Optional Protocol to the Convention Against Torture
| Optional Protocol to the Convention Against Torture and Other Cruel, Inhuman or Degrading Treatment or Punishment | |
|---|---|
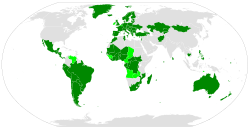 Ratified or acceded
Signed but not ratified
Non-parties | |
| Type | Human rights convention |
| Drafted | 18 December 2002[1] |
| Signed | 18 December 2002 |
| Location | New York |
| Effective | 22 June 2006[1] |
| Condition | 20 ratifications[2] |
| Signatories | 76[1] |
| Parties | 92[1] |
| Depositary | UN Secretary-General[3] |
| Languages | Arabic, Chinese, English, French, Russian and Spanish[4] |
The Optional Protocol to the Convention Against Torture and Other Cruel, Inhuman or Degrading Treatment or Punishment (commonly known as the Optional Protocol to the Convention Against Torture (OPCAT)) is a treaty that supplements to the 1984 United Nations Convention Against Torture. It establishes an international inspection system for places of detention modeled on the system that has existed in Europe since 1987 (the Committee for the Prevention of Torture).
The OPCAT was adopted by the United Nations General Assembly in New York on 18 December 2002,[1] and it entered into force on 22 June 2006.[1] As of March 2023, the Protocol has 76 signatories and 92 parties.[1]
History
The idea for this scheme of torture prevention goes back to the Swiss Committee for the Prevention of Torture (today Association for the Prevention of Torture, APT), founded in 1977 by Jean-Jacques Gautier in Geneva. It envisaged the establishment of a worldwide system of inspection of places of detention, which later took the form of an Optional Protocol to the UN Convention Against Torture and Other Cruel, Inhuman or Degrading Treatment or Punishment (1984). For a long time, however, the necessary support for such an optional protocol was not forthcoming. As a consequence, the UN Committee Against Torture (CAT) had at its disposal only relatively weak instruments: it could analyse and discuss the self-reports of the respective governments and create the institution of a Special Rapporteur on Torture. But neither CAT nor its Special Rapporteur had the power to visit countries, let alone inspect prisons, without the respective government's permission. In 1987, the Council of Europe realized the original idea on a regional level with its European Convention for the Prevention of Torture. On this basis, the European Committee for the Prevention of Torture has demonstrated that regular visits, reports and recommendations to the governments as well as the publication of these reports and the governments' reactions the viability of this model. This in turn led to a breakthrough within the United Nations: OPCAT was created and opened for signatures on 18 December 2002 by the UN General Assembly.
After ratification by 20 states, the Optional Protocol came into force on 22 June 2006.[1]
Ratification status
As of March 2023, 90 states have ratified the protocol: Afghanistan, Albania, Argentina, Armenia, Australia, Austria, Azerbaijan, Belize, Benin, Bolivia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Brazil, Bulgaria, Burkina Faso, Burundi, Cabo Verde, Cambodia, Central African Republic, Chile, Costa Rica, Côte d'Ivoire, Croatia, Cyprus, Czech Republic, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Denmark, Ecuador, Estonia, Finland, France, Gabon, Georgia, Germany, Ghana, Greece, Guatemala, Honduras, Hungary, Iceland, Italy, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Latvia, Lebanon, Liberia, Liechtenstein, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Madagascar, Maldives, Mali, Malta, Mauritania, Mauritius, Mexico, Mongolia, Montenegro, Morocco, Mozambique, Nauru, Netherlands, New Zealand, Nicaragua, Niger, Nigeria, North Macedonia, Norway, Panama, Paraguay, Peru, Philippines, Poland, Portugal, Republic of Moldova, Romania, Rwanda, Senegal, Serbia, Slovenia, South Africa, South Sudan, Spain, Sri Lanka, State of Palestine, Sweden, Switzerland, Togo, Tunisia, Türkiye, Ukraine, United Kingdom, and Uruguay.[1]
A further 13 states have signed but not ratified the protocol: Angola, Belgium, Cameroon, Chad, Republic of the Congo, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Ireland, Sierra Leone, Slovakia, Timor-Leste, Venezuela, and Zambia.[1]
See also
- Istanbul Protocol
- International Rehabilitation Council for Torture Victims
- Center for Victims of Torture
References
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j "Parties to the Optional Protocol to the Convention against Torture and Other Cruel, Inhuman or Degrading Treatment or Punishment". United Nations Treaty Collection. Retrieved 25 August 2023.
- ^ OPCAT Archived 2008-05-05 at the Wayback Machine, Article 28. Retrieved on 30 December 2008.
- ^ OPCAT Archived 2008-05-05 at the Wayback Machine, Article 27. Retrieved on 30 December 2008.
- ^ OPCAT Archived 2008-05-05 at the Wayback Machine, Article 37. Retrieved on 30 December 2008.
External links
- Text of the protocol — Office of the United Nations High Commissioner for Human Rights
- List of parties
- Association for the Prevention of Torture
- The Center for Victims of Torture
- Anti-torture treaties
- Human rights instruments
- United Nations treaties
- Treaties concluded in 2002
- Treaties entered into force in 2006
- Treaties of Albania
- Treaties of Argentina
- Treaties of Armenia
- Treaties of Austria
- Treaties of Azerbaijan
- Treaties of Belize
- Treaties of Benin
- Treaties of Bolivia
- Treaties of Bosnia and Herzegovina
- Treaties of Brazil
- Treaties of Bulgaria
- Treaties of Burkina Faso
- Treaties of Burundi
- Treaties of Cambodia
- Treaties of Cape Verde
- Treaties of the Central African Republic
- Treaties of Chile
- Treaties of Costa Rica
- Treaties of Croatia
- Treaties of Cyprus
- Treaties of the Czech Republic
- Treaties of the Democratic Republic of the Congo
- Treaties of Denmark
- Treaties of Ecuador
- Treaties of Estonia
- Treaties of Finland
- Treaties of France
- Treaties of Gabon
- Treaties of Georgia (country)
- Treaties of Germany
- Treaties of Ghana
- Treaties of Greece
- Treaties of Guatemala
- Treaties of Honduras
- Treaties of Hungary
- Treaties of Italy
- Treaties of Kazakhstan
- Treaties of Kyrgyzstan
- Treaties of Lebanon
- Treaties of Liberia
- Treaties of Liechtenstein
- Treaties of Lithuania
- Treaties of Luxembourg
- Treaties of Madagascar
- Treaties of the Maldives
- Treaties of Mali
- Treaties of Malta
- Treaties of Mauritania
- Treaties of Mauritius
- Treaties of Mexico
- Treaties of Mongolia
- Treaties of Montenegro
- Treaties of Morocco
- Treaties of Mozambique
- Treaties of Nauru
- Treaties of the Netherlands
- Treaties of New Zealand
- Treaties of Nicaragua
- Treaties of Niger
- Treaties of Nigeria
- Treaties of Norway
- Treaties of Panama
- Treaties of Paraguay
- Treaties of Peru
- Treaties of the Philippines
- Treaties of Poland
- Treaties of Portugal
- Treaties of Romania
- Treaties of Rwanda
- Treaties of Moldova
- Treaties of the State of Palestine
- Treaties of Sri Lanka
- Treaties of Senegal
- Treaties of Serbia
- Treaties of Slovenia
- Treaties of South Sudan
- Treaties of Spain
- Treaties of Sweden
- Treaties of Switzerland
- Treaties of North Macedonia
- Treaties of Togo
- Treaties of Tunisia
- Treaties of Turkey
- Treaties of Ukraine
- Treaties of the United Kingdom
- Treaties of Uruguay
- 2002 in New York City
- Treaties adopted by United Nations General Assembly resolutions
- Treaties extended to Greenland
- Treaties extended to the Faroe Islands
- Treaties extended to the Isle of Man
