E-commerce: Difference between revisions
m stoped greifers |
ClueBot NG (talk | contribs) m Reverting possible vandalism by ImmortalWriter to version by Woohookitty. False positive? Report it. Thanks, ClueBot NG. (971964) (Bot) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
DUM DUM ME LIKE GUM GUM!go awy ROCKETT |
|||
'''Electronic commerce''', commonly known as '''e-commerce''', '''ecommerce''', '''eCommerce''' or '''e-comm''', refers to the buying and selling of [[product (business)|product]]s or [[Service (economics)|service]]s over electronic systems such as the [[Internet]] and other [[computer network]]s. Electronic commerce draws on such technologies as [[electronic funds transfer]], [[supply chain management]], [[Internet marketing]], [[online transaction processing]], [[electronic data interchange]] (EDI), [[inventory management]] systems, and automated data collection systems. Modern electronic commerce typically uses the [[World Wide Web]] at least at one point in the transaction's life-cycle, although it may encompass a wider range of technologies such as [[e-mail]], mobile devices and telephones as well. |
'''Electronic commerce''', commonly known as '''e-commerce''', '''ecommerce''', '''eCommerce''' or '''e-comm''', refers to the buying and selling of [[product (business)|product]]s or [[Service (economics)|service]]s over electronic systems such as the [[Internet]] and other [[computer network]]s. Electronic commerce draws on such technologies as [[electronic funds transfer]], [[supply chain management]], [[Internet marketing]], [[online transaction processing]], [[electronic data interchange]] (EDI), [[inventory management]] systems, and automated data collection systems. Modern electronic commerce typically uses the [[World Wide Web]] at least at one point in the transaction's life-cycle, although it may encompass a wider range of technologies such as [[e-mail]], mobile devices and telephones as well. |
||
* Electronic commerce is generally considered to be the sales aspect of [[e-business]]. It also consists of the exchange of data to facilitate the financing and payment aspects of business transactions. |
* Electronic commerce is generally considered to be the sales aspect of [[e-business]]. It also consists of the exchange of data to facilitate the financing and payment aspects of business transactions. |
||
electronic commerce typically uses the [[World Wide Web]] at least at one point in the transaction's life-cycle, although it may encompass a wider range of technologies such as [[e-mail]], mobile devices and telephones as well. |
|||
* Electronic commerce is generally considered to be the sales aspect of [[e-business]]. It also consists of the exchange of data to facilitate the financing and payment aspects of business transactionselectronic commerce typically uses the [[World Wide Web]] at least at one point in the transaction's life-cycle, although it may encompass a wider range of technologies such as [[e-mail]], mobile devices and telephones as well. |
|||
* Electronic commerce is generally considered to be the sales aspect of [[e-business]]. It also consists of the exchange of data to facilitate the financing and payment aspects of business transactionselectronic commerce typically uses the [[World Wide Web]] at least at one point in the transaction's life-cycle, although it may encompass a wider range of technologies such as [[e-mail]], mobile devices and telephones as well. |
|||
* Electronic commerce is generally considered to be the sales aspect of [[e-business]]. It also consists of the exchange of data to facilitate the financing and payment aspects of business transactionselectronic commerce typically uses the [[World Wide Web]] at least at one point in the transaction's life-cycle, although it may encompass a wider range of technologies such as [[e-mail]], mobile devices and telephones as well. |
|||
E-commerce can be divided into: |
|||
* Electronic commerce is generally considered to be the sales aspect of [[e-business]]. It also consists of the exchange of data to facilitate the financing and payment aspects of business transactionselectronic commerce typically uses the [[World Wide Web]] at least at one point in the transaction's life-cycle, although it may encompass a wider range of technologies such as [[e-mail]], mobile devices and telephones as well. |
|||
* E-tailing or "virtual storefronts" on Web sites with online catalogs, sometimes gathered into a "virtual mall" |
|||
* The gathering and use of demographic data through Web contacts |
|||
* Electronic Data Interchange (EDI), the business-to-business exchange of data |
|||
* E-mail and fax and their use as media for reaching prospects and established customers (for example, with newsletters) |
|||
* Business-to-business buying and selling |
|||
* The security of business transactions |
|||
==History== |
|||
* Electronic commerce is generally considered to be the sales aspect of [[e-business]]. It also consists of the exchange of data to facilitate the financing and payment aspects of business transactionselectronic commerce typically uses the [[World Wide Web]] at least at one point in the transaction's life-cycle, although it may encompass a wider range of technologies such as [[e-mail]], mobile devices and telephones as well. |
|||
===Early development=== |
|||
Originally, electronic commerce was identified as the facilitation of commercial transactions electronically, using technology such as [[Electronic Data Interchange|Electronic Data Interchange (EDI)]] and [[Electronic funds transfer|Electronic Funds Transfer (EFT)]]. These were both introduced in the late 1970s, allowing businesses to send commercial documents like purchase orders or invoices electronically. The growth and acceptance of credit cards, automated teller machines (ATM) and telephone banking in the 1980s were also forms of electronic commerce. Another form of e-commerce was the airline reservation system typified by Sabre in the USA and Travicom in the UK. |
|||
From the 1990s onwards, electronic commerce would additionally include [[enterprise resource planning]] systems (ERP), [[data mining]] and [[data warehousing]] |
|||
* Electronic commerce is generally considered to be the sales aspect of [[e-business]]. It also consists of the exchange of data to facilitate the financing and payment aspects of business transactionselectronic commerce typically uses the [[World Wide Web]] at least at one point in the transaction's life-cycle, although it may encompass a wider range of technologies such as [[e-mail]], mobile devices and telephones as well. |
|||
In 1990, [[Tim Berners-Lee]] invented the [[WorldWideWeb]] [[web browser]] and transformed an academic telecommunication network into a worldwide everyman everyday communication system called internet/www. Commercial enterprise on the [[Internet]] was strictly prohibited by NSF until 1995.<ref>[[Kevin Kelly (editor)|Kevin Kelly]]: [http://www.wired.com/wired/archive/13.08/tech.html?pg=2 We Are the Web] [[Wired magazine]], Issue 13.08, August 2005</ref> Although the Internet became popular worldwide around 1994 with the adoption of [[Mosaic (web browser)|Mosaic]] web browser, it took about five years to introduce security protocols and [[DSL]] allowing continual connection to the Internet. By the end of 2000, many European and American business companies offered their services through the [[World Wide Web]]. Since then people began to associate a word "[[ecommerce]]" with the ability of purchasing various goods through the Internet using secure protocols and electronic payment services. |
|||
* Electronic commerce is generally considered to be the sales aspect of [[e-business]]. It also consists of the exchange of data to facilitate the financing and payment aspects of business transactionselectronic commerce typically uses the [[World Wide Web]] at least at one point in the transaction's life-cycle, although it may encompass a wider range of technologies such as [[e-mail]], mobile devices and telephones as well. |
|||
===Timeline=== |
|||
* Electronic commerce is generally considered to be the sales aspect of [[e-business]]. It also consists of the exchange of data to facilitate the financing and payment aspects of business transactionselectronic commerce typically uses the [[World Wide Web]] at least at one point in the transaction's life-cycle, although it may encompass a wider range of technologies such as [[e-mail]], mobile devices and telephones as well. |
|||
The timeline for e-commerce progression is shown below. |
|||
* 1979: [[Michael Aldrich]] invented [[online shopping]]<ref>{{cite book | last1 = Tkacz | first1 = Ewaryst | last2 = Kapczynski | first2 = Adrian | title = Internet - Technical Development and Applications | publisher = Springer | year = 2009 | page = 255 | url = http://books.google.com/books?id=a9_NJIBC87gC&dq | accessdate = 2011-03-28 | isbn = 978-3642050183 | quote = The first pilot system was installing in Tesco in the UK (first demonstrated in 1979 by Michael Aldrich).}}</ref> |
|||
* Electronic commerce is generally considered to be the sales aspect of [[e-business]]. It also consists of the exchange of data to facilitate the financing and payment aspects of business transactionselectronic commerce typically uses the [[World Wide Web]] at least at one point in the transaction's life-cycle, although it may encompass a wider range of technologies such as [[e-mail]], mobile devices and telephones as well. |
|||
* 1981: [[Thomson Holidays]], UK is first B2B online shopping{{Citation needed|date=November 2010}} |
|||
* 1982: [[Minitel]] was introduced nationwide in [[France]] by [[France Telecom]] and used for online ordering. |
|||
* 1984: [[Gateshead]] SIS/[[Tesco]] is first B2C online shopping and Mrs Snowball, 72, is the first online home shopper<ref name="Finding Mrs Snowball">{{cite web|last=Aldrich|first=Michael|url=http://www.aldricharchive.com/snowball.html|title=Finding Mrs Snowball|accessdate=8 March 2012}}</ref> |
|||
* 1984: In April 1984, [[CompuServe]] launches the Electronic Mall in the USA and Canada. It is the first comprehensive electronic commerce service.<ref>{{cite web| url=http://www.gsbrown.org/compuserve/electronic-mall-1984-04/ |title=Online Today, The Electronic Mall|publisher= CIS/CompuServe nostalgia}}</ref> |
|||
* 1985: [[Nissan]] UK sells cars and finance with credit checking to customers online from dealers' lots.{{Citation needed|date=November 2010}} |
|||
* 1987: [[Swreg]] begins to provide software and shareware authors means to sell their products online through an electronic [[Merchant account]].{{Citation needed|date=November 2010}} |
|||
* 1990: [[Tim Berners-Lee]] writes the first web browser, [[WorldWideWeb]], using a [[NeXTSTEP|NeXT]] computer. |
|||
* 1992: Terry Brownell launches first fully graphical, iconic navigated [[Bulletin board system]] online shopping using [[RoboBOARD/FX]]. |
|||
* 1994: [[Netscape Communications Corporation|Netscape]] releases the Navigator browser in October under the code name [[Mozilla]]. [[Pizza Hut]] offers online ordering on its Web page. The first online bank opens. Attempts to offer flower delivery and magazine subscriptions online. [[Pornographic|Adult]] materials also become commercially available, as do cars and bikes. [[Netscape Navigator|Netscape]] 1.0 is introduced in late 1994 [[Secure Sockets Layer|SSL]] encryption that made transactions secure. |
|||
* 1995: Thursday 27 April 1995, the purchase of a book by Paul Stanfield, Product Manager for [[CompuServe]] UK, from [[W H Smith]]’s shop within CompuServe’s UK Shopping Centre is the UK’s first national online shopping service secure transaction. The shopping service at launch featured [[WH Smith]], [[Tesco]], [[Virgin]]/[[Our Price]], Great Universal Stores/[[GUS]], [[Interflora]], [[Dixons Retail]], Past Times, [[PC World (retailer)]] and Innovations.<ref>{{cite web| url=http://m-ybooks.co.uk/news-imrg07.htm|title=IMRG Special Report - £100 bn spent online since 1995 |publisher= IMRG}}</ref> |
|||
* 1995: Jeff Bezos launches [[Amazon.com]] and the first commercial-free 24 hour, internet-only radio stations, Radio HK and [[NetRadio]] start broadcasting. [[Dell, Inc.|Dell]] and [[Cisco Systems|Cisco]] begin to aggressively use Internet for commercial transactions. [[eBay]] is founded by computer programmer Pierre Omidyar as AuctionWeb. |
|||
* 1998: [[Electronic stamp|Electronic postal stamps]] can be purchased and downloaded for printing from the Web. |
|||
* 1998: [[Alibaba Group]] is established in China. |
|||
* 1999: [[Business.com]] sold for US $7.5 million to eCompanies, which was purchased in 1997 for US $149,000. The peer-to-peer filesharing software [[Napster]] launches. [[ATG Stores]] launches to sell decorative items for the home online. |
|||
* 2000: The [[dot-com bust]]. |
|||
* 2001: [[Alibaba Group|Alibaba.com]] achieved profitability in December 2001. |
|||
* 2002: [[eBay]] acquires [[PayPal]] for $1.5 billion.<ref>{{cite web| url=http://investor.ebay.com/releasedetail.cfm?ReleaseID=84142|title=eBay acquires PayPal |publisher= eBay}}</ref> Niche retail companies [[Wayfair]] and [[NetShops]] are founded with the concept of selling products through several targeted domains, rather than a central portal. |
|||
* 2003: [[Amazon.com]] posts first yearly profit. |
|||
* 2004: [[DHgate.com]], China's first online b2b transaction platform, is established, forcing other b2b sites to move away from the "yellow pages" model.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.zwgl.com.cn/article_info.asp?nid=4243|title=Diane Wang: Rounding up the "Ant" Heroes|publisher= Sino Foreign Management|accessdate=2011-09-03}}</ref> |
|||
* 2005: [[Yuval Tal]] founds Payoneer- a secure online payment distribution solution |
|||
* 2007: [[Business.com]] acquired by [[R.H. Donnelley]] for $345 million.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://domainnamewire.com/2007/07/26/rh-donnelley-acquires-businesscom-for-345m/ |title=R.H. Donnelley Acquires Business.com for $345M |publisher=Domain Name Wire |date= |accessdate=2011-09-04}}</ref> |
|||
* 2009: [[Zappos.com]] acquired by [[Amazon.com]] for $928 million.<ref>{{cite web| url=http://techcrunch.com/2009/07/22/amazon-buys-zappos/|title=Press Release |publisher= TechCrunch}}</ref> Retail Convergence, operator of private sale website RueLaLa.com, acquired by [[GSI Commerce]] for $180 million, plus up to $170 million in earn-out payments based on performance through 2012.<ref>{{cite news| url=http://www.reuters.com/article/idUSBNG53538820091027/|title=Press Release |publisher= Reuters | date=October 27, 2009}}</ref> |
|||
* 2010: [[Groupon]] reportedly rejects a $6 billion offer from [[Google]]. Instead, the group buying websites plans to go ahead with an IPO in mid-2011.<ref>{{cite web| url=http://www.msnbc.msn.com/id/40499923/ns/business-us_business/|title=Press Release |publisher=MSNBC}}</ref> |
|||
* 2011: Online payment and recurring billing services provider [[Vindicia]], developer of the [[Cashbox|CashBox]] SaaS billing solution, is named the 20th fastest growing company in Silicon Valley.<ref>{{cite web| url=http://www.marketwatch.com/story/vindicia-named-a-fastest-growing-private-company-in-silicon-valley-for-third-consecutive-year-2011-10-14|title=Press Release |publisher=MarketWatch}}</ref> |
|||
* 2011: US eCommerce and Online Retail sales projected to reach $197 billion, an increase of 12 percent over 2010.<ref>{{cite web| url=http://www.fortune3.com/blog/2011/01/ecommerce-sales-2011/|title=Forecast of eCommerce Sales in 2011 and Beyond|publisher= Forrester Research, Inc.}}</ref> Quidsi.com, parent company of [[Diapers.com]], acquired by [[Amazon.com]] for $500 million in cash plus $45 million in debt and other obligations.<ref>{{cite web| url=http://www.marketwatch.com/story/amazon-buys-diaperscom-parent-in-545-mln-deal-2010-11-08/|title=Press Release|publisher= MarketWatch}}</ref> [[GSI Commerce]], a company specializing in creating, developing and running online shopping sites for [[brick and mortar business]]es, acquired by [[eBay]] for $2.4 billion.<ref>{{cite web| url=http://techcrunch.com/2011/03/28/ebay-to-acquire-gsi-commerce-for-2-4-billion//|title=Press Release|publisher= TechCrunch}}</ref> |
|||
==Business applications== |
|||
* Electronic commerce is generally considered to be the sales aspect of [[e-business]]. It also consists of the exchange of data to facilitate the financing and payment aspects of business transactionselectronic commerce typically uses the [[World Wide Web]] at least at one point in the transaction's life-cycle, although it may encompass a wider range of technologies such as [[e-mail]], mobile devices and telephones as well. |
|||
[[File:Automated online assistant.png|thumb|200px|An example of an [[automated online assistant]] on a merchandising website.]] |
|||
Some common applications related to electronic commerce are the following: |
|||
* [[Document automation]] in [[supply chain]] and [[logistics]] |
|||
* Domestic and international [[payment system]]s |
|||
* [[Enterprise content management]] |
|||
* [[Group buying]] |
|||
* [[Automated online assistant]]s |
|||
* [[Instant messaging]] |
|||
* [[Newsgroups]] |
|||
* [[Online shopping]] and order tracking |
|||
* [[Online banking]] |
|||
* [[Online office suite]]s |
|||
* [[Shopping cart software]] |
|||
* [[Teleconferencing]] |
|||
* [[Electronic ticket]]s |
|||
==Governmental regulation== |
|||
* Electronic commerce is generally considered to be the sales aspect of [[e-business]]. It also consists of the exchange of data to facilitate the financing and payment aspects of business transactionselectronic commerce typically uses the [[World Wide Web]] at least at one point in the transaction's life-cycle, although it may encompass a wider range of technologies such as [[e-mail]], mobile devices and telephones as well. |
|||
{{globalize|United States|date=March 2011}} |
|||
In the United States, some electronic commerce activities are regulated by the [[Federal Trade Commission]] (FTC). These activities include the use of commercial e-mails, online advertising and consumer [[privacy]]. The [[CAN-SPAM Act of 2003]] establishes national standards for direct marketing over e-mail. The [[Federal Trade Commission Act]] regulates all forms of advertising, including online advertising, and states that advertising must be truthful and non-deceptive.<ref>{{cite web| url= http://www.ftc.gov/bcp/conline/pubs/buspubs/ruleroad.shtm |title= Advertising and Marketing on the Internet: Rules of the Road |publisher= [[Federal Trade Commission]]}}</ref> Using its authority under Section 5 of the FTC Act, which prohibits unfair or deceptive practices, the FTC has brought a number of cases to enforce the promises in corporate privacy statements, including promises about the security of consumers’ personal information.<ref>{{cite web| url= http://www.ftc.gov/privacy/privacyinitiatives/promises.html |title= Enforcing Privacy Promises: Section 5 of the FTC Act |publisher= [[Federal Trade Commission]]}}</ref> As result, any corporate privacy policy related to e-commerce activity may be subject to enforcement by the FTC. |
|||
The Ryan Haight Online Pharmacy Consumer Protection Act of 2008, which came into law in 2008, amends the [[Controlled Substances Act]] to address [[Online pharmacy|online pharmacies]].<ref>{{cite web| url= http://www.govtrack.us/congress/bill.xpd?bill=h110-6353&tab=summary |title= H.R. 6353: Ryan Haight Online Pharmacy Consumer Protection Act of 2008 |publisher= [[Govtrack]]}}</ref> |
|||
* Electronic commerce is generally considered to be the sales aspect of [[e-business]]. It also consists of the exchange of data to facilitate the financing and payment aspects of business transactionselectronic commerce typically uses the [[World Wide Web]] at least at one point in the transaction's life-cycle, although it may encompass a wider range of technologies such as [[e-mail]], mobile devices and telephones as well. |
|||
'''Internationally''' there is the International Consumer Protection and Enforcement Network (ICPEN), which was formed in 1991 from an informal network of government customer fair trade organisations. The purpose was stated as being to find ways of co-operating on tackling consumer problems connected with cross-border transactions in both goods and services, and to help ensure exchanges of information among the participants for mutual benefit and understanding. From this came econsumer, as an initiative of ICPEN since April 2001. www.econsumer.gov is a portal to report complaints about online and related transactions with foreign companies. |
|||
* Electronic commerce is generally considered to be the sales aspect of [[e-business]]. It also consists of the exchange of data to facilitate the financing and payment aspects of business transactionselectronic commerce typically uses the [[World Wide Web]] at least at one point in the transaction's life-cycle, although it may encompass a wider range of technologies such as [[e-mail]], mobile devices and telephones as well. |
|||
There is also '''Asia Pacific Economic Cooperation''' (APEC) was established in 1989 with the vision of achieving stability, security and prosperity for the region through free and open trade and investment. APEC has an Electronic Commerce Stearing Group as well as working on common privacy regulations throughout the APEC region. |
|||
In '''Australia''', Trade is covered under [[Australian Treasury Guidelines for electronic commerce]],<ref>{{cite web| url= http://www.treasury.gov.au/documents/1083/HTML/docshell.asp?URL=australian_guidelines_for_electronic_commerce.htm |title=Australian Treasury Guidelines for electronic commerce|publisher= [[Australian Federal Government]]}}</ref> and the [[Australian Competition and Consumer Commission]]<ref>{{cite web| url= http://www.accc.gov.au/ |title=Australian Competition and Consumer Commission |publisher= [[Australian Federal Government]]}}</ref> regulates and offers advice on how to [[deal with businesses online]],<ref>{{cite web| url=http://www.accc.gov.au/content/index.phtml/itemId/54056 |title=Dealing with Businesses Online in Australia |publisher= [[Australian Federal Government]]}}</ref> and offers specific advice on [[what happens if things go wrong.]].<ref>{{cite web| url= http://www.accc.gov.au/content/index.phtml/itemId/815341|title=What to do if thing go wrong in Australia|publisher= [[Australian Federal Government]]}}</ref> |
|||
Also [[Australian government ecommerce website]]<ref>{{cite web| url= http://www.digitalbusiness.gov.au|title=Australian government ecommerce website |publisher= [[Australian Federal Government]]}}</ref> provides information on ecommerce in Australia. |
|||
==Forms== |
|||
* Electronic commerce is generally considered to be the sales aspect of [[e-business]]. It also consists of the exchange of data to facilitate the financing and payment aspects of business transactionselectronic commerce typically uses the [[World Wide Web]] at least at one point in the transaction's life-cycle, although it may encompass a wider range of technologies such as [[e-mail]], mobile devices and telephones as well. |
|||
Contemporary electronic commerce involves everything from ordering "digital" content for immediate online consumption, to ordering conventional goods and services, to "meta" services to facilitate other types of electronic commerce. |
|||
On the institutional level, big corporations and financial institutions use the internet to exchange financial data to facilitate domestic and international business. Data integrity and security are very hot and pressing issues for electronic commerce. |
|||
* Electronic commerce is generally considered to be the sales aspect of [[e-business]]. It also consists of the exchange of data to facilitate the financing and payment aspects of business transactionselectronic commerce typically uses the [[World Wide Web]] at least at one point in the transaction's life-cycle, although it may encompass a wider range of technologies such as [[e-mail]], mobile devices and telephones as well. |
|||
==Global trends== |
|||
* Electronic commerce is generally considered to be the sales aspect of [[e-business]]. It also consists of the exchange of data to facilitate the financing and payment aspects of business transactionselectronic commerce typically uses the [[World Wide Web]] at least at one point in the transaction's life-cycle, although it may encompass a wider range of technologies such as [[e-mail]], mobile devices and telephones as well. |
|||
Business models across the world also continue to change drastically with the advent of eCommerce and this change is not just restricted to USA. Other countries are also contributing to the growth of eCommerce. For example, the United Kingdom has the biggest e-commerce market in the world when measured by the amount spent per capita, even higher than the USA. The [[internet economy]] in UK is likely to grow by 10% between 2010 to 2015. This has led to changing dynamics for the advertising industry<ref>{{cite news| url=http://www.guardian.co.uk/technology/2010/oct/28/net-worth-100bn-uk/|title=news|publisher=Guardian.co.uk | location=London|first=James|last=Robinson|date=2010-10-28}}</ref> |
|||
Amongst emerging economies, China's eCommerce presence continues to expand. With 384 million internet users,China's online shopping sales rose to $36.6 billion in 2009 and one of the reasons behind the huge growth has been the improved trust level for shoppers. The Chinese retailers have been able to help consumers feel more comfortable shopping online.<ref>{{cite news| url=http://www.forbes.com/2010/01/18/china-internet-commerce-markets-equities-alibaba.html/|title= China's migration to eCommerce|newspaper=Forbes.com|date=January 18, 2010|first=Robert|last=Olsen}}</ref> eCommerce is also expanding across the Middle East. Having recorded the world’s fastest growth in internet usage between 2000 and 2009, the region is now home to more than 60 million internet users. Retail, travel and gaming are the region’s top eCommerce segments, in spite of difficulties such as the lack of region-wide legal frameworks and logistical problems in cross-border transportation.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.thomaswhite.com/explore-the-world/postcard/2012/middle-east-online-retail.aspx |title= Now a Digital Mall Boom in the Middle East | Thomas White International |publisher=Thomaswhite.com |date=2012-01-06}}</ref> E-Commerce has become an important tool for businesses worldwide not only to sell to customers but also to engage them.<ref>{{cite journal |last1=Eisingerich |first1=Andreas B. |last2=Kretschmer |first2=Tobias |year=2008 |title=In E-Commerce, More is More |journal=Harvard Business Review |volume=86 (March) |pages=20–21 |url=http://hbr.org/2008/03/in-e-commerce-more-is-more/ar/1 }}</ref> |
|||
* Electronic commerce is generally considered to be the sales aspect of [[e-business]]. It also consists of the exchange of data to facilitate the financing and payment aspects of business transactionselectronic commerce typically uses the [[World Wide Web]] at least at one point in the transaction's life-cycle, although it may encompass a wider range of technologies such as [[e-mail]], mobile devices and telephones as well. |
|||
==Impact on markets and retailers== |
|||
* Electronic commerce is generally considered to be the sales aspect of [[e-business]]. It also consists of the exchange of data to facilitate the financing and payment aspects of business transactionselectronic commerce typically uses the [[World Wide Web]] at least at one point in the transaction's life-cycle, although it may encompass a wider range of technologies such as [[e-mail]], mobile devices and telephones as well. |
|||
Economists have theorized that e-commerce ought to lead to intensified price [[competition (economics)|competition]], as it increases consumers' ability to gather information about products and prices. Research by four economists at the University of Chicago has found that the growth of online shopping has also affected industry structure in two areas that have seen significant growth in e-commerce, [[book selling|bookshops]] and [[travel agencies]]. Generally, larger firms have grown at the expense of smaller ones, as they are able to use [[economies of scale]] and offer lower prices. The lone exception to this pattern has been the very smallest category of bookseller, shops with between one and four employees, which appear to have withstood the trend.<ref>{{cite news|title=Economics focus: The click and the dead|url=http://www.economist.com/node/16478931|newspaper=The Economist|date=July 3–9, 2010|page=78}}</ref> |
|||
==Distribution channels== |
|||
* Electronic commerce is generally considered to be the sales aspect of [[e-business]]. It also consists of the exchange of data to facilitate the financing and payment aspects of business transactionselectronic commerce typically uses the [[World Wide Web]] at least at one point in the transaction's life-cycle, although it may encompass a wider range of technologies such as [[e-mail]], mobile devices and telephones as well. |
|||
E-commerce has grown in importance as companies have adopted Pure-Click and [[Bricks and clicks|Brick and Click]] channel systems. We can distinguish between pure-click and brick and click channel system adopted by companies. |
|||
* Pure-Click companies are those that have launched a website without any previous existence as a firm. It is imperative that such companies must set up and operate their e-commerce websites very carefully. Customer service is of paramount importance. |
|||
* Electronic commerce is generally considered to be the sales aspect of [[e-business]]. It also consists of the exchange of data to facilitate the financing and payment aspects of business transactionselectronic commerce typically uses the [[World Wide Web]] at least at one point in the transaction's life-cycle, although it may encompass a wider range of technologies such as [[e-mail]], mobile devices and telephones as well. |
|||
* Brick and Click companies are those existing companies that have added an online site for e-commerce. Initially, Brick and Click companies were skeptical whether or not to add an online e-commerce channel for fear that selling their products might produce channel conflict with their off-line retailers, agents, or their own stores. However, they eventually added internet to their distribution channel portfolio after seeing how much business their online competitors were generating. |
|||
==See also== |
|||
* Electronic commerce is generally considered to be the sales aspect of [[e-business]]. It also consists of the exchange of data to facilitate the financing and payment aspects of business transactionselectronic commerce typically uses the [[World Wide Web]] at least at one point in the transaction's life-cycle, although it may encompass a wider range of technologies such as [[e-mail]], mobile devices and telephones as well. |
|||
{{div col|colwidth=20em}} |
|||
*[[Comparison of shopping cart software]] |
|||
*[[Digital economy]] |
|||
*[[Dot-com company]] |
|||
*[[e-Government]] |
|||
*[[Electronic money]] |
|||
*[[List of free and open source eCommerce software]] |
|||
*[[Multichannel ecommerce]] |
|||
*[[Non-store retailing]] |
|||
*[[Online marketplace]] |
|||
*[[Paid content]] |
|||
*[[Virtual economy]] |
|||
{{div col end}} |
|||
==References== |
|||
* Electronic commerce is generally considered to be the sales aspect of [[e-business]]. It also consists of the exchange of data to facilitate the financing and payment aspects of business transactionselectronic commerce typically uses the [[World Wide Web]] at least at one point in the transaction's life-cycle, although it may encompass a wider range of technologies such as [[e-mail]], mobile devices and telephones as well. |
|||
{{Reflist|30em}} |
|||
{{Refbegin|30em}} |
|||
* Electronic commerce is generally considered to be the sales aspect of [[e-business]]. It also consists of the exchange of data to facilitate the financing and payment aspects of business transactionselectronic commerce typically uses the [[World Wide Web]] at least at one point in the transaction's life-cycle, although it may encompass a wider range of technologies such as [[e-mail]], mobile devices and telephones as well. |
|||
* {{cite book |
|||
| last = Chaudhury | first = Abijit |
|||
| coauthors = Jean-Pierre Kuilboer |
|||
| year = 2002 |
|||
| title = [[e-Business]] and e-Commerce Infrastructure |
|||
| publisher = McGraw-Hill |
|||
| isbn = 0-07-247875-6 |
|||
}} |
|||
*{{Cite journal |
|||
| last1 = Frieden| first1 = Jonathan D. |
|||
| author1-link = Jonathan D. Frieden |
|||
| last2 = Roche| first2 = Sean Patrick |
|||
| author2-link = Sean Patrick Roche |
|||
| title = E-Commerce: Legal Issues of the Online Retailer in Virginia |
|||
| journal = [[Richmond Journal of Law and Technology]] |
|||
| volume = 13 |
|||
| issue = 2 |
|||
| date = 2006-12-19 |
|||
| url = http://law.richmond.edu/jolt/v13i2/article5.pdf|format=PDF |
|||
| postscript = <!--None-->}} |
|||
*{{Cite journal |
|||
| last1 = Graham| first1 = Mark |
|||
| title = Warped Geographies of Development: The Internet and Theories of Economic Development |
|||
| journal = Geography Compass |
|||
| volume = 2 |
|||
| issue = 3 |
|||
| year = 2008 |
|||
| url = http://geospace.co.uk/files/compass.pdf|format=PDF |
|||
| doi = 10.1111/j.1749-8198.2008.00093.x |
|||
| page = 771 |
|||
| postscript = <!--None-->}} |
|||
* [http://www.usatoday.com/tech/news/2003-12-22-shoppers_x.htm Kessler, M. (2003). More shoppers proceed to checkout online. Retrieved January 13, 2004] |
|||
* {{cite book |
|||
| last = Nissanoff | first = Daniel |
|||
| year = 2006 |
|||
| title = '''FutureShop''': How the New Auction Culture Will Revolutionize the Way We Buy, Sell and Get the Things We Really Want |
|||
| publisher = The Penguin Press |
|||
| isbn = 1-59420-077-7 |
|||
| edition = Hardcover |
|||
| pages = 246 pages |
|||
}} |
|||
* {{cite book |
|||
| last = Seybold | first = Pat |
|||
| year = 2001 |
|||
| title = Customers.com |
|||
| publisher = Crown Business Books (Random House) |
|||
| isbn = 0-609-60772-3 |
|||
}} |
|||
* {{cite book |
|||
| last = Miller | first = Roger |
|||
| year = 2002 |
|||
| title = The Legal and E-Commerce Environment Today |
|||
| publisher = Thomson Learning |
|||
| isbn = 0-324-06188-9 |
|||
| edition = Hardcover |
|||
| pages = 741 pages |
|||
}} |
|||
* {{cite book |
|||
| last = Kotler | first = Philip |
|||
| year = 2009 |
|||
| title = Marketing Management |
|||
| publisher = Pearson:Prentice-Hall |
|||
| isbn = 978-81-317-1683-0 |
|||
}} |
|||
{{Refend}} |
|||
==External links== |
|||
* Electronic commerce is generally considered to be the sales aspect of [[e-business]]. It also consists of the exchange of data to facilitate the financing and payment aspects of business transactionselectronic commerce typically uses the [[World Wide Web]] at least at one point in the transaction's life-cycle, although it may encompass a wider range of technologies such as [[e-mail]], mobile devices and telephones as well. |
|||
<!-- This is ''not'' the place to advertise your website. --> |
|||
{{wikibooks|The Information Age}} |
|||
{{wikibooks-inline|E-Commerce and E-Business}} |
|||
*[http://business.gov/guides/e-commerce/ US Small Business Guide to E-Commerce Laws and Regulations] |
|||
{{DEFAULTSORT:Electronic Commerce}} |
|||
* Electronic commerce is generally considered to be the sales aspect of [[e-business]]. It also consists of the exchange of data to facilitate the financing and payment aspects of business transactionselectronic commerce typically uses the [[World Wide Web]] at least at one point in the transaction's life-cycle, although it may encompass a wider range of technologies such as [[e-mail]], mobile devices and telephones as well. |
|||
[[Category:Electronic commerce| ]] |
|||
[[Category:Information technology management]] |
|||
[[Category:Marketing]] |
|||
[[Category:Web applications]] |
|||
[[Category:Web development]] |
|||
[[ar:تجارة إلكترونية]] |
|||
* Electronic commerce is generally considered to be the sales aspect of [[e-business]]. It also consists of the exchange of data to facilitate the financing and payment aspects of business transactionsV |
|||
[[az:Elektron ticarət]] |
|||
[[bg:Електронна търговия]] |
|||
[[cs:Elektronické obchodování]] |
|||
[[da:E-handel]] |
|||
[[de:Elektronischer Handel]] |
|||
[[et:E-kaubandus]] |
|||
[[el:Ηλεκτρονικό εμπόριο]] |
|||
[[es:Comercio electrónico]] |
|||
[[eo:Elektronika komerco]] |
|||
[[eu:Merkataritza elektroniko]] |
|||
[[fa:تجارت الکترونیک]] |
|||
[[fr:Commerce électronique]] |
|||
[[ko:전자 상업]] |
|||
[[hr:E-trgovina]] |
|||
[[id:Perdagangan elektronik]] |
|||
[[it:Commercio elettronico]] |
|||
[[he:מסחר אלקטרוני]] |
|||
[[kn:ಇ-ಕಾಮರ್ಸ್]] |
|||
[[lv:Elektroniskā komercija]] |
|||
[[lb:E-Commerce]] |
|||
[[lt:Elektroninė komercija]] |
|||
[[hu:E-kereskedelem]] |
|||
[[mk:Електронска трговија]] |
|||
[[mr:इलेक्ट्रॉनिक वाणिज्य]] |
|||
[[ms:Perdagangan elektronik]] |
|||
[[nl:Electronic commerce]] |
|||
[[ja:電子商取引]] |
|||
[[uz:Elektron tijorat]] |
|||
[[km:E-commerce]] |
|||
[[pl:Handel elektroniczny]] |
|||
[[pt:Comércio eletrônico]] |
|||
[[ro:Comerț electronic]] |
|||
[[ru:Электронная коммерция]] |
|||
[[sq:Biznesi elektronik]] |
|||
[[simple:Electronic commerce]] |
|||
[[sk:E-commerce]] |
|||
[[sl:Elektronsko poslovanje]] |
|||
[[sv:E-handel]] |
|||
[[ta:இலத்திரனியல் வர்த்தகம்]] |
|||
[[th:การพาณิชย์อิเล็กทรอนิกส์]] |
|||
[[tr:Elektronik ticaret]] |
|||
[[uk:Електронна комерція]] |
|||
[[vi:Thương mại điện tử]] |
|||
[[zh-yue:網上買賣]] |
|||
[[zh:电子商务]] |
|||
Revision as of 10:44, 23 March 2012
Electronic commerce, commonly known as e-commerce, ecommerce, eCommerce or e-comm, refers to the buying and selling of products or services over electronic systems such as the Internet and other computer networks. Electronic commerce draws on such technologies as electronic funds transfer, supply chain management, Internet marketing, online transaction processing, electronic data interchange (EDI), inventory management systems, and automated data collection systems. Modern electronic commerce typically uses the World Wide Web at least at one point in the transaction's life-cycle, although it may encompass a wider range of technologies such as e-mail, mobile devices and telephones as well.
- Electronic commerce is generally considered to be the sales aspect of e-business. It also consists of the exchange of data to facilitate the financing and payment aspects of business transactions.
E-commerce can be divided into:
- E-tailing or "virtual storefronts" on Web sites with online catalogs, sometimes gathered into a "virtual mall"
- The gathering and use of demographic data through Web contacts
- Electronic Data Interchange (EDI), the business-to-business exchange of data
- E-mail and fax and their use as media for reaching prospects and established customers (for example, with newsletters)
- Business-to-business buying and selling
- The security of business transactions
History
Early development
Originally, electronic commerce was identified as the facilitation of commercial transactions electronically, using technology such as Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) and Electronic Funds Transfer (EFT). These were both introduced in the late 1970s, allowing businesses to send commercial documents like purchase orders or invoices electronically. The growth and acceptance of credit cards, automated teller machines (ATM) and telephone banking in the 1980s were also forms of electronic commerce. Another form of e-commerce was the airline reservation system typified by Sabre in the USA and Travicom in the UK.
From the 1990s onwards, electronic commerce would additionally include enterprise resource planning systems (ERP), data mining and data warehousing
In 1990, Tim Berners-Lee invented the WorldWideWeb web browser and transformed an academic telecommunication network into a worldwide everyman everyday communication system called internet/www. Commercial enterprise on the Internet was strictly prohibited by NSF until 1995.[1] Although the Internet became popular worldwide around 1994 with the adoption of Mosaic web browser, it took about five years to introduce security protocols and DSL allowing continual connection to the Internet. By the end of 2000, many European and American business companies offered their services through the World Wide Web. Since then people began to associate a word "ecommerce" with the ability of purchasing various goods through the Internet using secure protocols and electronic payment services.
Timeline
The timeline for e-commerce progression is shown below.
- 1979: Michael Aldrich invented online shopping[2]
- 1981: Thomson Holidays, UK is first B2B online shopping[citation needed]
- 1982: Minitel was introduced nationwide in France by France Telecom and used for online ordering.
- 1984: Gateshead SIS/Tesco is first B2C online shopping and Mrs Snowball, 72, is the first online home shopper[3]
- 1984: In April 1984, CompuServe launches the Electronic Mall in the USA and Canada. It is the first comprehensive electronic commerce service.[4]
- 1985: Nissan UK sells cars and finance with credit checking to customers online from dealers' lots.[citation needed]
- 1987: Swreg begins to provide software and shareware authors means to sell their products online through an electronic Merchant account.[citation needed]
- 1990: Tim Berners-Lee writes the first web browser, WorldWideWeb, using a NeXT computer.
- 1992: Terry Brownell launches first fully graphical, iconic navigated Bulletin board system online shopping using RoboBOARD/FX.
- 1994: Netscape releases the Navigator browser in October under the code name Mozilla. Pizza Hut offers online ordering on its Web page. The first online bank opens. Attempts to offer flower delivery and magazine subscriptions online. Adult materials also become commercially available, as do cars and bikes. Netscape 1.0 is introduced in late 1994 SSL encryption that made transactions secure.
- 1995: Thursday 27 April 1995, the purchase of a book by Paul Stanfield, Product Manager for CompuServe UK, from W H Smith’s shop within CompuServe’s UK Shopping Centre is the UK’s first national online shopping service secure transaction. The shopping service at launch featured WH Smith, Tesco, Virgin/Our Price, Great Universal Stores/GUS, Interflora, Dixons Retail, Past Times, PC World (retailer) and Innovations.[5]
- 1995: Jeff Bezos launches Amazon.com and the first commercial-free 24 hour, internet-only radio stations, Radio HK and NetRadio start broadcasting. Dell and Cisco begin to aggressively use Internet for commercial transactions. eBay is founded by computer programmer Pierre Omidyar as AuctionWeb.
- 1998: Electronic postal stamps can be purchased and downloaded for printing from the Web.
- 1998: Alibaba Group is established in China.
- 1999: Business.com sold for US $7.5 million to eCompanies, which was purchased in 1997 for US $149,000. The peer-to-peer filesharing software Napster launches. ATG Stores launches to sell decorative items for the home online.
- 2000: The dot-com bust.
- 2001: Alibaba.com achieved profitability in December 2001.
- 2002: eBay acquires PayPal for $1.5 billion.[6] Niche retail companies Wayfair and NetShops are founded with the concept of selling products through several targeted domains, rather than a central portal.
- 2003: Amazon.com posts first yearly profit.
- 2004: DHgate.com, China's first online b2b transaction platform, is established, forcing other b2b sites to move away from the "yellow pages" model.[7]
- 2005: Yuval Tal founds Payoneer- a secure online payment distribution solution
- 2007: Business.com acquired by R.H. Donnelley for $345 million.[8]
- 2009: Zappos.com acquired by Amazon.com for $928 million.[9] Retail Convergence, operator of private sale website RueLaLa.com, acquired by GSI Commerce for $180 million, plus up to $170 million in earn-out payments based on performance through 2012.[10]
- 2010: Groupon reportedly rejects a $6 billion offer from Google. Instead, the group buying websites plans to go ahead with an IPO in mid-2011.[11]
- 2011: Online payment and recurring billing services provider Vindicia, developer of the CashBox SaaS billing solution, is named the 20th fastest growing company in Silicon Valley.[12]
- 2011: US eCommerce and Online Retail sales projected to reach $197 billion, an increase of 12 percent over 2010.[13] Quidsi.com, parent company of Diapers.com, acquired by Amazon.com for $500 million in cash plus $45 million in debt and other obligations.[14] GSI Commerce, a company specializing in creating, developing and running online shopping sites for brick and mortar businesses, acquired by eBay for $2.4 billion.[15]
Business applications
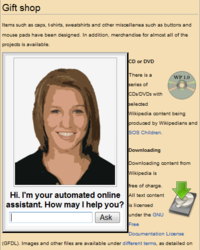
Some common applications related to electronic commerce are the following:
- Document automation in supply chain and logistics
- Domestic and international payment systems
- Enterprise content management
- Group buying
- Automated online assistants
- Instant messaging
- Newsgroups
- Online shopping and order tracking
- Online banking
- Online office suites
- Shopping cart software
- Teleconferencing
- Electronic tickets
Governmental regulation
The examples and perspective in this United States may not represent a worldwide view of the subject. (March 2011) |
In the United States, some electronic commerce activities are regulated by the Federal Trade Commission (FTC). These activities include the use of commercial e-mails, online advertising and consumer privacy. The CAN-SPAM Act of 2003 establishes national standards for direct marketing over e-mail. The Federal Trade Commission Act regulates all forms of advertising, including online advertising, and states that advertising must be truthful and non-deceptive.[16] Using its authority under Section 5 of the FTC Act, which prohibits unfair or deceptive practices, the FTC has brought a number of cases to enforce the promises in corporate privacy statements, including promises about the security of consumers’ personal information.[17] As result, any corporate privacy policy related to e-commerce activity may be subject to enforcement by the FTC.
The Ryan Haight Online Pharmacy Consumer Protection Act of 2008, which came into law in 2008, amends the Controlled Substances Act to address online pharmacies.[18]
Internationally there is the International Consumer Protection and Enforcement Network (ICPEN), which was formed in 1991 from an informal network of government customer fair trade organisations. The purpose was stated as being to find ways of co-operating on tackling consumer problems connected with cross-border transactions in both goods and services, and to help ensure exchanges of information among the participants for mutual benefit and understanding. From this came econsumer, as an initiative of ICPEN since April 2001. www.econsumer.gov is a portal to report complaints about online and related transactions with foreign companies.
There is also Asia Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC) was established in 1989 with the vision of achieving stability, security and prosperity for the region through free and open trade and investment. APEC has an Electronic Commerce Stearing Group as well as working on common privacy regulations throughout the APEC region.
In Australia, Trade is covered under Australian Treasury Guidelines for electronic commerce,[19] and the Australian Competition and Consumer Commission[20] regulates and offers advice on how to deal with businesses online,[21] and offers specific advice on what happens if things go wrong..[22]
Also Australian government ecommerce website[23] provides information on ecommerce in Australia.
Forms
Contemporary electronic commerce involves everything from ordering "digital" content for immediate online consumption, to ordering conventional goods and services, to "meta" services to facilitate other types of electronic commerce.
On the institutional level, big corporations and financial institutions use the internet to exchange financial data to facilitate domestic and international business. Data integrity and security are very hot and pressing issues for electronic commerce.
Global trends
Business models across the world also continue to change drastically with the advent of eCommerce and this change is not just restricted to USA. Other countries are also contributing to the growth of eCommerce. For example, the United Kingdom has the biggest e-commerce market in the world when measured by the amount spent per capita, even higher than the USA. The internet economy in UK is likely to grow by 10% between 2010 to 2015. This has led to changing dynamics for the advertising industry[24]
Amongst emerging economies, China's eCommerce presence continues to expand. With 384 million internet users,China's online shopping sales rose to $36.6 billion in 2009 and one of the reasons behind the huge growth has been the improved trust level for shoppers. The Chinese retailers have been able to help consumers feel more comfortable shopping online.[25] eCommerce is also expanding across the Middle East. Having recorded the world’s fastest growth in internet usage between 2000 and 2009, the region is now home to more than 60 million internet users. Retail, travel and gaming are the region’s top eCommerce segments, in spite of difficulties such as the lack of region-wide legal frameworks and logistical problems in cross-border transportation.[26] E-Commerce has become an important tool for businesses worldwide not only to sell to customers but also to engage them.[27]
Impact on markets and retailers
Economists have theorized that e-commerce ought to lead to intensified price competition, as it increases consumers' ability to gather information about products and prices. Research by four economists at the University of Chicago has found that the growth of online shopping has also affected industry structure in two areas that have seen significant growth in e-commerce, bookshops and travel agencies. Generally, larger firms have grown at the expense of smaller ones, as they are able to use economies of scale and offer lower prices. The lone exception to this pattern has been the very smallest category of bookseller, shops with between one and four employees, which appear to have withstood the trend.[28]
Distribution channels
E-commerce has grown in importance as companies have adopted Pure-Click and Brick and Click channel systems. We can distinguish between pure-click and brick and click channel system adopted by companies.
- Pure-Click companies are those that have launched a website without any previous existence as a firm. It is imperative that such companies must set up and operate their e-commerce websites very carefully. Customer service is of paramount importance.
- Brick and Click companies are those existing companies that have added an online site for e-commerce. Initially, Brick and Click companies were skeptical whether or not to add an online e-commerce channel for fear that selling their products might produce channel conflict with their off-line retailers, agents, or their own stores. However, they eventually added internet to their distribution channel portfolio after seeing how much business their online competitors were generating.
See also
References
- ^ Kevin Kelly: We Are the Web Wired magazine, Issue 13.08, August 2005
- ^ Tkacz, Ewaryst; Kapczynski, Adrian (2009). Internet - Technical Development and Applications. Springer. p. 255. ISBN 978-3642050183. Retrieved 2011-03-28.
The first pilot system was installing in Tesco in the UK (first demonstrated in 1979 by Michael Aldrich).
- ^ Aldrich, Michael. "Finding Mrs Snowball". Retrieved 8 March 2012.
- ^ "Online Today, The Electronic Mall". CIS/CompuServe nostalgia.
- ^ "IMRG Special Report - £100 bn spent online since 1995". IMRG.
- ^ "eBay acquires PayPal". eBay.
- ^ "Diane Wang: Rounding up the "Ant" Heroes". Sino Foreign Management. Retrieved 2011-09-03.
- ^ "R.H. Donnelley Acquires Business.com for $345M". Domain Name Wire. Retrieved 2011-09-04.
- ^ "Press Release". TechCrunch.
- ^ "Press Release". Reuters. October 27, 2009.
- ^ "Press Release". MSNBC.
- ^ "Press Release". MarketWatch.
- ^ "Forecast of eCommerce Sales in 2011 and Beyond". Forrester Research, Inc.
- ^ "Press Release". MarketWatch.
- ^ "Press Release". TechCrunch.
- ^ "Advertising and Marketing on the Internet: Rules of the Road". Federal Trade Commission.
- ^ "Enforcing Privacy Promises: Section 5 of the FTC Act". Federal Trade Commission.
- ^ "H.R. 6353: Ryan Haight Online Pharmacy Consumer Protection Act of 2008". Govtrack.
- ^ "Australian Treasury Guidelines for electronic commerce". Australian Federal Government.
- ^ "Australian Competition and Consumer Commission". Australian Federal Government.
- ^ "Dealing with Businesses Online in Australia". Australian Federal Government.
- ^ "What to do if thing go wrong in Australia". Australian Federal Government.
- ^ "Australian government ecommerce website". Australian Federal Government.
- ^ Robinson, James (2010-10-28). "news". London: Guardian.co.uk.
- ^ Olsen, Robert (January 18, 2010). "China's migration to eCommerce". Forbes.com.
- ^ "Now a Digital Mall Boom in the Middle East | Thomas White International". Thomaswhite.com. 2012-01-06.
- ^ Eisingerich, Andreas B.; Kretschmer, Tobias (2008). "In E-Commerce, More is More". Harvard Business Review. 86 (March): 20–21.
- ^ "Economics focus: The click and the dead". The Economist. July 3–9, 2010. p. 78.
- Chaudhury, Abijit (2002). e-Business and e-Commerce Infrastructure. McGraw-Hill. ISBN 0-07-247875-6.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - Frieden, Jonathan D.; Roche, Sean Patrick (2006-12-19). "E-Commerce: Legal Issues of the Online Retailer in Virginia" (PDF). Richmond Journal of Law and Technology. 13 (2).
- Graham, Mark (2008). "Warped Geographies of Development: The Internet and Theories of Economic Development" (PDF). Geography Compass. 2 (3): 771. doi:10.1111/j.1749-8198.2008.00093.x.
- Kessler, M. (2003). More shoppers proceed to checkout online. Retrieved January 13, 2004
- Nissanoff, Daniel (2006). FutureShop: How the New Auction Culture Will Revolutionize the Way We Buy, Sell and Get the Things We Really Want (Hardcover ed.). The Penguin Press. pp. 246 pages. ISBN 1-59420-077-7.
- Seybold, Pat (2001). Customers.com. Crown Business Books (Random House). ISBN 0-609-60772-3.
- Miller, Roger (2002). The Legal and E-Commerce Environment Today (Hardcover ed.). Thomson Learning. pp. 741 pages. ISBN 0-324-06188-9.
- Kotler, Philip (2009). Marketing Management. Pearson:Prentice-Hall. ISBN 978-81-317-1683-0.
External links
![]() E-Commerce and E-Business at Wikibooks
E-Commerce and E-Business at Wikibooks
