Apolipoprotein C
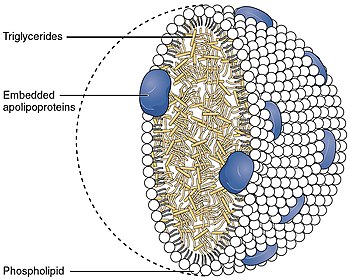
In the field of molecular biology, apolipoprotein C is a family of four low molecular weight apolipoproteins, designated as C-I, C-II, C-III, and C-IV that are surface components of chylomicrons, VLDL, and HDL. In the fasting state, the C apolipoproteins are mainly associated with HDL. During absorption of dietary fat, the C apolipoproteins preferentially redistribute to the surface of the triglyceride-rich chylomicrons and VLDL.[1]
References[edit]