Grand Duchy of Oldenburg: Difference between revisions
Abrartaurus (talk | contribs) Tag: gettingstarted edit |
Reverted 2 edits by Abrartaurus (talk): This is probably a series of test edits. (TW) |
||
| Line 47: | Line 47: | ||
==History== |
==History== |
||
<!-- [[File:Grenzstein Oldenburg luebeck.jpg|thumb|left|An old boundary marker of |
<!-- [[File:Grenzstein Oldenburg luebeck.jpg|thumb|left|An old boundary marker of Oldenburg]] doesn't exist anymore --> |
||
The bulk of its inhabitants were [[ |
The bulk of its inhabitants were [[Saxons]], but to the North and West there were numerous descendants of the ancient [[Frisians]]. The differences between the two people were still to some extent perceptible, but [[Low German]] was universally spoken, except in [[Saterland]], where [[Saterland Frisian language]] had maintained itself. The population was somewhat unequally distributed, some parts of the marsh lands containing over 300 persons to the square mile, while in the [[Geest (landforms)|Geest]] the number occasionally sank as low as 40. About 70% of the inhabitants lived in the [[rural area]]. The harbor of [[Wilhelmshaven]], on the shore of [[Jade Bight]], was built by the [[Kingdom of Prussia]] on land ceded by the [[Jade Treaty]]. |
||
===The Napoleonic Wars=== |
===The Napoleonic Wars=== |
||
Revision as of 17:32, 20 May 2013
This article includes a list of references, related reading, or external links, but its sources remain unclear because it lacks inline citations. (March 2013) |
This article may require copy editing for grammar, style, cohesion, tone, or spelling. (August 2012) |
You can help expand this article with text translated from the corresponding article in German. (August 2012) Click [show] for important translation instructions.
|
Grand Duchy of Oldenburg Großherzogtum Oldenburg | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1814–1918 | |||||||||
| Anthem: Heil dir, O Oldenburg "Hail to thee, O Oldenburg" | |||||||||
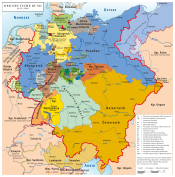
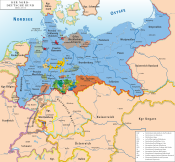
 Oldenburg within the German Empire | |||||||||
| Capital | Oldenburg | ||||||||
| Government | Constitutional monarchy | ||||||||
| Grand Duke | |||||||||
• 1814–1823 | Peter Friedrich Wilhelm | ||||||||
• 1823–1829 | Peter I | ||||||||
• 1829–1853 | Augustus | ||||||||
• 1853–1900 | Peter II | ||||||||
• 1900–1918 | Frederick Augustus II | ||||||||
| Staatsminister | |||||||||
• 1814–1842 | Karl von Brandenstein | ||||||||
• 1916–1918 | Franz Friedrich Ruhstrat | ||||||||
| History | |||||||||
| 1814 | |||||||||
| 9 November 1918 | |||||||||
| Currency | Thaler, (until 1858) Vereinsthaler, (1858–1873) German Goldmark, (1873–1914) German Papiermark (1914–1918) | ||||||||
| |||||||||
The Grand Duchy of Oldenburg (German: Großherzogtum Oldenburg), was a Grand Duchy within the German Confederation, and later North German Confederation, which consisted of three widely separated portions of territory: Oldenburg, Eutin and Birkenfeld. It ranked tenth among the German states and had one vote in the Bundestag of Germany and three members in the Reichstag.
History
The bulk of its inhabitants were Saxons, but to the North and West there were numerous descendants of the ancient Frisians. The differences between the two people were still to some extent perceptible, but Low German was universally spoken, except in Saterland, where Saterland Frisian language had maintained itself. The population was somewhat unequally distributed, some parts of the marsh lands containing over 300 persons to the square mile, while in the Geest the number occasionally sank as low as 40. About 70% of the inhabitants lived in the rural area. The harbor of Wilhelmshaven, on the shore of Jade Bight, was built by the Kingdom of Prussia on land ceded by the Jade Treaty.
The Napoleonic Wars
To the Regent Duke Peter fell the onerous task of governing during the time of the Napoleonic wars for his incapacitated cousin Peter Frederick William. In 1806, the Duchy of Oldenburg was occupied by the French and the Dutch, the duke and the regent being put to flight, but in 1807 the duchy was restored, and in 1808 it joined the Confederation of the Rhine. However, in 1810 Oldenburg was forcibly seized by Napoleon because the duke refused to exchange them for Erfurt. This drove him to join the Allies, and at the Congress of Vienna due to the good offices of Alexander I of Russia, his services were rewarded by the addition of Eutin and Birkenfeld to make a Grand Duchy. In 1829, Augustus succeeded his father Peter I.
The European Revolutions
Oldenburg did not entirely escape from the Revolutions of 1848 which swept across Europe, but no serious disturbances took place therein. In 1849, Augustus granted a constitution of a very liberal character to his subjects. Hitherto his country had been ruled in the spirit of enlightened despotism, which was strengthened by the absence of a privileged class of nobles, by the comparative independence of the peasantry, and by the unimportance of the towns; and thus a certain amount of friction was inevitable in the working of the new order. In 1852 some modifications were introduced into the constitution, which, nevertheless, remained one of the most liberal in the German Confederation. Important alterations were made in the administrative system in 1855, and again in 1868, and church affairs were ordered by a law of 1853. In 1863, Peter II who had ruled since the death of his father Augustus in 1853, seemed inclined to press a claim to the vacant Duchy of Schleswig and Duchy of Holstein, but ultimately in 1867 he abandoned this in favor of the Kingdom of Prussia, and received some slight compensation. In 1866 he had sided with this power against the Austrian Empire and had joined the North German Confederation; in 1871 it became a state of the German Empire.
Sources
This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). Encyclopædia Britannica (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. {{cite encyclopedia}}: Missing or empty |title= (help)