TOPEX/Poseidon
 Artist's rendering of the TOPEX/Poseidon satellite. | |
| Mission type | Remote sensing |
|---|---|
| Operator | NASA and CNES |
| COSPAR ID | 1992-052A |
| SATCAT no. | 22076 |
| Mission duration | Achieved: 13 years, 5 months In Orbit: 32 years, 4 months, 1 day |
| Spacecraft properties | |
| Launch mass | 2,400 kilograms (5,300 lb) |
| Start of mission | |
| Launch date | 10 August 1992 |
| Rocket | Ariane 42P |
| Launch site | Guiana Space Centre, Kourou |
| End of mission | |
| Declared | January 2006 |
| Orbital parameters | |
| Reference system | Geocentric |
| Regime | Non Sun-synchronous |
| Eccentricity | 0.000[1] |
| Perigee altitude | 1,340 kilometers (830 mi)[1] |
| Apogee altitude | 1,340 kilometers (830 mi)[1] |
| Inclination | 66 degrees[1] |
| Period | 112 minutes[1] |
TOPEX/Poseidon was a joint satellite altimeter mission between NASA, the U.S. space agency; and CNES, the French space agency, to map ocean surface topography. Launched on August 10, 1992, it was the first major oceanographic research satellite. TOPEX/Poseidon helped revolutionize oceanography by providing data previously impossible to obtain. Oceanographer Walter Munk described TOPEX/Poseidon as "the most successful ocean experiment of all time."[2] A malfunction ended normal satellite operations in January 2006.[3]
Description
Before TOPEX/Poseidon, scientists had only a brief glimpse of Earth's ocean as a whole from the pioneering but short-lived Seasat satellite. TOPEX/Poseidon's radar altimeter provided the first continuous global coverage of the surface topography of the oceans. From orbit 1,330 kilometers above Earth, TOPEX/Poseidon provided measurements of the surface height of 95 percent of the ice-free ocean to an accuracy of 3.3 centimeters. The satellite's measurements of the hills and valleys of the sea surface led to a fundamentally new understanding of ocean circulation and its effect on climate.
Goal
The mission's most important achievement was to determine the patterns of ocean circulation - how heat stored in the ocean moves from one place to another. Since the ocean holds most of the Earth's heat from the Sun, ocean circulation is a driving force of climate. TOPEX/Poseidon made it possible for the first time to compare computer models of ocean circulation with actual global observations and use the data to improve climate predictions.[4]
Results
While a three-year prime mission was planned, TOPEX/Poseidon delivered more than 10 years of data from orbit.[5] In those years, the mission:
- Measured sea level with an unprecedented accuracy
- Mapped global tides for the first time
- Monitored effects of currents on global climate change and produced the first global views of seasonal changes of currents
- Monitored large-scale ocean features like Rossby and Kelvin waves and studied such phenomena as El Niño, La Niña, and the Pacific Decadal Oscillation
- Mapped basin-wide current variations and provided global data to validate models of ocean circulation
- Mapped year-to-year changes in heat stored in the upper ocean
- Improved our knowledge of Earth's gravity field
- Observed the temperature of the ocean and main seas for over a period of 10 years
TOPEX/Poseidon was launched using an Ariane 42P expendable launch vehicle, along with Korea Institute of Technology's Kitsat-1 satellite and France's S80/T satellite . Lift-off from Kourou in French Guiana took place on 1992-08-10. At lift-off the mass of the satellite was 2,402 kilograms (5,296 lb).[6] The mission was named after the ocean TOPography EXperiment and the Greek god of the ocean Poseidon.
In October 2005 after more than 62,000 orbits, TOPEX/Poseidon stopped providing science data after a momentum wheel malfunctioned, and the satellite was turned off on January 18, 2006.[3]
Use of results
TOPEX/Poseidon's data have been the subject of more than 2,100 research publications.[3] Some of the areas in which the data are used include:[7]
- Climate Research
- Coral Reef Research
- El Niño & La Niña Forecasting
- Fisheries Management
- Hurricane Forecasting
- Marine Mammal Research
- Offshore Industries
- Ship Routing
Measurements continue
TOPEX/Poseidon's follow-on mission, Jason-1,[8] was launched in 2001 to continue the ongoing measurements of sea surface topography. The two satellites, TOPEX/Poseidon and Jason-1, flew in a tandem mission for three years providing twice the coverage of the sea surface and allowing scientists to study smaller features than could be seen by one satellite.
The record of global sea surface height begun by TOPEX/Poseidon and Jason-1 continues into the future with the Ocean Surface Topography Mission on the Jason-2 satellite, which launched in June 2008.[9] The Jason-3 mission launched January 17, 2016.[10][11]
Instruments
TOPEX/Poseidon flew two onboard altimeters sharing the same antenna, but only one altimeter was operated at any time, with TOPEX given preference (on average 9 in 10 cycles during the first 10 years of the mission).
- TOPEX: The NASA-built Nadir pointing Radar Altimeter using C band (5.3 GHz) and Ku band (13.6 GHz) for measuring height above sea surface.
- Poseidon: The CNES-built solid state Nadir pointing Radar Altimeter using Ku band (13.65 GHz).

In addition to the altimeters, the TOPEX Microwave Radiometer (TMR) operating at 18, 21, and 37 GHz was used to correct for atmospheric wet path delay.[clarification needed]
The satellite was also equipped with instruments to accurately pinpoint its location. Precise orbit determination is crucial because errors in locating the spacecraft would distort the sea level measurement calculated from the altimeter readings.
Three independent tracking systems determined the position of the spacecraft. The first, the NASA laser retroreflector array (LRA) reflected laser beams from a network of 10 to 15 ground-based laser ranging stations under clear skies. The second, for all-weather, global tracking, was provided by the CNES Doppler Orbitography and Radiopositioning Integrated by Satellite tracking system receiver (DORIS). This device uses microwave doppler techniques (changes in radio frequency corresponding to relative velocity) to track the spacecraft. DORIS consists of an on-board receiver and a global network of 40 to 50 ground-based transmitting stations.
The third system used an on-board experimental Global Positioning System (GPS) demonstration receiver to precisely determine the satellite's position continuously by analyzing the signals received from the U.S. Air Force's GPS constellation of Earth-orbiting satellites. TOPEX/Poseidon was the first mission to demonstrate that the Global Positioning System could be used to determine a spacecraft's exact location and track it in orbit. Knowing the satellite's precise position to within 2 centimeters (less than 1 inch) in altitude was a key component in making accurate ocean height measurements possible.
A number of satellites (See links) use exotic dual-band radar altimeters to measure height from a spacecraft. That measurement, coupled with orbital elements (possibly from GPS), enables determination of the topography. The two lengths of radio waves permit the altimeter to automatically correct for varying delays in the ionosphere.
Gallery
-
The Ariane 4 rocket, with TOPEX/Poseidon on board.
-
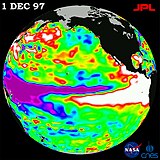
The 1997-98 El Nino
-
Jason-1 continued the same sea surface measurements begun by TOPEX/Poseidon, later succeeded by the Ocean Surface Topography Mission on Jason-2, and then Jason-3.
-
Diagram of the various systems on board.
See also
- French space program
- 1992 in spaceflight
- 2004 Indian Ocean earthquake
- Jason 1
- Ocean Surface Topography Mission/Jason-2
- Seasat
- Sea level rise
References
- ^ a b c d e "TOPEX/Poseidon". International Laser Ranging Service.
- ^ Munk.W.: Testimony Before the U.S. Commission on Ocean Policy, April 2002, http://govinfo.library.unt.edu/oceancommission/meetings/apr18_19_02/munk_statement.pdf
- ^ a b c "NASA's Topex/Poseidon Oceanography Mission Ends". NASA.
- ^ "Topex/Poseidon Sails Off Into the Sunset". NASA/JPL.
- ^ "Ocean Surface Topography from Space". NASA/JPL. Archived from the original on 2001-10-23.
- ^ "Topex/Poseidon - NSSDC ID: 1992-052A". NASA.
- ^ "Ocean Surface Topography from Space". NASA/JPL. Archived from the original on 2001-12-30.
- ^ "Ocean Surface Topography from Space". NASA/JPL. Archived from the original on 2001-10-11.
- ^ "NASA Launches Ocean Satellite to Keep a Weather, Climate Eye Open". NASA.
- ^ "CEOS Ocean Surface Topography (OST) Constellation Strategic Workshop". Eumetsat. Archived from the original on November 14, 2008.
- ^ "Jason-3". NASA JPL. Archived from the original on 2011-08-13.
External links
- Official site at CNES
- Official site at NASA
- TOPEX/Poseidon technical page at NASA (archived)
- Current technical page at NASA
- University of Colorado Sea Level Change site
- NASA TOPEX/Poseidon fact sheet
- TOPEX/Poseidon and Jason-1 data are available at http://sealevel.colorado.edu/ and http://podaac.jpl.nasa.gov/.