Fort McKinley (Maine)
Fort McKinley Historic District | |
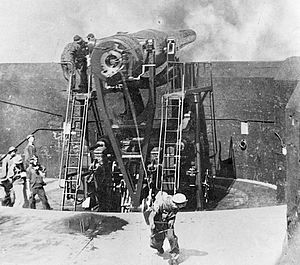 12-inch disappearing gun, similar to those mounted at Fort McKinley | |
| Location | Great Diamond Island, Maine |
|---|---|
| Coordinates | 43°40′45″N 70°11′50″W / 43.67917°N 70.19722°W |
| Area | 43 acres (17 ha) |
| Built | 1897 |
| Architect | US Army Corps of Engineers |
| NRHP reference No. | 85000611[1] |
| Added to NRHP | 21 March 1985 |
Fort McKinley is a former United States Army coastal defense fort on Great Diamond Island, Maine in Casco Bay, which operated from 1873 to 1947. It was named for President William McKinley. It included a sub-post, Fort Lyon, on Cow Island, just north of Great Diamond Island. Fort Lyon was named for Nathaniel Lyon. Both forts were part of the Coast Defenses of Portland, renamed the Harbor Defenses of Portland in 1925, a command which protected Portland's port and naval anchorage 1895-1950. In 1946 Fort Lyon was closed and turned over to the City of Portland.[2] After Fort McKinley's closure it was transferred to the United States Navy, which sold the site (via the General Services Administration) to private interests in 1961.[3] The Fort McKinley Historic District was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1985.[1]
History[edit]
Construction and armament[edit]
The Board of Fortifications, often called the Endicott Board, recommended a comprehensive program of new fortifications in 1885. Forts McKinley and Lyon were among the results. Construction on Fort McKinley began in 1897 and was complete by 1906. Fort McKinley totaled 111 acres (45 ha) resulting from two land purchases in 1873 and 1901. The fort was divided by Diamond Cove into a North Fork and a South Fork.[3] The entirety of Cow Island was acquired by the government in 1873; Fort Lyon was built on 22 acres (8.9 ha) of it and was complete by 1909.[2]


Fort McKinley was completed by 1906 with nine gun batteries as follows:[3][4]
North Fork:
| Name | No. of guns | Gun type | Carriage type | Years active |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ingalls | 8 | 12-inch (305 mm) mortar M1890 | barbette M1896 | 1904-1942 |
| Berry | 2 | 12-inch (305 mm) gun M1888 | disappearing M1896 | 1901-1943 |
| Thompson | 3 | 8-inch (203 mm) gun M1888 | disappearing M1896 | 1902-1942 |
| Acker | 2 | 6-inch (152 mm) gun M1897 | disappearing M1898 | 1902-1943 |
| Farry | 2 | 3-inch (76 mm) gun M1898 | masking parapet M1898 | 1902-1920 |
South Fork:
| Name | No. of guns | Gun type | Carriage type | Years active |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weymouth | 3 | 8-inch (203 mm) gun M1888 | disappearing M1896 | 1901-1942 |
| Honeycutt | 2 | 8-inch (203 mm) gun M1888 | disappearing M1896 | 1901-1942 |
| Carpenter | 2 | 6-inch (152 mm) gun M1900 | pedestal M1900 | 1906-1917, 1919-1947 |
| Ramsay | 2 | 3-inch (76 mm) gun M1898 | masking parapet M1898 | 1902-1920 |
Fort Lyon was completed by 1909 with two gun batteries as follows:[2]
| Name | No. of guns | Gun type | Carriage type | Years active |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bayard | 3 | 6-inch (152 mm) gun M1903 | disappearing M1903 | 1907-1917 |
| Abbot | 3 | 3-inch (76 mm) gun M1903 | pedestal M1903 | 1909-1946 |
At Fort McKinley, facilities supporting an underwater minefield were built on the South Fork and at Fort Lyon;[2] the 3-inch guns at both forts were intended to defend the minefield against minesweepers.[5] Construction of the original barracks and administration buildings at Fort McKinley began in 1902-1903 and lasted through 1906. This construction phase was sized for four companies. Four 109-man barracks were constructed along with four sets of duplex Non-Commissioned Officers' (NCO) quarters, six sets of duplex officers' quarters, three sets of single family officers' quarters and various administration and support buildings to accommodate a post of this size.[3]
A few buildings were built between 1905 and 1908, and a significant expansion to accommodate seven companies began in 1908-1909 and was largely complete by the end of 1910. The expansion included two additional barracks, one of which was a double barracks, four more sets of duplex NCO quarters and a ten-man Bachelor Officers' Quarters (BOQ). At this point, the fort had the capacity for 17 officers, 18 married NCOs, and 788 enlisted men. The existing hospital and guardhouse were expanded in 1910 to accommodate the increased population.[3]
World War I[edit]
During World War I, the forts were manned by artillery companies of the Coast Artillery Corps and Maine National Guard troops. After the American entry into World War I in 1917, the forts were partially disarmed so the guns could be shipped to the Western Front in France. Four of the eight mortars of Battery Ingalls were removed for conversion to railway artillery. This was done with most mortar batteries; with four mortars in each pit the reloading time was excessive due to crowding of men and equipment. So, mortars were removed to leave two mortars per pit. The mortars were not shipped to France; most railway mortars remained in reserve through World War II. Some of Fort McKinley's 8-inch (203 mm) guns were dismounted for railway conversion, but never left the fort and were later remounted.[3][6] The two 6-inch (152 mm) guns of Battery Carpenter and Fort Lyon's three six-inch guns were removed to be mounted on field carriages; all were shipped to France and later returned to the United States, with Battery Carpenter's guns returning to Fort McKinley.[3] The Fort Lyon guns were eventually used elsewhere on new mountings in World War II.[2] A history of the Coast Artillery in World War I states that none of the regiments in France equipped with 6-inch guns completed training in time to see action before the Armistice.[7]
In 1920 Fort McKinley lost both of its 3-inch gun batteries due to obsolescence; this was part of a general removal of all Driggs-Seabury 3-inch (76 mm) gun M1898 and their unique masking parapet mountings from service. The masking parapet mount was a simple form of disappearing mount; on 3-inch guns it could not be retracted in action and was locked in the up position after a few years in service.[3][8]
World War II[edit]
In 1940-1941 both forts were expanded to deal with the influx of draftees; a draft was instituted shortly after the outbreak of World War II in Europe in September 1939 and the National Guard was mobilized, which included Coast Artillery Corps units. Construction at Fort McKinley added six temporary enlisted barracks, one temporary officers' barracks, two mess halls, two administration buildings and two recreation buildings. This increased the post capacity to 62 officers, 18 married NCOs, 1438 enlisted men and 25 animals in Jun 1941.[3] In late 1941 Fort Lyon added three new temporary buildings, a wharf, and utilities to house 130 enlisted men and 6 officers. The three buildings included a 172-man mess hall, a 74-man enlisted barracks and a modified barracks to house 56 enlisted men and 6 officers. An antiaircraft battery was also deployed there.[2] At this time the major units garrisoning the Harbor Defenses of Portland were the 8th Coast Artillery Regiment of the Regular Army and the 240th Coast Artillery Regiment of the Maine National Guard.[9] However, most guns of the two forts would soon be removed and scrapped. A modernization centered on Battery Steele on Peaks Island was implemented, and by the end of 1943 all guns and mortars had been removed from both forts, except the two 6-inch (152 mm) guns at Battery Carpenter and three 3-inch (76 mm) guns at Battery Abbot.[2][3][4] With little threat to the East Coast from surface ships by 1944, the coast defenses were drawn down and the Coast Artillery regiments reduced to battalions or their personnel reassigned.[10] Shortly after the war the Army withdrew from Forts McKinley and Lyon and the properties were sold or transferred.
Present[edit]
Fort McKinley has been redeveloped as a gated community named Diamond Cove. Most of the batteries are heavily overgrown and on private property. Cow Island was redeveloped beginning in 2000 as a camp for environmental, adventure, and leadership development programs.[11]
See also[edit]
- Casco Bay
- Port of Portland (Maine)
- Seacoast defense in the United States
- United States Army Coast Artillery Corps
- List of coastal fortifications of the United States
- Harbor Defenses of Portland
- National Register of Historic Places listings in Cumberland County, Maine
References[edit]
- ^ a b "National Register Information System". National Register of Historic Places. National Park Service. July 9, 2010.
- ^ a b c d e f g FortWiki article on Fort Lyon
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j FortWiki article on Fort McKinley
- ^ a b Berhow, p. 202
- ^ Berhow, pp. 346-367
- ^ US Army Railway Artillery in WWI
- ^ History of the Coast Artillery Corps in WWI
- ^ Berhow, pp. 70-72, 202
- ^ Berhow, pp. 467-471
- ^ Stanton, Shelby L. (1991). World War II Order of Battle. Galahad Books. pp. 456, 470, 489. ISBN 0-88365-775-9.
- ^ Cow Island history at RippleEffect.com
- Berhow, Mark A., ed. (2004). American Seacoast Defenses, A Reference Guide (Second ed.). CDSG Press. ISBN 0-9748167-0-1.
- Lewis, Emanuel Raymond (1979). Seacoast Fortifications of the United States. Annapolis: Leeward Publications. ISBN 978-0-929521-11-4.
- United States Army (1941). Harbor Defenses of Portland, 1941: pictorial history. World War Regimental Histories. 99. Atlanta, GA: Army-Navy Publications.
External links[edit]
- 1929 film of mine planting operations in the Harbor Defenses of Portland, Maine
- List of all US coastal forts and batteries at the Coast Defense Study Group, Inc., website
- FortWiki, lists most CONUS and Canadian forts
- Gun types at FortWiki
- Historic American Engineering Record documentation, filed under Great Diamond Island, Portland, Cumberland County, ME:
- HAER No. ME-59, "Fort McKinley", 15 data pages
- HAER No. ME-59-A, "Fort McKinley, North Fork Mining Casemate, West side of Seal Cove Lane north of Wood Side Drive", 5 photos, 5 data pages, 2 photo caption pages
- HAER No. ME-59-B, "Fort McKinley, Battery Berry Observation Station, North side of Wood Side Drive approximately 80 feet east of Spring Cove Lane", 3 photos, 5 data pages, 2 photo caption pages
- HAER No. ME-59-C, "Fort McKinley, Battery Honeycutt Observation Station, East side of East Side Drive, approximately 225 feet south of Cove Side Drive", 3 photos, 5 data pages, 2 photo caption pages
- HAER No. ME-59-D, "Fort McKinley, Double Mine Building, East side of East Side Drive, approximately 125 feet south of Weymouth Way", 3 photos, 5 data pages, 21 photo caption pages
- HAER No. ME-59-E, "Fort McKinley, Battery Carpenter Observation Station, West side of East Side Drive, approximately 275 feet south of Weymouth Way", 3 photos, 5 data pages, 2 photo caption pages
- HAER No. ME-59-F, "Fort McKinley, South Fork Latrine, West side of East Side Drive, approximately 225 feet south of Weymouth Way", 4 photos, 5 data pages, 2 photo caption pages
- HAER No. ME-59-G, "Fort McKinley, Battery Weymouth Combined Observation Station, West side of East Side Drive, approximately 125 feet south of Weymouth Way", 2 photos, 5 data pages, 2 photo caption pages
- HAER No. ME-59-H, "Fort McKinley, South Fork Telephone Switchboard Building, South side of Weymouth Way, approximately 100 feet west of East Side Drive", 4 photos, 5 data pages, 2 photo caption pages
- HAER No. ME-59-I, "Fort McKinley, Meteorological Station, East side of Weymouth Way, approximately 225 feet south of Cove Side Drive", 3 photos, 4 data pages, 2 photo caption pages
- History of Maine
- Forts on the National Register of Historic Places in Maine
- Closed installations of the United States Army
- Historic American Engineering Record in Maine
- Historic districts on the National Register of Historic Places in Maine
- National Register of Historic Places in Portland, Maine
- 1897 establishments in Maine



