Siddhaṃ script
| Siddhaṃ | |
|---|---|
 The word Siddhaṃ in the Siddhaṃ script | |
| Script type | |
Time period | c. 600–c. 1200 in India, and to the present in East Asia |
| Direction | Left-to-right |
| Region | India China Japan |
| Languages | Sanskrit |
| Related scripts | |
Parent systems | |
Child systems | Bengali script, Tibetan and its descendants |
Sister systems | Nāgarī Śāradā |
[a] The Semitic origin of the Brahmic scripts is not universally agreed upon. | |
Siddhaṃ (Sanskrit सिद्धं, "accomplished" or "perfected"; སིད་དྷཾ།; Chinese: 悉昙文字) —, also called Siddhamātṛkā,[1] is the name of a North Indian script used for writing Sanskrit during the period ca 600-1200 CE. It is descended from the Brahmi script via the Gupta script, which also gave rise to the Devanāgarī script as well as a number of other Asian scripts such as Tibetan script. There is some confusion over the spelling: Siddhāṃ and Siddhaṃ are both common, though Siddhaṃ is correct. The script is a refinement of the script used during the Indian Gupta Empire. The name arose from the practice of writing the word Siddhaṃ, or Siddhaṃ astu (may there be perfection) at the head of documents.
Siddhaṃ is an abugida or alphasyllabary rather than an alphabet because each character indicates a syllable, but it does not include every possible syllable. If no other mark occurs then the short 'a' is assumed. Diacritic marks indicate the other vowels, the pure nasal (anusvāra), and the aspirated vowel (visarga). A special mark (virama) can be used to indicate that the letter stands alone with no vowel, which sometimes happens at the end of Sanskrit words. See links below for examples.
History



Many of the Buddhist texts which were taken to China along the Silk Road were written using a version of the Siddhaṃ script. This continued to evolve, and minor variations are seen across time, and in different regions. Importantly it was used for transmitting the Buddhist tantra texts. At the time it was considered important to preserve the pronunciation of mantras, and Chinese was not suitable for writing the sounds of Sanskrit. This led to the retention of the Siddhaṃ Script in East Asia. The practice of writing using Siddhaṃ survived in East Asia where Tantric Buddhism persisted.
Kūkai introduced the Siddhaṃ script to Japan when he returned from China in 806, where he studied Sanskrit with Nalanda-trained monks including one known as Prajñā. By the time Kūkai learned this script, the trading and pilgrimage routes over land to India, were closed by the expanding Islamic empire of the Abbasids.
In Japan the writing of mantras and copying of Sutras using the Siddhaṃ script is still practiced in the esoteric Buddhist schools of Shingon and Tendai as well as in the syncretic sect of Shugendō. The characters are known as shittan (悉曇) or bonji (梵字). The Taisho edition of the Chinese Tripiṭaka preserves the Siddhaṃ characters for most mantras, and Korean Buddhists still write seed syllables in a modified form of Siddhaṃ. A recent innovation is the writing of Japanese language slogans on T-shirts using Bonji. Japanese Siddhaṃ has evolved from the original script used to write sūtras and is now somewhat different from the ancient script.
It is more typical to see Siddhaṃ written with brushes like Chinese writing, and is also written with a bamboo pen; in Japan, a special brush called a bokuhitsu (朴筆) is used for formal Siddhaṃ calligraphy.
In the middle of the 9th century, China experienced a series of purges of "foreign religions", thus cutting Japan off from the sources of Siddhaṃ texts. In time, other scripts, particularly Devanagari, replaced Siddhaṃ in India, leaving East Asia as the only region where Siddhaṃ is used.
Alphabet
Vowels
Independent form Romanized As diacritic with 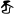
Independent form Romanized As diacritic with 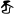

a 

ā 

i 

ī 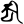

u 

ū 

e 
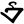
ai 

o 
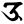
au 

aṃ 

aḥ 
Consonants
Stop Nasal Approximant Fricative Voiceless Voiced Unaspirated Aspirated Unaspirated Aspirated Glottal 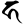 h
h
Velar 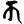 k
k
 kh
kh
 g
g
 gh
gh
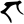 ṅ
ṅ
Palatal  c
c
 ch
ch
 j
j
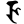 jh
jh
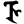 ñ
ñ
 y
y
 ś
ś
Retroflex  ṭ
ṭ
 ṭh
ṭh
 ḍ
ḍ
 ḍh
ḍh
 ṇ
ṇ
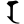 r
r
 ṣ
ṣ
Dental  t
t
 th
th
 d
d
 dh
dh
 n
n
 l
l
 s
s
Bilabial  p
p
 ph
ph
 b
b
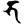 bh
bh
 m
m
Labiodental  v
v
Conjuncts

kkṣ -ya -ra -la -va -ma -na 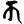 k
k
 kya
kya
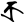 kra
kra
 kla
kla
 kva
kva
 kma
kma
 kna
kna
 rk
rk
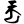 rkya
rkya
 rkra
rkra
 rkla
rkla
 rkva
rkva
 rkma
rkma
 rkna
rkna
 kh
kh
total 68 rows.
- ↑ The combinations that contain adjoining duplicate letters should be deleted in this table。
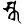 ska
ska
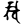 skha
skha
 dga
dga
 dgha
dgha
 ṅktra
ṅktra
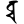 vca/bca
vca/bca
 vcha/bcha
vcha/bcha
 vja/bja
vja/bja
 vjha/bjha
vjha/bjha
 jña
jña
 ṣṭa
ṣṭa
 ṣṭha
ṣṭha
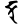 dḍa
dḍa
 dḍha
dḍha
 ṣṇa
ṣṇa
 sta
sta
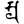 stha
stha
 vda/bda
vda/bda
 vdha/bdha
vdha/bdha
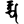 rtsna
rtsna
 spa
spa
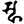 spha
spha
 dba
dba
 dbha
dbha
 rkṣma
rkṣma
- Alternative forms of conjuncts that contain ṇ.
ṛ syllables
Some sample syllables
 rka
rka
 rkā
rkā
 rki
rki
 rkī
rkī
 rku
rku
 rkū
rkū
 rke
rke
 rkai
rkai
 rko
rko
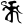 rkau
rkau
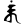 rkaṃ
rkaṃ
 rkaḥ
rkaḥ
 ṅka
ṅka
 ṅkā
ṅkā
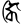 ṅki
ṅki
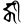 ṅkī
ṅkī
 ṅku
ṅku
 ṅkū
ṅkū
 ṅke
ṅke
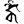 ṅkai
ṅkai
 ṅko
ṅko
 ṅkau
ṅkau
 ṅkaṃ
ṅkaṃ
 ṅkaḥ
ṅkaḥ
Siddhaṃ Fonts
Siddhaṃ is still largely a hand written script. Some efforts have been made to create computer fonts though to date none of these are capable of reproducing all of the Siddhaṃ conjunct consonants. Notably the Chinese Buddhist Electronic Texts Association have created a Siddhaṃ font for their electronic version of the Taisho Tripiṭaka, though this does not contain all possible conjuncts. The software Mojikyo also contains fonts for Siddham, but split Siddham in different blocks and needs different fonts to render one document.
A siddhaṃ input system relies on the CBETA font, Siddhamkey 3.0 has been produced.
Siddhaṃ is not included in the Unicode 5.1 standard. As yet there is no firm proposal for a Siddhaṃ Unicode encoding but there is a draft layout and the script has been tentatively located at the 11380-113DF coderange in the SMP Roadmap.
Notes
External links
- Siddham alphabet on Omniglot
- Examples of Siddham mantras Chinese language website.
- Visible Mantra an extensive collection of mantras and some sūtras in Siddhaṃ script
- Bonji Siddham Character and Pronunciation
- SiddhamKey Software for inputting Siddham characters
Sources
- Bonji Taikan (梵字大鑑). (Tōkyō: Meicho Fukyūkai, 1983)
- Stevens, John. Sacred Calligraphy of the East. (Boston: Shambala, 1995).
- Van Gulik, R.H. Siddham : An Essay on the History of Sanskrit Studies in China and Japan (New Delhi, Jayyed Press, 1981).
- YAMASAKI, Taikō. Shingon: Japanese Esoteric Buddhism. (Fresno: Shingon Buddhist International Institute, 1988).


