Phenacemide
Appearance
(Redirected from Fenylacetylmocovina)
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Phenurone |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Micromedex Detailed Consumer Information |
| ATC code | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Elimination half-life | 22–25 hours |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.519 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
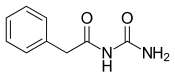
| Formula | C9H10N2O2 |
| Molar mass | 178.191 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Phenacemide (INN, BAN) (brand name Phenurone), also known as phenylacetylurea, is an anticonvulsant of the ureide (acetylurea) class.[1] It is a congener and ring-opened analogue of phenytoin (a hydantoin),[2][3] and is structurally related to the barbiturates and to other hydantoins.[4] Phenacemide was introduced in 1949 for the treatment of epilepsy, but was eventually withdrawn due to toxicity.[2][3]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ Ganellin CR, Triggle DJ (21 November 1996). Dictionary of Pharmacological Agents. CRC Press. pp. 1578–. ISBN 978-0-412-46630-4.
- ^ a b Prasad JP (2010). "Central Nervous System". Conceptual Pharmacology. Universities Press. pp. 236–. ISBN 978-81-7371-679-9.
- ^ a b Saxena AK, Saxena M (1995). "Developments in anticonvulsants". In deStevens G, Zingel V, Leschke C, Hoeprich P, Schultz R, Mehrotra P, et al. (eds.). Progress in Drug Research / Fortschritte der Arzneimittelforschung / Progrès des recherches pharmaceutiques. Vol. 44. Basel: Birkhäuser. pp. 185–291. doi:10.1007/978-3-0348-7161-7_6. ISBN 978-3-0348-7161-7. PMID 7644666.
{{cite book}}:|journal=ignored (help) - ^ Kadam SS, Mahadik KR, Bothara KG (1 July 2007). "Central Nervous System Depresants". Principles of Medicinal Chemistry. Vol. II. Pragati Books Pvt. Ltd. pp. 147–. ISBN 978-81-85790-03-9.
Further reading
[edit]- Coker SB (1986). "The use of phenacemide for intractable partial complex epilepsy in children". Pediatric Neurology. 2 (4): 230–232. doi:10.1016/0887-8994(86)90053-6. PMID 3508693.
- Coker SB, Holmes EW, Egel RT (December 1987). "Phenacemide therapy of complex partial epilepsy in children: determination of plasma drug concentrations". Neurology. 37 (12): 1861–1866. doi:10.1212/wnl.37.12.1861. PMID 3683877. S2CID 219205208.
