Luigi Mattei

Luigi Mattei (died 1665) was an Italian military General[1] and Marquis de Belmonte. During the 17th century he commanded troops loyal to the papal armies of Barberini Pope Urban VIII and Pamphili Pope Innocent X during the Wars of Castro.[2]
Biography[edit]
Mattei was the second son of Asdrubale Mattei, Marquis di Giove, of the House of Mattei and his wife Costanza Gonzaga of the House of Gonzaga.[3] His older brother, Girolamo Mattei, became Duca di Giove. He was the nephew of Ciriaco Mattei and Cardinal Girolamo Mattei.
He is variously described as Baron Mattei, a Papal Marquis and Papal Army Field Marshal.[4] It is more likely, though, that he was simply a skilled military leader (militia leader) loyal to the papacy of Pope Urban VIII and then later Pope Innocent X.
Military career[edit]
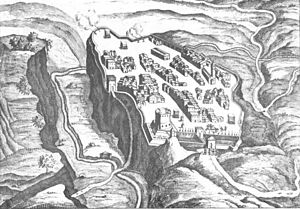
During the late 1630s, Pope Urban and his Barberini nephews came into conflict with the Farnese Dukes of Parma sparking the conflict known as the First War of Castro. In 1641, Mattei was appointed Lieutenant General of the papal armies and was accordingly given a monthly salary of 343 scudi.[5] On 12 October he led 12,000 infantry and 3,000 cavalry against the fortified town of Castro which was under the control of the Farnese. Though it is estimated that the Farnese had amassed a similarly sized army,[5] Mattei's forces were met with very little resistance and the town was forced to surrender. Mattei's victory at Castro was immortalised in song by Marco Marazzoli.[citation needed]
Evidence suggests that Mattei commanded his own private standing army (much smaller without additional Papal soldiers) of approximately 4000 troops.[6] After the initial contact with Farnese troops, Mattei's soldiers left the bulk of the papal army and followed him. They were involved in further skirmishes while remaining Papal troops returned to defend Rome.[7] Papal and Barberini forces suffered a number of decisive defeats and Pope Urban was eventually forced to agree to treaty terms with the Farnese to halt the conflict.[citation needed]
When Ranuccio II Farnese refused to pay the debts assigned to him in the treaty that ended the First War of Castro, Pope Innocent X sent a force to again occupy the city. The Duke rode out to challenge the papal forces but was routed by Mattei.[8] Forces loyal to Innocent X razed Castro and it was never rebuilt. Thus ended the Second War of Castro.
See also[edit]
- Belmonte Calabro
- Wars of Castro
- Early modern warfare - Europe
- House of Mattei
- Palazzo Mattei
- Barberini
References[edit]
- ^ Idea Padova (It) - The Virgin in Piazza di San Pietro in Casale
- ^ "Olive University - Wars of Castro". Archived from the original on 2017-07-03. Retrieved 2010-07-02.
- ^ Pier Francesco Mola Archived 2011-05-11 at the Wayback Machine (.pdf)
- ^ Antichità estensi - Wars of Castro
- ^ a b Storia economica della Guerra by Catia Eliana Gentilucci (2007)
- ^ Wikisource: Antiques Este, Muratori (1740)
- ^ A number of other duchies sided with the Farnese and moved to attack Rome itself; the centre of Papal power.
- ^ Cours d'histoire des états européens depuis le bouleversement de l'Empire by Maximilian Samson Friedrich Schoell
External links[edit]
- Brunelli, Giampiero (2009). "MATTEI, Ludovico, detto Luigi". Dizionario Biografico degli Italiani, Volume 72: Massimo–Mechetti (in Italian). Rome: Istituto dell'Enciclopedia Italiana. ISBN 978-8-81200032-6.
