Large grey babbler
| Large grey babbler | |
|---|---|

| |
| Calling flock | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Passeriformes |
| Family: | Leiothrichidae |
| Genus: | Argya |
| Species: | A. malcolmi
|
| Binomial name | |
| Argya malcolmi (Sykes, 1832)
| |
| |
| Synonyms | |
| |
The large gray babbler (Argya malcolmi) is a member of the family Leiothrichidae found across India and far western Nepal. They are locally common in the scrub, open forest and gardenland. They are usually seen in small groups and are easily distinguished from other babblers in the region by their nasal call and the whitish outer feathers to their long tail. It is one of the largest babblers in the region.[2]
Description
[edit]This long-tailed and large babbler has a brown body with creamy white outer tail feathers which are easily visible as they fly with fluttery wing beats low over the ground. The lores are dark and forehead is grey with white shaft streaks on the feathers. The rump and uppertail covers are pale grey. The mantle has dusky blotches and no shaft streaks.[2] The three outer tail feathers are white and the fourth pair has the outer web white. The wings are darker brown. The iris is yellow and the upper mandible is dark brown while the lower mandible is yellowish. The tail is faintly cross barred.[3] Abnormal specimens showing albinism or leucism have been reported.[4]
The species was first described from the Deccan Plateau region. The scientific name was given by Colonel W H Sykes in appreciation of support that he received from Major-General Sir John Malcolm.[5]
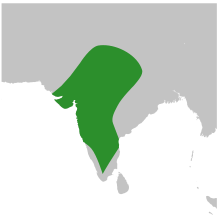
Distribution and habitat
[edit]Found throughout the Indian subcontinent, south of the Himalayas, east of the Thar desert until Bihar. The species is not found in Kerala and records from the Sind area are not confirmed. It is found mainly in open dry scrub forest and cultivated areas.[3] It is not found in the eastern dry zone of Tamil Nadu; however, an exhausted specimen has been observed in Pondicherry.[6]
Behaviour and ecology
[edit]
The species is found in small flocks which keep in contact with loud nasal calls. Members of the flock may join in defending against predators.[7] Individuals may also attack their own reflections.[8][9][10] They are mostly seen in open scrub country where they forage on or close to the ground. They hop and leap on the ground in search of prey.[11] Individuals in a group may indulge in play behaviour.[12] They feed mainly on insects but also feed on small lizards, molluscs and arachnids. They also feed on seeds, grains and berries.[13] They are found in gardens within some cities such as Pune and Ahmedabad. In other cities such as Bangalore, they are seen only on the outskirts of the expanding urban zone.
They are known to breed through the year but mainly during the rainy season from March to September.[2] The usual clutch is four eggs. The nest is a shallow cup placed in a shrub often of thorny species. Their nests are parasitized by the pied cuckoo[14] and the common hawk-cuckoo.[15] It has been suggested that more than one female may lay eggs in a single nest and help in incubation; however, this has not been verified.[3][16][17]
Although secure with a wide distribution, some local populations are threatened by hunting for meat.[18] An endoparasitic cestode Vogea vestibularis has been described from this species.[19]
References
[edit]- ^ BirdLife International (2016). "Argya malcolmi". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T22716361A94492467. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T22716361A94492467.en. Retrieved 12 November 2021.
- ^ a b c Rasmussen, P.C.; Anderton J. C. (2005). Birds of South Asia. The Ripley Guide. Vol. 2. Smithsonian Institution & Lynx Edicions. p. 444.
- ^ a b c Ali, S; S D Ripley (1996). Handbook of the birds of India and Pakistan. Vol. 6 (2nd ed.). Oxford University Press. pp. 220–222.
- ^ Sharma, S. K. (2003). "Total albinism in large grey babbler Turdoides malcolmi". J. Bombay Nat. Hist. Soc. 100 (1): 144–145.
- ^ Sykes, W.H. (1830–1831). "Catalogue of birds of the raptorial and insessorial orders (systematically arranged,) observed in the Dukhun by Lt. Col. W.H. Sykes". Proceedings of the Zoological Society of London. Part 1. ZSL: 88.
- ^ Neville, Shantha (1974). "News from Auroville". Newsletter for Birdwatchers. 16 (5): 15–16.
- ^ Dharmakumarsinhji, RS (1961). "Communal distraction display in Large Grey Babbler, [Turdoides malcolmi (Sykes)]". J. Bombay Nat. Hist. Soc. 58 (2): 512.
- ^ Alexander,HG (1950). "Large Grey Babbler attacking metal hub-cap of wheel of car". J. Bombay Nat. Hist. Soc. 49 (3): 550.
- ^ Ali, Hamid A (1951). "Large Grey Babbler attacking metal hub-cap of car". J. Bombay Nat. Hist. Soc. 50 (1): 171.
- ^ Singh,JL (1977). "Grey Babblers pecking at window panes". Newsletter for Birdwatchers. 17 (10): 12.
- ^ Bharos,AMK (1996). "Sideways leap-frogging by the Large Grey Babblers, Turdoides malcolmi (Sykes)". J. Bombay Nat. Hist. Soc. 93 (1): 93.
- ^ Gaston, A. J. (1977). "Social behaviour within groups of jungle babblers Turdoides striatus". Animal Behaviour. 25: 828–848. doi:10.1016/0003-3472(77)90036-7. S2CID 53146659.
- ^ Toor,HS; Saini,MS (1986). "Feeding ecology of the Large Grey Babbler Turdoides malcolmi" (PDF). Proc. Indian Acad. Sci. Anim. Sci. 95 (4): 429–436. doi:10.1007/BF03179379. S2CID 84465452.
- ^ Whistler, Hugh (1949). Popular handbook of Indian birds. Gurney and Jackson. pp. 45–46. ISBN 1-4067-4576-6.
- ^ Blanford, WT (1895). The Fauna of British India, Including Ceylon and Burma. Birds Volume 3. Taylor and Francis, London. pp. 213–214.
- ^ Macdonald, Malcolm (1959). "Communal nest-feeding in Babblers". J. Bombay Nat. Hist. Soc. 56 (1): 132–134.
- ^ Baker ECS (1922). The Fauna of British India, Including Ceylon and Burma. Birds. Volume 1 (2nd ed.). pp. 200–201.
- ^ Bharos, A. M. K. (2001). "Large grey babbler (Turdoides malcolmi) trapped for the table". J. Bombay Nat. Hist. Soc. 98 (3): 452.
- ^ Johri, GN (1959). "Vogea vestibularis n. g., n. sp., a Dilepidid Cestode from the Intestine of the Large Grey Babbler, Argya malcolmi". The Journal of Parasitology. 45 (3): 287–290. doi:10.2307/3274500. JSTOR 3274500. PMID 13665467.
Other sources
[edit]- Gupta, R. C. Midha, M. (1997) Breeding Biology of Large Grey Babbler, Turdoides malcolmi. Geobios (Jodhpur, India) 24(4):214-218.
- Gupta,RC; Midha, Meenu (1995) Drinking and bathing behaviour of Large Grey Babbler Turdoides malcolmi (Sykes). Zoos' Print Journal 10(5):23.
- Gupta,RC; Midha, Meenu (1994) Observations on the behaviour of Large Grey Babbler, Turdoides malcolmi (Sykes). Cheetal 33(2):42-51.

