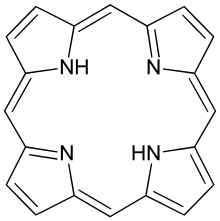
Porphine
| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
Porphin
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.002.690 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C20H14N4 | |
| Molar mass | 310.35196 g/mol |
| Appearance | Dark red, shiny leaflets |
| Melting point | N/A |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Porphine or porphin is an organic compound of empirical formula C20H14N4. It is heterocyclic and aromatic. The molecule is a flat macrocycle, consisting of four pyrrole-like rings joined by four methine bridges, which makes it the simplest of the tetrapyrroles.[1]
The nonpolar tetrapyrrolic ring structure of porphine means it is poorly soluble in most organic solvents and hardly water soluble.[2] As a result, porphine is mostly of theoretical interest. It has been detected in GC-MS of certain fractions of Piper betle.[3]
Porphine derivatives: porphyrins[edit]
Substituted derivatives of porphine are called porphyrins. Many porphyrins are found in nature with the dominant example being protoporphyrin IX.[4] Many synthetic porphyrins are also known, including octaethylporphyrin[5] and tetraphenylporphyrin.[6]
- Common porphyrins
-
Derivatives of protoporphyrin IX are common in nature, the precursor to hemes.
-
Octaethylporphyrin (H2OEP) is a synthetic analogue of protoporphyrin IX. Unlike the natural porphyrin ligands, OEP2− is highly symmetrical.
-
Tetraphenylporphyrin (H2TPP)is another synthetic analogue of protoporphyrin IX. Unlike the natural porphyrin ligands, TPP2− is highly symmetrical. Another difference is that its methine centers are occupied by phenyl groups.

Further reading[edit]
- Budavari, Susan (1989). "7574. Porphine". The Merck Index (11th ed.). Merck & Co., Inc. p. 1210. ISBN 0-911910-28-X. LCCN 89-60001.
References[edit]
- ^ "Porphyrin". Encyclopedia of Inorganic and Bioinorganic Chemistry. Wiley-VCH. 2011. doi:10.1002/9781119951438.eibd0638. ISBN 9781119951438.
- ^ Senge, Mathias O.; Davis, Mia (2010). "Porphyrin (porphine) — A neglected parent compound with potential" (PDF). Journal of Porphyrins and Phthalocyanines. 14 (07): 557–567. doi:10.1142/s1088424610002495. ISSN 1088-4246.
- ^ Karak S, Das S, Biswas M, Choudhury A, Dutta M, Chaudhury K, De B (December 2019). "Phytochemical composition, β-glucuronidase inhibition, and antioxidant properties of two fractions of Piper betle leaf aqueous extract". Journal of Food Biochemistry. 43 (12): e13048. doi:10.1111/jfbc.13048. PMID 31581322. S2CID 203661105.
- ^ Paul R. Ortiz de Montellano (2008). "Hemes in Biology". Wiley Encyclopedia of Chemical Biology. John Wiley & Sons. doi:10.1002/9780470048672.wecb221. ISBN 978-0470048672.
- ^ Jonathan L. Sessler; Azadeh Mozaffari; Martin R. Johnson (1992). "3,4-Diethylpyrrole and 2,3,7,8,12,13,17,18-Octaethylporphyrin". Org. Synth. 70: 68. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.070.0068.
- ^ Lindsey, Jonathan S. (2000). "Synthesis of meso-substituted porphyrins". In Kadish, Karl M.; Smith, Kevin M.; Guilard, Roger (eds.). Porphyrin Handbook. Vol. 1. pp. 45–118. ISBN 0-12-393200-9.



