Bell's theorem
Bell's theorem proves that quantum physics is incompatible with local hidden-variable theories. It was introduced by physicist John Stewart Bell in a 1964 paper titled "On the Einstein Podolsky Rosen Paradox", referring to a 1935 thought experiment that Albert Einstein, Boris Podolsky and Nathan Rosen used to argue that quantum physics is an "incomplete" theory.[1][2] By 1935, it was already recognized that the predictions of quantum physics are probabilistic. Einstein, Podolsky and Rosen presented a scenario that, in their view, indicated that quantum particles, like electrons and photons, must carry physical properties or attributes not included in quantum theory, and the uncertainties in quantum theory's predictions were due to ignorance of these properties, later termed "hidden variables". Their scenario involves a pair of widely separated physical objects, prepared in such a way that the quantum state of the pair is entangled.
Bell carried the analysis of quantum entanglement much further. He deduced that if measurements are performed independently on the two separated halves of a pair, then the assumption that the outcomes depend upon hidden variables within each half implies a constraint on how the outcomes on the two halves are correlated. This constraint would later be named the Bell inequality. Bell then showed that quantum physics predicts correlations that violate this inequality. Consequently, the only way that hidden variables could explain the predictions of quantum physics is if they are "nonlocal", somehow associated with both halves of the pair and able to carry influences instantly between them no matter how widely the two halves are separated.[3][4] As Bell wrote later, "If [a hidden-variable theory] is local it will not agree with quantum mechanics, and if it agrees with quantum mechanics it will not be local."[5]
Multiple variations on Bell's theorem were proved in the following years, introducing other closely related conditions generally known as Bell (or "Bell-type") inequalities. These have been tested experimentally in physics laboratories many times since 1972. Often, these experiments have had the goal of ameliorating problems of experimental design or set-up that could in principle affect the validity of the findings of earlier Bell tests. This is known as "closing loopholes in Bell tests". To date, Bell tests have found that the hypothesis of local hidden variables is inconsistent with the way that physical systems do, in fact, behave.[6][7]
The exact nature of the assumptions required to prove a Bell-type constraint on correlations has been debated by physicists and by philosophers. While the significance of Bell's theorem is not in doubt, its full implications for the interpretation of quantum mechanics remain unresolved.
Theorem
There are many variations on the basic idea, some employing stronger mathematical assumptions than others.[8] Significantly, Bell-type theorems do not refer to any particular theory of local hidden variables, but instead show that quantum physics violates general assumptions behind classical pictures of nature. The original theorem proved by Bell in 1964 is not the most amenable to experiment, and it is convenient to introduce the genre of Bell-type inequalities with a later example.[9]
Alice and Bob stand in widely separated locations. Victor prepares a pair of particles and sends one to Alice and the other to Bob. When Alice receives her particle, she chooses to perform one of two possible measurements (perhaps by flipping a coin to decide which). Denote these measurements by and . Both and are binary measurements: the result of is either or , and likewise for . When Bob receives his particle, he chooses one of two measurements, and , which are both also binary.
Suppose that each measurement reveals a property that the particle already possessed. For instance, if Alice chooses to measure and obtains the result , then the particle she received carried a value of for a property .[note 1] Consider the following combination:
Because both and take the values , then either or . In the former case, , while in the latter case, . So, one of the terms on the right-hand side of the above expression will vanish, and the other will equal . Consequently, if the experiment is repeated over many trials, with Victor preparing new pairs of particles, the average value of the combination across all the trials will be less than or equal to 2. No single trial can measure this quantity, because Alice and Bob can only choose one measurement each, but on the assumption that the underlying properties exist, the average value of the sum is just the sum of the averages for each term. Using angle brackets to denote averages, This is a Bell inequality, specifically, the CHSH inequality.[9]: 115 Its derivation here depends upon two assumptions: first, that the underlying physical properties , , , and exist independently of being observed or measured (sometimes called the assumption of realism); and second, that Alice's choice of action cannot influence Bob's result or vice versa (often called the assumption of locality).[9]: 117
Quantum mechanics can violate the CHSH inequality, as follows. Victor prepares a pair of qubits which he describes by the Bell state Victor then passes the first qubit to Alice and the second to Bob. Alice and Bob's choices of possible measurements are defined by the Pauli matrices. Alice measures either of the two observables and : and Bob measures either of the two observables Victor can calculate the quantum expectation values for pairs of these observables using the Born rule: While only one of these four measurements can be made in a single trial of the experiment, the sum gives the sum of the average values that Victor expects to find across multiple trials. This value exceeds the classical upper bound of 2 that was deduced from the hypothesis of local hidden variables.[9]: 116 The value is in fact the largest that quantum physics permits for this combination of expectation values, making it a Tsirelson bound.[12]: 140
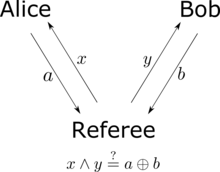
The CHSH inequality can also be thought of as a game in which Alice and Bob try to coordinate their actions.[13][14] Victor prepares two bits, and , independently and at random. He sends bit to Alice and bit to Bob. Alice and Bob win if they return answer bits and to Victor, satisfying Or, equivalently, Alice and Bob win if the logical AND of and is the logical XOR of and . Alice and Bob can agree upon any strategy they desire before the game, but they cannot communicate once the game begins. In any theory based on local hidden variables, Alice and Bob's probability of winning is no greater than , regardless of what strategy they agree upon beforehand. However, if they share an entangled quantum state, their probability of winning can be as large as
Variations and related results
Bell (1964)
Bell's 1964 paper points out that under restricted conditions, local hidden variable models can reproduce the predictions of quantum mechanics. He then demonstrates that this cannot hold true in general.[2] Bell considers a refinement by David Bohm of the Einstein–Podolsky–Rosen (EPR) thought experiment. In this scenario, a pair of particles are formed together in such a way that they are described by a spin singlet state (which is an example of an entangled state). The particles then move apart in opposite directions. Each particle is measured by a Stern–Gerlach device, a measuring instrument that can be oriented in different directions and that reports one of two possible outcomes, representable by and . The configuration of each measuring instrument is represented by a vector, and the quantum-mechanical prediction for the correlation between two detectors with settings and is
In particular, if the orientation of the two detectors is the same (), then the outcome of one measurement is certain to be the negative of the outcome of the other, giving . And if the orientations of the two detectors are orthogonal (), then the outcomes are uncorrelated, and . Bell proves by example that these special cases can be explained in terms of hidden variables, then proceeds to show that the full range of possibilities involving intermediate angles cannot.
Bell posited that a local hidden variable model for these correlations would explain them in terms of an integral over the possible values of some hidden parameter : where is a probability density function. The two functions and provide the responses of the two detectors given the orientation vectors and the hidden variable: Crucially, the outcome of detector does not depend upon , and likewise the outcome of does not depend upon , because the two detectors are physically separated. Now we suppose that the experimenter has a choice of settings for the second detector: it can be set either to or to . Bell proves that the difference in correlation between these two choices of detector setting must satisfy the inequality However, it is easy to find situations where quantum mechanics violates the Bell inequality.[15]: 425–426 For example, let the vectors and be orthogonal, and let lie in their plane at a 45° angle from both of them. Then while but Therefore, there is no local hidden variable model that can reproduce the predictions of quantum mechanics for all choices of , , and . Experimental results contradict the classical curves and match the curve predicted by quantum mechanics as long as experimental shortcomings are accounted for.[8]
Bell's 1964 theorem requires the possibility of perfect anti-correlations: the ability to make a probability-1 prediction about the result from the second detector, knowing the result from the first. This is related to the "EPR criterion of reality", a concept introduced in the 1935 paper by Einstein, Podolsky, and Rosen. This paper posits, "If, without in any way disturbing a system, we can predict with certainty (i.e., with probability equal to unity) the value of a physical quantity, then there exists an element of reality corresponding to that quantity."[1]
GHZ–Mermin
Greenberger, Horne, and Zeilinger presented a four-particle thought experiment, which Mermin then simplified to use only three particles.[16][17] In this thought experiment, Victor generates a set of three spin-1/2 particles described by the quantum state where as above, and are the eigenvectors of the Pauli matrix . Victor then sends a particle each to Alice, Bob, and Charlie, who wait at widely-separated locations. Alice measures either or on her particle, and so do Bob and Charlie. The result of each measurement is either or . Applying the Born rule to the three-qubit state , Victor predicts that whenever the three measurements include one and two 's, the product of the outcomes will always be . This follows because is an eigenvector of with eigenvalue , and likewise for and . Therefore, knowing Alice's result for a measurement and Bob's result for a measurement, Victor can predict with probability 1 what result Charlie will return for a measurement. According to the EPR criterion of reality, there would be an "element of reality" corresponding to the outcome of a measurement upon Charlie's qubit. Indeed, this same logic applies to both measurements and all three qubits. Per the EPR criterion of reality, then, each particle contains an "instruction set" that determines the outcome of a or measurement upon it. The set of all three particles would then be described by the instruction set with each entry being either or , and each or measurement simply returning the appropriate value.
If Alice, Bob, and Charlie all perform the measurement, then the product of their results would be . This value can be deduced from because the square of either or is . Each factor in parentheses equals , so and the product of Alice, Bob, and Charlie's results will be with probability unity. But this is inconsistent with quantum physics: Victor can predict using the state that the measurement will yield with probability unity.
Kochen–Specker theorem
In quantum theory, orthonormal bases for a Hilbert space represent measurements than can be performed upon a system having that Hilbert space. Each vector in a basis represents a possible outcome of that measurement.[note 2] Suppose that a hidden variable exists, so that knowing the value of would imply certainty about the outcome of any measurement. Given a value of , each measurement outcome — that is, each vector in the Hilbert space — is either impossible or guaranteed. A Kochen–Specker configuration is a finite set of vectors made of multiple interlocking bases, with the property that a vector in it will always be impossible when considered as belonging to one basis and guaranteed when taken as belonging to another. In other words, a Kochen–Specker configuration is an "uncolorable set" that demonstrates the inconsistency of assuming a hidden variable can be controlling the measurement outcomes.[22]: 196–201
Free will theorem
The Kochen–Specker type of argument, using configurations of interlocking bases, can be combined with the idea of measuring entangled pairs that underlies Bell-type inequalities. This was noted beginning in the 1980s by Heywood and Redhead,[23] Stairs,[24] and Brown and Svetlichny.[25] As EPR pointed out, obtaining a measurement outcome on one half of an entangled pair implies certainty about the outcome of a corresponding measurement on the other half. The "EPR criterion of reality" posits that because the second half of the pair was not disturbed, that certainty must be due to a physical property belonging to it.[26] In other words, by this criterion, a hidden variable must exist within the second, as-yet unmeasured half of the pair. No contradiction arises if only one measurement on the first half is considered. However, if the observer has a choice of multiple possible measurements, and the vectors defining those measurements form a Kochen–Specker configuration, then some outcome on the second half will be simultaneously impossible and guaranteed.
This type of argument gained significant attention when an instance of it was advanced by John Conway and Simon Kochen under the name of the free will theorem.[27] The Conway–Kochen theorem uses a pair of entangled qutrits and a Kochen–Specker configuration discovered by Asher Peres.[28]
Quasiclassical entanglement
As Bell pointed out, some predictions of quantum mechanics can be replicated in local hidden variable models, including special cases of correlations produced from entanglement. This topic has been studied systematically in the years since Bell's theorem. In 1989, Reinhard Werner introduced what are now called Werner states, joint quantum states for a pair of systems that yield EPR-type correlations but also admit a hidden-variable model.[29] Werner states are bipartite quantum states that are invariant under unitaries of symmetric tensor-product form:
More recently, Robert Spekkens introduced a toy model that starts with the premise of local, discretized degrees of freedom and then imposes a "knowledge balance principle" that restricts how much an observer can know about those degrees of freedom, thereby making them into hidden variables. The allowed states of knowledge ("epistemic states") about the underlying variables ("ontic states") mimic some features of quantum states. Correlations in the toy model can emulate some aspects of entanglement, like monogamy, but by construction, the toy model can never violate a Bell inequality.[30][31]
History
Background
The question of whether quantum mechanics can be "completed" by hidden variables dates to the early years of quantum theory. In his 1932 textbook on quantum mechanics, the Hungarian-born polymath John von Neumann presented what he claimed to be a proof that there could be no "hidden parameters". The validity and definitiveness of von Neumann's proof were questioned by Hans Reichenbach,[32][33]: 276 in more detail by Grete Hermann,[34] and possibly in conversation though not in print by Albert Einstein.[35]: 286 (Simon Kochen and Ernst Specker rejected von Neumann's key assumption as early as 1961, but did not publish a criticism of it until 1967.[36])
Einstein argued persistently that quantum mechanics could not be a complete theory. His preferred argument relied on a principle of locality:
- Consider a mechanical system constituted of two partial systems A and B which have interaction with each other only during limited time. Let the ψ function before their interaction be given. Then the Schrödinger equation will furnish the ψ function after their interaction has taken place. Let us now determine the physical condition of the partial system A as completely as possible by measurements. Then the quantum mechanics allows us to determine the ψ function of the partial system B from the measurements made, and from the ψ function of the total system. This determination, however, gives a result which depends upon which of the determining magnitudes specifying the condition of A has been measured (for instance coordinates or momenta). Since there can be only one physical condition of B after the interaction and which can reasonably not be considered as dependent on the particular measurement we perform on the system A separated from B it may be concluded that the ψ function is not unambiguously coordinated with the physical condition. This coordination of several ψ functions with the same physical condition of system B shows again that the ψ function cannot be interpreted as a (complete) description of a physical condition of a unit system.[37]
The EPR thought experiment is similar, also considering two separated systems A and B described by a joint wave function. However, the EPR paper adds the idea later known as the EPR criterion of reality, according to which the ability to predict with probability 1 the outcome of a measurement upon B implies the existence of an "element of reality" within B.[38]
In 1951, David Bohm proposed a variant of the EPR thought experiment in which the measurements have discrete ranges of possible outcomes, unlike the position and momentum measurements considered by EPR.[39] The year before, Chien-Shiung Wu and Irving Shaknov had successfully measured polarizations of photons produced in entangled pairs, thereby making the Bohm version of the EPR thought experiment practically feasible.[40]
By the late 1940s, the mathematician George Mackey had grown interested in the foundations of quantum physics, and in 1957 he drew up a list of postulates that he took to be a precise definition of quantum mechanics.[41] Mackey conjectured that one of the postulates was redundant, and shortly thereafter, Andrew M. Gleason proved that it was indeed deducible from the other postulates.[42][43] Gleason's theorem provided an argument that a broad class of hidden-variable theories are incompatible with quantum mechanics.[note 3] More specifically, Gleason's theorem rules out hidden-variable models that are "noncontextual". Any hidden-variable model for quantum mechanics must, in order to avoid the implications of Gleason's theorem, involve hidden variables that are not properties belonging to the measured system alone but also dependent upon the external context in which the measurement is made. This type of dependence is often seen as contrived or undesirable; in some settings, it is inconsistent with special relativity.[4][45] The Kochen–Specker theorem refines this statement by constructing a specific finite subset of rays on which no such probability measure can be defined.[4][46]
Tsung-Dao Lee came close to deriving Bell's theorem in 1960. He considered events where two kaons were produced traveling in opposite directions, and came to the conclusion that hidden variables could not explain the correlations that could be obtained in such situations. However, complications arose due to the fact that kaons decay, and he did not go so far as to deduce a Bell-type inequality.[note 4]
Bell's publications
Bell chose to publish his theorem in a comparatively obscure journal because it did not require page charges, and at the time it in fact paid the authors who published there. Because the journal did not provide free reprints of articles for the authors to distribute, however, Bell had to spend the money he received to buy copies that he could send to other physicists.[47] While the articles printed in the journal themselves listed the publication's name simply as Physics, the covers carried the trilingual version Physics Physique Физика to reflect that it would print articles in English, French and Russian.[35]: 92–100, 289
Prior to proving his 1964 result, Bell also proved a result equivalent to the Kochen–Specker theorem (hence why the latter is sometimes also known as the Bell–Kochen–Specker or Bell–KS theorem). However, publication of this theorem was inadvertently delayed until 1966.[4][48]
Experiments
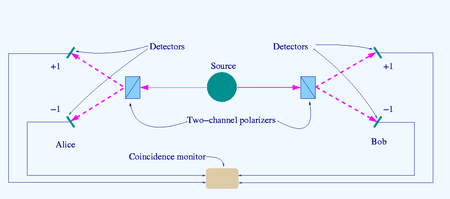
The source S produces pairs of "photons", sent in opposite directions. Each photon encounters a two-channel polariser whose orientation (a or b) can be set by the experimenter. Emerging signals from each channel are detected and coincidences of four types (++, −−, +− and −+) counted by the coincidence monitor.
In 1967, the unusual title Physics Physique Физика caught the attention of John Clauser, who then discovered Bell's paper and began to consider how to perform a Bell test in the laboratory.[49] Clauser and Stuart Freedman would go on to perform a Bell test in 1972.[50][51] This was only a limited test, because the choice of detector settings was made before the photons had left the source. In 1982, Alain Aspect and collaborators performed the first Bell test to remove this limitation.[52] This began a trend of progressively more stringent Bell tests. The GHZ thought experiment was implemented in practice, using entangled triplets of photons, in 2000.[53] By 2002, testing the CHSH inequality was feasible in undergraduate laboratory courses.[54]
In Bell tests, there may be problems of experimental design or set-up that affect the validity of the experimental findings. These problems are often referred to as "loopholes". The purpose of the experiment is to test whether nature can be described by local hidden-variable theory, which would contradict the predictions of quantum mechanics.
The most prevalent loopholes in real experiments are the detection and locality loopholes.[55] The detection loophole is opened when a small fraction of the particles (usually photons) are detected in the experiment, making it possible to explain the data with local hidden variables by assuming that the detected particles are an unrepresentative sample. The locality loophole is opened when the detections are not done with a spacelike separation, making it possible for the result of one measurement to influence the other without contradicting relativity. In some experiments there may be additional defects that make "local realist" explanations of Bell test violations possible.[56]
Although both the locality and detection loopholes had been closed in different experiments, a long-standing challenge was to close both simultaneously in the same experiment. This was finally achieved in three experiments in 2015.[57][58][59][60][61] Regarding these results, Alain Aspect writes that "... no experiment ... can be said to be totally loophole-free," but he says the experiments "remove the last doubts that we should renounce local realism," and refers to examples of remaining loopholes as being "far fetched" and "foreign to the usual way of reasoning in physics."[62]
Detection loophole
A common problem in optical Bell tests is that only a small fraction of the emitted photons are detected. It is then possible that the correlations of the detected photons are unrepresentative: although they show a violation of a Bell inequality, if all photons were detected the Bell inequality would actually be respected. This was first noted by Pearle in 1970,[63] who devised a local hidden variable model that faked a Bell violation by letting the photon be detected only if the measurement setting was favourable. The assumption that this does not happen, i.e., that the small sample is actually representative of the whole is called the fair sampling assumption.
To do away with this assumption it is necessary to detect a sufficiently large fraction of the photons. This is usually characterized in terms of the detection efficiency , defined as the probability that a photodetector detects a photon that arrives at it. Garg and Mermin showed that when using a maximally entangled state and the CHSH inequality an efficiency of is required for a loophole-free violation.[64] Later Eberhard showed that when using a partially entangled state a loophole-free violation is possible for ,[65] which is the optimal bound for the CHSH inequality.[66] Other Bell inequalities allow for even lower bounds. For example, there exists a four-setting inequality which is violated for .[67]
Historically, only experiments with non-optical systems have been able to reach high enough efficiencies to close this loophole, such as trapped ions,[68] superconducting qubits,[69] and nitrogen-vacancy centers.[70] These experiments were not able to close the locality loophole, which is easy to do with photons. More recently, however, optical setups have managed to reach sufficiently high detection efficiencies by using superconducting photodetectors,[60][61] and hybrid setups have managed to combine the high detection efficiency typical of matter systems with the ease of distributing entanglement at a distance typical of photonic systems.[59]
Locality loophole
One of the assumptions of Bell's theorem is the one of locality, namely that the choice of setting at a measurement site does not influence the result of the other. The motivation for this assumption is the theory of relativity, that prohibits communication faster than light. For this motivation to apply to an experiment, it needs to have space-like separation between its measurements events. That is, the time that passes between the choice of measurement setting and the production of an outcome must be shorter that the time it takes for a light signal to travel between the measurement sites.[71]
The first experiment that strived to respect this condition was Alain Aspect's 1982 experiment.[72] In it the settings were changed fast enough, but deterministically. The first experiment to change the settings randomly, with the choices made by a quantum random number generator, was Weihs et al.'s 1998 experiment.[73] Scheidl et al. improved on this further in 2010 by conducting an experiment between locations separated by a distance of 144 km (89 mi).[74]
Coincidence loophole
In many experiments, especially those based on photon polarization, pairs of events in the two wings of the experiment are only identified as belonging to a single pair after the experiment is performed, by judging whether or not their detection times are close enough to one another. This generates a new possibility for a local hidden variables theory to "fake" quantum correlations: delay the detection time of each of the two particles by a larger or smaller amount depending on some relationship between hidden variables carried by the particles and the detector settings encountered at the measurement station.[75]
The coincidence loophole can be ruled out entirely simply by working with a pre-fixed lattice of detection windows which are short enough that most pairs of events occurring in the same window do originate with the same emission and long enough that a true pair is not separated by a window boundary.
Memory loophole
In most experiments, measurements are repeatedly made at the same two locations. Under local realism, there could be effects of memory leading to statistical dependence between subsequent pairs of measurements. Moreover, physical parameters might be varying in time. It has been shown that, provided each new pair of measurements is done with a new random pair of measurement settings, that neither memory nor time inhomogeneity have a serious effect on the experiment.[76][77][78]
Interpretations of Bell's theorem
The Copenhagen Interpretation
The Copenhagen interpretation is a collection of views about the meaning of quantum mechanics principally attributed to Niels Bohr and Werner Heisenberg. It is one of the oldest of numerous proposed interpretations of quantum mechanics, as features of it date to the development of quantum mechanics during 1925–1927, and it remains one of the most commonly taught.[79] There is no definitive historical statement of what is the Copenhagen interpretation. In particular, there were fundamental disagreements between the views of Bohr and Heisenberg.[80][81][82] Some basic principles generally accepted as part of the Copenhagen collection include the idea that quantum mechanics is intrinsically indeterministic, with probabilities calculated using the Born rule,[83] and the complementarity principle: certain properties cannot be jointly defined for the same system at the same time. In order to talk about a specific property of a system, that system must be considered within the context of a specific laboratory arrangement. Observable quantities corresponding to mutually exclusive laboratory arrangements cannot be predicted together, but considering multiple such mutually exclusive experiments is necessary to characterize a system.[80] Bohr himself used complementarity to argue that the EPR "paradox" was fallacious. Because measurements of position and of momentum are complementary, making the choice to measure one excludes the possibility of measuring the other. Consequently, he argued, a fact deduced regarding one arrangement of laboratory apparatus could not be combined with a fact deduced by means of the other, and so, the inference of predetermined position and momentum values for the second particle was not valid.[33]: 194–197 Bohr concluded that EPR's "arguments do not justify their conclusion that the quantum description turns out to be essentially incomplete."[84]
Copenhagen-type interpretations generally take the violation of Bell inequalities as grounds to reject what Bell called "realism", which is not necessarily the same as abandoning realism in a broader philosophical sense.[85][86] For example, Roland Omnès argues for the rejection of hidden variables and concludes that "quantum mechanics is probably as realistic as any theory of its scope and maturity ever will be."[87]: 531 This is also the route taken by interpretations that descend from the Copenhagen tradition, such as consistent histories (often advertised as "Copenhagen done right"),[88] as well as QBism.[89]
Many-worlds interpretation of quantum mechanics
The Many-Worlds interpretation, also known as the Everett interpretation, is local and deterministic, as it consists of the unitary part of quantum mechanics without collapse. It can generate correlations that violate a Bell inequality because it doesn't satisfy the implicit assumption that Bell made that measurements have a single outcome. In fact, Bell's theorem can be proven in the Many-Worlds framework from the assumption that a measurement has a single outcome. Therefore a violation of a Bell inequality can be interpreted as a demonstration that measurements have multiple outcomes.[90]
The explanation it provides for the Bell correlations is that when Alice and Bob make their measurements, they split into local branches. From the point of view of each copy of Alice, there are multiple copies of Bob experiencing different results, so Bob cannot have a definite result, and the same is true from the point of view of each copy of Bob. They will obtain a mutually well-defined result only when their future light cones overlap. At this point we can say that the Bell correlation starts existing, but it was produced by a purely local mechanism. Therefore the violation of a Bell inequality cannot be interpreted as a proof of non-locality.[91]
Non-local hidden variables
Most advocates of the hidden-variables idea believe that experiments have ruled out local hidden variables.[note 5] They are ready to give up locality, explaining the violation of Bell's inequality by means of a non-local hidden variable theory, in which the particles exchange information about their states. This is the basis of the Bohm interpretation of quantum mechanics, which requires that all particles in the universe be able to instantaneously exchange information with all others. A 2007 experiment ruled out a large class of non-Bohmian non-local hidden variable theories, though not Bohmian mechanics itself.[93]
The transactional interpretation, which postulates waves traveling both backwards and forwards in time, is likewise non-local.[94]
Superdeterminism
A necessary assumption to derive Bell's theorem is that the hidden variables are not correlated with the measurement settings. This assumption has been justified on the grounds that the experimenter has "free will" to choose the settings, and that it is necessary to do science in the first place. A (hypothetical) theory where the choice of measurement is determined by the system being measured is known as superdeterministic.[55]
A few advocates of deterministic models have not given up on local hidden variables. For example, Gerard 't Hooft has argued that superdeterminism cannot be dismissed.[95]
Other criticism
There have also been repeated claims that Bell's arguments are irrelevant because they depend on hidden assumptions that, in fact, are questionable. For example, Karl Hess et.al. [96] Another example, E. T. Jaynes[92] argued in 1989 that there are two hidden assumptions in Bell's theorem that limit its generality. According to Jaynes:
- Bell interpreted conditional probability P(X | Y) as a causal influence, i.e. Y exerted a causal influence on X in reality. This interpretation is a misunderstanding of probability theory. As Jaynes shows,[92] "one cannot even reason correctly in so simple a problem as drawing two balls from Bernoulli's Urn, if he interprets probabilities in this way."
- Bell's inequality does not apply to some possible hidden variable theories. It only applies to a certain class of local hidden variable theories. In fact, it might have just missed the kind of hidden variable theories that Einstein is most interested in.
Richard D. Gill claimed that Jaynes misunderstood Bell's analysis. Gill points out that in the same conference volume in which Jaynes argues against Bell, Jaynes confesses to being extremely impressed by a short proof by Steve Gull presented at the same conference, that the singlet correlations could not be reproduced by a computer simulation of a local hidden variables theory.[97] According to Jaynes (writing nearly 30 years after Bell's landmark contributions), it would probably take us another 30 years to fully appreciate Gull's stunning result.
In 2006 a flurry of activity about implications for determinism arose with John Horton Conway and Simon B. Kochen's free will theorem,[98] which stated "the response of a spin 1 particle to a triple experiment is free—that is to say, is not a function of properties of that part of the universe that is earlier than this response with respect to any given inertial frame."[99] This theorem raised awareness of a tension between determinism fully governing an experiment (on the one hand) and Alice and Bob being free to choose any settings they like for their observations (on the other).[100][101] The philosopher David Hodgson supports this theorem as showing that determinism is unscientific, thereby leaving the door open for our own free will.[102]
See also
Notes
- ^ We are for convenience assuming that the response of the detector to the underlying property is deterministic. This assumption can be replaced; it is equivalent to postulating a joint probability distribution over all the observables of the experiment.[10][11]
- ^ In more detail, as developed by Paul Dirac,[18] David Hilbert,[19] John von Neumann,[20] and Hermann Weyl,[21] the state of a quantum mechanical system is a vector belonging to a (separable) Hilbert space . Physical quantities of interest — position, momentum, energy, spin — are represented by "observables", which are self-adjoint linear operators acting on the Hilbert space. When an observable is measured, the result will be one of its eigenvalues with probability given by the Born rule: in the simplest case the eigenvalue is non-degenerate and the probability is given by , where is its associated eigenvector. More generally, the eigenvalue is degenerate and the probability is given by , where is the projector onto its associated eigenspace. For the purposes of this discussion, we can take the eigenvalues to be non-degenerate.
- ^ A hidden-variable theory that is deterministic implies that the probability of a given outcome is always either 0 or 1. For example, a Stern–Gerlach measurement on a spin-1 atom will report that the atom's angular momentum along the chosen axis is one of three possible values, which can be designated , and . In a deterministic hidden-variable theory, there exists an underlying physical property that fixes the result found in the measurement. Conditional on the value of the underlying physical property, any given outcome (for example, a result of ) must be either impossible or guaranteed. But Gleason's theorem implies that there can be no such deterministic probability measure, because it proves that any probability measure must take the form of a mapping for some density operator . This mapping is continuous on the unit sphere of the Hilbert space, and since this unit sphere is connected, no continuous probability measure on it can be deterministic.[44]: §1.3
- ^ This was reported by Max Jammer.[33]: 308 Lee is best known for his prediction with Chen-Ning Yang of the violation of parity conservation, a prediction that earned them the Nobel Prize after it was confirmed by Chien-Shiung Wu, who did not share in the Prize.
- ^ E. T. Jaynes was one exception,[92] but Jaynes' arguments have not generally been found persuasive.[78]
References
- ^ a b Einstein, A.; Podolsky, B.; Rosen, N. (1935-05-15). "Can Quantum-Mechanical Description of Physical Reality be Considered Complete?". Physical Review. 47 (10): 777–780. Bibcode:1935PhRv...47..777E. doi:10.1103/PhysRev.47.777.
- ^ a b Bell, J. S. (1964). "On the Einstein Podolsky Rosen Paradox" (PDF). Physics Physique Физика. 1 (3): 195–200. doi:10.1103/PhysicsPhysiqueFizika.1.195.
- ^ Parker, Sybil B. (1994). McGraw-Hill Encyclopaedia of Physics (2nd ed.). McGraw-Hill. p. 542. ISBN 978-0-07-051400-3.
- ^ a b c d Mermin, N. David (July 1993). "Hidden Variables and the Two Theorems of John Bell" (PDF). Reviews of Modern Physics. 65 (3): 803–15. arXiv:1802.10119. Bibcode:1993RvMP...65..803M. doi:10.1103/RevModPhys.65.803. S2CID 119546199.
- ^ Bell, John S. (1987). Speakable and Unspeakable in Quantum Mechanics. Cambridge University Press. p. 65. ISBN 9780521368698. OCLC 15053677.
- ^ The BIG Bell Test Collaboration (9 May 2018). "Challenging local realism with human choices". Nature. 557 (7704): 212–216. arXiv:1805.04431. Bibcode:2018Natur.557..212B. doi:10.1038/s41586-018-0085-3. PMID 29743691. S2CID 13665914.
- ^ Wolchover, Natalie (2017-02-07). "Experiment Reaffirms Quantum Weirdness". Quanta Magazine. Retrieved 2020-02-08.
- ^ a b Shimony, Abner. "Bell's Theorem". In Zalta, Edward N. (ed.). Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy.
- ^ a b c d Nielsen, Michael A.; Chuang, Isaac L. (2010). Quantum Computation and Quantum Information (2nd ed.). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-1-107-00217-3. OCLC 844974180.
- ^ Fine, Arthur (1982-02-01). "Hidden Variables, Joint Probability, and the Bell Inequalities". Physical Review Letters. 48 (5): 291–295. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.48.291. ISSN 0031-9007.
- ^ Braunstein, Samuel L.; Caves, Carlton M. (August 1990). "Wringing out better Bell inequalities". Annals of Physics. 202 (1): 22–56. doi:10.1016/0003-4916(90)90339-P.
- ^ Rau, Jochen (2021). Quantum theory : an information processing approach. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-192-65027-6. OCLC 1256446911.
- ^ Cleve, R.; Hoyer, P.; Toner, B.; Watrous, J. (2004). "Consequences and limits of nonlocal strategies". Proceedings. 19th IEEE Annual Conference on Computational Complexity, 2004. IEEE. pp. 236–249. arXiv:quant-ph/0404076. Bibcode:2004quant.ph..4076C. doi:10.1109/CCC.2004.1313847. ISBN 0-7695-2120-7. OCLC 55954993. S2CID 8077237.
- ^ Barnum, H.; Beigi, S.; Boixo, S.; Elliott, M. B.; Wehner, S. (2010-04-06). "Local Quantum Measurement and No-Signaling Imply Quantum Correlations". Physical Review Letters. 104 (14): 140401. arXiv:0910.3952. Bibcode:2010PhRvL.104n0401B. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.104.140401. ISSN 0031-9007. PMID 20481921. S2CID 17298392.
- ^ Griffiths, David J. (2005). Introduction to Quantum Mechanics (2nd ed.). Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson Prentice Hall. ISBN 0-13-111892-7. OCLC 53926857.
- ^ Greenberger, D.; Horne, M.; Shimony, A.; Zeilinger, A. (1990). "Bell's theorem without inequalities". American Journal of Physics. 58 (12): 1131. Bibcode:1990AmJPh..58.1131G. doi:10.1119/1.16243.
- ^ Mermin, N. David (1990). "Quantum mysteries revisited". American Journal of Physics. 58 (8): 731–734. Bibcode:1990AmJPh..58..731M. doi:10.1119/1.16503.
- ^ Dirac, Paul Adrien Maurice (1930). The Principles of Quantum Mechanics. Oxford: Clarendon Press.
- ^ Hilbert, David (2009). Sauer, Tilman; Majer, Ulrich (eds.). Lectures on the Foundations of Physics 1915–1927: Relativity, Quantum Theory and Epistemology. Springer. doi:10.1007/b12915. ISBN 978-3-540-20606-4. OCLC 463777694.
- ^ von Neumann, John (1932). Mathematische Grundlagen der Quantenmechanik. Berlin: Springer. English translation: Mathematical Foundations of Quantum Mechanics. Translated by Beyer, Robert T. Princeton University Press. 1955.
- ^ Weyl, Hermann (1950) [1931]. The Theory of Groups and Quantum Mechanics. Translated by Robertson, H. P. Dover. ISBN 978-0-486-60269-1. Translated from the German Gruppentheorie und Quantenmechanik (2nd ed.). S. Hirzel Verlag. 1931.
- ^ Peres, Asher (1993). Quantum Theory: Concepts and Methods. Kluwer. ISBN 0-7923-2549-4. OCLC 28854083.
- ^ Heywood, Peter; Redhead, Michael L. G. (May 1983). "Nonlocality and the Kochen–Specker paradox". Foundations of Physics. 13 (5): 481–499. doi:10.1007/BF00729511. ISSN 0015-9018. S2CID 120340929.
- ^ Stairs, Allen (December 1983). "Quantum Logic, Realism, and Value Definiteness". Philosophy of Science. 50 (4): 578–602. doi:10.1086/289140. ISSN 0031-8248. S2CID 122885859.
- ^ Brown, H. R.; Svetlichny, G. (November 1990). "Nonlocality and Gleason's lemma. Part I. Deterministic theories". Foundations of Physics. 20 (11): 1379–1387. doi:10.1007/BF01883492. ISSN 0015-9018. S2CID 122868901.
- ^ Glick, David; Boge, Florian J. (2019-10-22). "Is the Reality Criterion Analytic?". Erkenntnis. 86 (6): 1445–1451. arXiv:1909.11893. Bibcode:2019arXiv190911893G. doi:10.1007/s10670-019-00163-w. ISSN 0165-0106. S2CID 202889160.
- ^ Conway, John; Kochen, Simon (2006). "The Free Will Theorem". Foundations of Physics. 36 (10): 1441. arXiv:quant-ph/0604079. Bibcode:2006FoPh...36.1441C. doi:10.1007/s10701-006-9068-6. S2CID 12999337.
- ^ Conway, John H.; Kochen, Simon (2009). "The strong free will theorem" (PDF). Notices of the AMS. 56 (2): 226–232.
- ^ Werner, Reinhard F. (1989-10-01). "Quantum states with Einstein-Podolsky-Rosen correlations admitting a hidden-variable model". Physical Review A. 40 (8): 4277–4281. Bibcode:1989PhRvA..40.4277W. doi:10.1103/PhysRevA.40.4277. ISSN 0556-2791. PMID 9902666.
- ^ Spekkens, Robert W. (2007-03-19). "Evidence for the epistemic view of quantum states: A toy theory". Physical Review A. 75 (3): 032110. arXiv:quant-ph/0401052. Bibcode:2007PhRvA..75c2110S. doi:10.1103/PhysRevA.75.032110. ISSN 1050-2947. S2CID 117284016.
- ^ Catani, Lorenzo; Browne, Dan E. (2017-07-27). "Spekkens' toy model in all dimensions and its relationship with stabiliser quantum mechanics". New Journal of Physics. 19 (7): 073035. doi:10.1088/1367-2630/aa781c. ISSN 1367-2630. S2CID 119428107.
- ^ Reichenbach, Hans (1944). Philosophic Foundations of Quantum Mechanics. University of California Press. p. 14. OCLC 872622725.
- ^ a b c Jammer, Max (1974). The Philosophy of Quantum Mechanics. John Wiley and Sons. ISBN 0-471-43958-4.
- ^ Mermin, N. David; Schack, Rüdiger (2018). "Homer nodded: von Neumann's surprising oversight". Foundations of Physics. 48 (9): 1007–1020. arXiv:1805.10311. doi:10.1007/s10701-018-0197-5. S2CID 118951033.
- ^ a b Wick, David (1995). The Infamous Boundary: Seven Decades of Heresy in Quantum Physics. Springer New York. doi:10.1007/978-1-4612-4030-3_11. ISBN 978-0-387-94726-6.
- ^ Conway, John; Kochen, Simon (2002). "The Geometry of the Quantum Paradoxes". In Bertlmann, Reinhold A.; Zeilinger, Anton (eds.). Quantum [Un]speakables: From Bell to Quantum Information. Berlin: Springer. pp. 257–269. ISBN 3-540-42756-2. OCLC 49404213.
- ^ Einstein, Albert (March 1936). "Physics and reality". Journal of the Franklin Institute. 221 (3): 349–382. Bibcode:1936FrInJ.221..349E. doi:10.1016/S0016-0032(36)91047-5.
- ^ Harrigan, Nicholas; Spekkens, Robert W. (2010). "Einstein, incompleteness, and the epistemic view of quantum states". Foundations of Physics. 40 (2): 125. arXiv:0706.2661. Bibcode:2010FoPh...40..125H. doi:10.1007/s10701-009-9347-0. S2CID 32755624.
- ^ Bohm, David (1951). Quantum Theory. Prentice-Hall.
- ^ Wu, C.-S.; Shaknov, I. (1950). "The Angular Correlation of Scattered Annihilation Radiation". Physical Review. 77 (1): 136. Bibcode:1950PhRv...77..136W. doi:10.1103/PhysRev.77.136.
- ^ Mackey, George W. (1957). "Quantum Mechanics and Hilbert Space". The American Mathematical Monthly. 64 (8P2): 45–57. doi:10.1080/00029890.1957.11989120. JSTOR 2308516.
- ^ Gleason, Andrew M. (1957). "Measures on the closed subspaces of a Hilbert space". Indiana University Mathematics Journal. 6 (4): 885–893. doi:10.1512/iumj.1957.6.56050. MR 0096113.
- ^ Chernoff, Paul R. "Andy Gleason and Quantum Mechanics" (PDF). Notices of the AMS. 56 (10): 1253–1259.
- ^ Wilce, A. (2017). "Quantum Logic and Probability Theory". Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy.
- ^ Shimony, Abner (1984). "Contextual Hidden Variable Theories and Bell's Inequalities". British Journal for the Philosophy of Science. 35 (1): 25–45. doi:10.1093/bjps/35.1.25.
- ^ Peres, Asher (1991). "Two simple proofs of the Kochen-Specker theorem". Journal of Physics A: Mathematical and General. 24 (4): L175–L178. Bibcode:1991JPhA...24L.175P. doi:10.1088/0305-4470/24/4/003. ISSN 0305-4470.
- ^ Whitaker, Andrew (2016). John Stewart Bell and Twentieth Century Physics: Vision and Integrity. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-874299-9.
- ^ Bell, J. S. (1966). "On the problem of hidden variables in quantum mechanics". Reviews of Modern Physics. 38 (3): 447–452. Bibcode:1966RvMP...38..447B. doi:10.1103/revmodphys.38.447. OSTI 1444158.
- ^ Kaiser, David (2012-01-30). "How the Hippies Saved Physics: Science, Counterculture, and the Quantum Revival [Excerpt]". Scientific American. Retrieved 2020-02-11.
- ^ Freedman, S. J.; Clauser, J. F. (1972). "Experimental test of local hidden-variable theories" (PDF). Physical Review Letters. 28 (938): 938–941. Bibcode:1972PhRvL..28..938F. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.28.938.
- ^ 'Experimental test of local hidden-variable theories' by Stuart Jay Freedman, May 5, 1972
- ^ Aspect, Alain; Dalibard, Jean; Roger, Gérard (1982). "Experimental Test of Bell's Inequalities Using Time-Varying Analyzers". Physical Review Letters. 49 (25): 1804–7. Bibcode:1982PhRvL..49.1804A. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.49.1804.
- ^ Pan, Jian-Wei; Bouwmeester, D.; Daniell, M.; Weinfurter, H.; Zeilinger, A. (2000). "Experimental test of quantum nonlocality in three-photon GHZ entanglement". Nature. 403 (6769): 515–519. Bibcode:2000Natur.403..515P. doi:10.1038/35000514. PMID 10676953. S2CID 4309261.
- ^ Dehlinger, Dietrich; Mitchell, M. W. (2002). "Entangled photons, nonlocality, and Bell inequalities in the undergraduate laboratory". American Journal of Physics. 70 (9): 903–910. arXiv:quant-ph/0205171. doi:10.1119/1.1498860. S2CID 49487096.
- ^ a b Larsson, Jan-Åke (2014). "Loopholes in Bell inequality tests of local realism". Journal of Physics A: Mathematical and Theoretical. 47 (42): 424003. arXiv:1407.0363. doi:10.1088/1751-8113/47/42/424003. S2CID 40332044.
- ^ Gerhardt, I.; Liu, Q.; Lamas-Linares, A.; Skaar, J.; Scarani, V.; et al. (2011). "Experimentally faking the violation of Bell's inequalities". Physical Review Letters. 107 (17): 170404. arXiv:1106.3224. Bibcode:2011PhRvL.107q0404G. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.107.170404. PMID 22107491. S2CID 16306493.
- ^ Merali, Zeeya (27 August 2015). "Quantum 'spookiness' passes toughest test yet". Nature News. 525 (7567): 14–15. doi:10.1038/nature.2015.18255. PMID 26333448. S2CID 4409566.
- ^ Markoff, Jack (21 October 2015). "Sorry, Einstein. Quantum Study Suggests 'Spooky Action' Is Real". New York Times. Retrieved 21 October 2015.
- ^ a b Hensen, B.; et al. (21 October 2015). "Loophole-free Bell inequality violation using electron spins separated by 1.3 kilometres". Nature. 526 (7575): 682–686. arXiv:1508.05949. Bibcode:2015Natur.526..682H. doi:10.1038/nature15759. PMID 26503041. S2CID 205246446.
- ^ a b Shalm, L. K.; et al. (16 December 2015). "Strong Loophole-Free Test of Local Realism". Physical Review Letters. 115 (25): 250402. arXiv:1511.03189. Bibcode:2015PhRvL.115y0402S. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.115.250402. PMC 5815856. PMID 26722906.
- ^ a b Giustina, M.; et al. (16 December 2015). "Significant-Loophole-Free Test of Bell's Theorem with Entangled Photons". Physical Review Letters. 115 (25): 250401. arXiv:1511.03190. Bibcode:2015PhRvL.115y0401G. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.115.250401. PMID 26722905. S2CID 13789503.
- ^ Aspect, Alain (December 16, 2015). "Closing the Door on Einstein and Bohr's Quantum Debate". Physics. 8: 123. Bibcode:2015PhyOJ...8..123A. doi:10.1103/Physics.8.123.
- ^ Pearle, Philip M. (1970). "Hidden-Variable Example Based upon Data Rejection". Physical Review D. 2 (8): 1418–25. Bibcode:1970PhRvD...2.1418P. doi:10.1103/PhysRevD.2.1418.
- ^ Garg, Anupam; Mermin, N. David (1987). "Detector inefficiencies in the Einstein-Podolsky-Rosen experiment". Physical Review D. 25 (12): 3831–5. Bibcode:1987PhRvD..35.3831G. doi:10.1103/PhysRevD.35.3831. PMID 9957644.
- ^ Eberhard, P. H. (1993). "Background level and counter efficiencies required for a loophole-free Einstein-Podolsky-Rosen experiment". Physical Review A. 47 (2): 747–750. doi:10.1103/PhysRevA.47.R747. PMID 9909100.
- ^ Larsson, Jan-Åke; Semitecolos, Jason (2001). "Strict detector-efficiency bounds for n-site Clauser-Horne inequalities". Physical Review A. 63 (2): 022117. arXiv:quant-ph/0006022. doi:10.1103/PhysRevA.63.022117. S2CID 119469607.
- ^ Vértesi, Tamás; Pironio, Stefano; Brunner, Nicolas (2010). "Closing the detection loophole in Bell experiments using qudits". Physical Review Letters. 104 (6): 060401. arXiv:0909.3171. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.104.060401. PMID 20366808. S2CID 22053479.
- ^ Rowe, M. A.; Kielpinski, D.; Meyer, V.; Sackett, C. A.; Itano, W. M.; et al. (2001). "Experimental violation of a Bell's inequality with efficient detection" (PDF). Nature. 409 (6822): 791–94. Bibcode:2001Natur.409..791K. doi:10.1038/35057215. hdl:2027.42/62731. PMID 11236986. S2CID 205014115.
- ^ Ansmann, M.; Wang, H.; Bialczak, R. C.; Hofheinz, M.; Lucero, E.; et al. (24 September 2009). "Violation of Bell's inequality in Josephson phase qubits". Nature. 461 (7263): 504–506. Bibcode:2009Natur.461..504A. doi:10.1038/nature08363. PMID 19779447. S2CID 4401494.
- ^ Pfaff, W.; Taminiau, T. H.; Robledo, L.; Bernien, H.; Markham, M.; et al. (2013). "Demonstration of entanglement-by-measurement of solid-state qubits". Nature Physics. 9 (1): 29–33. arXiv:1206.2031. Bibcode:2013NatPh...9...29P. doi:10.1038/nphys2444. S2CID 2124119.
- ^ Bell, J. S. (1980). "Atomic-cascade photons and quantum-mechanical nonlocality". Comments on Atomic and Molecular Physics. 9: 121–126. Reprinted as Bell, J. S. (1987). "Chapter 13". Speakable and Unspeakable in Quantum Mechanics. Cambridge University Press. p. 109.
- ^ Aspect, Alain; Dalibard, Jean; Roger, Gérard (1982). "Experimental Test of Bell's Inequalities Using Time-Varying Analyzers". Physical Review Letters. 49 (25): 1804–7. Bibcode:1982PhRvL..49.1804A. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.49.1804.
- ^ Weihs, G.; Jennewein, T.; Simon, C.; Weinfurter, H.; Zeilinger, A. (1998). "Violation of Bell's inequality under strict Einstein locality conditions". Physical Review Letters. 81 (23): 5039–5043. arXiv:quant-ph/9810080. Bibcode:1998PhRvL..81.5039W. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.81.5039. S2CID 29855302.
- ^ Scheidl, Thomas; Ursin, Rupert; Kofler, Johannes; Ramelow, Sven; Ma, Xiao-Song; Herbst, Thomas; Ratschbacher, Lothar; Fedrizzi, Alessandro; Langford, Nathan K.; Jennewein, Thomas; Zeilinger, Anton; et al. (2010). "Violation of local realism with freedom of choice". PNAS. 107 (46): 19708–19713. arXiv:0811.3129. Bibcode:2010PNAS..10719708S. doi:10.1073/pnas.1002780107. PMC 2993398. PMID 21041665.
- ^ Larsson, Jan-Åke; Gill, Richard (2004). "Bell's inequality and the coincidence-time loophole". Europhysics Letters. 67 (5): 707. arXiv:quant-ph/0312035. doi:10.1209/epl/i2004-10124-7. S2CID 17135877.
- ^ Barrett, Jonathan; Collins, Daniel; Hardy, Lucien; Kent, Adrian; Popescu, Sandu (2002). "Quantum nonlocality, Bell inequalities and the memory loophole". Physical Review A. 66 (4). 042111. arXiv:quant-ph/0205016. Bibcode:2002PhRvA..66d2111B. doi:10.1103/PhysRevA.66.042111. S2CID 6524446.
- ^ Gill, Richard D. (2003). "Accardi contra Bell (cum mundi): The Impossible Coupling". In M. Moore; S. Froda; C. Léger (eds.). Mathematical Statistics and Applications: Festschrift for Constance van Eeden. IMS Lecture Notes — Monograph Series. Vol. 42. Beachwood, Ohio: Institute of Mathematical Statistics. pp. 133–154. arXiv:quant-ph/0110137.
- ^ a b Gill, Richard D. (2002). "Time, Finite Statistics, and Bell's Fifth Position". Proceedings of the Conference Foundations of Probability and Physics - 2 : Växjö (Soland), Sweden, June 2-7, 2002. Vol. 5. Växjö University Press. pp. 179–206. arXiv:quant-ph/0301059. Bibcode:2003quant.ph..1059G.
- ^ Siddiqui, Shabnam; Singh, Chandralekha (2017). "How diverse are physics instructors' attitudes and approaches to teaching undergraduate level quantum mechanics?". European Journal of Physics. 38 (3): 035703. Bibcode:2017EJPh...38c5703S. doi:10.1088/1361-6404/aa6131.
- ^ a b Faye, Jan (2019). "Copenhagen Interpretation of Quantum Mechanics". In Zalta, Edward N. (ed.). Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy. Metaphysics Research Lab, Stanford University. Archived from the original on 2019-04-29. Retrieved 2021-09-16.
- ^ Camilleri, K.; Schlosshauer, M. (2015). "Niels Bohr as Philosopher of Experiment: Does Decoherence Theory Challenge Bohr's Doctrine of Classical Concepts?". Studies in History and Philosophy of Modern Physics. 49: 73–83. arXiv:1502.06547. Bibcode:2015SHPMP..49...73C. doi:10.1016/j.shpsb.2015.01.005. S2CID 27697360.
- ^ Peres, Asher (2002). "Popper's experiment and the Copenhagen interpretation". Studies in History and Philosophy of Modern Physics. 33: 23. arXiv:quant-ph/9910078. Bibcode:1999quant.ph.10078P. doi:10.1016/S1355-2198(01)00034-X.
- ^ Bohr, N. (1928). "The Quantum Postulate and the Recent Development of Atomic Theory". Nature. 121 (3050): 580–590. Bibcode:1928Natur.121..580B. doi:10.1038/121580a0., p. 586: "In this connexion [Born] succeeded in obtaining a statistical interpretation of the wave functions, allowing a calculation of the probability of the individual transition processes required by the quantum postulate."
- ^ Bohr, N. (1935-10-13). "Can Quantum-Mechanical Description of Physical Reality be Considered Complete?" (PDF). Physical Review. 48 (8): 696–702. Bibcode:1935PhRv...48..696B. doi:10.1103/PhysRev.48.696. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2020-01-09. Retrieved 2021-09-16.
- ^ Werner, Reinhard F. (2014-10-24). "Comment on 'What Bell did'". Journal of Physics A: Mathematical and Theoretical. 47 (42): 424011. Bibcode:2014JPhA...47P4011W. doi:10.1088/1751-8113/47/42/424011. ISSN 1751-8113.
- ^ Żukowski, Marek (2017), Bertlmann, Reinhold; Zeilinger, Anton (eds.), "Bell's Theorem Tells Us Not What Quantum Mechanics Is, but What Quantum Mechanics Is Not", Quantum [Un]Speakables II, The Frontiers Collection, Cham: Springer International Publishing, pp. 175–185, arXiv:1501.05640, Bibcode:2015arXiv150105640Z, doi:10.1007/978-3-319-38987-5_10, ISBN 978-3-319-38985-1, S2CID 119214547
- ^ Omnès, R. (1994). The Interpretation of Quantum Mechanics. Princeton University Press. ISBN 978-0-691-03669-4. OCLC 439453957.
- ^ Hohenberg, P. C. (2010-10-05). "Colloquium : An introduction to consistent quantum theory". Reviews of Modern Physics. 82 (4): 2835–2844. arXiv:0909.2359. Bibcode:2010RvMP...82.2835H. doi:10.1103/RevModPhys.82.2835. ISSN 0034-6861. S2CID 20551033.
- ^ Healey, Richard (2016). "Quantum-Bayesian and Pragmatist Views of Quantum Theory". In Zalta, Edward N. (ed.). Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy. Metaphysics Research Lab, Stanford University. Archived from the original on 2021-08-17. Retrieved 2021-09-16.
- ^ David Deutsch; Patrick Hayden (2000). "Information flow in entangled quantum systems". Proceedings of the Royal Society A. 456 (1999): 1759–1774. arXiv:quant-ph/9906007. Bibcode:2000RSPSA.456.1759D. doi:10.1098/rspa.2000.0585. S2CID 13998168.
- ^ Harvey R. Brown; Christopher G. Timpson (2016). "Bell on Bell's Theorem: The Changing Face of Nonlocality". In Mary Bell; Shan Gao (eds.). Quantum Nonlocality and Reality: 50 years of Bell's theorem. Cambridge University Press. pp. 91–123. arXiv:1501.03521. doi:10.1017/CBO9781316219393.008. ISBN 9781316219393. S2CID 118686956.
- ^ a b c Jaynes, E. T. (1989). "Clearing up Mysteries — the Original Goal". Clearing up Mysteries—The Original Goal (PDF). pp. 1–27. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.46.1264. doi:10.1007/978-94-015-7860-8_1. ISBN 978-90-481-4044-2. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2011-10-28. Retrieved 2011-10-18.
{{cite book}}:|journal=ignored (help) - ^ Gröblacher, Simon; Paterek, Tomasz; Kaltenbaek, Rainer; Brukner, Časlav; Żukowski, Marek; Aspelmeyer, Markus; Zeilinger, Anton (2007). "An experimental test of non-local realism". Nature. 446 (7138): 871–5. arXiv:0704.2529. Bibcode:2007Natur.446..871G. doi:10.1038/nature05677. PMID 17443179. S2CID 4412358.
- ^ Kastner, Ruth E. (May 2010). "The quantum liar experiment in Cramer's transactional interpretation". Studies in History and Philosophy of Science Part B: Studies in History and Philosophy of Modern Physics. 41 (2): 86–92. arXiv:0906.1626. Bibcode:2010SHPMP..41...86K. doi:10.1016/j.shpsb.2010.01.001. S2CID 16242184. Archived from the original on 2018-06-24. Retrieved 2021-09-16.
- ^ 't Hooft, Gerard (2016). The Cellular Automaton Interpretation of Quantum Mechanics. Fundamental Theories of Physics. Vol. 185. Springer. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-41285-6. ISBN 978-3-319-41284-9. OCLC 951761277. S2CID 7779840. Archived from the original on 2021-12-29. Retrieved 2020-08-27.
- ^ https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.1088/0031-8949/2012/T151/014002
- ^ Gill, Richard D. (2003). "Time, Finite Statistics, and Bell's Fifth Position". Proc. Of "Foundations of Probability and Physics - 2", Ser. Math. Modelling in Phys., Engin., and Cogn. Sc. 5/2002: 179–206. arXiv:quant-ph/0301059. Bibcode:2003quant.ph..1059G.
- ^ Conway, John; Kochen, Simon (2006). "The Free Will Theorem". Foundations of Physics. 36 (10): 1441–1473. arXiv:quant-ph/0604079. Bibcode:2006FoPh...36.1441C. doi:10.1007/s10701-006-9068-6. S2CID 12999337.
- ^ Conway, John H.; Kochen, Simon (2009). "The strong free will theorem" (PDF). Notices of the AMS. 56 (2): 226–232. arXiv:0807.3286. Bibcode:2008arXiv0807.3286C.
- ^ Cator, Eric & Klaas Landsman (2014). "Constraints on determinism: Bell versus Conway–Kochen". Foundations of Physics. 44 (7): 781–791. arXiv:1402.1972. Bibcode:2014FoPh...44..781C. doi:10.1007/s10701-014-9815-z. S2CID 14532489.
- ^ Esfeld, Michael (2015). "Bell's Theorem and the Issue of Determinism and Indeterminism". Foundations of Physics. 45 (5): 471–482. arXiv:1503.00660. Bibcode:2015FoPh...45..471E. doi:10.1007/s10701-015-9883-8. S2CID 49363278.
- ^ David Hodgson (2012). "Chapter 7: Science and determinism". Rationality + Consciousness = Free Will. Oxford University Press. ISBN 9780199845309. Archived from the original on 2021-12-29. Retrieved 2020-11-02.
Further reading
The following are intended for general audiences.
- Aczel, Amir D. (2001). Entanglement: The greatest mystery in physics. New York: Four Walls Eight Windows.
- Afriat, A.; Selleri, F. (1999). The Einstein, Podolsky and Rosen Paradox. New York and London: Plenum Press.
- Baggott, J. (1992). The Meaning of Quantum Theory. Oxford University Press.
- Gilder, Louisa (2008). The Age of Entanglement: When Quantum Physics Was Reborn. New York: Alfred A. Knopf.
- Greene, Brian (2004). The Fabric of the Cosmos. Vintage. ISBN 0-375-72720-5.
- Mermin, N. David (1981). "Bringing home the atomic world: Quantum mysteries for anybody". American Journal of Physics. 49 (10): 940–943. Bibcode:1981AmJPh..49..940M. doi:10.1119/1.12594. S2CID 122724592.
- Mermin, N. David (April 1985). "Is the moon there when nobody looks? Reality and the quantum theory". Physics Today. 38 (4): 38–47. Bibcode:1985PhT....38d..38M. doi:10.1063/1.880968.
The following are more technically oriented.
- Aspect, A.; et al. (1981). "Experimental Tests of Realistic Local Theories via Bell's Theorem". Phys. Rev. Lett. 47 (7): 460–463. Bibcode:1981PhRvL..47..460A. doi:10.1103/physrevlett.47.460.
- Aspect, A.; et al. (1982). "Experimental Realization of Einstein–Podolsky–Rosen–Bohm Gedankenexperiment: A New Violation of Bell's Inequalities". Phys. Rev. Lett. 49 (2): 91–94. Bibcode:1982PhRvL..49...91A. doi:10.1103/physrevlett.49.91.
- Aspect, A.; Grangier, P. (1985). "About resonant scattering and other hypothetical effects in the Orsay atomic-cascade experiment tests of Bell inequalities: a discussion and some new experimental data". Lettere al Nuovo Cimento. 43 (8): 345–348. doi:10.1007/bf02746964. S2CID 120840672.
- Bell, J. S. (1971). "Introduction to the hidden variable question". Proceedings of the International School of Physics 'Enrico Fermi', Course IL, Foundations of Quantum Mechanics. pp. 171–81.
- Bell, J. S. (2004). "Bertlmann's Socks and the Nature of Reality". Speakable and Unspeakable in Quantum Mechanics. Cambridge University Press. pp. 139–158.
- Clauser, J. F.; Shimony, A. (1978). "Bell's theorem: experimental tests and implications" (PDF). Reports on Progress in Physics. 41 (12): 1881–1927. Bibcode:1978RPPh...41.1881C. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.482.4728. doi:10.1088/0034-4885/41/12/002. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2017-09-23. Retrieved 2017-10-28.
- D'Espagnat, B. (1979). "The Quantum Theory and Reality" (PDF). Scientific American. 241 (5): 158–181. Bibcode:1979SciAm.241e.158D. doi:10.1038/scientificamerican1179-158. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2009-03-27. Retrieved 2009-03-18.
- Fry, E. S.; Walther, T.; Li, S. (1995). "Proposal for a loophole-free test of the Bell inequalities" (PDF). Phys. Rev. A. 52 (6): 4381–4395. Bibcode:1995PhRvA..52.4381F. doi:10.1103/physreva.52.4381. hdl:1969.1/126533. PMID 9912775. Archived from the original on 2021-12-29. Retrieved 2018-03-19.
- Fry, E. S.; Walther, T. (2002). "Atom based tests of the Bell Inequalities — the legacy of John Bell continues". In Bertlmann, R. A.; Zeilinger, A. (eds.). Quantum [Un]speakables. Berlin-Heidelberg-New York: Springer. pp. 103–117.
- Goldstein, Sheldon; et al. (2011). "Bell's theorem". Scholarpedia. 6 (10): 8378. Bibcode:2011SchpJ...6.8378G. doi:10.4249/scholarpedia.8378.
- Griffiths, R. B. (2001). Consistent Quantum Theory. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-80349-6. OCLC 1180958776.
- Hardy, L. (1993). "Nonlocality for 2 particles without inequalities for almost all entangled states". Physical Review Letters. 71 (11): 1665–1668. Bibcode:1993PhRvL..71.1665H. doi:10.1103/physrevlett.71.1665. PMID 10054467. S2CID 11839894.
- Matsukevich, D. N.; Maunz, P.; Moehring, D. L.; Olmschenk, S.; Monroe, C. (2008). "Bell Inequality Violation with Two Remote Atomic Qubits". Phys. Rev. Lett. 100 (15): 150404. arXiv:0801.2184. Bibcode:2008PhRvL.100o0404M. doi:10.1103/physrevlett.100.150404. PMID 18518088. S2CID 11536757.
- Rieffel, Eleanor G.; Polak, Wolfgang H. (4 March 2011). "4.4 EPR Paradox and Bell's Theorem". Quantum Computing: A Gentle Introduction. MIT Press. pp. 60–65. ISBN 978-0-262-01506-6.
- Sulcs, S. (2003). "The Nature of Light and Twentieth Century Experimental Physics". Foundations of Science. 8 (4): 365–391. doi:10.1023/A:1026323203487. S2CID 118769677.
- van Fraassen, B. C. (1991). Quantum Mechanics: An Empiricist View. Clarendon Press. ISBN 978-0-198-24861-3. OCLC 22906474.
External links
- Mermin: Spooky Actions At A Distance? Oppenheimer Lecture
- Quantum Entanglement, by Dr Andrew H. Thomas.
- Bell's Theorem with Easy Math, by David R. Schneider. Another simple explanation of Bell's Inequality.
- Interactive experiments with single photons: entanglement and Bell's theorem
- "Bell's theorem". Internet Encyclopedia of Philosophy.
- "Bell inequalities", Encyclopedia of Mathematics, EMS Press, 2001 [1994]
- Spooky Action at a Distance: an Explanation of Bell's Theorem



















































































