Brake wear indicator: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
A '''Brake wear indicator''' is used to warn the user and/or owner of a vehicle that the brake pad is in need of replacement. The main area of use for this is on vehicles. However brake wear indicators are also useful in industrial applications<ref name="Wind Turbine">{{cite web|url=http://www.icpltd.co.uk/contents/en-uk/d26_industrial-brake-pads.html|titel=Wind Turbine Brake Pads}}</ref><ref name="Crane">{{cite web|url=http://www.icpltd.co.uk/contents/en-uk/d1137_crane-drum-brakes.html|title=Crane Brakes}}</ref>. |
A '''Brake wear indicator''' is used to warn the user and/or owner of a vehicle that the brake pad is in need of replacement. The main area of use for this is on vehicles. However brake wear indicators are also useful in industrial applications<ref name="Wind Turbine">{{cite web|url=http://www.icpltd.co.uk/contents/en-uk/d26_industrial-brake-pads.html|titel=Wind Turbine Brake Pads}}</ref><ref name="Crane">{{cite web|url=http://www.icpltd.co.uk/contents/en-uk/d1137_crane-drum-brakes.html|title=Crane Brakes}}</ref>. |
||
This article refers to disc brakes as an example, but the principle is the same for other types of friction brakes. |
|||
== Types of indicators == |
== Types of indicators == |
||
Revision as of 08:10, 5 October 2013
A Brake wear indicator is used to warn the user and/or owner of a vehicle that the brake pad is in need of replacement. The main area of use for this is on vehicles. However brake wear indicators are also useful in industrial applications[1][2].
This article refers to disc brakes as an example, but the principle is the same for other types of friction brakes.
Types of indicators
There are different types of wear indicators for brake pads:
- Ocular inspection: A cut is made in the pad material to the depth where it shall be replaced. Requires manual inspection of the pads.
- Mechanical[3][4]: A metal plate is designed to scratch the brake disk causing a noise when the pad has worn down to the desired level.
- Electrical[5]: A metal body is embedded in the pad material that comes in contact with the rotor when the desired wear level is reached. This will light an indicator in the instrument cluster.
- Position sensor[6]: A sensor that measures the position of the brake mechanics and indicates to the driver when the desired position has been achieved.
Of the alternatives above the first three are simple and cheap since their lifetime coincides with the lifetime of the brake pad. The last one is more expensive since the sensors needs to be designed to survive the design lifetime of the vehicle. This means that the last alternative is usually only seen on heavy duty vehicles.
The idea is that in all cases alert the driver and/or owner of the vehicle that it is time to replace the brake pads to ensure that the traffic safety is preserved for the vehicle.
Detailed description
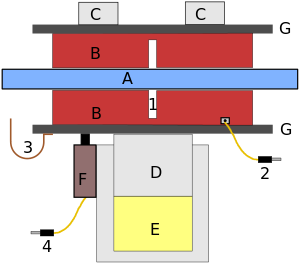
Pads B are mounted on carriers G. These are pushed against the rotor A by the piston D which is pushed by the brake fluid E. This induces wear on the pads. The rotor A also experiences some wear, but to a lesser extent than the brake pads. The modules C are joined to the cylinder that houses the piston D and acts as counter-force to the piston D.
References
- ^ http://www.icpltd.co.uk/contents/en-uk/d26_industrial-brake-pads.html.
{{cite web}}: Missing or empty|title=(help); Unknown parameter|titel=ignored (|title=suggested) (help) - ^ "Crane Brakes".
- ^ "How Stuff Works: How Disc Brakes Work".
- ^ "Installing Subaru 4-Pot Brakes".
- ^ "Professional Motor Mechanic; Brake Pads - Questions and Answers".
- ^ "Gill Sensors; Through-Hole Position Sensor".
