Fruit and a Jug on a Table (Metzinger)
| Fruit and a Jug on a Table | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Artist | Jean Metzinger |
| Year | 1916–1918 |
| Medium | Oil on canvas |
| Dimensions | 115.9 cm × 81 cm (45+5⁄8 in × 31+7⁄8 in) |
| Location | Museum of Fine Arts, Boston, Boston |
Fruit and a Jug on a Table (also titled Melon et compotier) is a Cubist painting dated 1916 by the French artist and theorist Jean Metzinger. In 1919 the painting was exhibited in Paris at Léonce Rosenberg's, Galerie de l'Effort Moderne. The painting was reproduced in the June 1924 (n. 6) issue of Bulletin de l'Effort Moderne.[1] The work is on view at Charlotte F. and Irving W. Rabb Gallery (Europe, 1900–1960, Modernism), Museum of Fine Arts, Boston.[2]
Description[edit]
Fruit and a Jug on a Table is an oil and sand on canvas, signed JMetzinger, lower left, and inscribed on the reverse; Peint par moi / en 1916 / Metzinger.[3] The work represents a diverse grouping of objects—a bowl of fruit, a carafe (or jug), a glass, and a bottle labelled BANYU. Banyuls-sur-Mer is a commune in the Pyrénées-Orientales department in southern France, located near Cerbère and Collioure. The foothills of Pyrenees run into the Mediterranean Sea in Banyuls-sur-Mer, creating a steep cliff line. Banyuls-sur-Mer is known for its wines, such as the sweet wine Banyuls: a fortified apéritif or dessert wine made from old vines cultivated in terraces on the slopes of the French and Catalan Pyrenees.
The style of Fruit and a Jug on a Table, its colors, the placement of objects and the background textures differ from Metzinger's earlier Crystal Cubist style of 1914–1916. According to Joann Moser, this work was most likely executed around 1917 or 1918.[3]
From 1914 through 1916 Metzinger's work was more abstract, overlapping volumetric forms were replaced with flattened surfaces, such as circles, squares, and rectangles.[4]
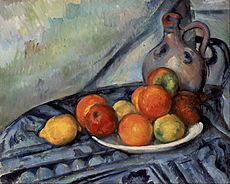
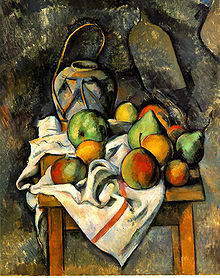
Fruit and a Jug on a Table represent a more naturalistic approach expressed by the artist after 1917. Temporal and spatial effects are more subdued. The multiple perspective and Riemannian geometry seen in his 1910–1912 works is no longer to be seen overtly, yet the perspective reminiscent of Paul Cézanne—the angle of the table and the still life elements on it—are unmistakably active, still. Decorative patterns likewise present, and surface impasto, visibly thicker and more ubiquitously prevalent than previous years, are typical of Metzinger's 1917–18 works.[4]
Provenance[edit]
In April 1919, the painting was with Léonce Rosenberg, Galerie de l'Effort Moderne, Paris.[5] There is a partial label dated April 1919 on the verso from Galerie de l'Effort Moderne. Metzinger had a solo exhibit at Léonce Rosenberg's l'Effort moderne gallery in January 1919. Metzinger's show was followed by exhibitions by Fernand Léger (February), Georges Braque (March), Juan Gris (April), Gino Severini (May), Pablo Picasso (June), Henri Hayden (December 1919), Jacques Lipchitz (January – February 1920), along with several group shows in which Metzinger participated, such as Les Maitres du Cubisme 3 May – 30 October 1920; an exhibit by the same name May 1921; Du cubisme à une renaissance plastique, 1922, and another solo exhibition 16 April – 10 May 1928.[2]
The painting was reproduced in the June 1924 (n. 6) issue of Bulletin de l'Effort Moderne.[1]
In 1955, Fruit and a Jug on a Table appeared in a public auction in Paris, and was purchased by Marlborough Fine Art, Ltd., London. In 1957, the painting was purchased from the Marlborough gallery by the Museum of Fine Arts, Boston, for £1,200.[2]
Published 1920[edit]
Fruit and a Jug on a Table was reproduced in Paul Erich Küppers, Der Kubismus; ein künstlerisches Formproblem unserer Zeit, 1920. The painting was titled Stilleben and dated 1917.[6]
See also[edit]
Notes and references[edit]
- ^ a b "Bulletin de l'Effort moderne, June 1924, No. 6, reproduced, titled Melon et compotier, dated 1919". Archived from the original on 2020-11-18. Retrieved 2019-01-09.
- ^ a b c Museum of Fine Arts, Boston
- ^ a b Joann Moser, Jean Metzinger in Retrospect, with Daniel Robbins, The University of Iowa Museum of Art, J. Paul Getty Trust, University of Washington Press, 1985
- ^ a b "Alex Mittelmann, 2012, Jean Metzinger, Divisionism, Cubism, Neoclassicism and Post Cubism". Archived from the original on 2012-11-05. Retrieved 2013-08-10.
- ^ "Collection de Léonce Rosenberg, marchand d'art, Jean Metzinger, Nature morte, Ministère de la Culture (France) – Médiathèque de l'architecture et du patrimoine". Archived from the original on 2015-02-05. Retrieved 2015-03-31.
- ^ Der Kubismus; ein künstlerisches Formproblem unserer Zeit, 1920. Read online

