State Parliament (Germany)
| This article is part of a series on the |
| Politics of Germany |
|---|
 |
In the federal system of the Federal Republic of Germany, the state parliaments embody the legislative power in the sixteen states. In thirteen of the sixteen German states, the state parliament is known as the Landtag (an old German term that roughly means state parliament). In the states Free Hanseatic City of Bremen and Free and Hanseatic City of Hamburg, the state parliament is called Bürgerschaft (Citizenry), in Berlin it is called Abgeordnetenhaus (House of Representatives).
Election process, constitutional functions and powers
As the German constitution (Basic Law) defines the Federal Republic of Germany as a federation, each German state has its own constitution. The Basic Law gives the states a broad discretion to determine their respective state structure, only stating that each German state has to be a social and democratic republic under the rule of law and that the people in every state must have an elected representation, without giving further details (Article 28.1). In practice, all states are parliamentary republics in which the legislative branch of government is assigned to an elected parliament. Since the abolition of the Bavarian Senate in 1999, all sixteen state parliaments are unicameral.
Among the most important functions of the state parliaments are the election of the Minister President, the control of the state government and the adoption of state laws. They have no influence on federal legislation, but participate in the election of the President of Germany by electing state electors to the Federal Convention.
In terms of these functions, the state parliaments work very similarly. However, there are also some significant differences between the states. This begins with the electoral system: Similar to federal elections, many states use a mixed-member proportional representation system in which each voter casts one vote for a constituency candidate and a second vote determines the proportional share of seats. However, this is not the case in all states, the main exception being Baden-Württemberg, which uses a complex first-past-the-post voting system in which seats are allocated to "lucky-loser" candidates in addition to the elected constituency candidates in order to establish proportionality. In all states there is a 5%-threshold which must be exceeded for a party to be considered in the proportional distribution of seats, although in Bremen it is sufficient to exceed the threshold in only one of the two cities that make up the state (Bremen City and Bremerhaven). The electoral system of some states also includes a basic mandate clause which allows parties to be taken into account in the proportional distribution of seats regardless of the 5%-threshold if they win a certain number of constituencies. As at the federal level, parties representing national minorities are excluded from both the 5%-threshold and the basic mandate clause. This provision is of particular importance in Schleswig-Holstein, where the SSW, a party which represents the minorities of Danes and Frisians, regularly participates in state elections.
In contrast to the Bundestag on federal level, all states have adopted legislative periods of five years, with the sole exception of Bremen, which still uses four-year-terms (a cross-party attempt to introduce five-year-terms was defeated in a referendum in 2017[1]). Another difference to the Bundestag are the conditions for early new elections: While the Bundestag does not have the right of self-dissolution and can only be dissolved by the President of Germany (and even this only under certain conditions which are precisely defined in the Basic Law), the state parliaments have the right of self-dissolution (even if the procedure differs according to the state constitutions). In addition to this, some state constitutions also provide for an automatic dissolution of the parliament in certain situations and in some states, the parliament can also be dissolved by a referendum. Neither an automatic dissolution nor a dissolution by referendum has ever happened in any state, though.
| State | Name | Election system | Threshold conditions | Seats | Term | Premature dissolution procedures |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baden-Württemberg[2] | Landtag of Baden-Württemberg | first-past-the-post in 70 constituencies with at least 50 "lucky loser"-seats (Zweitmandate), in order to achieve proportional representation | 5% of votes statewide | 120+ | 5 years | -self dissolution (motion must be tabled by at least one quarter and accepted by at least two thirds of members) -referendum (request must be made by at least one sixth of the state population eligible to vote and must be accepted by a majority of the population eligible to vote) |
| Free State of Bavaria | Landtag of Bavaria | mixed-member proportional representation with two votes (both votes counting towards proportional representation) | 5% of votes statewide | 180+ | 5 years | -self dissolution (simple motion sufficient) -referendum (request must be made by at least one million citizens eligible to vote and must be accepted by a simple majority) -automatic dissolution (if the Landtag fails to elect a Minister President within four weeks after a vacancy occurred) |
| Berlin[3][4] | House of Representatives of Berlin | mixed-member proportional representation with two votes | 5% of second votes statewide or one constituency |
130+ | 5 years | -self dissolution (motion must be accepted by two thirds of members) -referendum (state constitution does not specify details) |
| Brandenburg | Landtag of Brandenburg | mixed-member proportional representation with two votes | 5% of second votes statewide or one constituency |
88+ (maximum of 110) | 5 years | -self dissolution (motion must be accepted by two thirds of members) |
| Free Hanseatic City of Bremen[5] | Bürgerschaft of Bremen | Personalized proportional representation with cumulative voting and panachage (five votes) in two separate voting areas (Bremen City and Bremerhaven) | 5% of votes in one of the two voting areas | 84 (69 for Bremen City and 15 for Bremerhaven) | 4 years | -self dissolution (motion must be tabled by at least one third and must be accepted by at least two thirds of members) -referendum (request must be made by at least one fifth of the state population eligible to vote and must be accepted by a majority of the population eligible to vote) |
| Free Hanseatic City of Hamburg | Bürgerschaft of Hamburg | Personalized proportional representation with cumulative voting and panachage on state level and in multi member constituencies (10 votes: 5 for state lists, 5 for constituency candidates) | 5% of state list-votes | 121+ | 5 years | -self dissolution (motion must be tabled by at least one quarter and must be accepted by a majority of members) |
| Hesse | Landtag of Hesse | mixed-member proportional representation with two votes | 5% of second votes statewide | 110+ | 5 years | -self dissolution (motion must be accepted by a majority of members) |
| Lower Saxony | Landtag of Lower Saxony | mixed-member proportional representation with two votes | 5% of second votes statewide | 135+ | 5 years | -self dissolution (the state constitution defines two scenarios for a self dissolution: [A] one third of members may table a motion of self dissolution, which must be accepted by two thirds of members present, who have to equal at least a majority of all members [Art. 10]. [B] Nonwithstanding variant A, the Landtag may dissolve itself with a majority of members, if it has failed to elect a Minister President within 21 days after a vacancy occurred – alternatively it may elect a Minister President with a plurality of votes [Art. 30]) |
| Mecklenburg-Vorpommern | Landtag of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern | mixed-member proportional representation with two votes | 5% of second votes statewide | 71+ | 5 years | -self dissolution (the state constitution defines two scenarios for a self dissolution: [A] one third of members may table a motion of self dissolution, which must be accepted by two thirds of members [Art. 42.2]. [B] Nonwithstanding variant A, the Landtag may dissolve itself with a majority of members, if it has failed to elect a Minister President within 28 days after a vacancy occurred – alternatively it may elect a Minister President with a plurality of votes [Art. 30]) |
| North Rhine-Westphalia | Landtag of North Rhine-Westphalia | mixed-member proportional representation with two votes | 5% of second votes statewide | 181+ | 5 years | -self dissolution (motion must accepted by a majority of members) |
| Rhineland-Palatinate | Landtag of Rhineland-Palatinate | mixed-member proportional representation with two votes | 5% of second votes statewide | 101+ | 5 years | -self dissolution (simple motion) -automatic dissolution (if a motion of no confidence against the Minister President has been successful and the Landtag fails to elect a new office-holder within four weeks) |
| Saarland | Landtag of Saarland | proportional representation with one vote, which counts both for a list in a multi member constituency and a state list | 5% of votes statewide | 51(+?)[a] | 5 years | -self dissolution (motion must be accepted by two thirds of members) -automatic dissolution (if a motion of no confidence against the Minister President has been successful and the Landtag fails to elect a new office-holder within four weeks) |
| Free State of Saxony | Landtag of Saxony | mixed-member proportional representation with two votes | 5% of second votes statewide or two constituencies |
120+ | 5 years | -self dissolution (motion must be accepted by two thirds of members) -automatic dissolution (if the Landtag fails to elect a Minister President within four months after a vacancy occurred) |
| Saxony-Anhalt | Landtag of Saxony-Anhalt | mixed-member proportional representation with two votes | 5% of second votes statewide | 87+[b] | 5 years | -self dissolution (the state constitution defines two scenarios for a self dissolution: [A] one fourth of members may table a self dissolution motion, which has to be accepted by two thirds of members. This is however not possible during the first six months of a legislative period [Art. 60]. [B] Nonwithstanding variant A, the Landtag may dissolve itself with a majority of members, if it has failed to elect a Minister President on the first two ballots – alternatively it may elect a Minister President with a plurality of votes on the third ballot [Art. 65.2]) |
| Schleswig-Holstein | Landtag of Schleswig-Holstein | mixed-member proportional representation with two votes | 5% of second votes statewide or one constituency |
69+ | 5 years | -self dissolution (motion must be accepted by at least two thirds of members) |
| Free State of Thuringia | Landtag of Thuringia | mixed-member proportional representation with two votes | 5% of second votes statewide | 88+ | 5 years | -self dissolution (motion must be tabled by at least one third and must be accepted by at least two thirds of members) -automatic dissolution (if the Minister President has lost a confidence motion and the Landtag fails to elect a new Minister President within 21 days) |
- ^ The electoral system of Saarland has a regulatory gap for the (unlikely but theoretically possible) case that a party is proportionally entitled to more seats in the multi member constituencies than would be the case on state level. The election law code does not state, whether this would lead to overhang or even compensation seats or whether the relevant party would lose its entitlement to the overhang mandates.[6]
- ^ With effect to the next state election it was decided to reduce the number of seats to 83. Overhang and compensation seats remain possible.
List of state parliaments
The following list shows the sixteen state parliaments in their current composition. The arc-diagrams show the strength of the parties, from left to right first the governing parties from the largest to the smallest, then the opposition parties from the largest to the smallest. The actual seating arrangements may (and do) differ.
| Plenar hall | Name | Legislative period |
Diagram | Composition | Presidium | Last election | Next election[7] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Baden-Württemberg |
 |
Landtag | 16th | 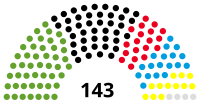 |
Government (90) Alliance 90/The Greens (47) CDU (43) Opposition (53) SPD (19) AfD (18) FDP (12) Non-inscrits (4) |
Muhterem Aras (Alliance 90/The Greens) President Sabine Kurtz (CDU) Vice President |
2016 | 14 March 2021 |
 Free State of Bavaria |
 |
Landtag | 18th | 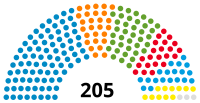 |
Government (112) CSU (85) Free Voters (27) Opposition (93) Alliance 90/The Greens (38) SPD (22) AfD (20) FDP (11) Non-inscrits (2) |
Ilse Aigner (CSU) President Karl Freller (CSU) Thomas Gering (Alliance 90/The Greens) Alexander Hold (Free Voters) Markus Rinderspacher (SPD) Wolfgang Heubisch (FDP) Vice Presidents |
2018 | 2023 |
 Berlin |
 |
Abgeordnetenhaus | 18th | 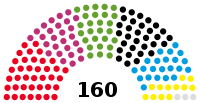 |
Government (92) SPD (38) The Left (27) Alliance 90/The Greens (27) Opposition (68) CDU (31) AfD (22) FDP (12) Non-inscrits (3) |
Ralf Wieland (SPD) President Cornelia Seibeld (CDU) Manuela Schmidt (The Left) Vice Presidents |
2016 | 26 September 2021 |
 Brandenburg |
 |
Landtag | 7th | 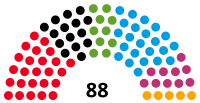 |
Government (50) SPD (25) CDU (15) Alliance 90/The Greens (10) Opposition (38) AfD (23) The Left (10) BVB/Free Voters (5) |
Ulrike Liedtke (SPD) President Andreas Galau (AfD) Barbara Richstein (CDU) Vice Presidents |
2019 | 2024 |
 Free Hanseatic City of Bremen |
 |
Bürgerschaft | 20th | 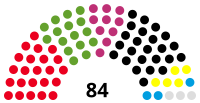 |
Government (49) SPD (23) Alliance 90/The Greens (16) The Left (10) Opposition (35) CDU (24) FDP (5) AfD/Magnitz-Runge-Felgenträger (3) Non-inscrits (3) |
Frank Imhoff (CDU) President Sülmez Dogan (Alliance 90/The Greens) Antje Grotheer (SPD) Vice Presidents |
2019 | 2023 |
 Free Hanseatic City of Hamburg |
 |
Bürgerschaft | 22nd | 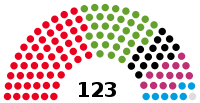 |
Government (87) SPD (54) Alliance 90/The Greens (33) Opposition 36 CDU (15) The Left (13) AfD (7) Non-inscrits (1) |
Carola Veit (SPD) President Mareike Engels (Alliance 90/The Greens) Frank Schmitt (SPD) André Trepoll (CDU) Deniz Çelik (The Left) Vice Presidents |
2020 | 2025 |
 Hesse |
 |
Landtag | 20th | 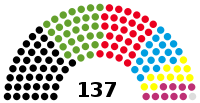 |
Government (69) CDU (40) Alliance 90/The Greens (29) Opposition (68) SPD (29) AfD (18) FDP (11) The Left (9) Non-inscrits (1) |
Boris Rhein (CDU) President Frank Lortz (CDU) Karin Müller (Alliance 90/The Greens) Heike Hofmann (SPD) Jörg-Uwe Hahn (FDP) Ulrich Wilken (The Left) Vice Presidents |
2018 | 2023 |
 Lower Saxony |
 |
Landtag | 18th |  |
Government (104) SPD (54) CDU (50) Opposition (33) Alliance 90/The Greens (12) FDP (11) Non-inscrits (10) |
Gabriela Andretta (SPD) President Petra Emmerich-Kopatsch (SPD) Bernd Busemann (CDU) Frank Oesterhellweg (CDU) Meta Janssen-Kucz (Alliance 90/The Greens) Vice Presidents |
2017 | 2022 |
 Mecklenburg-Vorpommern |
 |
Landtag | 7th | 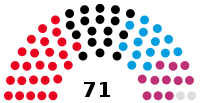 |
Government (44) SPD (26) CDU (18) Opposition (27) AfD (14) The Left (11) Non-inscrits (2) |
Birgit Hesse (SPD) President Beate Schlupp (CDU) Mignon Schwenke (The Left) Vice Presidents |
2016 | 26 September 2021 |
 North Rhine-Westphalia |
 |
Landtag | 17th | 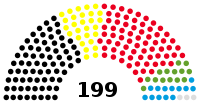 |
Government (100) CDU (72) FDP (28) Opposition (99) SPD (69) Alliance 90/The Greens (14) AfD (13) Non-inscrits (3) |
André Kuper (CDU) President Carina Gödecke (SPD) Angela Freimuth (FDP) Oliver Keymis (Alliance 90/The Greens) Vice Presidents |
2017 | 2022 |
 Rhineland-Palatinate |
 |
Landtag | 17th | 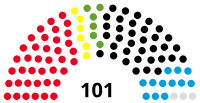 |
Government (51) SPD (39) FDP (6) Alliance 90/The Greens (6) Opposition (50) CDU (35) AfD (12) Non-inscrits (3) |
Hendrik Hering (SPD) President Astrid Schmitt (SPD) Hans-Josef Bracht (CDU) Vice Presidents |
2016 | 14 March 2021 |
 Saarland |
 |
Landtag | 16th | 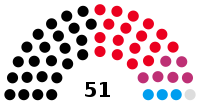 |
Government (41) CDU (24) SPD (17) Opposition (10) The Left (6) AfD (3) Non-inscrits (1) |
Stephan Toscani (CDU) President Isolde Fries (SPD) Günter Heinrich (CDU) Vice Presidents |
2017 | 2022 |
 Free State of Saxony |
 |
Landtag | 7th | 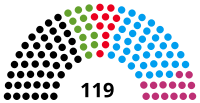 |
Government (67) CDU (45) Alliance 90/The Greens (12) SPD (10) Opposition (52) AfD (38)[a] The Left (14) |
Matthias Rößler (CDU) President Andrea Dombois (CDU) André Wendt (AfD) Luise Neuhaus-Wartenberg (The Left) Vice Presidents |
2019 | 2024 |
 Saxony-Anhalt |
 |
Landtag | 7th | 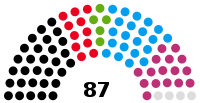 |
Government (46) CDU (30) SPD (11) Alliance 90/The Greens (5) Opposition (41) AfD (21) The Left (16) Non-inscrits (4) |
Gabriele Brakebusch (CDU) President Willi Mittelstädt (AfD) Wulf Gallert (The Left) Vice Presidents |
2016 | 6 June 2021 |
 Schleswig-Holstein |
 |
Landtag | 19th |  |
Government (44) CDU (25) Alliance 90/The Greens (10) FDP (9) Opposition (29) SPD (21) AfD (4) SSW (3) Non-inscrits (1) |
Klaus Schlie (CDU) President Kirsten Eickhoff-Weber (SPD) Aminata Touré (Alliance 90/The Greens) Annabell Krämer (FDP) Vice Presidents |
2017 | 2022 |
 Free State of Thuringia |
 |
Landtag | 7th | 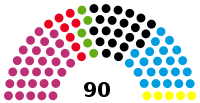 |
Government (42) The Left (29) SPD (8) Alliance 90/The Greens (5) Confidence and Supply (21) CDU (21) Opposition (27) AfD (22) FDP (5) |
Birgit Keller (The Left) President Michael Kaufmann (AfD) Henry Worm (CDU) Dorothea Marx (SPD) Astrid Rothe-Beinlich (Alliance 90/The Greens) Dirk Bergner (FDP) Vice Presidents |
2019 | 2024 (26 September 2021)[b] |
- ^ According to their vote-share in the 2019 election, the AfD would be entitled to a 39th seat, but their list was cut short after the 30th position before the election due to irregularities in the candidate-appointment and only eight of the party's constituency candidates, who did not also run on the state list, were successful. Therefore, the 120th seat of the Landtag will remain empty.
- ^ An election in 2024 is the default constitutional position. On 21 February 2020, The Left, the SPD, Alliance 90/The Greens and the CDU agreed on filing a self dissolution-motion early in 2021 and, if successful, dating a snap election to 25 April 2021, in order to solve the 2020 Thuringian government crisis.[8] On 14 January 2021 and due to the COVID-19 pandemic, the minority-coalition and the CDU decided to postpone these steps, now aiming for a snap election on 26 September 2021, the likely date of the 2021 German federal election as well as the 2021 Berlin and Mecklenburg-Vorpommern state elections.[9]
References
- ^ https://www.weser-kurier.de/deutschland-welt/bundestagswahl-2017_artikel,-volksentscheid-und-bundestagwahl-so-hat-bremen-abgestimmt-_arid,1651043.html
- ^ https://www.lpb-bw.de/bwverf/bwverf.htm#Landtag
- ^ https://www.berlin.de/rbmskzl/regierender-buergermeister/verfassung/artikel.41546.php
- ^ http://www.wahlrecht.de/landtage/berlin.htm
- ^ https://www.wahlrecht.de/landtage/bremen.htm
- ^ http://www.wahlrecht.de/landtage/regelungsluecke-saarland.html
- ^ https://www.wahlrecht.de/termine.htm#ltw-be-2016
- ^ https://www.mdr.de/thueringen/statement-gespraeche-linke-spd-gruene-cdu-100.html
- ^ https://www.tagesschau.de/eilmeldung/eilmeldung-5379.html
