Portal:Turkey: Difference between revisions
Maintenance: Expanded portal with new content, a general images section that displays images from topically-related articles: Culture of Turkey, History of Turkey, Geography of Turkey |
Added the single article from Portal:Turkey/History to SA section (Seljuk Empire), then removed the history section, as it is dated, and content is being consolidated |
||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
|6=Göbekli Tepe |
|6=Göbekli Tepe |
||
|7=Turkish art |
|7=Turkish art |
||
|8=Seljuk Empire |
|||
|8= |
|||
|9= |
|9= |
||
|10= |
|10= |
||
| Line 117: | Line 117: | ||
{{/box-header|Featured picture|Portal:Turkey/Featured picture|}} |
{{/box-header|Featured picture|Portal:Turkey/Featured picture|}} |
||
{{/Featured picture}} |
{{/Featured picture}} |
||
{{Box-footer}} |
|||
{{/box-header|'''History, people, places'''|Portal:Turkey/History|}} |
|||
{{/History}} |
|||
{{Box-footer}} |
{{Box-footer}} |
||
Revision as of 16:28, 4 April 2020
| This portal or section is in a state of significant expansion or restructuring. You are welcome to assist in its construction by editing it as well. If this portal has not been edited in several days, please remove this template. If you are the editor who added this template and you are actively editing, please be sure to replace this template with {{in use}} during the active editing session. Click on the link for template parameters to use.
This page was last edited by Northamerica1000 (talk | contribs) 4 years ago. (Update timer) |
Merhaba! Welcome to the Turkey portal
 | |
| |
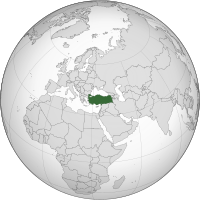
Turkey, officially the Republic of Türkiye, is a country mainly located in Anatolia in West Asia, with a smaller part called East Thrace in Southeast Europe. It borders the Black Sea to the north; Georgia, Armenia, Azerbaijan, and Iran to the east; Iraq, Syria, and the Mediterranean Sea to the south; and the Aegean Sea, Greece, and Bulgaria to the west. Turkey is home to over 85 million people; most are ethnic Turks, while ethnic Kurds are the largest ethnic minority. Officially a secular state, Turkey has a Muslim-majority population. Ankara is Turkey's capital and second-largest city, while Istanbul is its largest city and economic and financial center, as well as the largest city in Europe. Other major cities include İzmir, Bursa, and Antalya.
Turkey was first inhabited by modern humans during the Late Paleolithic. Home to important Neolithic sites like Göbekli Tepe and some of the earliest farming areas, present-day Turkey was inhabited by various ancient peoples. The Hattians were assimilated by the Anatolian peoples, such as the Hittites. Classical Anatolia transitioned into cultural Hellenization following the conquests of Alexander the Great; Hellenization continued during the Roman and Byzantine eras. The Seljuk Turks began migrating into Anatolia in the 11th century, starting the Turkification process. The Seljuk Sultanate of Rum ruled Anatolia until the Mongol invasion in 1243, when it disintegrated into Turkish principalities. Beginning in 1299, the Ottomans united the principalities and expanded; Mehmed II conquered Istanbul in 1453. During the reigns of Selim I and Suleiman the Magnificent, the Ottoman Empire became a global power. From 1789 onwards, the empire saw a major transformation, reforms, and centralization while its territory declined.
In the 19th and early 20th centuries, persecution of Muslims during the Ottoman contraction and in the Russian Empire resulted in large-scale loss of life and mass migration into modern-day Turkey from the Balkans, Caucasus, and Crimea. Under the control of the Three Pashas, the Ottoman Empire entered World War I in 1914, during which the Ottoman government committed genocides against its Armenian, Greek, and Assyrian subjects. Following Ottoman defeat, the Turkish War of Independence resulted in the abolition of the sultanate and the signing of the Treaty of Lausanne. The Republic was proclaimed on 29 October 1923, modelled on the reforms initiated by the country's first president, Mustafa Kemal Atatürk. Turkey remained neutral during most of World War II, but was involved in the Korean War. Coups in 1960 and 1980 interrupted the transition to a multi-party system.
Turkey is an upper-middle-income and emerging country; its economy is the world's 18th-largest by nominal and 11th-largest by PPP-adjusted GDP. It is a unitary presidential republic. Turkey is a founding member of the OECD, G20, and Organization of Turkic States. With a geopolitically significant location, Turkey is a regional power and an early member of NATO. An EU candidate, Turkey is part of the EU Customs Union, CoE, OIC, and TURKSOY.
Turkey has coastal plains, a high central plateau, and various mountain ranges; its climate is temperate with harsher conditions in the interior. Home to three biodiversity hotspots, Turkey is prone to frequent earthquakes and is highly vulnerable to climate change. Turkey has a universal healthcare system, growing access to education, and increasing levels of innovativeness. It is a leading TV content exporter. With 21 UNESCO World Heritage sites, 30 UNESCO intangible cultural heritage inscriptions, and a rich and diverse cuisine, Turkey is the fifth most visited country in the world. (Full article...)
Selected article -

Turkish art (Turkish: Türk sanatı) refers to all works of visual art originating from the geographical area of what is present day Turkey since the arrival of the Turks in the Middle Ages. Turkey also was the home of much significant art produced by earlier cultures, including the Hittites, Ancient Greeks, and Byzantines. Ottoman art is therefore the dominant element of Turkish art before the 20th century, although the Seljuks and other earlier Turks also contributed. The 16th and 17th centuries are generally recognized as the finest period for art in the Ottoman Empire, much of it associated with the huge Imperial court. In particular the long reign of Suleiman the Magnificent from 1520 to 1566 brought a combination, rare in any ruling dynasty, of political and military success with strong encouragement of the arts.
The nakkashane, as the palace workshops are now generally known, were evidently very important and productive, but though there is a fair amount of surviving documentation, much remains unclear about how they operated. They operated over many different media, but apparently not including pottery or textiles, with the craftsmen or artists apparently a mixture of slaves, especially Persians, captured in war (at least in the early periods), trained Turks, and foreign specialists. They were not necessarily physically located in the palace, and may have been able to undertake work for other clients as well as the sultan. Many specialities were passed from father to son. (Full article...)
List of selected articles
|
|---|
Featured picture

Lake Abant National Park (Turkish: Abant Gölü Milli Parkı), established on 10 June 2022, is the 48th national park in Turkey. It is located in Mudurnu district of Bolu Province, northwestern Anatolia. (Full article...)
Did you know...
- See Portal:Turkey/Did you know/Archive for all DYK listings.
Featured at Did you know section at the Wikipedia's Main Page
- ...that the Mosque of the Rose in Istanbul is so named because on the day of the Fall of Constantinople the building was adorned with garlands of roses?
- ...that SantralIstanbul, an art museum in Istanbul, Turkey, is located in what was the first power station of the Ottoman Empire?
- ...that the Romanian crude oil tanker MT Independența burnt for weeks in 1979 after colliding with a freighter?
- ...that Wilhelm von Pressel designed the first railroad in Turkey?
- ...that the 1621 Battle of Khotyn resulted directly in the death of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth leader, hetman Jan Karol Chodkiewicz, and indirectly in the death of the Ottoman Empire commander, sultan Osman II?
- ...that the Crusade of Varna required simultaneous attacks on the Muslim Ottoman Empire by Christian Hungary and the Muslim Karamanids, which did not take place?
Selected biography -

Nureddin Ibrahim Pasha (Turkish: Nurettin Paşa, Nureddin İbrahim Paşa; 1873 – 18 February 1932), known as Nureddin İbrahim Konyar from 1934, was a Turkish military officer who served in the Ottoman Army during World War I and in the Turkish Army during the Western Front of the Turkish War of Independence. He was called Bearded Nureddin (Turkish: Sakallı Nurettin) because being the only high-ranking Turkish officer during the Turkish War of Independence sporting a beard. He is known as one of the most important commanders of the war. He ordered several murders and massacres. (Full article...)
Selected video
Quotes
| This page is currently inactive and is retained for historical reference. Either the page is no longer relevant or consensus on its purpose has become unclear. To revive discussion, seek broader input via a forum such as the village pump. |
| “ | Gözden uzak olan gönülden de uzak olur. (Who is far from the eye will also be far from the heart.) | ” |
Recognized content
Related portals
Religions in Turkey
Neighbouring countries
Countries with related heritage
Turkish wikipedia
 |
|
General images
Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wikivoyage
Free travel guide -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus