Crossover distortion
This article needs additional citations for verification. (December 2009) |
Crossover distortion is a type of distortion which is caused by switching between devices driving a load.[1] It is most commonly seen in complementary, or "push-pull", class-B amplifier stages, although it is occasionally seen in other types of circuits as well.
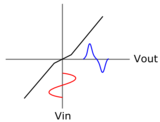
The term crossover signifies the "crossing over" of the signal between devices, in this case, from the upper transistor to the lower and vice versa. The term is not related to the audio loudspeaker crossover filter—a filtering circuit which divides an audio signal into frequency bands to drive separate drivers in multiway speakers.
Distortion mechanism
[edit]
The image shows a typical class-B emitter-follower complementary output stage. Under no signal conditions, the output is exactly midway between the supplies (i.e., at 0 V). When this is the case, the base-emitter bias of both the transistors is zero, so they are in the cut-off region where the transistors are not conducting.
Consider a positive-going swing: As long as the input is less than the required forward VBE drop (≈ 0.65 V) of the upper NPN transistor, it will remain off or conduct very little. This is the same as a diode operation as far as the base circuit is concerned, and the output voltage does not follow the input (the lower PNP transistor is still off because its base-emitter diode is being reverse biased by the positive-going input). The same applies to the lower transistor but for a negative-going input. Thus, between about ±0.65 V of input, the output voltage is not a true replica or amplified version of the input, and we can see that as a "kink" in the output waveform near 0 V (or where one transistor stops conducting and the other starts). This kink is the most pronounced form of crossover distortion, and it becomes more evident and intrusive when the output voltage swing is reduced.
Less pronounced forms of distortion may be observed in this circuit as well. An emitter-follower will have a voltage gain of just under 1. In the circuit shown, the NPN emitter-follower and the PNP emitter-follower will generally have very slightly different voltage gains, leading to slightly different gains above and below ground. Other more subtle forms of crossover distortion, stemming from slight differences between the PNP and NPN devices, exist.
Possible solutions
[edit]
As with most kinds of distortion, another way in which crossover distortion can be reduced is through the use of feedback. By comparing the output to the desired output, and adjusting the input to correct for any error, we can significantly reduce distortion. This may be done with an operational amplifier, as shown below, or with a discrete circuit.
In the example shown, the operational amplifier is used to reduce the distortion of a push-pull pair. Operational amplifiers are differential voltage amplifiers with very high gain (sometimes modeled as infinite gain). In an ideal model, the output of the op amp is held such that both inputs of the op amp must be at exactly the same voltage. In this case, since the inverting input is directly connected to the output, the voltage at the non-inverting input is always equal to the voltage at the output and inverting input, hence eliminating distortion. With a more precise model of an operational amplifier (with non-infinite gain) distortion is reduced by a factor equal to the gain of the op amp.
Most modern power amplifiers (including those used in hi-fi) employ both techniques, using both class-AB in their output stages, and feedback, offering reasonable efficiency and good distortion figures.
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ "Preface to the Sixth Edition - Audio Power Amplifier Design, 6th Edition [Book]". www.oreilly.com. Retrieved 2022-12-04.
