Iberian Peninsula: Difference between revisions
Undid revision 347164178 by 189.62.162.15 (talk) - see talk page/please discuss |
|||
| Line 79: | Line 79: | ||
| {{convert|7|km2|sqmi|abbr=on}} |
| {{convert|7|km2|sqmi|abbr=on}} |
||
| <1% |
| <1% |
||
| a tiny [[British overseas territory]] |
| a tiny [[British overseas territory]] near the southernmost tip of the peninsula |
||
|} |
|} |
||
Revision as of 21:36, 1 March 2010



The Iberian Peninsula, or Iberia, is located in the extreme southwest of Europe and includes modern-day states Portugal, Spain, Andorra and Gibraltar and a very small area of France. It is the westernmost of the three major southern European peninsulas—the Iberian, Italian, and Balkan peninsulas. It is bordered on the southeast and east by the Mediterranean Sea, and on the north, west and southwest by the Atlantic Ocean. The Pyrenees form the northeast edge of the peninsula, separating it from the rest of Europe. In the south, it approaches the northern coast of Africa. It is the second-largest peninsula in Europe, with an area of 582,860 square kilometres (225,040 sq mi).
Name
Greek name
The English word Iberia was adapted from the use of the Ancient Greek word Ἱβηρία (Ibēría) by the Greek geographers under the Roman Empire to refer to what is known today in English as the Iberian Peninsula.[1] The name was not then used to mean a single political country or a population speaking a single language.[2] Strabo's Iberia was delineated from Keltikē by the Pyrenees and included the entire land mass south (he mistakenly said west) of there.
The Ancient Greeks discovered Iberia by voyaging westward. Hecataeus of Miletus was the first known to use the term around 500 BC.[3] Herodotus of Halicarnassus says of the Phocaeans that "it was they who made the Greeks acquainted with ... Iberia."[4] According to Strabo[5] prior historians used Iberia to mean the country "this side of the Ἶβηρος (Ibēros)" as far north as the Rhone river in France but currently they set the Pyrenees as the limit. Polybius respects that limit[6] but identifies Iberia as the Mediterranean side as far south as Gibraltar, with the Atlantic side having no name. Elsewhere[7] he says that Saguntum is "on the seaward foot of the range of hills connecting Iberia and Celtiberia."
Strabo[8] refers to the Carretanians as people "of the Iberian stock" living in the Pyrenees, who are to be distinguished from either Celts or Celtiberians.
Roman names
When the Romans encountered the Greek geographers they used Iberia poetically and spoke of the Iberi, the population of Iberia.[9] First mention was in 200 BC by the poet Quintus Ennius. The Romans had already had independent experience with the peoples on the peninsula during the long conflict with Carthage. The Roman geographers and other prose writers from the time of the late Roman Republic called the entire peninsula Hispania.
As they became politically interested in the former territories of Carthage the Romans came to use Hispania Citerior and Hispania Ulterior for "near" and "far Spain". Even at that time large sections of it were Lusitania (Portugal), Celtiberia (central Spain), Baetica (Andalusia), Cantabria (northwest Spain) and the Vascones (Basques). Strabo says[5] that the Romans use Hispania and Iberia synonymously, and distance them as near and far. He was living in a time when the peninsula was divided into Roman provinces, some belonging "to the people and the Senate" and some to "the Roman emperor." Baetia was distinguished by being the only one belonging "to the people." Whatever language may have been spoken on the peninsula soon gave way to Latin, except for Basque, protected by the Pyrenees. Template:Details3
Etymology

"Iberia" has always been associated with the Ebro river, Ibēros in ancient Greek and Ibērus or Hibērus in Latin. The association was so well known it was hardly necessary to state; for example, Ibēria was the country "this side of the Ibērus" in Strabo. Pliny goes so far as to assert that the Greeks had called "the whole of Spain" Hiberia because of the river Hiberus.[10] The river appears in the Ebro Treaty of 226 BC between Rome and Carthage, setting the limit of Carthaginian interest at the Ebro. The fullest description of the treaty, stated in Appian,[11] uses Ibērus. With reference to this border, Polybius[12] states that the "native name" is Ibēr, apparently the original word, stripped of its Greek or Latin -os or -us termination.
The early range of these natives, stated by the geographers and historians to be from southern Spain to southern France along the Mediterranean coast, is marked by instances of a readable script expressing a yet unknown language, dubbed "Iberian." Whether this was the native name or was given to them by the Greeks for their residence on the Ebro remains unknown. Credence in Polybius imposes certain limitations on etymologizing: if the language remains unknown, the meanings of the words, including Iber, must remain unknown also.
Geography
Overall characteristics

The Iberian peninsula extends from the southernmost extremity at Punta de Tarifa (36°00′15″N 5°36′37″W / 36.00417°N 5.61028°W) to the northernmost extremity at Estaca de Bares Point (43°47′38″N 7°41′17″W / 43.79389°N 7.68806°W) over a distance between lines of latitude of about 865 kilometres (537 mi) based on a degree length of 111 km per degree, and from the westernmost extremity at Cabo da Roca (38°46′51″N 9°29′54″W / 38.78083°N 9.49833°W) to the easternmost extremity at Cap de Creus (42°19′09″N 3°19′19″E / 42.31917°N 3.32194°E) over a distance between lines of longitude at 40° N latitude of about 1,155 kilometres (718 mi) based on an estimated degree length of about 90 km for that latitude. The irregular, roughly octagonal shape of the peninsula contained within this spherical quadrangle was compared to an ox-hide by the geographer, Strabo.[13]
Approximately 3/4 of the octagon is the Meseta Central, a low and rolling plateau of up to several hundred meters in altitude.[14] It is located roughly in the center, staggered slightly to the east and tilted slightly toward the west. (The conventional center of the Iberian Peninsula has long been considered to be Getafe just south of Madrid.) It is ringed by mountains and contains the sources of most of the rivers, which find their way through gaps in the mountain barriers on all sides.
Coastline
The coastline of the Iberian Peninsula is 3,313 km (2,059 mi), 1,660 km (1,030 mi) on the Mediterranean side and 1,653 km (1,027 mi) on the Atlantic side.[15] The coast is a drowned one, with sea levels having risen from a minimum of 115 metres (377 ft) to 120 metres (390 ft) lower than today at the Last Glacial Maximum (LGM) to its current level at 4000 years BP.[16] The coastal shelf created by sedimentation during that time remains below the surface; however, it was never very extensive on the Atlantic side, as the continental shelf drops rather steeply into the depths. An estimated 700 km (430 mi) length of Atlantic shelf is only 10 km (6.2 mi) to 65 km (40 mi) wide. At the 500 m (1,600 ft) isobath, on the edge, the shelf drops off to 1,000 m (3,300 ft).[17]
The submarine topography of the coastal waters of the Iberian Peninsula has been studied extensively in the process of drilling for oil. Ultimately the shelf drops into the Bay of Biscay on the north (an abyss), the Iberia abyssal plain at 4,800 m (15,700 ft) on the west and Tagus abyssal plain to the south. In the north between the continental shelf and the abyss is an extension, the Galicia Bank, a plateau containing also the Porto, Vigo and Vasco da Gama seamounts, creating the Galicia interior basin. The southern border of these features is marked by Nazare Canyon, splitting the continental shelf and leading directly into the abyss.
Mountains
Mountains consist mainly of serrated ridges aligned in an east-west direction, due to the orogenic factors of the region's geologic history. Rivers generally flow through the valleys between the ridges. In a counterclockwise direction, the major mountain ranges are: the Pyrenees crossing the isthmus of the peninsula so completely as to allow no passage except by mountain road or trail or coastal road, the Cantabrian Mountains perched on the northern coastline, a series of ridges straddling Portugal and Spain: the Sierra de Guadarrama, the Sierra de Gredos, the Sierra de Gata, and the Serra da Estrela; across the south: the Sierra Morena and the Sierra Nevada.
Rivers
Modern countries and territories
Political divisions of the Iberian Peninsula sorted by area:
| Country/Territory | Peninsular area | Share | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 493,519 km2 (190,549 sq mi) | 85% | occupies most of the peninsula | |
| 89,261 km2 (34,464 sq mi) | 15% | occupies most of the west of the peninsula | |
| 540 km2 (210 sq mi) | <1% | French Cerdagne is a small territory in the Pyrenees technically located in the Iberian peninsula | |
| 468 km2 (181 sq mi) | <1% | a northern edge of the peninsula in the Pyrenees between Spain and France | |
| 7 km2 (2.7 sq mi) | <1% | a tiny British overseas territory near the southernmost tip of the peninsula |
Major cities
The principal urban centers are: Madrid, Barcelona, Lisbon, Valencia, Porto, Seville, Bilbao, Zaragoza, Braga, Coimbra, Malaga, Vigo and Valladolid.
Various other notable cities with smaller populations are also present on the peninsula.
Ecology
Forests
East Atlantic flyway
The Iberian Peninsula in an important stopover on the East Atlantic flyway for birds migrating from northern Europe to Africa. For example, Calidis ferruginea rests in the region of Cadiz Bay.[18]
In addition to the birds migrating through, some seven million wading birds from the north spend the winter in the estuaries and wetlands of the Iberian Peninsula, mainly at locations on the Atlantic coast. In Galicia are the Ria de Arousa (a home of Pluvialis squatarola), Ria de Ortigueira, Ria de Corme and Ria de Laxe. In Portugal the Aveiro Lagoon hosts Recurvirostra avosetta, Charadrius hiaticula, Pluvialis squatarola and Calidris minuta. Ribatejo on the Tagus River supports Recurvirostra arosetta, Pluvialis squatarola, Culidris alpina, Limosa lapponica and Tringa totanus. In the Estuário do Sado are Calidris alpina, Numenius arquata, Pluvialis squatarola and Tringa totanus. The Algarve hosts Calidris canutus, Tringa nebularia and Arenaria interpres. The Marismas de Guadalquivir region of Andalusia and the Salinas de Cadiz are especially rich in wintering wading birds: Charadrius alexandrinus, Charadrius hiaticula, Calidris alba, and Limosa limosa in addition to the others. And finally, the Ebro delta is home to all the species mentioned above.[19]
Geology
Prehistory
Palaeolithic

The Iberian Peninsula has been inhabited for at least 1,000,000 years as remains found in the sites at Atapuerca demonstrate. Among these sites is the cave of Gran Dolina, where six hominin skeletons, dated between 780,000 and one million years ago, were found in 1994. Experts have debated whether these skeletons belong to the species Homo erectus, Homo heidelbergensis, or a new species called Homo antecessor.
Around 200,000 BC, during the Lower Paleolithic period, Neanderthals first entered the Iberian Peninsula. Around 70,000 BC, during the Middle Paleolithic period, the last ice age began and the Neanderthal Mousterian culture was established. Around 35,000 BC, during the Upper Paleolithic, the Neanderthal Châtelperronian cultural period began. Emanating from Southern France this culture extended into Northern Iberia. It continued to exist until around 28,000 BC when Neanderthal man faced extinction.
At about the 40th millennium BC Modern Humans entered the Iberian peninsula, coming from Southern France. Here, this genetically homogeneous population (characterized by the M173 mutation in the Y chromosome), developed the M343 mutation, giving rise to the R1b Haplogroup, still the most common in modern Portuguese and Spanish males. In Iberia, Modern Humans developed a series of different cultures, such as the Aurignacian, Gravettian, Solutrean and Magdalenian cultures, some of them characterized by complex forms of Paleolithic art.
Neolithic
During the Neolithic expansion, various megalithic cultures developed in Iberia. An open seas navigation culture from the east Mediterranean, called the Cardium culture, also extended its influence to the eastern coasts of Iberia, possibly as early as the 5th millennium BC These people may have had some relation to the subsequent development of the Iberian civilization.
Chalcolithic
In the Chalcolithic or Copper Age (c. 3000 BC in Iberia) a series of complex cultures developed, which would give rise to the first civilizations in Iberia and to extensive exchange networks reaching to the Baltic, the Middle East and North Africa. At about 2150 BC the Bell Beaker culture intruded into Chalcolithic Iberia, being of Central European origin.
Bronze Age

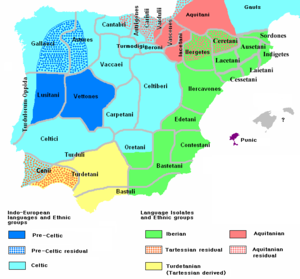
Bronze Age cultures developed beginning c.1800 BC, when the civilization of Los Millares was followed by that of El Argar. From this center, bronze technology spread to other areas, such as those of the Bronze of Levante, South-Western Iberian Bronze and Cogotas I.
In the Late Bronze Age the urban civilization of Tartessos developed in the area of modern western Andalusia, characterized by Phoenician influence and using the Tartessian script for its Tartessian language, a language isolate not related to the Iberian language.
Early in the first millennium BC, several waves of Pre-Celts and Celts migrated from central Europe, thus partially changing the ethnic landscape of Iberia into Indo-European space in its northern and western regions.
Proto-history
By the Iron Age, starting in the 7th century BC, the global panorama in Iberia was one of complex agrarian and urban civilizations, either Pre-Celtic or Celtic (such as the Lusitanians, the Celtiberians, the Gallaeci, the Astur, or the Celtici, amongst others), the cultures of the Iberians in the eastern and southern zones of Iberia and the cultures of the Aquitanian in the western portion of the Pyrenees.
The seafaring Phoenicians, Greeks and Carthaginians successively settled along the Mediterranean coast and founded trading colonies there over a period of several centuries. Around 1100 BC Phoenician merchants founded the trading colony of Gadir or Gades (modern day Cádiz) near Tartessos. In the 8th century BC the first Greek colonies, such as Emporion (modern Empúries), were founded along the Mediterranean coast on the East, leaving the south coast to the Phoenicians. The Greeks are responsible for the name Iberia, after the river Iber (Ebro). In the 6th century BC the Carthaginians arrived in Iberia while struggling with the Greeks for control of the Western Mediterranean. Their most important colony was Carthago Nova (Latin name of modern day Cartagena).
History
Roman Iberia
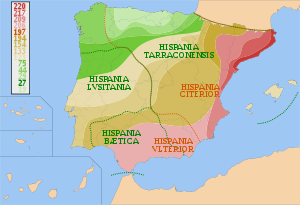
In 219 BC, the first Roman troops invaded the Iberian Peninsula, during the Second Punic war against the Carthaginians, and annexed it under Augustus after two centuries of war with the Celtic and Iberian tribes and the Phoenician, Greek and Carthaginian colonies, resulting in the creation of the province of Hispania. It was divided into Hispania Ulterior and Hispania Citerior during the late Roman Republic, and during the Roman Empire, it was divided into Hispania Taraconensis in the northeast, Hispania Baetica in the south and Lusitania in the southwest.
Hispania supplied the Roman Empire with food, olive oil, wine and metal. The emperors Trajan, Hadrian and Theodosius I, the philosopher Seneca and the poets Martial and Lucan were born from families living in Iberia.
Germanic Iberia

In the early 5th century, Germanic tribes invaded the peninsula, namely the Suevi, the Vandals (Silingi and Hasdingi) and their allies, the Sarmatian Alans. Only the kingdom of the Suevi (Quadi and Marcomanni) would endure after the arrival of another wave of Germanic invaders, the Visigoths, who conquered all of the Iberian peninsula and expelled or partially integrated the Vandals and the Alans. The Visigoths eventually conquered the Suevi kingdom and its capital city Bracara (modern day Braga) in 584-585. They would also conquer the province of the Byzantine Empire (552-624) of Spania in the south of the peninsula and the Balearic Islands.
Islamic Iberia
In 711 AD, a North African Moorish Umayyad army invaded Visigothic Christian Hispania. Under their leader Tariq ibn-Ziyad, they landed at Gibraltar and brought most of the Iberian Peninsula under Islamic rule in an eight-year campaign. Al-ʾAndalūs (Arabic الإندلس : Land of the Vandals) is the Arabic name given the Iberian Peninsula by its Muslim conquerors and its subsesquent inhabitants.
From the 8th to the 15th centuries, parts of the Iberian peninsula were ruled by the Moors (mainly Berber and Arab) who had crossed over from North Africa.
Reconquest

Many of the ousted Gothic nobles took refuge in the unconquered north Asturian highlands. From there they aimed to reconquer their lands from the Moors: this war of reconquest is known as the Reconquista. Christian and Muslim kingdoms fought and allied among themselves. The Muslim taifa kings competed in patronage of the arts, the Way of Saint James attracted pilgrims from all Western Europe and the Jewish population of Iberia set the basis of Sephardic culture.[citation needed]
In medieval times the peninsula housed many small states including Castile, Aragon, Navarre, León and Portugal. The peninsula was part of the Islamic Almohad empire until they were finally uprooted. The last major Muslim stronghold was Granada which was eliminated by a combined Castilian and Aragonese force in 1492.
Post reconquest
The small states gradually amalgamated over time, with the exception of Portugal, even if for a brief period (1580-1640) the whole peninsula was united politically under the Iberian Union. After that point the modern position was reached and the peninsula now consists of the countries of Spain and Portugal (excluding their islands - the Portuguese Azores and Madeira Islands and the Spanish Canary Islands and Balearic Islands; and the Spanish exclaves of Ceuta and Melilla), Andorra, French Cerdagne and Gibraltar.
See also
References
- ^ First known use in that sense dates to 1618. "Iberian". Online Etymological Dictionary.
- ^ Strabo. "Book III Chapter 1 Section 6". Geographica.
And also the other Iberians use an alphabet, though not letters of one and the same character, for their speech is not one and the same.
- ^ Strabo (MCMLXXXVIII). The Geography (in ancient Greek and English). Vol. II. Cambridge: Harvard University Press. p. 118, Note 1 on 3.4.19.
{{cite book}}: Check date values in:|date=(help); Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help)CS1 maint: unrecognized language (link) - ^ I.163.
- ^ a b III.4.19.
- ^ III.37.
- ^ III.17.
- ^ III.4.11.
- ^ "Iberia, Iberi". Félix Gaffiot's Dictionnaire Illustré Latin Français. Librairie Hachette. 1934.
- ^ III.3.21.
- ^ White, Horace. "Appian's History of Rome: The Spanish Wars (§§6-10)". livius.org. pp. Chapter 7. Retrieved 2008-12-01.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ "Polybius: The Histories: III.6.2". Bill Thayer.
- ^ III.1.3.
- ^ Fischer, T (1920). "The Iberian Peninsula: Spain". In Mill, Hugh Robert (ed.). The International Geography. New York and London: D. Appleton and Company. pp. 368–377. Downloadable Google Books
- ^ These figures sum the figures given in the Wikipedia articles on the geography of Spain and Portugal. Most figures from Internet sources on Spain and Portugal include the coastlines of the islands owned by each country and thus are not a reliable guide to the coastline of the peninsula. Moreover, the length of a coastline may vary significantly depending on where and how it is measured.
- ^ Edmunds, WM (2001). "Evolution of groundwater systems at the European coastline". In Edmunds, W. M.; Milne, C. J. (eds.). Palaeowaters in Coastal Europe: Evolution of Groundwater Since the Late Pleistocene. Geological Society. p. 305. ISBN 186239086X, ISBN 9781862390867.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|city=ignored (|location=suggested) (help); Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ "Iberian Peninsula – Atlantic Coast". An Atlas of Oceanic Internal Solitary Waves (pdf). Global Ocean Associates. February 2004. Retrieved 2008-12-09.
- ^ Hortas, Francisco (2006). "Migration pattern of Curlew Sandpipers Calidris ferruginea on the south-western coastline of the Iberian Peninsula" (pdf). International Wader Studies. 19: 144–147. Retrieved 2008-12-07.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Dominguez, Jesus (1990). "Distribution of estuarine waders wintering in the Iberian Peninsula in 1978-1982" (PDF). Wader Study Group Bulletin. 59: 25–28.
External links
- Arioso, Pāolā. "Iberian Peninsula•Links". Stone Pages. Retrieved 2008-12-05.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - Flores, Carlos (2004). "Reduced genetic structure of the Iberian peninsula revealed by Y-chromosome analysis: implications for population demography" (pdf). European Journal of Human Genetics. 12 (10): 855–863. doi:10.1038/sj.ejhg.5201225. PMID 15280900. Retrieved 2008-12-05.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - Loyd, Nick (2007). "IberiaNature: A guide to the environment, climate, wildlife, geography and nature of Spain". Retrieved 2008-12-04.
- Silva, Luís Fraga de. "Ethnologic Map of Pre-Roman Iberia (circa 200 B.C.). NEW VERSION #10" (in English, Portuguese, and Latin). Associação Campo Arqueológico de Tavira, Tavira, Portugal. Retrieved 2008-12-04.
