Southern bottlenose whale
| Southern bottlenose whale | |
|---|---|
| |
| Size comparison of a Southern Bottlenose Whale against an average human | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Artiodactyla |
| Infraorder: | Cetacea |
| Family: | Ziphiidae |
| Subfamily: | Hyperoodontinae |
| Genus: | Hyperoodon Lacépède, 1804 |
| Species | |
| |
| |
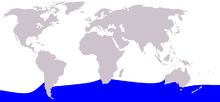
| Southern Bottlenose Whale (Hyperoodon planifrons) range | |
The Southern bottlenose whale (Hyperoodon planifrons) is a species of whale, in the ziphiid family, one of two members of the Hyperoodon genus. The southern bottlenose has been rarely observed, was seldom hunted, and is probably the most abundant whale in Antarctic waters. The species was first described by English zoologist William Henry Flower in 1882, based on a water-worn skull from Lewis Island, in the Dampier Archipelago, Western Australia.
Physical description
It is fairly rotund and measures 7.5 metres (25 ft) in length when physically mature. The melon is extremely bluff. The beak is long and white on males but grey on females. The dorsal fin is relatively small at 30–38 centimetres (12–15 in) and set behind the middle of the back. It is falcate (sickle-shaped) and usually pointed. The back is light-to-mid grey. It has a lighter underside.
Feeding
Southern Bottlenose Whales feed mainly on squid and krill.
Population and distribution
The southern bottlenose whale has a circumpolar distribution in the Southern Ocean. It is found as far south as the Antarctic coast and as north as the tip of South Africa, New Zealand's North Island and the southern parts of Brazil. The global population is unknown.
Sightings of bottlenose whales in tropical and subtropical waters belong to a poorly known species, Longman's beaked whale.
Conservation
The southern bottlenose whale is not believed to be threatened by human actions. The species has seldom been hunted. Forty-two were caught in the Antarctic by Soviet whalers between 1970 and 1982. In addition, the Southern bottlenose whale is covered by the Memorandum of Understanding for the Conservation of Cetaceans and Their Habitats in the Pacific Islands Region. (Pacific Cetaceans MOU)
Specimens
- MNZ MM002233 Southern bottlenose whale Hyperoodon planifrons, collected from peninsula at entrance to Ohiwa lagoon, Bay of Plenty, New Zealand on 2 April 1996.
Notes
References
- Bottlenose Whales in the Encyclopedia of Marine Mammals Shannon Gowans, 1998. ISBN 0-12-551340-2
- National Audubon Society Guide to Marine Mammals of the World Reeves et al., 2002. ISBN 0-375-41141-0.
- Whales, Dolphins and Porpoises Carwardine, 1995. ISBN 0-7513-2781-6
- Template:IUCN2008
External links
- Marine Bio: Southern Bottlenose Whale
- Polar Conservation Organization - information on the Bottlenose Whale
- Whale & Dolphin Conservation Society (WDCS)
- Southern Bottlenose Whale - The Beaked Whale Resource
- Official webpage of the Memorandum of Understanding for the Conservation of Cetaceans and Their Habitats in the Pacific Islands Region

