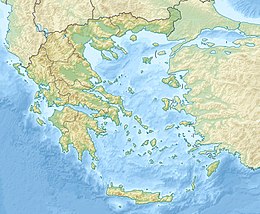
2021 Lasithi earthquake
| UTC time | 2021-10-12 09:24:03 |
|---|---|
| ISC event | 621146229 |
| USGS-ANSS | ComCat |
| Local date | 12 October 2021 |
| Local time | 12:24 |
| Magnitude | 6.4 Mw (USGS) 6.3 Mw (ITSAK)[1] |
| Depth | 10 km (6.2 mi) 11 km (6.8 mi) |
| Epicenter | 35°11′35″N 26°15′22″E / 35.193°N 26.256°E 34°58′N 26°23′E / 34.96°N 26.38°E[2] |
| Type | Normal |
| Max. intensity | MMI VIII (Severe) |
| Peak acceleration | 0.45 g[1] |
| Tsunami | Minor |
| Casualties | None |
On October 12, 2021 12:24 (UTC+3:30) offshore the island of Crete with a magnitude 6.4 Mw earthquake occurred with a maximum Intensity of VIII (Severe) on the Modified Mercalli Intensity Scale.[3] The quake was also said to have been felt as far as Cairo and Istanbul but with low intensities.[4]
Coincidentally, this quake occurred right on the anniversary of the 1856 Heraklion earthquake which killed about 600 people. It also occurred about two weeks after the 2021 Crete earthquake. Weak tremors were felt in Giza and Cairo, which also coincided with the anniversary of the 1992 Cairo earthquake.[5]
Earthquake
The quake was recorded as a 6.3 earthquake by the European-Mediterranean Seismological Centre, but was upgraded to 6.4 in magnitude. Efthymios Lekkas, president of the Earthquake Planning and Protection Organisation, said that the quake was not directly related to the first tremor a month ago, but instead was a sign of the activation of the Eastern part of the Hellenic arc.[6] According to a moment tensor solution by the U.S. Geological Survey, the earthquake was associated with shallow normal faulting within the Aegean Sea Plate at a depth of 10 km.[3]
Due to the distance between the 6.4 and 6.0 events, spaced far apart, it is not likely they are directedly related. Greek seismologists added that the two earthquakes occurred by chance despite saying that the chances of two large events happening in the same region is low. The lack of aftershocks sparked concern among seismologists due to the lack of aftershocks following the quake. The rate of aftershocks were substantially lower than expected for an earthquake of its size.[7]
Tectonic setting
The island of Crete, and the country of Greece in general is prone to seismic activity and is home to one of the most destructive earthquakes in all of Europe. Crete lies in the so-called Hellenic arc which is the result of the subduction of the Eurasian Plate (specifically the Aegean Sea plate) and the African Plate. This has lead to generating numerous powerful tremors in the past and even until this day.
Damage
According to the Mayor of Sitia, the town hall of was confirmed to have sustained damage.[8] The church of Saint Nicholas in Xerokampos, Sitia collapsed, but no casualties were reported as the structure was vacant during the time of the shock.[9][10][11] Efthymios Lekkas, a professor of dynamic tectonic applied geology & disaster management at the National and Kapodistrian University of Athens said that fortunately damage was minimal and was only observed in old or abandoned masonry buildings.[6] At Xerokampos, the quake knocked off items off shelves at shops. The town hall building of [[ According to the Mayor of Sitia, the town hall of was confirmed to have sustained damage.[12] The church of Saint Nicholas in Xerokampos, Sitia collapsed, but no casualties were reported as the structure was vacant during the time of the shock.[9][13][14] Efthymios Lekkas, a professor of dynamic tectonic applied geology & disaster management at the National and Kapodistrian University of Athens said that fortunately damage was minimal and was only observed in old or abandoned masonry buildings.[6] At Xerokampos, the quake knocked off items off shelves at shops. The town hall building of Sitia suffered minor fracturing on the facade.[15]
Tsunami
A small tsunami was detected by instruments in the sea, prompting coastal residents to stay away from the sea.[16][17] OASP President Efthymios Lekkas said in a statement: "We have issued a tsunami alert but nothing alarming. We are talking about 10 kilometers southeast of Zakros. The phenomenon has arrived and may not be visible in some areas. The quake was small to create a large tsunami. Apart from Crete, the whole southern Aegean has been shaken," Geodynamics Institute in Athens director Vassilis Karastathis also said in an interview with popular Greek newspaper Proto Thema saying: "There is always an announcement when there is a strong earthquake in the sea. To understand what happens when we have a strong seismic event at sea because we are dealing with time in relation to the tsunami we do not wait for time to pass and until we see all the data from the warning systems we send the announcement for good and for bad. So depending on some rules of earthquake magnitude and distance from the shores and of course to be in the sea then we issue a warning. So here, since it is not on land and it was at sea, we made the announcement ".[18]
Response
Stavros Arnaoutakis, the Governor of Crete calmed the people, saying "We have to be cool, so far I have no reports of injuries." He also said in an interview with Greek newspaper Proto Thema: "We were rocking for 15 seconds."[19]
The municipality of Malevezi has issued the cancellations of schools and kindergartens. The further inspection of damaged infrastructure and irrigation networks were also observed in the Municipality. The Emergency Response Plan and the Immediate or the Short-term Management of the Consequences of the Earthquake Event "EKKELADOS" which was already present since September 27 after the initial quake a month earlier was re-implemented as well as the return of the mobilization of the Civil Protection in the municipality.[20]
See also
- List of earthquakes in 2021
- List of earthquakes in Greece
- 1856 Heraklion earthquake
- 2021 Crete earthquake
References
- ^ a b "Seismic Stations". ITSAK. Institute of Engineering Seismology and Earthquake Engineering. 12 October 2021. Retrieved 12 October 2021.
- ^ "ITSAK ShakeMap: E of Crete Isl. - S. Greece". ITSAK. Institute of Engineering Seismology and Earthquake Engineering. Retrieved 12 October 2021.
- ^ a b "M 6.4 - 0 km SSE of Palekastro, Greece". earthquake.usgs.gov. Retrieved 2021-10-12.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "Powerful earthquake strikes Crete, Greece for 2nd time in under a month". The Jerusalem Post | JPost.com. Retrieved 2021-10-12.
- ^ "Earthquake in Crete: It was also felt in Egypt". Proto Thema. Athens News Agency. 12 October 2021. Retrieved 12 October 2021.
- ^ a b c "Σεισμός στην Κρήτη – Λέκκας: Πιθανή ενεργοποίηση στο ανατολικό τμήμα του σεισμικού τόξου – Δόνηση 3,3R και στην Κάσο". ProtoThema (in Greek). 2021-10-12. Retrieved 2021-10-12.
- ^ Newsroom (13 October 2021). "Σεισμός στην Κρήτη: Ανησυχούν οι ειδικοί γιατί δεν έχει καταγραφεί μεγάλος μετασεισμός" [Earthquake in Crete: Experts worry because no major earthquake has been recorded]. CNN.gr. Retrieved 13 October 2021.
- ^ NEWSROOM (2021-10-12). "Σεισμός 6,3 Ρίχτερ ανοιχτά της Κρήτης - Αναφορές για ζημιές και μεγάλη ανησυχία στο νησί". Eretikos.gr (in Greek). Retrieved 2021-10-12.
- ^ a b Drakontidis, Frixos (12 October 2021). "Εικόνες αποκάλυψης από την κατάρρευση του ναού Αγίου Νικολάου στη Σητεία - «Ευτυχώς δεν θρηνήσαμε θύματα»" [Images of revelation from the collapse of the church of Agios Nikolaos in Sitia - "Fortunately we did not mourn the victims"]. Proto Thema. Retrieved 12 October 2021.
- ^ "Ισχυρός σεισμός 6,3 Ρίχτερ στην Κρήτη - Ανάστατοι οι κάτοικοι - Τι φοβίζει τους ειδικούς [Strong 6.3 Richter earthquake in Crete - The inhabitats are upset - What fears the experts". ΤΑ ΝΕΑ (in Greek). 12 October 2021. Retrieved 12 October 2021.
- ^ Newsroom. "Σεισμός 6,3 Ρίχτερ στην Κρήτη: Κατέρρευσε εκκλησάκι στη Σητεία, ζημιές σε κτίρια | Η ΚΑΘΗΜΕΡΙΝΗ". www.kathimerini.gr. Retrieved 2021-10-12.
- ^ NEWSROOM (2021-10-12). "Σεισμός 6,3 Ρίχτερ ανοιχτά της Κρήτης - Αναφορές για ζημιές και μεγάλη ανησυχία στο νησί". Eretikos.gr (in Greek). Retrieved 2021-10-12.
- ^ "Ισχυρός σεισμός 6,3 Ρίχτερ στην Κρήτη - Ανάστατοι οι κάτοικοι - Τι φοβίζει τους ειδικούς [Strong 6.3 Richter earthquake in Crete - The inhabitats are upset - What fears the experts". ΤΑ ΝΕΑ (in Greek). 12 October 2021. Retrieved 12 October 2021.
- ^ Newsroom. "Σεισμός 6,3 Ρίχτερ στην Κρήτη: Κατέρρευσε εκκλησάκι στη Σητεία, ζημιές σε κτίρια | Η ΚΑΘΗΜΕΡΙΝΗ". www.kathimerini.gr. Retrieved 2021-10-12.
- ^ "Κρήτη: Ο σεισμός οδήγησε σε κατολίσθηση - Βράχια έπεσαν στην παραλία του Κουρεμένου (βίντεο)" [Crete: Earthquake leads to landslide - Rocks fell on Kouremenos beach (video)] (in Greek). newshub.gr. 12 October 2021. Retrieved 13 October 2021.
- ^ "Tsunami is heading to the coast of Crete after the strong earthquake of 6.3 Richter". Debater (in Greek). Retrieved 12 October 2021.
- ^ Fthis Team (12 October 2021). "Crete Earthquake: Small tsunami after 6.3 Richter - "Get off the coast"" (in Greek). FThis GR. Retrieved 12 October 2021.
- ^ "Σεισμός στην Κρήτη: Προειδοποίηση για κίνδυνο μικρού τσουνάμι μετά τα 6,3 Ρίχτερ". ProtoThema (in Greek). 2021-10-12. Retrieved 2021-10-12.
- ^ "Σεισμός 6,3R στην Κρήτη - «15 δευτερόλεπτα κουνιόμασταν» λέει ο Περιφερειάρχης". ProtoThema (in Greek). 2021-10-12. Retrieved 2021-10-12.
- ^ "Σεισμός στην Κρήτη: Κλειστά αύριο τα σχολεία στο Μαλεβίζι". ProtoThema (in Greek). 2021-10-12. Retrieved 2021-10-12.