Guettarda speciosa
| Guettarda speciosa | |
|---|---|

| |

| |
| Guettarda speciosa (artist John Lindley) | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| (unranked): | |
| (unranked): | |
| (unranked): | |
| Order: | |
| Family: | |
| Genus: | |
| Species: | G. speciosa
|
| Binomial name | |
| Guettarda speciosa | |
| |
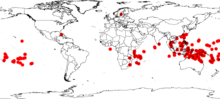
| Occurrence data from GBIF[1] | |
Guettarda speciosa, with common names sea randa,[2][3] or zebra wood,[2][3] is a species of shrub in the family Rubiaceae found in coastal habitats in tropical areas around the Pacific Ocean, including the coastline of central and northern Queensland and Northern Territory in Australia, and Pacific Islands, including Micronesia, French Polynesia and Fiji, Malaysia and Indonesia, Maldives and the east coast of Africa. It reaches 6 m in height, has fragrant white flowers, and large green prominently-veined leaves. It grows in sand above the high tide mark.
Taxonomy and naming
Alternate names in the Cook Islands include Ano, Hano, Fano, and Puapua. The last is also used in Samoa, and the similar Puopua in Tonga.[4] It is known as utilomar [wudˠiːlʲɔːmʲɑrˠ] in the Marshall Islands.[5]
It was originally described by Carl Linnaeus. The genus was named in honour of the 18th century French naturalist Jean-Étienne Guettard, while the specific epithet is derived from the Latin speciosus 'showy'.[6]
Description
It is a perennial shrub or small tree 2–6 m (6.6–19.7 ft) tall by 1–3 m (3.3–9.8 ft) wide with smooth creamy grey bark. The large oval-shaped leaves are 15–23 cm (6–9 in) long by 10–18 cm (4–7 in) wide. Dark green and smooth above with prominent paler veins, they are finely hairy underneath. Flowering is from October to May, the fragrant white flowers are 2.5–3 cm (1–1+1⁄4 in) long with 4–9 lobes. These are followed by sweet-smelling globular hard fruit, measuring 2.5 cm–2.8 cm × 2.2 cm–2.5 cm (0.98 in–1.10 in × 0.87 in–0.98 in), which mature September to March.[7][8]
Distribution and habitat
Guettarda speciosa is found in coastal habitats in tropical areas around the Pacific Ocean, including the coastline of central and northern Queensland and Northern Territory in Australia, and Pacific Islands, including Micronesia, French Polynesia and Fiji, Malaysia and Indonesia, Maldives and the east coast of Africa. As its name suggests, the beach gardenia grows on beaches and sandy places above the high tide level.[7]
Ecology
The Mariana Fruit Bat (Pteropus mariannus) feeds on the fruit and flowers, acting as a vector for the dispersal of seeds.[citation needed]
Human use
Use by indigenous cultures
The large leaves were used in various ways by the indigenous people of northern Australia; they could hold food, and when heated, they were given to relieve headaches and aches in limbs. The stems could be used to make Macassan pipes.[9] The flowers were used to scent coconut oil on the Cook Islands, and the wood for dwellings and canoes.[4]
Cultivation
A very useful plant for seaside planting in tropical climates, it needs a sunny aspect and well-drained soil. It has proven difficult to propagate, as this must be done by seed which may take months to germinate.[7]
References
- ^ Guettarda speciosa GBIF.org (28 November 2018) GBIF Occurrence Download https://doi.org/10.15468/dl.ncywcn
- ^ a b "Guettarda speciosa". Germplasm Resources Information Network. Agricultural Research Service, United States Department of Agriculture. Retrieved 21 November 2014.
- ^ a b Guettarda speciosa Australian Tropical Rainforest Plants Retrieved 28 November 2018.
- ^ a b McCormack G (2007). "Guettarda speciosa". Bishop Museum: Cook Islands Biodiversity Database. Bishop Museum. Retrieved 1 June 2008.
- ^ http://www.trussel2.com/MOD/MED2U.htm#utilomar
- ^ Simpson DP (1979). Cassell's Latin Dictionary (5th ed.). London: Cassell Ltd. p. 883. ISBN 0-304-52257-0.
- ^ a b c Elliot, Rodger W.; Jones, David L.; Blake, Trevor (1990). Encyclopaedia of Australian Plants Suitable for Cultivation: Vol. 5. Port Melbourne: Lothian Press. p. 162. ISBN 0-85091-285-7.
- ^ Brock, John (2001) [1988]. Native plants of northern Australia. Frenchs Forest, New South Wales: New Holland Press. p. 211. ISBN 1-876334-67-3.
- ^ Levitt, Dulcie (1981). Plants and People: Aboriginal Uses of Plants on Groote Eylandt. Canberra: Australian Institute of Aboriginal Studies. ISBN 0-391-02205-9.
External links
 Media related to Guettarda speciosa at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Guettarda speciosa at Wikimedia Commons Data related to Guettarda speciosa at Wikispecies
Data related to Guettarda speciosa at Wikispecies
