945 - 1948 | 857,000 | Germans | Poland | Poland | West Germany, Middle Germany | 185,000 |
| 1945 - 1948 | 320,000 | Baltic Germans, Romanian-Germans, etc. | Poland, Soviet Union | Poland, East Germany | West Germany, Middle Germany | 99,000 |
| 1945 - 1948 | 30,000 | Baltic Germans, Romanian-Germans, etc. | Soviet Union | Poland, East Germany | Siberia, Central Asia | 10,000 |
| 1945 - 1946 | 280,000 | Russian-Germans | Soviet Union, Western Allies | Middle Germany | Siberia, Central Asia, etc. | 90,000 |
| 1946 - 1948 | 250,000 | Germans | Hungary | Hungary | Germany, Austria | 6,000 |
| Totals | 13,567,000 | 2,207,500 |
This more detailed accounting is susceptible to specific objections and questions about the meaning of the numbers. While the table is presented as estimates of the number of expelled, and column Expelled by suggests which government was responsible, these assertions have been questioned. The following points are relevant to the interpretation of the above statistics
- The statistics used to compile the list of dead by the Centre Against Expulsions are derived from the Schieder commission reports and the 1958 the West German Government Demographic Study Die deutschen Vertreibungsverluste. Ingo Haar maintains that the statistical basis of the data used by the Centre Against Expulsions is empirically unsound. Haar believes out that the statistics include missing persons whose fate in Central and Eastern Europe could not be clarified during the cold war and does not necessarily mean that they were deaths in the expulsions. Haar points out that the Centre Against Expulsions includes deaths in the wartime flight with the subsequent expulsions.[141]
- Many Germans were evacuated by German authorities and died during Soviet military operations, starvation and extreme cold during the final months of the war. The German population arrived in a post war Germany that was ravaged by starvation and disease.[10] Polish historians maintain that most of the deaths occurred during the flight and evacuation during the war, the deportation to the U.S.S.R. for forced labor and after the resettlement due to the harsh conditions in the Soviet occupation zone in post war Germany.[142] This is in sharp contrast to the position Centre Against Expulsions which implies that these deaths were due to the post war expulsions.[141]
- The number of Germans who were expelled was a fraction of those who arrived in Germany. Of the total 11.6 million persons listed by Germany as Expellees, 4.5 million fled during the war, 2.6 million were returned POW and 4.5 million were actually deported to Germany after the war.[143]
- Poland, Hungary and Romania were controlled by Soviet authorities during the post war era when the expulsions occurred. The nominal governments did not have control over policy. Yugoslavia was controlled by Titoist partisans at this time. Czechoslovakia did not come under direct Communist control until 1948.[144]
- The basis of great part of the expulsion was Potsdam Agreement (Article 12) agreed by the US, UK and the USSR.[145]
Allied Strategic Bombing[edit]
In early 1945, the then German city of Swinemünde (Świnoujście in contemporary Poland) was the destination port for refugees from East Prussia. On the 12th of March 1945, the US Eighth Air Force raided the city.[146] Due to uncertainty concerning the number of refugees within the city the exact number of casualties is unknown. As the capacity of air raid shelters was limited to the regular populace, many refugees were killed at the spa gardens.[147] The motor vessel Andros, carrying about 2,000 refugees, had just arrived at the harbour and was sunk with the loss of about 570 people.[147] About 500 victims of the raid were identified and buried close to the entrance of the cemetery and the remaining dead were buried in mass graves. The estimated number of victims, including residents of Swinemünde who were also encompassed by the expulsions, varies from about 5,000 to 23,000.[148] 1958 the West German Government demographic study of expellee deaths estimated the total civilian dead in the East Pommerian region due to Anglo-American air raids after 1/31/45 at 8,000.[149] The German War Graves Commission estimates that 20,000 victims are buried at the Golm War Cemetery with further burials within the town limits.
An unknown number of refugees from the east were among the estimated total 18,000-25,000 dead in the Bombing of Dresden in World War II. The German historian Rüdiger Overmans believes that “the number of refugee dead in the Dresden bombing was only a few hundred, hardly thousands or tens of thousands”[150]
Estimates concerning the Czech Republic only[edit]
In the 1930 census the German-speaking population of Czechoslovakia was 3,231,688, 22.3% of the total population.[151][152] Polish demographer Piotr Eberhardt maintains that the figure for the German-speaking population in Czechoslovakia included 75,000 Jews in 1930.[153]
The West German Statistisches Bundesamt put the 1939 German population in Czechoslovakia at 3,477,000. (This figure is detailed in a schedule below.) Sources in English dealing with the expulsions put the number of Germans in Czechoslovakia at about 3.5 million persons based on this West German analysis.[154][155] According to Eberhardt, the figure for the ethnic German population in the Sudetenland based on the May 1939 census is disputed by "Czech authors". They maintain that the German figures included 300,000 persons of Czech ethnicity in the Sudeten German population.[156][157]
| Description | Total | Ethnic Germans | Others |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sudeten Germans | 3,037,361 | 3,037,361 | – |
| Jews | 2,035 | 2,035 | – |
| Czechs | 193,786 | - | 193,786 |
| Other ethnic groups | 3,670 | - | 3,670 |
| Foreign nationals | 39,747 | 11,754 | 27,993 |
| Stateless | 3,415 | 2,454 | 961 |
| Undetermined citizenship | 128,435 | 10,811 | 117,624 |
| Sudetenland German census of May 1939 | 3,408,449 | 3,064,415 | 344,034 |
| Protectorate of Bohemia and Moravia (ration cards) | - | 259,000 | - |
| German population in Slovakia | - | 154,000 | - |
| Total German population in Czechoslovakia 1939 | - | 3,477,000 | - |
Notes:
- A. The figures for Sudetenland include a non-resident population of 27,283 Sudeten Germans who were in military or labor service.
- B. The Statistisches Bundesamt estimated the total ethnic Czech population in the Sudetenland at 319,000 persons by including those with undetermined or undeclared citizenship in the census as Czechs.
- C. The number of Jews from Sudetenland in the May 1939 census who were foreign nationals, stateless or of undetermined citizenship was not given in the Statistisches Bundesamt report. A separate breakout of Jews in the Sudetenland was published in the Statistisches Jahrbuch Für Das Deutsche Reich 1941/42 which gives a total figure of 2,363 Jews; there were an additional 3,579 persons who were of half or quarter Jewish ancestry. These figures encompass about 85% of the population in the annexed territory of the Sudetenland and do not include Bohemia-Moravia and Slovakia.[159]
- D. The estimated May 1939 German population of 259,000 in the Protectorate of Bohemia and Moravia is based on 1 October 1940 ration cards of the German occupation regime. The Statistisches Bundesamt maintains that the figure of 259,000 is only the pre-war resident German population, not including persons resettled during the occupation.
- E. The German population in Slovakia of 154,000 is based on the 1940 Slovak census that put the number of Germans at 130,192 and 23,000 Germans in the Slovak territory annexed by Hungary estimated in 1941 by the German occupation regime in the Protectorate of Bohemia and Moravia.
- F. These figures do not include ethnic Germans in the Czech portion of Cieszyn Silesia which is included with Poland by the Statistisches Bundesamt.
The estimated German population of 3,477,000 persons, based on the May 1939 census and the Bohemia and Moravia wartime ration cards, was used by the Statistisches Bundesamt when they estimated expulsion losses of 273,000 civilians in Czechoslovakia.[160] The German historians Hans Henning Hahn and Eva Hahn pointed out that the Statistisches Bundesamt report for Czechoslovakia was the work of Alfred Bohmann, an ex-Nazi party member who had served in the wartime SS. Bohmann was a journalist for an ultra-nationalist Sudeten-Deutsch newspaper in post-war West Germany.[161] The Statistisches Bundesamt estimate for the expulsion death toll of 273,000 civilians is often cited in historical literature.[162]
In the Czech Republic these events are not referred to as expulsions, rather they use the expression "Odsun" meaning "evacuation" in English. In the case of Czech Republic, The 1996 Report of the Commission on the losses connected with the transfer, which was prepared at the joint Czech-German Historical Commission . It reported that the number of deaths was 15,000 to 30,000 and that number of 220,000 estimated by the Centre Against Expulsions is not supported by the evidence. The Commission was able to confirm 15,580 deaths related to the expulsions and an additional 6,667 suicides, a total of 22,247 confirmed deaths. In the final report the Commission raised the total estimated maximum to 30,000 deaths in order to account for the possibility of unreported deaths.The commission found that the demographic estimates by the German government of 220,000 to 270,000 civilian deaths due to expulsions from Czechoslovakia were based on faulty data. The Commission determined that the demographic estimates by the German government counted as missing 90,000 ethnic Germans assimilated into the Czech population; military deaths were understated and that the 1950 census data used to compute the demographic losses was unreliable.[136] [6][136]
Developing a clear picture of the expulsion of Germans from Czechoslovakia is difficult because of the chaotic conditions that existed at the end of the war. There was no stable central government and record-keeping was non-existent. Many of the events that occurred during that period were spontaneous and local rather than being the result of coordinated policy directives from a central government. Among these spontaneous events was the removal and detention of the Sudeten Germans which was triggered by the strong anti-German sentiment at the grass-roots level and organized by local officials.
Records of food rationing coupons show approximately 3,325,000 inhabitants of occupied Sudetenland in May 1945. Of these, about 500,000 were Czechs or other non-Germans. Thus, there were approximately 2,725,000 Germans in occupied Sudetenland in May 1945.
On the initiative of the joint Czech-German Commission of Historians, a statistical and demographic investigation was conducted, resulting in the publication of the "Opinion of the Commission on the losses connected with the transfer". The number that the commission arrived at has since been accepted by a large section of the historians, press and media in other countries:
- Figures for the victims of the transfer vary enormously and are thus extremely controversial. The values given in German statistical calculations [for deaths resulting from expulsion of Germans from Czechoslovakia] vary between 220,000 and 270,000 cases that are unaccounted for, which are in many cases interpreted as deaths; the figures given in research carried out so far varies between 15,000 and 30,000 deaths.
- The discrepancy is due to differing notions of the term "victims of the transfer".
- In the commission's view, a particular problem with the "balance-sheet" approach is that most of the data it works with are based on model calculations and estimates that are derived from quantities that cannot be compared with one another.
Tracing the Fates of Individuals In Yugoslavia[edit]
A. The organizations of the ethnic German Expellees from Yugoslavia have traced the fate of the civilians who perished in the expulsions. In 1991-1995 the results of their research were published in a four volume study[163] that listed the names and cause of death of each person. The following is a summary of their findings.
| Description | Before Internment | In Internment Camps | In Flight from Internment Camps |
In the USSR | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Murdered | 7,199 | 558 | 79 | 7,836 | |
| Suicides | 154 | 60 | 214 | ||
| Deaths while escaping | 143 | 143 | |||
| Starvation | 47,654 | 47,654 | |||
| In Forced Labor(USSR) | 1,994 | 1,994 | |||
| Missing | 696 | 175 | 18 | 889 | |
| Total | 8,049 | 48,447 | 240 | 1,994 | 58,730 |
The report also listed the deaths of 605 civilians killed in military operations outside of Yugoslavia and 26,064 men who were dead and missing in the German Armed forces. The report mentioned that a total of 166,970 civilians were interned by the Yugoslav authorities and an additional 12,380 were deported to the USSR as forced laborers.[164]
B. The German Church Search Service figures issued in 1965 are as follows: 55,300 confirmed deaths:(5,538 violent deaths; 2,052 deported for forced labor USSR; 43,274 in internment camps; 1,960 during the wartime Flight and 287 in the course of the expulsions). In addition the German Church Search Service listed 36,164 "unsolved cases" of civilians listed as missing and 29,745 military dead.[165]
C. The Schieder commission figures published in 1961 are as follows: c. 69,000 civilian casualties including (5,777 violent deaths; 5,683 dead and missing persons deported for forced labor in the USSR; 48,027 in internment camps; 2,361 during the wartime Flight,187 in prisons and 6,273 missing persons).[104]
Estimates concerning Poland only[edit]
Poland expulsions and deportations[edit]
In Poland, these events are not referred to as expulsions, rather they use the expression Wysiedlenie i emigracja ludności niemieckiej – The Deportation and Emigration of the German people.
A 2005 study in Poland reported the data of Polish government indicated that about 4 million Germans remained on Polish territory in mid-1945, out of the pre-war population of about 10 million. The remaining balance were killed in the war, held as POWs or had fled to Germany in the final months of the war. By 1950, about three million persons had been deported from Poland and 1.1 million persons were verified as Polish citizens.[57]
By 1964, the Suchdienst (search service) of the German churches was able to confirm 367,392 civilian deaths from the territory of contemporary Poland (detailed as follows: 44,603 violent deaths; 10,330 suicides; 32,947 forced labor dead; 27,847 in the transit camps prior to expulsion; 86,860 during the flight west; 57,814 after the expulsions; and 106,991 cause undetermined). There were an additional 1,404,993 unconfirmed cases of persons reported dead and missing.[5]
The 1974 report of the German archives estimated that east of the Oder-Neisse line 60,000 German civilians died on Polish territory in communist internment camps and 40,0000 in Soviet forced labor in the Kaliningrad Oblast, not including 100,000 killed by the Red Army and their Allies during the war and 200,000 in forced labor in the USSR.[81]
The Polish historian Bernadetta Nitschke has provided a summary of the research in Poland on the calculation of German losses due to the flight and resettlement of the Germans from Poland only, not including other Central and Eastern European countries. Nitschke contrasted the estimate of 1.6 million deaths in Poland reported in 1958 by the West German government with the more recent figure of 400,000 that was detailed by Rudiger Overmans in 1994. She noted that the Polish researcher Stefan Banasiak estimated in 1963 that the death toll during the post-war deportations was 1,136 persons, a figure accepted by other Polish historians who maintain that most of the deaths occurred during the flight and evacuation during the war, the deportation to the U.S.S.R. for forced labor and after the resettlement due to the harsh conditions in the Soviet occupation zone in post war Germany.[142] This is in sharp contrast to the 1958 West German government Schieder commission report, which maintained that these deaths occurred after the war on Polish territory.
2,612,000 Germans left Poland from February 1946 to December 1949 according to S. Jankowiak,[166] as cited by B. Nitschke.
During the pre-Potsdam expulsions, many Germans were forced to march over 100 and sometimes even 200 kilometres.[167] Different estimates of the number of Germans expelled by People's Army of Poland alone during pre-Potsdam deportations (all numbers after Jankowiak):[168] 365,000 to 1,200,000 Germans were deported by Polish administration.[169]
The 1958 German government report of 1958 listed 7,960,000 expellees from Poland (including the pre-war territories of Germany, Poland and Danzig). This figure includes those persons who fled during the war and returned POWs as well as those who left Poland after the war.
Expelled from Poland July- Dec. 1945"[170]
- 1,222 thousand, according to K.Kersten, 1964 [170]
- 300 thousand, according to S.Banasiak [170]
- 400 thousand, K.Skubiszewski [170]
- 500 thousand, A.Ogrodowczyk [170]
- 350-450 thousand, A.Magierska, 1978 [170]
- 200-250 thousand, T.Białecki, 1970 [170]
- 620-630 thousand, S.Zwoniński, 1983 [170]
Estimated deaths
- In 1965 Andrzej Brożek quoted the losses at 1,020,000 in Poland.[171] Barbara Nitschke dismissed this number as too high.[170]
- 300-400 thousand, S.Chojnecki, 1980 [citation needed]
- 230-250 thousand, Cz. Osękowski [citation needed]
- 500–550 thousand, Z. Romanow [citation needed]
- 400 thousand, B.Nitschke [170]
- 400 thousand, M.Wille, 1996 [citation needed]
- 600–700 thousand [172]
- 1.6 million per 1958 German government statement[173][174]
- 367,000 confirmed deaths 1965 German Search Service.[175]
- 400,000 per 1974 German Archives study[176]
Germans remaining in Poland[edit]
Former German citizens remaining in Poland after 1950 in the Oder-Neisse territories are put at 1.1 million according to 1950 Polish Census figures including "autochthons" – Polish-speaking or bilingual German citizens – in Upper Silesia, Masuria and West Prussia.[57] This figure was confirmed by the 1950 German government demographic study of the population. Dr. Gerhard Reichling in 1995 put the total number at 1.3 million in 1950(Note: A significant proportion of Germans remaining in postwar Poland were allowed to emigrate after 1956 and benefited as a result of Brandt's Ostpolitik.)
Casualties[edit]
Summary of the death toll estimates of flight, evacuation and expulsion[edit]
| Year | Estimate | Source | Reference | Provided in | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1950 | 3,000,000 | Government of West Germany | Wirtschaft und Statistik April 1950 | U.S. Congressman B. Carroll Reece Charged that 3 million German civilians had died during the expulsions[177] |
This was a preliminary demographic estimate of the losses by the West German government which included 1.5 million from pre-war eastern Germany and 1.5 million ethnic Germans from East Europe. At that time only 162,000 missing had been registered with the government.[5] |
| 1953 | 3,140,000 | de:Gotthold Rhode | Zeitschrift für Ostforschung | The first attempt to compute the losses was made in 1953 by the German scholar Gotthold Rhode who estimated losses in the area of the expulsions at 3,140,000. Details by country Oder-Neisse region 1,640,000; Poland 280,000, Danzig 90,000; Czechoslovakia 450,000; Yugoslavia 385,000; Rumania 150,000; Hungary 100,000; Baltic States 45,500.[178] | |
| 1953 | 800,000 | de:Bruno Gleitze | Vierteljahrshefte zur Wirtschaftsforschung.[95] | Gleitze estimated 800,000 civilian deaths (for Germany within 1937 borders only) among only "Eastern Germans" in the area of the expulsions. The figures in the Gleitze study were ignored by the Schieder commission report, issued in 1953, which gave a figure of 1.617 million civilian deaths among the eastern Germans (in 1937 borders) | |
| 1954–1961 | 2,340,600 | Schieder commission | Dokumentation der Vertreibung der Deutschen aus Ost-Mitteleuropa | Details by country Germany within 1937 borders 2,167,000(figure includes 500,000 military and 50,000 civilian air raid dead); Poland(1939 borders) 217,000; Danzig100,000; Czechoslovakia 225,600; Yugoslavia 69,000; Rumania 40,000; Hungary 6,000[179] Not included are Germans in the USSR. The statistical information in the Schieder Report was later superseded by the 1958 German Government demographic study. | |
| 1958 | 2,225,000 | Government of West Germany (Statistiches Bundesamt/Destatis; eng. Federal Statistical Office of Germany) | Die deutschen Vertreibungsverluste, 1939–50 (German losses from expulsion, 1939–50) (August 1958) | Dr. Rudiger Overmans provided an analysis in 1994.[5] | This is the official German government report on losses. Details by country Germany within 1937 borders 1,338,700; Poland 185,000, Baltic States 51,400; Danzig 83,200; Czechoslovakia 272,900; Yugoslavia 135,800; Rumania 101,000; Hungary 57,000. Figures do not include 1,088,000 military and 11,500 civilian air raid dead; also not included are Soviet Germans or Germans resettled in Poland during the war. |
| 1958 | 2,098,400 | Government of West Germany (Statistiches Bundesamt/Destatis; eng. Federal Statistical Office of Germany) | Wirtschaft und Statistik November 1958 | The Statistisches Bundesamt issued a revised figure for Germany within 1937 borders 1,212,100; Ethnic Germans from East-Central Europe 886,300. Figures do not include 1,088,000 military and 11,500 civilian air raid dead; also not included are Soviet Germans or Germans resettled in Poland during the war. | |
| 1965 | 2,379,004 (473,013 Confirmed dead and 1,905,991 Unsolved Cases) | German Church Search Service/Red Cross | Gesamterhebung zur Klärung des Schicksals der deutschen Bevölkerung in den Vertreibungsgebieten, (General compilation towards accounting for the fate of the German population in the areas of expulsion), Munich, 1965-[180] | Dr. Rudiger Overmans has provided an analysis in 1994 of this unpublished internal report of the German Church Service[5] | This report was kept secret until 1986. A brief summary of data from the report was published in 1987.[181] |
| 1966 | 2,111,000 | Federal Ministry for Expellees, Refugees and War Victims | Facts concerning the problem of the German expellees and refugees | Figure cited in A Terrible Revenge by Alfred de Zayas | Germany within 1937 borders 1,225,000; Ethnic Germans from East-Central Europe 886,000 |
| 1974 | 600,000 | German Federal Archives | Vertreibung und Vertreibungsverbrechen, 1945-1948 : Bericht des Bundesarchivs vom 28. Mai 1974 : Archivalien und ausgewählte Erlebnisberichte | Dr. Rudiger Overmans provided an analysis in 1994.[5] | This report was archived and not published until 1989. Figure includes 150,000 deaths due to acts of violence, 250,000 deaths in internment camps and 200,000 forced labor in the USSR. Authors of report maintain that figures exclude additional losses resulting from malnutrition and disease. |
| 1982 | 2,800,000 | Heinz Nawratil | Schwarzbuch der Vertreibung 1945 bis 1948 (the Black Book of the Expulsions 1945 to 1948) (Universitas Verlag, Munich, 9th edition 2001, p. 75) | According to the webpage of Heinz Nawratil the Munich Institut für Zeitgeschichte (Institute of Contemporary History)was rebuked and cautioned by the Bavarian State Government in April 1985 for its criticism of the Sudetendeutsche Volksgruppe.[182] In 1987 the German historian Martin Broszat head of the Institut für Zeitgeschichte (Institute of Contemporary History) between 1972 and 1989 described Nawratil's writings as "polemics with a nationalist-rightist point of view and exaggerates in an absurd manner the scale of "expulsion crimes".[183] | Nawratil's figures include the 1958 German government figure of 2.2 million dead plus his estimate of 350,000 Soviet Germans and 250,000 Germans who were resettled in the Poland during the war which were not included in the 1958 demographic study. |
| 1982 | 2,000,000 to 2,500,000 | West German Interior Ministry[184] | Eingliederung der Vertriebenen, Flüchtlinge und Kriegsgeschädigten in der Bundesrepublik Deutschland | Figure of Statistisches Bundesamt (German Federal Statistics Office) | |
| 1986 | 2,020,000 | Dr. Gerhard Reichling | Die deutschen Vertriebenen in Zahlen (the German expellees in figures), Teil 1, Bonn 1995, Tabelle 7, page 36 | This report has the endorsement of the German government. Includes those who perished as a result of the expulsion and deportation for Forced labor of Germans in the Soviet Union. Includes the deaths of 310,000 Soviet Germans, and 108,000 Germans resettled in Poland during the war not included in 1958 report. | |
| 1995 | 2.2 million | German Church Search Service/Red Cross | Figure cited by Hans Henning Hahn and Eva Hahn[132] | The German Red Cross issued a statement that their research confirmed the results of the 1958 Demographic study that put total losses at 2.2 million. | |
| 2000 | 500,000 confirmed deaths; 2,000,000 total demographic estimate | Rudiger Overmans | Deutsche Militärische Verluste im Zweiten Weltkrieg (German military losses in the Second World War) | The Overmans study did not investigate civilian losses, only military casualties, he merely noted that other studies of expulsion losses put confirmed dead at about 500,000. | Overmans believes new research on the number of expulsion deaths is needed since only 500,000 of the reported 2,000,00 deaths are confirmed.[5] |
| 2001 | 600,000 total; 400,000 in Poland | Bernadetta Nitschke | Wysiedlenie czy wypedzenie? ludnosc niemiecka w Polsce w latach 1945-1949 p. 240. German translation Vertreibung und Aussiedlung der deutschen Bevölkerung aus Polen 1945 bis 1949 | Nitschke cites 1994 report of Rudiger Overmans as source for figures.[5] | Figures from 1974 German Archives report mentioned above. |
| 2005 | 2,251,500 | German Church Search Service/Red Cross | Willi Kammerer; Anja Kammerer- Narben bleiben die Arbeit der Suchdienste - 60 Jahre nach dem Zweiten Weltkrieg Berlin, Dienststelle 2005 ( Published by the Search Service of the German red Cross. The foreword to the book was written by German President Horst Köhler and the German interior minister Otto Schily)[185] | The German Red Cross did not provide details of this figure. | |
| 2006 | 500,000 to 600,000 | Ingo Haar | Interview on German Radio German Radio web site | Harr has published three articles on the historiography of the expulsions in post war West Germany.[99][97][98] | Figures from German Church Service and German Archives reports mentioned above. |
| 2006 | 473,000 | Ingo Haar | In 2006 the German historian Ingo Haar called into question the validity of the official government figure of 2.0 million expulsion deaths in an article in the German newspaper Süddeutsche Zeitung.[186] Polish translation of Haar in Gazeta Wyborcza. | Gazeta Wyborcza | Harr maintains that confirmed deaths of 473,000 is the correct figure, he does not include 1,906,000 unresolved cases that he believes to be unreliable. |
| 2006 | 400,000 | Ingo Haar | Polish translation of Haar after Süddeutsche Zeitung | Gazeta Wyborcza | Figures from German Federal Archive Report mentioned above for Poland only |
| 2006 | 2,000,000-2,500,000 | Government of Germany | Statement on German Radio .[10] | In a rebuttal to Ingo Harr, Christoph Bergner, Secretary of State in Germany's Bureau for Inner Affairs stated the position of the German government that 2 million died in expulsions. | |
| 2010 | 473,016 | Hans Henning Hahn and Eva Hahn | Hans Henning Hahn and Eva Hahn : Die Vertreibung im deutschen Erinnern. Legenden, Mythos, Geschichte. Paderborn 2010, | Figure from German Church Service mentioned above. The Hahn's maintain that most of the losses occurred in the flight during the war and about 80,000 occurred in the post-war period. | |
| 2013 | 600,000 | German Historical Museum | Die Flucht der deutschen Bevölkerung | They maintain the official figure of 2 million cannot be supported. |
Sources[edit]
- R.M. Douglas: Orderly and Humane. The Expulsion of the Germans after the Second World War. Yale University Press, 2012. ISBN 978-0300166606.
- Hans Henning Hahn and Eva Hahn : Die Vertreibung im deutschen Erinnern. Legenden, Mythos, Geschichte. Paderborn 2010, ISBN 978-3-506-77044-8
- Ursprünge, Arten und Folgen des Konstrukts „Bevölkerung“ vor, im und nach dem „Dritten Reich“ Zur Geschichte der deutschen Bevölkerungswissensch: Ingo Haar Die deutschen ›Vertreibungsverluste‹ – Forschungsstand, Kontexte und Probleme, in Ursprünge, Arten und Folgen des Konstrukts „Bevölkerung“ vor, im und nach dem „Dritten Reich“ Springer 2009: ISBN 978-3-531-16152-5
- Herausforderung Bevölkerung : zu Entwicklungen des modernen Denkens über die Bevölkerung vor, im und nach dem Dritten Reich Ingo Haar, Bevölkerungsbilanzen“ und „Vertreibungsverluste. Zur Wissenschaftsgeschichte der deutschen Opferangaben aus Flucht und Vertreibung Verlag für Sozialwissenschaften 2007 ISBN 978-3-531-15556-2
- Ingo Haar, Die Deutschen „Vertreibungsverluste –Zur Entstehung der „Dokumentation der Vertreibung - Tel Aviver Jahrbuch, 2007, Tel Aviv : Universität Tel Aviv, Fakultät für Geisteswissenschaften, Forschungszentrum für Geschichte; Gerlingen [Germany] : Bleicher Verlag
- Ingo Haar, Straty zwiazane z wypedzeniami: stan badañ, problemy, perspektywy. Polish Diplomatic Review. 2007, nr 5 (39)
- Piotr Eberhard Political Migrations In Poland 1939-1948 Warsaw2006
- Stanisław Jankowiak, Wysiedlenie i emigracja ludności niemieckiej w polityce władz polskich w latach 1945-1970, Instytut Pamięci Narodowej, Warzaw 2005, ISBN 83-89078-80-5
- Prauser, Steffen and Rees, Arfon: The Expulsion of the "German" Communities from Eastern Europe at the End of the Second World War. Florence, Italy, Europe. University Institute, 2004.
- ZENTRUM GEGEN VERTREIBUNGEN Chronik der Vertreibungen europäischer Völker im 20. Jahrhundert 2004
- Bernadetta Nitschke. Vertreibung und Aussiedlung der deutschen Bevölkerung aus Polen 1945 bis 1949. München, Oldenbourg Verlag, 2003. ISBN 3-486-56832-9. German translation of . Wysiedlenie czy wypedzenie? ludnosc niemiecka w Polsce w latach 1945-1949
- Hoensch, Jörg K. und Hans Lemberg, Begegnung und Konflikt. Schlaglichter auf das Verhältnis von Tschechen, Slowaken und Deutschen 1815 - 1989 Bundeszentrale für politische Bildung 2001 ISBN 3-89861-002-0
- Final Statement and Conclusions of the Czech-German Historical Commission 1996
- Česko-německá komise historiků a Slovensko-německá komise historiků
- Naimark, Norman: Fires of Hatred. Ethnic Cleansing in Twentieth -Century - Europe. Cambridge, Harvard University Press, 2001.
- Dr. Gerhard Reichling, Die deutschen Vertriebenen in Zahlen, Teil 1, Bonn 1995
- Dr. Rűdiger Overmans- Personelle Verluste der deutschen Bevölkerung durch Flucht und Vertreibung. (A parallel Polish summary translation was also included, this paper was a presentation at an academic conference in Warsaw Poland in 1994), Dzieje Najnowsze Rocznik XXI-1994
- Pistohlkors, Gert : Informationen zur Klärung der Schicksale von Flüchtlingen aus den. Vertreibungsgebieten östlich von Oder und Neiße. Published in Schulze, Rainer, Flüchtlinge und Vertriebene in der westdeutschen Nachkriegsgeschichte : Bilanzierung der Forschung und Perspektiven für die künftige Forschungsarbeit Hildesheim : A. Lax, 1987
- German Federal Archive Spieler, Silke. ed. Vertreibung und Vertreibungsverbrechen 1945-1948. Bericht des Bundesarchivs vom 28. Mai 1974. Archivalien und ausgewählte Erlebnisberichte.. Bonn: Kulturstiftung der deutschen Vertriebenen. (1989). ISBN 3-88557-067-X.
- Federal Ministry for Expellees, Refugees and War Victims, Facts concerning the problem of the German expellees and refugees, Bonn 1966- Table 4
- Gesamterhebung zur Klärung des Schicksals der deutschen Bevölkerung in den Vertreibungsgebieten. Band 1.München : Zentralstelle des Kirchl. Suchdienstes, [1965]
- Die deutschen Vertreibungsverluste. Bevölkerungsbilanzen für die deutschen Vertreibungsgebiete 1939/50. Herausgeber: Statistisches Bundesamt - Wiesbaden. - Stuttgart: Kohlhammer Verlag, 1958
- Documents on the expulsion of the Germans from eastern-central-Europe. Vol 1-4 Bonn : Federal Ministry for Expellees, Refugees and War Victims. 1960 ( English translation of selections from the Schieder commission report)
- Schieder commission Bundesministerium für Vertriebene, Dokumentation der Vertreibung der Deutschen aus Ost-Mitteleuropa Vol. 1–5, Bonn, 1954–1961
- Rhode, Gotthold, Die Deutschen im Osten nach 1945. Zeitschrift für Ostforschung, Heft 3, 1953
- de Zayas, Alfred M.: A Terrible Revenge. Palgrave/Macmillan, New York, 1994. ISBN 1-4039-7308-3.
- de Zayas, Alfred M.: Nemesis at Potsdam. London, 1977, ISBN 0-8032-4910-1.
- de Zayas, Alfred M.: 50 Theses on the Expulsion of the Germans from Central and Eastern Europe 1944–1948. 2012. ISBN 978-3-9812110-4-7.
References[edit]
- ^ Die Flucht der deutschen Bevölkerung 1944/45
- ^ Bundesministerium für Vertriebene, Flüchtlinge und Kriegsgeschädigte (Hrsg.): Dokumentation der Vertreibung der Deutschen aus Ost-MitteleuropaZur Zusammensetzung der Autorengruppe vgl. Bernd Faulenbach: Einführung in die Dokumentation. Archived 2012-02-05 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Die deutschen Vertreibungsverluste. Bevölkerungsbilanzen für die deutschen Vertreibungsgebiete 1939/50. Herausgeber: Statistisches Bundesamt - Wiesbaden. - Stuttgart: Kohlhammer Verlag, 1958
- ^ Pistohlkors, Gert : Informationen zur Klärung der Schicksale von Flüchtlingen aus den. Vertreibungsgebieten östlich von Oder und Neiße. Published in Schulze, Rainer, Flüchtlinge und Vertriebene in der westdeutschen Nachkriegsgeschichte : Bilanzierung der Forschung und Perspektiven für die künftige Forschungsarbeit Hildesheim : A. Lax, 1987
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o Dr. Rűdiger Overmans- Personelle Verluste der deutschen Bevölkerung durch Flucht und Vertreibung. (A parallel Polish summary translation was also included, this paper was a presentation at an academic conference in Warsaw Poland in 1994), Dzieje Najnowsze Rocznik XXI-1994
- ^ a b c d Gesamterhebung zur Klärung des Schicksals der deutschen Bevölkerung in den Vertreibungsgebieten, München : Zentralstelle des Kirchl. Suchdienstes, 1965
- ^ German Federal Archive Spieler, Silke. ed. Vertreibung und Vertreibungsverbrechen 1945-1948. Bericht des Bundesarchivs vom 28. Mai 1974. Archivalien und ausgewählte Erlebnisberichte.. Bonn: Kulturstiftung der deutschen Vertriebenen. (1989). ISBN 3-88557-067-X.
- ^ a b c Ingo Haar, Deutschlandfunk interview of 14 November 2006, [1]
- ^ Rüdiger Overmans, Deutschlandfunk interview of 6 December 2006 [2]
- ^ a b c d Christoph Bergner, Secretary of State in Germany's Bureau for Inner Affairs, outlines the stance of the respective governmental institutions in Deutschlandfunk on 29 November 2006, [3]
- ^ a b c Willi Kammerer; Anja Kammerer- Narben bleiben die Arbeit der Suchdienste - 60 Jahre nach dem Zweiten Weltkrieg Berlin Dienststelle 2005 ( Published by the Search Service of the German Red Cross. The foreword to the book was written by German President Horst Köhler and the German interior minister Otto Schily)
- ^ a b Gesetz über die Angelegenheiten der Vertriebenen und Flüchtlinge
- ^ Cf. Federal Expellee Law, § 2 (1).
- ^ Federal Ministry for Expellees, Refugees and War Victims. Facts concerning the problem of the German expellees and refugees, Bonn: 1967.
- ^ David P. Forsythe, Encyclopedia of Human Rights, Volume 1, Oxford University Press, Oxford, 2009, p. 164.
- ^ Donald Bloxham & A. Dirk Moses, The Oxford Handbook of Genocide Studies, Oxford University Press, Oxford (2010).
- ^ Douglas, R.M., Orderly and Humane: The Expulsion of the Germans after the Second World War, Yale University Press, New Haven, 2012, p. 1
- ^ Ulrich Merten, Forgotten Voices: The Expulsion of the Germans from Eastern Europe after World War II, Transaction 2012 preface, p. xii
- ^ Alfred M. de Zayas, A terrible Revenge, St. Martin's (1994), p. 1
- ^ a b Gerhard Reichling, Die deutschen Vertriebenen in Zahlen, part 1, Bonn: 1995, pp. 44–59.(in German)
- ^ a b Manfred Görtemaker, Geschichte der Bundesrepublik Deutschland: Von der Gründung bis zur Gegenwart, Munich: C.H. Beck, 1999, p. 169; ISBN 3-406-44554-3; accessed 26 May 2015.
- ^ Michael Levitin, Germany provokes anger over museum to refugees who fled Poland during WWII, Telegraph.co.uk; accessed 6 December 2014.
- ^ Steffen Prauser and Arfon Rees, The Expulsion of 'German' Communities from Eastern Europe at the end of the Second World War, European University Institute, Florence. HEC No. 2004/1, p. 4; accessed 26 May 2015.
- ^ Pertti Ahonen (2003). After the expulsion: West Germany and Eastern Europe, 1945–1990. Oxford University Press. p. 20. ISBN 0-19-925989-5.
- ^ Raport GUS. W Polsce jest 148 tysięcy Niemców, nto.pl; accessed 6 December 2014.(in Polish)
- ^ This legal definition, although the term is colloquially often used as a synecdoche pars pro toto for all refugees and expellees, is used to differentiate Heimatvertriebene from others defined as expellees, such as those subsumed under No. 2, who were not denied to return to their homeland, at least if it was west of the Oder and Neisse, or Umsiedler (see No. 3 below) who had left their original homeland already during the Nazi population transfers, or expelled German expatriates (No. 4) who – at least in theory – were considered not to regard their former places of residence as their homeland, or Aussiedler (see No. 5 below) who usually left without the opportunity to return – like expellees – but chose a new place within Germany to be their homeland.
- ^ However, in the terminology of East Germany Umsiedler (i.e. resettler, repatriate) was the term used for all refugees and expellees in order to avoid these terms indicating the unvoluntary conditions.
- ^ Gerhard Reichling, Die deutschen Vertriebenen in Zahlen, Teil 1, Bonn: 1995, pp. 44–59.
- ^ Cf. the Gesetz über die Rechtsstellung heimatloser Ausländer im Bundesgebiet (shorthand: HAuslG; literally: law on the legal status of homeless foreigners in the federal territory).
- ^ Hans Henning Hahn & Eva Hahn, Die Vertreibung im deutschen Erinnern. Legenden, Mythos, Geschichte, Paderborn: Schöningh, 2010, p. 659
- ^ Gerhard Reichling, Die deutschen Vertriebenen in Zahlen, part 1, Bonn: 1995, pp. 44–59
- ^ "Wer infolge von Kriegseinwirkungen Aufenthalt in den in Absatz 1 genannten Gebieten genommen hat, ist jedoch nur dann Vertriebener, wenn es aus den Umständen hervorgeht, dass er sich auch nach dem Kriege in diesen Gebieten ständig niederlassen wollte oder wenn er diese Gebiete nach dem 31. Dezember 1989 verlassen hat.", gesetze-im-internet.de; accessed 26 May 2015.(in German)
- ^ Gesetz über die Angelegenheiten der Vertriebenen und Flüchtlinge (Bundesvertriebenengesetz - BVFG), gesetze-im-internet.de; accessed 25 May 2015.(in German)
- ^ Gerhard Reichling, Die deutschen Vertriebenen in Zahlen, part 1, Bonn: 1995, pp. 23-27
- ^ a b Gerhard Reichling, Die deutschen Vertriebenen in Zahlen, part 1, Bonn: 1995, pp. 55-58
- ^ Source: Gerhard Reichling, Die deutschen Vertriebenen in Zahlen, part 1, Bonn: 1995, pp. 44–59.
- ^ a b Axel Schildt, Deutsche Geschichte im 20. Jahrhundert: ein Lexikon, Munich: C.H. Beck, 2005, p. 159; ISBN 3-406-51137-6
- ^ a b c Wacław Długoborski, Zweiter Weltkrieg und sozialer Wandel: Achsenmächte und besetzte Länder, Göttingen: Vandenhoeck & Ruprecht, 1981, pp. 119seq; ISBN 3-525-35705-2.
- ^ a b c Ahonen, Pertti (2003). After the expulsion: West Germany and Eastern Europe, 1945–1990. Oxford University Press. p. 21. ISBN 0-19-925989-5.: "roughly 8 million" West Germany, "some four million" East Germany, 500,000 Austria and other countries. Total = 12.5 million (1950).
- ^ Ahonen, Pertti (2003). After the expulsion: West Germany and Eastern Europe, 1945–1990. Oxford University Press. p. 21. ISBN 0-19-925989-5.
- ^ Philipp Ther, Geglückte Integration?: Spezifika und Vergleichbarkeiten der Vertriebenen-Eingliederung in der SBZ/DDR by Dierk Hoffmann & Michael Schwartz, Munich: Oldenbourg Wissenschaftsverlag, 1999, pp. 140seq; ISBN 348664503X Google.de; accessed 26 MAy 2015.(in German)
- ^ a b Philipp Ther, Deutsche und Polnische Vertriebene: Gesellschaft und Vertriebenenpolitik in SBZ/ddr und in Polen 1945–1956, 1998, p. 13; ISBN 3-525-35790-7, ISBN 978-3-525-35790-3.(in German)
- ^ Pertti Ahonen (2003). After the expulsion: West Germany and Eastern Europe, 1945–1990. Oxford University Press. p. 274. ISBN 0-19-925989-5.
- ^ Gerhard Reichling, Die deutschen Vertriebenen in Zahlen, part 1, Bonn: 1995, pp. 8
- ^ Gerhard Reichling, Die deutschen Vertriebenen in Zahlen, part 1, Bonn: 1995, pp. 19–20.
- ^ "Der Sammelbegriff 'sonstige' umfasst andre Bekenntnisse (mosaische Gemeinden und Landesverbände, andre Volks- und Weltreligionen, freireligiöse und Weltanschauungsgemeinschaften) und Bekenntnisslose sowie Personen ohne Angabe eines Religionsbekenntnisses."
- ^ a b Statisches Jahrbuch für das Deutsche Reich, 1941/42, pp. 27/28. Available online at http://www.digizeitschriften.de
- ^ In the Statisches Jahrbuch für das Deutsche Reich 1941/42. On page 27 the total (27,526) of full Jews by province was: East Prussia 3,169; Pomerania 3,417; Brandenburg 4,019; and Silesia 16,921)
- ^ A source published in Poland in the communist era puts the actual number of full Jews east of the Oder–Neisse line at about 23,000 because a section of the provinces of Pomerania and Brandenburg were west of the Oder–Neisse line; see Stanisaw Schimitzek, Truth or conjecture?: German civilian war losses in the East, Warsaw: 1966, p. 72
- ^ Ingo Haar, "Hochgerechnetes Unglück, Die Zahl der deutschen Opfer nach dem Zweiten Weltkrieg wird übertrieben", Süddeutsche Zeitung, 14 November 2006.
- ^ Eberhardt, Piotr. Ethnic Groups and Population Changes in Twentieth-Century Central-Eastern Europe: History, Data, Analysis. M.E. Sharpe, 2002; ISBN 0-7656-0665-8, p. 129; Eberhardt did not give a figure for Slovakia
- ^ Die deutschen Vertreibungsverluste. Bevölkerungsbilanzen für die deutschen Vertreibungsgebiete 1939/50, Statistisches Bundesamt, Wiesbaden (ed.), Stuttgart: Kohlhammer Verlag, 1958, pp. 322–339.
- ^ Piotr Eberhardt, Ethnic Groups and Population Changes in Twentieth-Century Central-Eastern Europe: History, Data, Analysis M.E. Sharpe, 2002, p. 293; ISBN 0-7656-0665-8
- ^ U.S. Bureau of the Census, The Population of Poland. Ed. W. Parker Mauldin, Washington, D.C., 1954 p. 148
- ^ Dokumentation der Vertreibung der Deutschen aus Ost-Mitteleuropa complete ed., "Das Schicksal der Deutschen in Jugoslawien", p. 19.
- ^ Hans Henning Hahn & Eva Hahn, Die Vertreibung im deutschen Erinnern. Legenden, Mythos, Geschichte. Paderborn: Schöningh, 2010, pp. 679–681; ISBN 978-3-506-77044-8.(in German)
- ^ a b c Gawryszewski, Andrzej. Ludność Polski w XX wieku.Warszawa : Instytut Geografii i Przestrzennego Zagospodarowania im. Stanisława Leszczyckiego PAN, 2005
- ^ Gerhard Reichling, Die deutschen Vertriebenen in Zahlen, part 1, Bonn: 1995, pp. 23-27
- ^ Piotr Eberhardt, Ethnic Groups and Population Changes in Twentieth-Century Central-Eastern Europe: History, Data, Analysis, M. E. Sharpe (2002); ISBN 0-7656-0665-8
- ^ Pistohlkors, Gert : Informationen zur Klärung der Schicksale von Flüchtlingen aus den. Vertreibungsgebieten östlich von Oder und Neiße. Published in Schulze, Rainer, Flüchtlinge und Vertriebene in der westdeutschen Nachkriegsgeschichte : Bilanzierung der Forschung und Perspektiven für die künftige Forschungsarbeit Hildesheim : A. Lax, 1987
- ^ Hans Henning Hahn and Eva Hahn
- Die Vertreibung im deutschen Erinnern. Legenden, Mythos, Geschichte. Paderborn 2010, ISBN 978-3-506-77044-8 Pages 724
- ^ a b Pistohlkors, Gert : Informationen zur Klärung der Schicksale von Flüchtlingen aus den. Vertreibungsgebieten östlich von Oder und Neiße. Publish<ed in Schulze, Rainer, Flüchtlinge und Vertriebene in der westdeutschen Nachkriegsgeschichte : Bilanzierung der Forschung und Perspektiven für die künftige Forschungsarbeit Hildesheim : A. Lax, 1987
- ^ Pistohlkors, Gert : Informationen zur Klärung der Schicksale von Flüchtlingen aus den. Vertreibungsgebieten östlich von Oder und Neiße. Published in Schulze, Rainer, Flüchtlinge und Vertriebene in der westdeutschen Nachkriegsgeschichte : Bilanzierung der Forschung und Perspektiven für die künftige Forschungsarbeit Hildesheim : A. Lax, 1987
- ^ Die Vertreibung im deutschen Erinnern. Legenden, Mythos, Geschichte. Hans Henning Hahn and Eva Hahn Paderborn 2010, Page-702
- ^ Herausforderung Bevölkerung : zu Entwicklungen des modernen Denkens über die Bevölkerung vor, im und nach dem Dritten Reich Ingo Haar, Bevölkerungsbilanzen“ und „Vertreibungsverluste. Zur Wissenschaftsgeschichte der deutschen Opferangaben aus Flucht und Vertreibung Verlag für Sozialwissenschaften 2007 ISBN 978-3-531-15556-2 Page 278
- ^ a b Hans Henning Hahn and Eva Hahn : Die Vertreibung im deutschen Erinnern. Legenden, Mythos, Geschichte. Paderborn 2010, ISBN 978-3-506-77044-8 Pages 659-726
- ^ Bohmann, Alfred. Menschen und Grenzen/ 4, Bevölkerung und Nationalitäten in der Tschechoslowakei, Cologne: Verl. Wissenschaft u. Politik, 1975. pp. 434, 467
- ^ a b c Herausforderung Bevölkerung : zu Entwicklungen des modernen Denkens über die Bevölkerung vor, im und nach dem "Dritten Reich" Pages 267-281 Ingo Haar,Bevölkerungsbilanzen“ und „Vertreibungsverluste“. Zur Wissenschaftsgeschichte der deutschen Opferangaben aus Flucht und Vertreibung Verlag für Sozialwissenschaften 2007 ISBN 978-3-531-15556-2
- ^ a b c Ingo Haar, Straty zwiazane z wypedzeniami: stan badañ, problemy, perspektywy. Polish Diplomatic Review. 2007, nr 5 (39) [4] Archived 2011-03-02 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ German Federal Archive (1989). Spieler, Silke (ed.). Vertreibung und Vertreibungsverbrechen 1945-1948. Bericht des Bundesarchivs vom 28. Mai 1974. Archivalien und ausgewählte Erlebnisberichte. Bonn: Kulturstiftung der deutschen Vertriebenen. p. 17. ISBN 3-88557-067-X.
- ^ German Federal Archive (1989). Spieler, Silke (ed.). Vertreibung und Vertreibungsverbrechen 1945-1948. Bericht des Bundesarchivs vom 28. Mai 1974. Archivalien und ausgewählte Erlebnisberichte. Bonn: Kulturstiftung der deutschen Vertriebenen. pp. 17–18. ISBN 3-88557-067-X.
- ^ German Federal Archive (1989). Spieler, Silke (ed.). Vertreibung und Vertreibungsverbrechen 1945-1948. Bericht des Bundesarchivs vom 28. Mai 1974. Archivalien und ausgewählte Erlebnisberichte. Bonn: Kulturstiftung der deutschen Vertriebenen. p. 18. ISBN 3-88557-067-X.
- ^ a b c German Federal Archive (1989). Spieler, Silke (ed.). Vertreibung und Vertreibungsverbrechen 1945-1948. Bericht des Bundesarchivs vom 28. Mai 1974. Archivalien und ausgewählte Erlebnisberichte. Bonn: Kulturstiftung der deutschen Vertriebenen. p. 19. ISBN 3-88557-067-X.
- ^ a b German Federal Archive (1989). Spieler, Silke (ed.). Vertreibung und Vertreibungsverbrechen 1945-1948. Bericht des Bundesarchivs vom 28. Mai 1974. Archivalien und ausgewählte Erlebnisberichte. Bonn: Kulturstiftung der deutschen Vertriebenen. p. 20. ISBN 3-88557-067-X.
- ^ a b German Federal Archive (1989). Spieler, Silke (ed.). Vertreibung und Vertreibungsverbrechen 1945-1948. Bericht des Bundesarchivs vom 28. Mai 1974. Archivalien und ausgewählte Erlebnisberichte. Bonn: Kulturstiftung der deutschen Vertriebenen. p. 21. ISBN 3-88557-067-X.
- ^ a b German Federal Archive (1989). Spieler, Silke (ed.). Vertreibung und Vertreibungsverbrechen 1945-1948. Bericht des Bundesarchivs vom 28. Mai 1974. Archivalien und ausgewählte Erlebnisberichte. Bonn: Kulturstiftung der deutschen Vertriebenen. p. 22. ISBN 3-88557-067-X.
- ^ a b c d e German Federal Archive (1989). Spieler, Silke (ed.). Vertreibung und Vertreibungsverbrechen 1945-1948. Bericht des Bundesarchivs vom 28. Mai 1974. Archivalien und ausgewählte Erlebnisberichte. Bonn: Kulturstiftung der deutschen Vertriebenen. p. 38. ISBN 3-88557-067-X.
- ^ a b c d German Federal Archive (1989). Spieler, Silke (ed.). Vertreibung und Vertreibungsverbrechen 1945-1948. Bericht des Bundesarchivs vom 28. Mai 1974. Archivalien und ausgewählte Erlebnisberichte. Bonn: Kulturstiftung der deutschen Vertriebenen. p. 39. ISBN 3-88557-067-X.
- ^ a b German Federal Archive (1989). Spieler, Silke (ed.). Vertreibung und Vertreibungsverbrechen 1945-1948. Bericht des Bundesarchivs vom 28. Mai 1974. Archivalien und ausgewählte Erlebnisberichte. Bonn: Kulturstiftung der deutschen Vertriebenen. p. 40. ISBN 3-88557-067-X.
- ^ German Federal Archive (1989). Spieler, Silke (ed.). Vertreibung und Vertreibungsverbrechen 1945-1948. Bericht des Bundesarchivs vom 28. Mai 1974. Archivalien und ausgewählte Erlebnisberichte. Bonn: Kulturstiftung der deutschen Vertriebenen. pp. 40–41. ISBN 3-88557-067-X.
- ^ a b c d German Federal Archive (1989). Spieler, Silke (ed.). Vertreibung und Vertreibungsverbrechen 1945-1948. Bericht des Bundesarchivs vom 28. Mai 1974. Archivalien und ausgewählte Erlebnisberichte. Bonn: Kulturstiftung der deutschen Vertriebenen. p. 41. ISBN 3-88557-067-X.
- ^ a b German Federal Archive (1989). Spieler, Silke (ed.). Vertreibung und Vertreibungsverbrechen 1945-1948. Bericht des Bundesarchivs vom 28. Mai 1974. Archivalien und ausgewählte Erlebnisberichte. Bonn: Kulturstiftung der deutschen Vertriebenen. p. 46. ISBN 3-88557-067-X.
- ^ a b c German Federal Archive (1989). Spieler, Silke (ed.). Vertreibung und Vertreibungsverbrechen 1945-1948. Bericht des Bundesarchivs vom 28. Mai 1974. Archivalien und ausgewählte Erlebnisberichte. Bonn: Kulturstiftung der deutschen Vertriebenen. p. 47. ISBN 3-88557-067-X.
- ^ a b c d German Federal Archive (1989). Spieler, Silke (ed.). Vertreibung und Vertreibungsverbrechen 1945-1948. Bericht des Bundesarchivs vom 28. Mai 1974. Archivalien und ausgewählte Erlebnisberichte. Bonn: Kulturstiftung der deutschen Vertriebenen. p. 51. ISBN 3-88557-067-X.
- ^ German Federal Archive (1989). Spieler, Silke (ed.). Vertreibung und Vertreibungsverbrechen 1945-1948. Bericht des Bundesarchivs vom 28. Mai 1974. Archivalien und ausgewählte Erlebnisberichte. Bonn: Kulturstiftung der deutschen Vertriebenen. pp. 51–52. ISBN 3-88557-067-X.
- ^ a b German Federal Archive (1989). Spieler, Silke (ed.). Vertreibung und Vertreibungsverbrechen 1945-1948. Bericht des Bundesarchivs vom 28. Mai 1974. Archivalien und ausgewählte Erlebnisberichte. Bonn: Kulturstiftung der deutschen Vertriebenen. p. 52. ISBN 3-88557-067-X.
- ^ a b c d e German Federal Archive (1989). Spieler, Silke (ed.). Vertreibung und Vertreibungsverbrechen 1945-1948. Bericht des Bundesarchivs vom 28. Mai 1974. Archivalien und ausgewählte Erlebnisberichte. Bonn: Kulturstiftung der deutschen Vertriebenen. p. 53. ISBN 3-88557-067-X.
- ^ Pavel Polian-Against Their Will: The History and Geography of Forced Migrations in the USSR Central European University Press 2003 ISBN 963-9241-68-7
- ^ a b Kurt W. Böhme - Gesucht wird - Die dramtische Geschichte des Suchdienstes Süddeutscher Verlag, München 1965 Page 274
- ^ Hoensch, Jörg K. und Hans Lemberg, Begegnung und Konflikt. Schlaglichter auf das Verhältnis von Tschechen, Slowaken und Deutschen 1815 - 1989 Bundeszentrale für politische Bildung 2001 ISBN 3-89861-002-0
- ^ Die Vertreibung im deutschen Erinnern. Legenden, Mythos, Geschichte. Hans Henning Hahn and Eva Hahn Paderborn 2010, Page-700
- ^ Sienkiewicz, Witold Hryciuk, Grzegorz; Wysiedlenia, wypędzenia i ucieczki 1939-1959 : atlas ziem Polski : Polacy, Żydzi, Niemcy, Ukraińcy Warszawa : Demart, 2008. Page 187 Efektem były liczne zgony, których nie można dokładnie określic z powodu brak statystyk lub ich fałszowania. Okresowo mogly one sięgać kilkudziesięciu procent osadzonych. Szacunki mówią o 200-250 tys internowanych Niemców i ludności rodzimej, a czego zginąć moglo od 15 do aż 60tys. osób.
- ^ Wirtschaft und Statistik April 1950
- ^ Gotthold Rhode, Zeitschrift für Ostforschung 1953 Heft 3
- ^ a b B. Gleitze, Deutschlands Bevölkerungsverluste durch den Zweiten Weltkrieg, Vierteljahrshefte zur Wirtschaftsforschung 1953, s. 375-384
- ^ Dokumentation der Vertreibung der Deutschen aus Ost-Mitteleuropa
- ^ a b Ursprünge, Arten und Folgen des Konstrukts „Bevölkerung“ vor, im und nach dem „Dritten Reich“ Zur Geschichte der deutschen Bevölkerungswissensch: Ingo Haar Die deutschen ›Vertreibungsverluste‹ – Forschungsstand, Kontexte und Probleme, in Ursprünge, Arten und Folgen des Konstrukts „Bevölkerung“ vor, im und nach dem „Dritten Reich“ Springer 2009: ISBN 978-3-531-16152-5
- ^ a b Herausforderung Bevölkerung : zu Entwicklungen des modernen Denkens über die Bevölkerung vor, im und nach dem Dritten Reich Ingo Haar, Bevölkerungsbilanzen“ und „Vertreibungsverluste. Zur Wissenschaftsgeschichte der deutschen Opferangaben aus Flucht und Vertreibung Verlag für Sozialwissenschaften 2007 ISBN 978-3-531-15556-2
- ^ a b Ingo Haar, Die Deutschen „Vertreibungsverluste –Zur Entstehung der „Dokumentation der Vertreibung - Tel Aviver Jahrbuch, 2007, Tel Aviv : Universität Tel Aviv, Fakultät für Geisteswissenschaften, Forschungszentrum für Geschichte; Gerlingen [Germany] : Bleicher Verlag
- ^ a b Theodor Schieder, Dokumente der Vertreibung der Deutschen aus Ost-MittelEuropa. Band I/1 und I/2. Die Vertreibung der Deutschen Bevölkerung aus den Gebieten östlich der Oder-Neisse Herausgegeben vom Bundesministerium für Vertriebene 2 Bände, Bonn 1954, Page 160
- ^ a b Theodor Schieder, Dokumente der Vertreibung der Deutschen aus Ost-MittelEuropa. Band II. Das Schicksal der Deutschen in Ungarn, Bonn 1957, Page 72
- ^ Theodor Schieder, Dokumentation der Vertreibung der Deutschen aus Ost-Mitteleuropa. Herausg. vom Bundesministerium für Vertriebene, Flüchtlinge und Kriegsgeschädigte. Band IV/2. Die Vertreibung der Deutschen Bevölkerung aus der Tschechoslowakei, Bonn 1957, Page 135
- ^ Theodor Schieder, Dokumentation der Vertreibung der Deutschen aus Ost-Mitteleuropa. Das Schicksal der Deutschen in Rumänien. Band III, Bonn 1957 Page 80, Pages 121-122
- ^ a b Theodor Schieder Dokumentation der Vertreibung der Deutschen aus Ost-Mitteleuropa. Herausg. vom Bundesministerium für Vertriebene, Flüchtlinge und Kriegsgeschädigte. Band V: Das Schicksal der Deutschen in Jugoslawien, Bonn 1961, Page 131
- ^ Theodor Schieder, Dokumente der Vertreibung der Deutschen aus Ost-MittelEuropa. Band I/1 und I/2. Die Vertreibung der Deutschen Bevölkerung aus den Gebieten östlich der Oder-Neisse Herausgegeben vom Bundesministerium für Vertriebene 2 Bände, Bonn 1954, Page 159-160
- ^ a b Theodor Schieder, Dokumente der Vertreibung der Deutschen aus Ost-MittelEuropa. Band I/1 und I/2. Die Vertreibung der Deutschen Bevölkerung aus den Gebieten östlich der Oder-Neisse Herausgegeben vom Bundesministerium für Vertriebene 2 Bände, Bonn 1954, Page 65
- ^ Theodor Schieder, Dokumente der Vertreibung der Deutschen aus Ost-MittelEuropa. Band I/1 und I/2. Die Vertreibung der Deutschen Bevölkerung aus den Gebieten östlich der Oder-Neisse Herausgegeben vom Bundesministerium für Vertriebene 2 Bände, Bonn 1954, Page 158
- ^ Theodor Schieder, Dokumentation der Vertreibung der Deutschen aus Ost-Mitteleuropa. Das Schicksal der Deutschen in Rumänien. Band III, Bonn 1957, Page 80 and pages 121-122
- ^ Theodor Schieder Dokumentation der Vertreibung der Deutschen aus Ost-Mitteleuropa. Herausg. vom Bundesministerium für Vertriebene, Flüchtlinge und Kriegsgeschädigte. Band V: Das Schicksal der Deutschen in Jugoslawien, Bonn 1961, Page131
- ^ Die deutschen Vertreibungsverluste. Bevölkerungsbilanzen für die deutschen Vertreibungsgebiete 1939/50. Herausgeber: Statistisches Bundesamt - Wiesbaden. - Stuttgart: Kohlhammer Verlag, 1958Pages 35-36
- ^ Wirtschaft und Statistik 11-1958 Pages 600-604
- ^ Die deutschen Vertreibungsverluste. Bevölkerungsbilanzen für die deutschen Vertreibungsgebiete 1939/50. Herausgeber: Statistisches Bundesamt - Wiesbaden. - Stuttgart: Kohlhammer Verlag, 1958
- ^ Die deutschen Vertreibungsverluste. Bevölkerungsbilanzen für die deutschen Vertreibungsgebiete 1939/50. Herausgeber: Statistisches Bundesamt - Wiesbaden. - Stuttgart: Kohlhammer Verlag, 1958 See pages 102, 143,174,323 381
- ^ The Die deutschen Vertreibungsverluste used the definition "ungeklärte Fälle (Nachkriegsverluste), "Unsolved Cases (postwar losses)" when referring to those persons who were presumed dead
- ^ (these figures are a brief summary of the data from tables on pages 38 and 46 of the text)
- ^ R. J. Rummel. Statistics of democide : Genocide and Mass Murder since 1900 (1,863,000 in post war expulsions and an additional 1.0 million in wartime flight)
- ^ Alfred M. de Zayas: A terrible Revenge. Palgrave/Macmillan, New York, 1994. ISBN 1-4039-7308-3. page 152- (2,111,000)
- ^ Charles S Maier, The Unmasterable Past: History, Holocaust, and German National Identity Harvard Univ, MA, 1988 ISBN 0-674-92975-6 page 75- (2,000,000)
- ^ Douglas Botting, The Aftermath: Europe (World War II), Time-Life Books, 1983, ISBN 0-8094-3411-3, Pages 21 and 81- (2,000,000)
- ^ H.W. Schoenberg, Germans from the East: A Study of their migration, resettlement and subsequent group history, since 1945, Springer London, Limited, 1970 ISBN 90-247-5044-X page 33- (2,225,000)
- ^ Hermann Kinder, Werner Hilgemann, Ernest A. Menze, Anchor Atlas of World History, Vol. 2: 1978- (3,000,000)
- ^ Encyclopædia Britannica- 1992- (2,384,000)
- ^ Kurt Glaser & Stephan Possony, Victims of Politics -1979 - (2,111,000)
- ^ John Keegan, The Second World War 1989- (3.1 million including 1.0 million during wartime flight)
- ^ The Expulsion of 'German' Communities from Eastern Europe at the end of the Second World War, Steffen Prauser and Arfon Rees, European University Institute, Florence. HEC No. 2004/1. p. 4- (2,000,000)
- ^ German President Horst Köhler, Speech on September 2, 2006 "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2012-12-02. Retrieved 2013-05-27.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ^ "Ingo Haar, Ile było ofiar wypędzenia? Gazeta Wyborcza November 21, 2006". Archived from the original on May 26, 2011. Retrieved March 26, 2007.
- ^ Süddeutsche Zeitung 14. November 2006 Ingo Haar Hochgerechnetes Unglück, Die Zahl der deutschen Opfer nach dem Zweiten Weltkrieg wird übertrieben
- ^ Dr. Rűdiger Overmans-Personelle Verluste der deutschen Bevölkerung durch Flucht und Vertreibung. (A parallel Polish translation was also included, this paper was a presentation at an academic conference in Warsaw Poland in 1994), Dzieje Najnowsze Rocznik XXI-1994
- ^ Rűdiger Overmans. Deutsche militärische Verluste im Zweiten Weltkrieg. Oldenbourg 2000. ISBN 3-486-56531-1
- ^ pl:Piotr Eberhardt, Political Migrations In Poland 1939-1948 Warsaw2006 "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2011-10-18. Retrieved 2016-02-08.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) Pages 53-54 - ^ a b Hans Henning Hahn and Eva Hahn : Die Vertreibung im deutschen Erinnern. Legenden, Mythos, Geschichte. Paderborn 2010, ISBN 978-3-506-77044-8 Pages 659-726
- ^ Hans Henning Hahn and Eva Hahn : Die Vertreibung im deutschen Erinnern. Legenden, Mythos, Geschichte. Paderborn 2010, ISBN 978-3-506-77044-8 Pages 712-715
- ^ Hans Henning Hahn and Eva Hahn : Die Vertreibung im deutschen Erinnern. Legenden, Mythos, Geschichte. Paderborn 2010, ISBN 978-3-506-77044-8 Pages 679-681
- ^ Leidensweg der Deutschen im kommunistischen Jugoslawien / verfasst vom Arbeitskreis Dokumentation im Bundesverband der Landsmannschaft der Donauschwaben aus Jugoslawien, Sindelfingen, und in der Donauschwäbischen Kulturstiftung, München. Imprint München : Die Stiftung, 1991-1995. Vol 4 p. 1018–1019
- ^ a b c Hoensch, Jörg K. und Hans Lemberg, Begegnung und Konflikt. Schlaglichter auf das Verhältnis von Tschechen, Slowaken und Deutschen 1815 - 1989 Bundeszentrale für politische Bildung 2001 ISBN 3-89861-002-0
- ^ "Stellungnahme der Deutsch-Tschechischen Historikerkommission zu den Vertreibungsverlusten :: Tschechien-portal | nemecko-portal .info :: Informationsnetzwerk | Informaèní si»". Archived from the original on 2011-07-22. Retrieved 2016-12-01. Stellungnahme der Deutsch-Tschechischen Historikerkommission zu den Vertreibungsverlusten
- ^ Dr. Gerhard Reichning, Die deutschen Vertriebenen in Zahlen, Teil 1, Bonn 1995
- ^ Die Vertreibung im deutschen Erinnern. Legenden, Mythos, Geschichte. Hans Henning Hahn and Eva Hahn Paderborn 2010, Pages 721-722
- ^ Foundation Centre Against Expulsions, data and sources, "Zentrum gegen Vertreibungen". Archived from the original on 2009-08-02. Retrieved 2009-03-22.
- ^ a b Ursprünge, Arten und Folgen des Konstrukts „Bevölkerung“ vor, im und nach dem „Dritten Reich“ Zur Geschichte der deutschen Bevölkerungswissensch: Ingo Haar Die deutschen ›Vertreibungsverluste‹ – Forschungsstand, Kontexte und Probleme, in Ursprünge, Arten und Folgen des Konstrukts „Bevölkerung“ vor, im und nach dem „Dritten Reich“ Pages 376-377Springer 2009: ISBN 978-3-531-16152-5
- ^ a b Bernadetta Nitschke. Vertreibung und Aussiedlung der deutschen Bevölkerung aus Polen 1945 bis 1949. München, Oldenbourg Verlag, 2003. ISBN 3-486-56832-9. S. 269-282.
- ^ Hans Henning Hahn and Eva Hahn Die Vertreibung im deutschen Erinnern. Legenden, Mythos, Geschichte. Paderborn 2010, Page-659
- ^ Stephane Courtois, The Black Book of Communism: Crimes, Terror, Repression, Harvard Univ Pr, 1999 ISBN 0-674-07608-7 P.361-456
- ^ Alfred-Maurice de Zayas A Terrible Revenge: The Ethnic Cleansing of the East European Germans Palgrave Macmillan, 2006 ISBN 1-4039-7308-3
- ^ Rolf-Dieter Müller, Florian Huber, Johannes Eglau, Der Bombenkrieg 1939-1945 Christoph Verlag, 2004 [5] p.224
- ^ a b Das geplante Inferno Der Spiegel 1 April 2003 (in German)
- ^ Blank, Ralf (1990). Germany and the Second World War. Militärgeschichtliches Forschungsamt. p. 472. ISBN 978-0-19-928277-7.
- ^ Die deutschen Vertreibungsverluste. Bevölkerungsbilanzen für die deutschen Vertreibungsgebiete 1939/50. Herausgeber: Statistisches Bundesamt - Wiesbaden. - Stuttgart: Kohlhammer Verlag, 1958 p. 113
- ^ BOMBENANGRIFFE AUF DRESDEN 1945 Der Spiegel 3 October 2008
- ^ Steffen Prauser and Arfon Rees, The Expulsion of 'German' Communities from Eastern Europe at the end of the Second World War Archived 2009-10-01 at the Wayback Machine, European University Institute, Florence. HEC No. 2004/1. pp. 11seq.
- ^ Theodor Schieder, Die Vertreibung der deutschen Bevölkerung aus der Tschechoslowakei, Bonn: 1957, p. 7;(in German); 3,231,688 Czechoslovak citizens were ethnic Germans and an additional 86,757 Germans of other nations resided in Czechoslovakia.
- ^ Piotr Eberhardt, Ethnic Groups and Population Changes in Twentieth-Century Central-Eastern Europe: History, Data, Analysis, M.E. Sharpe, 2002, p. 129; ISBN 0-7656-0665-8; accessed 26 May 2015.
- ^ Alfred M. de Zayas, A Terrible Revenge. New York: Palgrave Macmillan, 1994; ISBN 1-4039-7308-3, pp. 152- (3,477,000)
- ^ H.W. Schoenberg, Germans from the East: A Study of Their Migration, Resettlement and Subsequent Group History, since 1945, London, UK: Springer, 1970; ISBN 90-247-5044-X, p. 3- (3,453,000)
- ^ Piotr Eberhardt, Ethnic Groups and Population Changes in Twentieth-Century Central-Eastern Europe: History, Data, Analysis, M.E. Sharpe, 2002, ISBN 0-7656-0665-8, p. 128; Eberhardt did not cite the "Czech authors" disputing the German figures.
- ^ ushmm.org; accessed 25 May 2015.
- ^ Source: Die deutschen Vertreibungsverluste. Bevölkerungsbilanzen für die deutschen Vertreibungsgebiete 1939/50, Statistisches Bundesamt, Wiesbaden (ed.), Stuttgart: Kohlhammer Verlag, 1958, pp. 322–39.
- ^ Statistisches Jahrbuch für das Deutsche Reich 1941/42 is available online here
- ^ Die deutschen Vertreibungsverluste. Bevölkerungsbilanzen für die deutschen Vertreibungsgebiete 1939/50, Statistisches Bundesamt, Wiesbaden (ed.), Stuttgart: Kohlhammer Verlag, 1958, pp. 322–325.(in German)
- ^ Hans Henning Hahn & Eva Hahn, Die Vertreibung im deutschen Erinnern. Legenden, Mythos, Geschichte, Paderborn: Schöningh, 2010, pp. 712–15; ISBN 978-3-506-77044-8.(in German)
- ^ Alfred M. de Zayas, A Terrible Revenge, p. 152.
- ^ Leidensweg der Deutschen im kommunistischen Jugoslawien / verfasst vom Arbeitskreis Dokumentation im Bundesverband der Landsmannschaft der Donauschwaben aus Jugoslawien, Sindelfingen, und in der Donauschwäbischen Kulturstiftung, München. Imprint München : Die Stiftung, 1991-1995.
- ^ Leidensweg der Deutschen im kommunistischen Jugoslawien / verfasst vom Arbeitskreis Dokumentation im Bundesverband der Landsmannschaft der Donauschwaben aus Jugoslawien, Sindelfingen, und in der Donauschwäbischen Kulturstiftung, München. Imprint München : Die Stiftung, 1991-1995. Vol 4 p. 1018–1019 These figures are only a brief summary of the data in the text
- ^ Alfred Bohmann, Menschen und Grenzen/ 2, Bevölkerung und Nationalitäten in Südosteuropa. Köln : Verl. Wissenschaft u. Politik, 1969. p. 276
- ^ Stanisław Jankowiak, Wysiedlenie i emigracja ludności niemieckiej w polityce władz polskich w latach 1945-1970, p. 207, Instytut Pamięci Narodowej, Warsaw 2005, ISBN 83-89078-80-5
- ^ Stanisław Jankowiak, Wysiedlenie i emigracja ludności niemieckiej w polityce władz polskich w latach 1945-1970, p. 91, Instytut Pamięci Narodowej, Warsaw 2005, ISBN 83-89078-80-5, after H. Szczegóła: "Die Aussiedlung der Deutschen aus Polen vor der Potsdamer Konferenz", 1994
- ^ Stanisław Jankowiak, Wysiedlenie i emigracja ludności niemieckiej w polityce władz polskich w latach 1945-1970, p. 93, Instytut Pamięci Narodowej, Warsaw 2005, ISBN 83-89078-80-5
- ^ Stanisław Jankowiak, Wysiedlenie i emigracja ludności niemieckiej w polityce władz polskich w latach 1945-1970, p.!!), Instytut Pamięci Narodowej, Warsaw 2005, ISBN 83-89078-80-5
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j Nitschke, "Wysiedlenie ...", p. 240
- ^ Andrzej Brożek (1965). Losy Niemców w Polsce po roku 1944/1945 : fikcja liczb zachodnioniemieckich a rzeczywisty bilans ludnościowy [The plight of Germans in Poland after 1944–45 : West German fiction and the real numbers]. Opole: Zarząd Wojewódzki Towarzystwa Rozwoju Ziem Zachodnich TRZZ. p. 16.
- ^ Stanisław Jankowiak, Wysiedlenie i emigracja ludności niemieckiej w polityce władz polskich w latach 1945-1970, p. 95, Instytut Pamięci Narodowej, Warsaw 2005, ISBN 83-89078-80-5
- ^ Die deutschen Vertreibungsverluste. Bevölkerungsbilanzen für die deutschen Vertreibungsgebiete 1939/50.Herausgeber: Statistisches Bundesamt - Wiesbaden. - Stuttgart: Kohlhammer Verlag, 1958 pp38-46
- ^ The Statistisches Jahrbuch für die Bundesrepublik Deutschland 1960, Page 78
- ^ Rüdiger Overmans, "Personelle Verluste der deutschen Bevölkerung durch Flucht und Vertreibung" (a parallel Polish summary translation was also included, this paper was a presentation at an academic conference in Warsaw in 1994), Dzieje Najnowsze Rocznik, XXI (1994).(in Polish)
- ^ Silke Spieler (ed.), Vertreibung und Vertreibungsverbrechen 1945–1948. Bericht des Bundesarchivs vom 28. Mai 1974. Archivalien und ausgewählte Erlebnisberichte, Bonn: Kulturstiftung der deutschen Vertriebenen (1989), pp. 38–41; ISBN 3-88557-067-X
- ^ Reece, B. Carroll, On German Provinces East of the Oder-Neisse Line and the Economic, Historical and Political Aspects Involved (speech by B. Carroll Reece of Tennessee in Washington DC 1958), translation: Das Recht auf Deutschlands Osten (Rautenberg 1957). See also Das Schicksal der Sudetendeutschen Die Sudetenfrage im US Kongress (Munich 1960), with Usher L. Burdick and John L. Rhodes; original title unknown. (All authors were members of US House of Representatives).
- ^ Rhode, Gotthold, Die Deutschen im Osten nach 1945. Zeitschrift für Ostforschung, Heft 3, 1953
- ^ Bundesministerium für Vertriebene, Dokumentation der Vertreibung der Deutschen aus Ost-Mitteleuropa Vol. 1-5, Bonn, 1954-1961
- ^ Gesamterhebung zur Klärung des Schicksals der deutschen Bevölkerung in den Vertreibungsgebieten. Band 1.München : Zentralstelle des Kirchl. Suchdienstes, [1965]
- ^ Pistohlkors, Gert : Informationen zur Klärung der Schicksale von Flüchtlingen aus den. Vertreibungsgebieten östlich von Oder und Neiße. Published in Schulze, Rainer, Flüchtlinge und Vertriebene in der westdeutschen Nachkriegsgeschichte : Bilanzierung der Forschung und Perspektiven für die künftige Forschungsarbeit Hildesheim : A. Lax, 1987
- ^ Webpage of Heinz Nawratil
- ^ Ursprünge, Arten und Folgen des Konstrukts „Bevölkerung“ vor, im und nach dem „Dritten Reich“ Zur Geschichte der deutschen Bevölkerungswissensch: Ingo Haar Die deutschen ›Vertreibungsverluste‹ – Forschungsstand, Kontexte und Probleme, in Ursprünge, Arten und Folgen des Konstrukts „Bevölkerung“ vor, im und nach dem „Dritten Reich“ Springer 2009: ISBN 978-3-531-16152-5 Page 373 Ingo Harr wrote Martin Brozat, der damalige Direktor des Instituts für Zeitgeschichte (IfZ), bewertete Nawratil's Werke bereites 1987 als polemische Trakate uas rechtsnationaler Ecke, die die Definition und das Ausmass der - Vertreibungsverbrechen "in absurder Weise ausweiten"
- ^ Bundesministerium des Innern- Eingliederung der Vertriebenen, Flüchtlinge und Kriegsgeschädigten in der Bundesrepublik Deutschland Bonn 1982 Page 18
- ^ Willi Kammerer; Anja Kammerer- Narben bleiben die Arbeit der Suchdienste - 60 Jahre nach dem Zweiten Weltkrieg Berlin, Dienststelle 2005
- ^ Ingo Haar, "Hochgerechnetes Unglück, Die Zahl der deutschen Opfer nach dem Zweiten Weltkrieg wird übertrieben", in: Süddeutsche Zeitung, 14 November 2006.
