Lumbar arteries
This article includes a list of references, related reading, or external links, but its sources remain unclear because it lacks inline citations. (June 2015) |
| Lumbar arteries | |
|---|---|
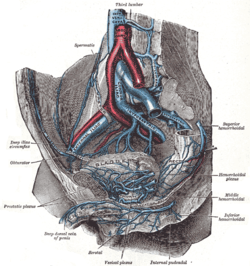 The veins of the right half of the male pelvis (lumbar arteries not labeled, but third lumbar vein labeled at center top) | |
| Details | |
| Source | Abdominal aorta |
| Vein | Lumbar veins |
| Supplies | Quadratus lumborum |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Arteriae lumbares |
| TA98 | A12.2.12.004 |
| TA2 | 4208 |
| FMA | 70807 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The lumbar arteries are arteries located in the lower back or lumbar region. The lumbar arteries are in parallel with the intercostals.
They are usually four in number on either side, and arise from the back of the aorta, opposite the bodies of the upper four lumbar vertebrae.
A fifth pair, small in size, is occasionally present: they arise from the middle sacral artery.
They run lateralward and backward on the bodies of the lumbar vertebrae, behind the sympathetic trunk, to the intervals between the adjacent transverse processes, and are then continued into the abdominal wall.
The arteries of the right side pass behind the inferior vena cava, and the upper two on each side run behind the corresponding crus of the diaphragm.
The arteries of both sides pass beneath the tendinous arches which give origin to the psoas major, and are then continued behind this muscle and the lumbar plexus.
They now cross the quadratus lumborum, the upper three arteries running behind, the last usually in front of the muscle.
At the lateral border of the quadratus lumborum they pierce the posterior aponeurosis of the transversus abdominis and are carried forward between this muscle and the obliquus internus.
They anastomose with the lower intercostal, the subcostal, the iliolumbar, the deep iliac circumflex, and the inferior epigastric arteries.
Additional images
-
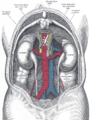
The relations of the viscera and large vessels of the abdomen.
See also
References
 This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 612 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 612 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
External links
- Anatomy photo:40:11-0201 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center - "Branches of the Abdominal Aorta"
- Atlas image: abdo_wall75 at the University of Michigan Health System - "The Abdominal Aorta"
- Anatomy figure: 40:05-07 at Human Anatomy Online, SUNY Downstate Medical Center - "Parietal and visceral branches of the abdominal aorta."