Tabaristan
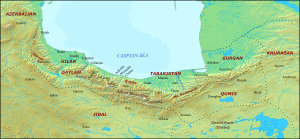
Tabaristan or Tabarestan (Persian: طبرستان, romanized: Ṭabarestān, or Mazanderani: تبرستون, romanized: Tabarestun, ultimately from Middle Persian: ![]() , Tapur(i)stān), was a mountainous region located on the Caspian coast of northern Iran. It corresponded to the present-day province of Mazandaran, which became the predominant name of the area from the 11th-century onwards.[1]
, Tapur(i)stān), was a mountainous region located on the Caspian coast of northern Iran. It corresponded to the present-day province of Mazandaran, which became the predominant name of the area from the 11th-century onwards.[1]
History
[edit]Pre-Islamic era
[edit]Tabaristan was named after the Tapurians, who had been deported there from Parthia by the Parthian king Phraates I (r. 176–171 BC).[2][3] At the advent of the Sasanians, the region, along with Gilan and Daylam, was part of the Padishkhwargar kingdom of king Gushnasp, who is mentioned in the Letter of Tansar. He submitted to the first Sasanian King of Kings (shahanshah) Ardashir I (r. 224–242 AD) after being guaranteed to keep his kingdom.[4][5] His line would continue ruling Padishkhwargar until the second reign of Kavad I (r. 488–496, 498–531), who removed the dynasty from power and appointed his son Kawus in its stead.[6] Under the Sasanians, Tabaristan enjoyed considerable autonomy.[1] They most likely left most of the affairs to the locals. The mint signature of "AM" is generally presumed to be an abbreviation for the Amul, the main city of the region.[7] The first known Sasanian monarch to have minted coins with the signature was Bahram V (r. 420–438),[8] whilst the last was Boran (r. 630–630, 631–632).[7]
Islamic era
[edit]Dabuyid rule
[edit]
In the 640s, the Dabuyid prince Gil Gavbara (r. 642–660), who was a great-grandson of shahanshah Jamasp (r. 496–498/9), conquered all of Daylam and Gilan and planned on extending his conquests to Tabaristan. Its governor, Adhar Valash, requested the aid of (shahanshah) Yazdegerd III (r. 632–651). Being unable to suppress the revolt, Yazdegerd III instead acknowledged Gil Gavbara as the ruler of the regions, presumably to deter him from creating an independent realm. Gil Gavbara was given the titles of Padashwārgarshāh (shah of Padishkhwargar) and "Ispahbad of Khorasan", possibly indicating Dabuyid rule in eastern Iran. Gil Gavbara maintained the independence of his realm during the Arab invasion of Iran, which had resulted in the collapse of the Sasanian Empire.[9][10]
His son Baduspan I was granted control over Ruyan (a district that encompassed the western part of Tabaristan) in 665, thus forming the Baduspanid dynasty, which would rule the region until the 1590s.[11] Rule in the mountains of Tabaristan was maintained by two Dabuyid vassal kingdoms, the Qarinvandids and Bavandids. In 716, the Dabuyid ruler Farrukhan the Great (r. 712–728) successfully contained a large-scale invasion by the Umayyad general Yazid ibn al-Muhallab.[10] Farrukhan's son and successor Dadhburzmihr (r. 720–740) may have temporarily lost control of Tabaristan to the Arabs, as indicated by his lack of coinage. However, this may also mean the Dabuyids lacked funds to circulate throughout their realm.[12] The last Dabuyid ruler Khurshid (r. 740–760) managed to safeguard his realm against the Umayyads, but after its replacement by the Abbasid Caliphate, he was finally defeated in 760 by Abbasid general Abu al-Khaṣīb Marzuq.[13][14] Tabaristan was subsequently made a regular province of the caliphate, ruled from Amul by an Arab governor, although the local dynasties of the Bavandids, Qarinvandids, the Zarmihrids and Baduspanids, formerly subject to the Dabuyids, continued to control the mountainous interior as tributary vassals of the Abbasid government.[15][16][17] These rulers were largely if not completely autonomous.[17]
Caliphate rule
[edit]
Under the caliphate, Amul became the leading town of Tabaristan, being the primary manufacturer of the silk fabrics that the region was famous for. Throughout history, many prominent figures with the nisba al-Tabari were from the city, such as Muhammad ibn Jarir (died 923), the author of the Qur'anic commentary Tafsir al-Tabari and the historical chronicle Tarikh al-Rusul wa al-Muluk (History of the Prophets and Kings).[18]
Abu al-Khaṣīb Marzuq was the first Abbasid governor of Tabaristan, who constructed a great mosque in Sari.[19] The second governor, Khalid ibn Barmak,[20] had attempted to build towns and befriend the Qarinvand ruler Wandad Hurmuzd (r. 765–809) in order to increase Abbasid influence there. After he left the region, however, the Bavandid ruler Sharwin I (r. 772–817) destroyed his constructions. Although Wandad Hurmuzd and Sharwin I had reassured their pledge to the caliph al-Mahdi in 781, they mounted a threatening anti-Muslim rebellion with the Masmughan of Miyanrud two years later. According to local accounts, the rebels massacred all the Muslim inhabitants of Tabaristan in one day. The modern historian Wilferd Madelung considers it exaggerated, and suggests that the massacres only took place in the highlands and segments of the lowlands that the rebels where able to penetrate. The rebels were initially successful, defeating the Muslim forces and their leaders. This alarmed al-Mahdi, who in 783/4 sent his son Musa with "a huge army and equipment such as no one previously had been equipped, to Gurgan to direct the war against Wandad Hurmuzd and Sharwin, the two lords of Tabaristan."[21]
The following year, a force of 40,000 soldiers under Sa'id al-Harashi finally defeated the rebels. Wandad Hurmuzd was wounded and captured, but he was soon pardoned and allowed to return to his lands. Following this, relations between the Muslim governors and local rulers of Tabaristan became friendly for a period. Wandad Hurmuzd bought considerable amounts of land outside of Sari from the governor Jarid ibn Yazid. Tensions arose once again at the end of the reign of caliph Harun al-Rashid (r. 786–809). The Bavandids and Qarinvandids disallowed any Muslim to get buried in Tabaristan, and the soldiers of Sharwin I had killed the caliphal deputy of the region, who was the nephew of the governor Khalifa ibn Sa'id. In 805, Wandad Hurmuzd's brother Vindaspagan killed a Muslim tax collector who had been sent to inspect his villages.[22]
Harun al-Rashid, who was at the city of Ray to address an issue with the governor of Khurasan, summoned the two rulers. There they both guaranteed their loyalty to the caliph, promising him to pay the land tax. On the request of Wandad Hurmuzd, Harun al-Rashid replaced the governor of Tabaristan. However, the new governor was instructed to confine the power of the local rulers to the highlands. Wandad Hurmuzd's son Qarin, as well Sharwin I's son Shahriyar, were taken to Baghdad as hostages as proof of their loyalty. After Harun al-Rashid's death in 809, they were returned to Tabaristan.[23] Shahriyar (now known as Shahriyar I), after succeeding his father sometime before 817, expelled the Qarinvand ruler Mazyar (a grandson of Wandad Hurmuzd) with the help of the latter's uncle Vinda-Umid ibn Vindaspagan.[24]
Culture
[edit]
Mazandarani, the local language of Tabaristan, is first attested in the works of early Muslim geographers, who refer it as Tabari. The geographical distribution of the language almost remains the same till this day. To the west it extended to Tammisha; on the other side the inhabitants spoke the "lotara of Astarabad and Persian of Gurgan". The eastern limit of the language was a bit further than present-day, reaching as far as Malat. The writing tradition of the language is approximately as old as that of New Persian. This was due to the long-lasting independent and semi-independent local kingdoms, ruled by the ispahbads. The oldest known work in Tabari, which has only survived in the Persian translation, is the Marzban-nama, written by the Bavandid ispahbad al-Marzuban in the late 10th-century or early 11th-century.[25]
Islam was first properly established in Tabaristan (as well as Gilan and Daylam) with the advent of Zaydi Shi'ism in the 9th and 10th centuries.[26] Christian tribes also inhabited Tabaristan, and fought the Arabs around 660, but were defeated after heavy resistance and either killed or enslaved if they did not convert to Islam.[27] The tradition of using Pahlavi script for lapidary and monumental purposes, and possibly for chancery as well, endured longer in the Caspian region. The Bavandid ispahbads made use of Pahlavi legends as late as the early 11th-century.[26] Hunting, which had already been widely popular under the Sasanians, was particularly popular amongst the Iranians. Khurshid had parks filled with wild boars, hares, wolves and leopards, which he used as a hunting ground.[28]
For a certain period, the Caspian shore of Iran served as a center for ancient Iranian national consciousness. In 783, during a rebellion in Tabaristan, the locals gave up their Arab husbands to the rebels.[29] Dynasties such as the Bavandids and Ziyarids continued to commemorate their pre-Islamic background, with traditional Iranian festivals such as Nowruz and Mehregan continuing to exist in Tabaristan.[26]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ a b Webb 2018.
- ^ Brunner 1983, p. 766.
- ^ Minorsky, Bosworth & Vasmer 1991, p. 935.
- ^ Brunner 1983, p. 765.
- ^ Felix & Madelung 1995, pp. 342–347.
- ^ Pourshariati 2008, p. 288.
- ^ a b Malek 2017, pp. 101–102.
- ^ Malek 2020, p. 162.
- ^ Yavari 2020.
- ^ a b Madelung 1993, pp. 541–544.
- ^ Ghereghlou 2018.
- ^ Malek 2017, p. 104.
- ^ Malek 2017, p. 105.
- ^ Malek, Hodge M. 2004, p. 14.
- ^ Madelung 1975, pp. 200–201.
- ^ Rekaya 1986, pp. 68–70.
- ^ a b Malek 2017, p. 106.
- ^ Barthold 2015, p. 239.
- ^ Malek, Hodge M. 2004, p. 5.
- ^ Malek 2017, pp. 105–107.
- ^ Madelung 1975, p. 200.
- ^ Madelung 1975, p. 202.
- ^ Madelung 1975, pp. 202–204.
- ^ Madelung 1984, pp. 747–753.
- ^ Borjian 2004, p. 291.
- ^ a b c Curtis & Stewart 2009, p. 32.
- ^ Spuler 2014, p. 201.
- ^ Spuler 2014, p. 509.
- ^ Spuler 2014, p. 223.
Sources
[edit]- Barthold, V. V. (2015). "Chapter XV. Gīlān And Māzandarān". An Historical Geography of Iran. Princeton University Press. pp. 230–242. ISBN 9781400853229. JSTOR j.ctt7zvv3z. (registration required)
- Malek, Hodge M. (2004). The Dābūyid Ispahbads and Early 'Abbāsid Governors of Tabaristān: History and Numismatics. Royal Numismatic Society. ISBN 978-0-901405-83-8.
- Bosworth, C. E. (1968). "The Political and Dynastic History of the Iranian World (A.D. 1000–1217)". In Boyle, John Andrew (ed.). The Cambridge History of Iran, Volume 5: The Saljuq and Mongol Periods. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. pp. 1–201. ISBN 0-521-06936-X.
- Borjian, Habib (2004). "Māzandarān: Language and People (The State of Research)". Iran & the Caucasus. 8 (2): 289–328. doi:10.1163/1573384043076045. JSTOR 4030997. (registration required)
- Blois, F. C. de (2000). "Tansar". In Bearman, P. J.; Bianquis, Th.; Bosworth, C. E.; van Donzel, E. & Heinrichs, W. P. (eds.). The Encyclopaedia of Islam, Second Edition. Volume X: T–U. Leiden: E. J. Brill. ISBN 978-90-04-11211-7.
- Brunner, Christopher (1983). "Geographical and Administrative divisions: Settlements and Economy". In Yarshater, Ehsan (ed.). The Cambridge History of Iran, Volume 3(2): The Seleucid, Parthian and Sasanian Periods. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. pp. 747–778. ISBN 0-521-24693-8.
- Curtis, Vesta Sarkhosh; Stewart, Sarah (2009). The Rise of Islam: The Idea of Iran Vol 4. I.B. Tauris. ISBN 978-1845116910.
- Felix, Wolfgang; Madelung, Wilferd (1995). "Deylamites". Encyclopaedia Iranica, Vol. VII, online edition, Fasc. 4. New York. pp. 342–347.
{{cite encyclopedia}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - Ghereghlou, Kioumars (2018). "Bādūsbānids". In Fleet, Kate; Krämer, Gudrun; Matringe, Denis; Nawas, John; Rowson, Everett (eds.). Encyclopaedia of Islam (3rd ed.). Brill Online. ISSN 1873-9830.
- Madelung, W. (1975). "The Minor Dynasties of Northern Iran". In Frye, Richard N. (ed.). The Cambridge History of Iran, Volume 4: From the Arab Invasion to the Saljuqs. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. pp. 198–249. ISBN 0-521-20093-8.
- Madelung, W. (1984). "ĀL-E BĀVAND (BAVANDIDS)". Encyclopaedia Iranica, Vol. I, Fasc. 7. London u.a.: Routledge & Kegan Paul. pp. 747–753. ISBN 90-04-08114-3.
- Madelung, Wilfred (1993). "Dabuyids". Encyclopædia Iranica, Vol. VI, online edition, Fasc. 5. New York. pp. 541–544.
{{cite encyclopedia}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - Malek, Hodge Mehdi (1995). "The Dabuyid Ispahbads of Tabaristan". The American Numismatic Society: 105–160.
- Malek, Hodge Mehdi (2017). "Tabaristān During the 'Abbāsid Period: The Overlapping Coinage of the Governors and Other Officials (144-178H)". In Faghfoury, Mostafa (ed.). Iranian Numismatic Studies. A Volume in Honor of Stephen Album. Lancaster and London: Classical Numismatic Group. pp. 101–126.
- Malek, Hodge Mehdi (2020). "Sasanian Coins from Amul, Tabaristan". Ancient Iranian Numismatics: 157–191. doi:10.1163/9789004460720_009. ISBN 9789004460720. S2CID 241393278.
- Melville, Charles (2020). The Timurid Century: The Idea of Iran Vol. 9. University of Cambridge, English: Bloomsbury Publishing. ISBN 9781838606152.
- Minorsky, V.; Bosworth, C. E. & Vasmer, R. (1991). "Māzandarān". In Bosworth, C. E.; van Donzel, E. & Pellat, Ch. (eds.). The Encyclopaedia of Islam, Second Edition. Volume VI: Mahk–Mid. Leiden: E. J. Brill. ISBN 978-90-04-08112-3.
- Minorsky, V. (1995). "Rūyān". In Bosworth, C. E.; van Donzel, E.; Heinrichs, W. P. & Lecomte, G. (eds.). The Encyclopaedia of Islam, Second Edition. Volume VIII: Ned–Sam. Leiden: E. J. Brill. ISBN 978-90-04-09834-3.
- Pourshariati, Parvaneh (2008). Decline and Fall of the Sasanian Empire: The Sasanian-Parthian Confederacy and the Arab Conquest of Iran. I.B. Tauris. ISBN 978-1-84511-645-3.
- Rekaya, M. (1986). "Khurshīd". In Bosworth, C. E.; van Donzel, E.; Lewis, B. & Pellat, Ch. (eds.). The Encyclopaedia of Islam, Second Edition. Volume V: Khe–Mahi. Leiden: E. J. Brill. pp. 68–70. ISBN 978-90-04-07819-2.
- Spuler, Bertold (2014). Iran in the Early Islamic Period: Politics, Culture, Administration and Public Life between the Arab and the Seljuk Conquests, 633-1055. Leiden: Brill. ISBN 978-90-04-28209-4.
- Webb, Peter (2018). "Tabarestan". In Nicholson, Oliver (ed.). The Oxford Dictionary of Late Antiquity. Oxford: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-866277-8.
- Yavari, Neguin (2020). "Dābūyids". In Fleet, Kate; Krämer, Gudrun; Matringe, Denis; Nawas, John; Rowson, Everett (eds.). Encyclopaedia of Islam (3rd ed.). Brill Online. ISSN 1873-9830.
