London Borough of Harrow
London Borough of Harrow | |
|---|---|
| Motto(s): Salus populi suprema lex (The well-being of the people is the highest law)[1] | |
 Harrow shown within Greater London | |
| Coordinates: 51°34′N 0°20′W / 51.567°N 0.333°W | |
| Sovereign state | United Kingdom |
| Constituent country | England |
| Region | London |
| Ceremonial county | Greater London |
| Created | 1 April 1965 |
| Admin HQ | Civic Centre Station Road Harrow |
| Government | |
| • Type | London borough council |
| • Body | Harrow London Borough Council |
| • Leadership | Leader and Cabinet (Conservative) |
| • Mayor | Cllr Janet Mote[2] |
| • London Assembly | Krupesh Hirani AM for Brent and Harrow |
| • MPs | Gareth Thomas Bob Blackman David Simmonds |
| • Council leader | Cllr Paul Osborn (Conservative)[3] |
| Area | |
• Total | 19.49 sq mi (50.47 km2) |
| • Rank | 243rd (of 296) |
| Population (2022) | |
• Total | 261,185 |
| • Rank | 71st (of 296) |
| • Density | 13,000/sq mi (5,200/km2) |
| Time zone | UTC (GMT) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+1 (BST) |
| Postcodes | |
| Area code | 020 |
| ISO 3166 code | GB-HRW |
| ONS code | 00AQ |
| GSS code | E09000015 |
| Police | Metropolitan Police |
| Website | http://www.harrow.gov.uk/ |
The London Borough of Harrow (/ˈhæroʊ/)[4] is a London borough in northwest London, England; it forms part of Outer London. It borders four other London boroughs – Barnet to the east of ancient Watling Street (now the A5 road), Brent to the southeast, Ealing to the south and Hillingdon to the west – plus the Hertfordshire districts of Three Rivers and Hertsmere to the north. The local authority is Harrow London Borough Council. The London borough was formed in 1965, based on boundaries that had been established in 1934. The borough is made up of three towns: Harrow, Pinner and Stanmore, but also includes western parts of Edgware.
Administrative history
The modern borough has its roots in three Ancient Parishes: Harrow on the Hill and the much smaller areas of Great Stanmore and Little Stanmore (also known as Whitchurch). These had consistent boundaries from the High Middle Ages down to the modern era. Pinner became independent of Harrow on the Hill in 1766 and the remaining area split into four daughter parishes in 1894: Harrow Weald, Harrow, Wealdstone and Wembley (the latter now part of the London Borough of Brent).[5]

Harrow Urban District was formed in 1934 as an urban district of Middlesex by the Middlesex Review Order 1934, as a merger of the former area of Harrow on the Hill Urban District, Wealdstone Urban District and most of Hendon Rural District. The local authority was Harrow Urban District Council.
The urban district gained the status of municipal borough on 4 May 1954 and the urban district council became Harrow Borough Council. The 50th anniversary of the incorporation as a borough was celebrated in April 2004, which included a visit by Queen Elizabeth II.
In 1965, the municipal borough was abolished, and its former area was transferred to Greater London from Middlesex under the London Government Act 1963 to form the London Borough of Harrow. It is the only London borough to replicate almost exactly the unchanged boundaries of a single former district.[6] This was probably because its population was large enough; according to the 1961 census, it had a population of 209,080, making it the largest local government district in Middlesex. Harrow's boundaries, however, have been altered slightly, as it originally included part of Elstree; on 1 April 1993 this was transferred to Hertfordshire (and its district of Hertsmere).[7]
The coat of arms were first granted to Harrow Urban District Council in 1938. Supporters to the arms were granted in 1954, when the urban district was incorporated as a municipal borough. The municipal borough became the London Borough of Harrow in 1965, with unaltered boundaries, and thus the council retained use of the arms. The arms are also used by Harrow Borough F.C. The motto reads as "Salus Populi Suprema Lex" which translates from Latin as "The well-being of the people is the highest law."[8]
Demographics

Location
Its site on and near the greenbelt and ease of access to central London (20 minutes by train to Marylebone and 12 minutes to Euston via West Midlands Trains) make Harrow a convenient place to live. Rising property prices in all London areas have helped to see a large increase in property redevelopment of its existing Edwardian and 1920s to 1940s housing stock.
Ethnicity

Harrow is a diverse borough, having 63.8% of its population from the BME (Black and Minority Ethnic) communities, with the largest group being of Indian ethnicity (specifically those from Gujarat and South India). The borough can also claim to have the largest concentration of Sri Lankan Tamils in the UK and Ireland as well as having the highest density of Gujarati Hindus in the UK.[9]
| Ethnic Group | 1981 estimations[10] | 1991[11] | 2001[12] | 2011[13] | 2021[14] | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | % | Number | % | Number | % | Number | % | Number | % | |
| White: Total | 164,957 | 84.7% | 147,669 | 73.7% | 121,543 | 58.77% | 100,991 | 42.07% | 95,233 | 36.46% |
| White: British | – | – | – | – | 103,207 | 49.90% | 73,826 | 30.8% | 53,567 | 20.51% |
| White: Irish | – | – | – | – | 9,057 | 4.38% | 7,336 | 3.0% | 5,608 | 2.15% |
| White: Gypsy or Irish Traveller | – | – | – | – | – | – | 181 | 0.07% | 179 | 0.07% |
| White: Other | – | – | – | – | 9,279 | 4.49% | 19,648 | 8.2% | 34,458 | 13.19% |
| Asian or Asian British: Total | – | – | 41,360 | 20.6% | 61,314 | 29.65% | 101,808 | 42.2% | 118,152 | 45.23% |
| Asian or Asian British: Indian | – | – | 32,145 | 16.1% | 45,310 | 21.91% | 63,051 | 26.3% | 74,744 | 28.62% |
| Asian or Asian British: Pakistani | – | – | 2,339 | 1.2% | 4,317 | 2.09% | 7,797 | 3.2% | 10,264 | 3.93% |
| Asian or Asian British: Bangladeshi | – | – | 546 | 0.3% | 953 | 0.46% | 1,378 | 0.5% | 1,820 | 0.70% |
| Asian or Asian British: Chinese | – | – | 1,797 | 0.9% | 2,567 | 1.24% | 2,629 | 1.0% | 2,784 | 1.07% |
| Asian or Asian British: Other Asian | – | – | 4,533 | 2.3% | 10,734 | 5.19% | 26,953 | 11.2% | 28,540 | 10.93% |
| Black or Black British: Total | – | – | 7,459 | 3.7% | 12,703 | 6.14% | 19,708 | 8.1% | 19,151 | 7.33% |
| Black or Black British: African | – | – | 1,699 | 0.8% | 5,656 | 2.73% | 8,526 | 3.5% | 10,584 | 4.05% |
| Black or Black British: Caribbean | – | – | 4,411 | 2.2% | 6,116 | 2.96% | 6,812 | 2.8% | 6,514 | 2.49% |
| Black or Black British: Other Black | – | – | 1,349 | 0.7% | 931 | 0.45% | 4,370 | 1.8% | 2053 | 0.79% |
| Mixed or British Mixed: Total | – | – | – | – | 5,840 | 2.82% | 9,499 | 3.8% | 9,833 | 3.76% |
| Mixed: White and Black Caribbean | – | – | – | – | 1,371 | 0.66% | 2,344 | 0.9% | 2,187 | 0.84% |
| Mixed: White and Black African | – | – | – | – | 633 | 0.31% | 1,053 | 0.4% | 1,104 | 0.42% |
| Mixed: White and Asian | – | – | – | – | 2,018 | 0.98% | 3,417 | 1.4% | 3,140 | 1.20% |
| Mixed: Other Mixed | – | – | – | – | 1,818 | 0.88% | 2,685 | 1.1% | 3,402 | 1.30% |
| Other: Total | – | – | 3,612 | 1.8% | 2,847 | 1.38% | 7,050 | 2.8% | 18,836 | 7.21% |
| Other: Arab | – | – | – | – | – | – | 3,708 | 1.5% | 6,239 | 2.39% |
| Other: Any other ethnic group | – | – | 3612 | 1.8% | 2,847 | 1.38% | 3,342 | 1.3% | 12,597 | 4.82% |
| Ethnic minority: Total | 29,761 | 15.3% | 52,431 | 26.1% | 85,271 | 41.23% | 138,065 | 57.93% | 165,972 | 63.54% |
| Total | 194,718 | 100% | 200,100 | 100% | 206,814 | 100.00% | 239,056 | 100.00% | 261,205 | 100.00% |
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
|---|---|---|
| 1801 | 3,240 | — |
| 1811 | 3,969 | +22.5% |
| 1821 | 4,383 | +10.4% |
| 1831 | 5,342 | +21.9% |
| 1841 | 5,829 | +9.1% |
| 1851 | 5,980 | +2.6% |
| 1861 | 7,424 | +24.1% |
| 1871 | 8,869 | +19.5% |
| 1881 | 10,313 | +16.3% |
| 1891 | 12,231 | +18.6% |
| 1901 | 22,683 | +85.5% |
| 1911 | 42,065 | +85.4% |
| 1921 | 64,431 | +53.2% |
| 1931 | 98,694 | +53.2% |
| 1941 | 146,617 | +48.6% |
| 1951 | 217,811 | +48.6% |
| 1961 | 210,424 | −3.4% |
| 1971 | 203,309 | −3.4% |
| 1981 | 196,147 | −3.5% |
| 1991 | 203,769 | +3.9% |
| 2001 | 207,389 | +1.8% |
| 2011 | 239,056 | +15.3% |
| Source: A Vision of Britain through time, citing Census population | ||
Wards with the highest white British population were:
- Pinner
- Pinner South (a long-stretched ward covering Pinner Village, the area west of North Harrow and Rayners Lane, and east of Eastcote)
- Stanmore Park (an area mostly covering Stanmore)
The lowest wards meanwhile were:
- Kenton East (the area west of Honeypot Lane, bordering Kenton Lane),
- Queensbury (the area north of the station, around Honeypot Lane)
Since 2005, on the last Sunday in June Harrow Council hosts Under One Sky - Harrow's largest festival, to celebrate and the joint communities of Harrow. This has a programme of dance, world music, sports activity, youth music, spoken word, free children's activity, a carnival parade, information and stalls, health promotion, a world food zone and outside radio broadcast.
Religion
Religion in Harrow (2021)[15]

Harrow is the most religiously diverse local authority area in the UK, with a 62% chance that two random people are from different religions, according to Office for National Statistics, October 2006.[16] According to the 2011 census, 25.3% of Harrow's population identified themselves as Hindu - the highest in the UK. A large number of Jewish people live in Stanmore and Hatch End. The Stanmore and Canons Park Synagogue boasts the largest membership of any single synagogue in the whole of Europe.[17] Harrow also has a sizable Muslim community, about 1 in 10 of its population.
As per the 2011 census, Harrow has a larger than average Jewish, Hindu and Muslim population.
| Religion - 2021[18] | Harrow % |
National % |
|---|---|---|
| Christianity | 33.9 | 46.3 |
| Hinduism | 25.8 | 1.8 |
| Islam | 15.9 | 6.7 |
| Judaism | 2.8 | 0.5 |
| Jainism | 2.4 | 0.0 |
| Buddhism | 1.1 | 0.5 |
| Sikhism | 1.1 | 0.9 |
| No religion | 10.6 | 36.7 |
| Religion not stated | 5.9 | 6.0 |
Other
In a national detailed Land Use Survey by the Office for National Statistics in 2005 it was found that the London Borough of Harrow had the second highest proportion of land being domestic gardens: 34.7% of all 326 districts in England; this compared with the London Borough of Sutton's 35.1% (highest proportion nationally) and Bournemouth's 34.6%.[19]
Arts and culture
The first and only contemporary artist-led gallery in Harrow was set up in 2010 by the Usurp Art Collective. The space is called the Usurp Art Gallery & Studios and is based in West Harrow, a bohemian part of Harrow. Usurp Art provides professional support to artists and runs the only public artists studios in the borough. It is a flagship project for Arts Council England.[20][21][22][23]
There are 289 listed buildings located in the London Borough of Harrow, including more than 80 in Harrow-on-the-Hill ward and over 50 in Pinner ward.[24] Grade I and II* buildings in the borough include the Church of St Lawrence, Stanmore and Headstone Manor, and Grade II listed buildings include Bentley Priory, Grim's Dyke and Harrow and Wealdstone station.
Economy
Major employers included Kodak,[25] the Royal National Orthopaedic Hospital and Ladbrokes, which formally has its headquarters in Harrow.[26]
Crime
Crime figures are generally lower compared to the Greater London average; the borough had 2,618 notifiable offences in April 2009, compared with an average of 2,204 across London's boroughs.[27] Between the annual year of June 2017 to June 2018, Harrow was ranked 28th out of the 32 London boroughs in terms of number of criminal offences,[28] and recording just one murder in the period.[29] The Pinner South ward was recorded as having the lowest crime rate out of all wards of Greater London in 2014/15.[30]
Sport and leisure
The London Borough of Harrow has 4 non league football clubs: Barnet F.C., who moved to The Hive Stadium from the neighbouring London Borough of Barnet in 2013 who play in the National League (division); and three non-League clubs: Wealdstone FC who play at The Vale, Harrow Borough F.C. who play at Earlsmead Stadium and Rayners Lane F.C. who play at the Tithe Farm Social Club. Five of the 30 cricket clubs which play in the Middlesex County Cricket League are based in the London Borough of Harrow: Harrow, Harrow St Mary's, Harrow Town, Kenton and Stanmore. Hatch End Cricket Club previously played at Shaftesbury playing fields in Hatch End but following an arson attack on their clubhouse and a subsequent failure to raise enough funds to build a new one, the club moved to Elstree in 2011.
Harrow also had a professional rugby league team when London Broncos played at The Hive Stadium in 2014 and 2015. The club relocated to Ealing from 2016 onwards.
Governance
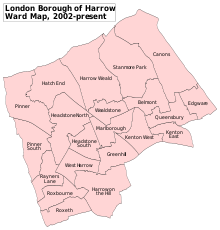

Harrow is divided into 21 wards, each represented by three councillors on Harrow London Borough Council. After the most recent council elections, the borough is controlled by the Labour party. The number of councillors are as follows: Conservative 31, Labour 24.[31]
Revised ward boundaries will be used for the May 2022 local elections following a review by the Local Government Boundary Commission which made its final recommendations in May 2019.[32]
Greater London representation
For elections to the Greater London Council, the borough formed the Harrow electoral division, electing three members. In 1973 it was divided into the single-member Harrow Central, Harrow East, and Harrow West electoral divisions.[33] The Greater London Council was abolished in 1986.
Since 2000, for elections to the London Assembly, the borough forms part of the Brent and Harrow constituency.
Education
The borough is often perceived as having a good educational record, and features many state-funded primary and secondary schools as well as a handful of large tertiary colleges.
For a long time the secondary schools of Harrow did not feature integrated sixth form education, with all school leavers having to join the tertiary colleges such as Harrow College and Stanmore College, or the faith-based St Dominic's Sixth Form College. The tertiary system was implemented in 1987 after years of discussions and delays, with Harrow becoming the first London borough with a complete change to tertiary; the Pinner Observer called it an education "revolution".[34][35] There have been critics of the tertiary colleges, with many arguing the standard of education does not continue the standard set by the Borough's secondary schools. The council eventually went into another re-organisation, creating the Harrow Sixth Form Collegiate, a co-ordinated partnership between many of the borough's secondary schools, which led to the first admission of school sixth form students in September 2008.[36] Both Catholic faith-based Salvatorian College and Sacred Heart Language College were unaffected, the students of which could transfer to St Dominic's Sixth Form College.
From September 2010, the primary sector was modified to enable transfer to secondary education at age 11 in line with other London Boroughs.[37]
The Borough has a Music Service which provides instrumental tuition for 15% of all Harrow state sector pupils (the national figure is 8% of all state pupils receiving instrumental tuition) and a range of ensemble opportunities for pupils.[38]
The independent schools of the Borough are dominated by the presence of Harrow School and John Lyon School for boys and North London Collegiate School for girls which consistently rank as among the best schools in the country. Notable independent primary schools include Orley Farm School and Reddiford School, both of which are co-educational.
There are also a number of voluntary aided schools in the Borough. These include: Salvatorian College (Roman Catholic, boys), Sacred Heart Language College (Roman Catholic, girls) and Moriah Jewish Day School (Jewish, co-ed).
There are two special needs high schools; Kingsley High School (co-ed) and Shaftesbury High School (co-ed).
Other state secondary schools in the London Borough of Harrow are: Whitefriars High School (co-ed); Bentley Wood High School (girls); Canons High School (co-ed); Harrow High School (co-ed); Hatch End High School (co-ed); Nower Hill High School (co-ed); Park High School (co-ed); Rooks Heath School (co-ed); Whitmore High School (co-ed). Mountview High School in Wealdstone - a comprehensive school formed out of Whitefriars Secondary Modern in the early 1970s - closed in 1986 with the site being partially redeveloped into industrial units. The catchment area was dispersed between Nower Hill and Hatch End Schools.
Middle schools include Whitchurch Middle School.
- GCSE examination performance
| School | A*-C Pass Rate 2008 |
A*-C Pass Rate 2009 |
A*-C Pass Rate 2010 |
English Baccalaureate Pass Rate 2010 |
A*-C Pass Rate 2011 |
English Baccalaureate Pass Rate 2011 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bentley Wood High School | 59% | 58% | 61% | 30% | 69% | 36% |
| Canons High School | 49% | 46% | 54% | 2% | 52% | 12% |
| Harrow High School | 52% | 43% | 31% | 5% | 35% | 3% |
| Hatch End High School | 51% | 59% | 55% | 24% | 49% | 20% |
| Nower Hill High School | 68% | 57% | 79% | 27% | 78% | 16% |
| Park High School | 66% | 72% | 66% | 15% | 71% | 23% |
| Rooks Heath School | 37% | 42% | 52% | 11% | 48% | 12% |
| Sacred Heart College | 76% | 86% | 77% | 53% | 84% | 59% |
| Salvatorian College | 67% | 67% | 74% | 27% | 73% | 26% |
| Whitmore High School | 65% | 64% | 60% | 35% | 70% | 40% |
| Average for London Borough of Harrow | 57.7% | 60.8% | 60.7% | 22.6% | tba | tba |
| Average for England | 47.6% | 50.7% | 55.2% | 15.1% | tba | tba |
- The table on shows the percentage of students gaining five A* to C grades, including English and Maths, for state schools in the London Borough of Harrow
- The rightmost column shows the percentage of students gaining five A* to C grades, in five core subjects - maths, English, two science qualifications, a foreign language and either history or geography.
- Source: Department for Education[39]
All of Harrow's pupils have the chance to be elected onto the Harrow Youth Parliament. This is a group of around 50 young people in the Borough who come together to work on projects that benefit other young people. They are also the official youth voice for the council and are in constant communication with the council on all youth matters.
Notable residents
Districts and postcodes
Transport
The London Borough of Harrow was historically in the heart of an area known as "Metro-land" and therefore is very well served by the London Underground compared with other boroughs in Outer London. It is located near the northwestern extremity of the modern-day network, with 4 lines serving the area. The Bakerloo and Jubilee lines terminate in the borough, at Harrow and Stanmore respectively. Meanwhile, the Piccadilly and Metropolitan lines pass through the southern edge of the borough on shared track before both terminating at Uxbridge. The Northern line terminates just outside Harrow at Edgware tube station in the London Borough of Barnet.
The London Overground also serves the borough, sharing track with the Bakerloo line between Queens Park and Harrow & Wealdstone before it continues beyond the latter station to eventually terminate at Watford Junction.
The numerous National Rail, London Overground and London Underground stations in the borough are:
- Canons Park
- Harrow & Wealdstone
- Harrow-on-the-Hill
- Hatch End
- Headstone Lane
- North Harrow
- Pinner
- Rayners Lane
- South Harrow
- Stanmore
- Sudbury Hill
- Sudbury Hill Harrow
- West Harrow
In March 2011, the main forms of transport that residents used to travel to work were: driving a car or van, 27.5% of all residents aged 16–74; underground, metro, light rail, tram, 5.9%; bus, minibus or coach, 5.9%; train, 4.5%; on foot, 4.3%; work mainly at or from home, 3.5%; passenger in a car or van, 1.6%.[40]
Town twinning
Harrow is twinned with:
 Douai, France
Douai, France
Freedom of the Borough
The following people and organisations have received the Freedom of the Borough of Harrow.
Individuals
- Sir Winston Churchill: 30 December 1955.[41]
- Sir Roger Bannister: May 2004.[42]
- Keith Toms: 26 November 2020.[43]
Military units
- 131 Independent Commando Squadron, Corps of Royal Engineers (Volunteers): 10 March 1983.
- 47 (Middlesex Yeomanry) Signal Squadron, 31st (Greater London) Signal Regiment Royal Corps of Signals: 10 March 1983.
- 257 (Southern) General Hospital Royal Army Medical Corps (Volunteers): 10 March 1983.
- RAF Stanmore Park: 20 October 1988.
- RAF Bentley Priory: 20 October 1988.
- Roxeth & Harrow Company, Church Lads' & Church Girls' Brigade: 20 October 1994
- Royal British Legion (Harrow Branch): 18 July 1996.
- Girls' Brigade North West London District: 1 May 2014.
- 1454 (Harrow) Squadron Air Training Corps: 1 May 2014.[44]
See also
References
- ^ Thain, Bruce (13 May 2014). "Translations of borough's motto needed for anniversary". Harrow Times. Retrieved 2 February 2021.
- ^ "The Mayor of Harrow".
- ^ "Councillor Paul Osborn". 24 September 2022.
- ^ Wells, John C. (2008), Longman Pronunciation Dictionary (3rd ed.), Longman, p. 368, ISBN 9781405881180
- ^ Youngs, Frederic A Jr. (1979). Guide to the Local Administrative Units of England, Vol.I: Southern England. London: Royal Historical Society. ISBN 0-901050-67-9
- ^ "The naming of the London Boroughs: Part One". LCC Municipal. 29 June 2018. Retrieved 20 August 2023.
- ^ "Elstree and Potters Bar". UK Births, Marriages and Deaths. Retrieved 8 November 2021.
- ^ "HARROW, LONDON BOROUGH OF". civicheraldry.co.uk.
- ^ "London against gun and knife crime". Archived from the original on 30 September 2007.
- ^ Equality, Commission for Racial (1985). "Ethnic minorities in Britain: statistical information on the pattern of settlement". Commission for Racial Equality: Table 2.2.
- ^ "1991 census – theme tables". NOMIS. Retrieved 20 January 2017.
- ^ "KS006 - Ethnic group". NOMIS. Retrieved 30 January 2016.
- ^ "Ethnic Group by measures". NOMIS. Retrieved 8 January 2016.
- ^ "Ethnic group - Office for National Statistics". www.ons.gov.uk. Retrieved 29 November 2022.
- ^ "Religion - Religion in England and Wales (detailed dataset including Jain: Census 2021, ONS".
- ^ "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 9 January 2007. Retrieved 9 January 2007.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link). National Statistics. Retrieved 8 October 2006. - ^ "Partnership2Gether". The Jewish Agency. Archived from the original on 26 April 2011. Retrieved 19 April 2018.
- ^ "Religion - Religion in England and Wales: Census 2021, ONS".
- ^ Physical Environment: Land Use Survey 2005 published alongside the data of the 2011 census see Physical Environment.
- ^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 4 September 2012. Retrieved 23 October 2012.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ^ "All the news from Harrow - getwestlondon". www.harrowobserver.co.uk. Retrieved 19 April 2018.
- ^ "Lifestyle: lifestyle news for West London - Get West London". www.harrowobserver.co.uk. Retrieved 19 April 2018.
- ^ "Home and Away: Group for War and Culture Studies – the Institute for Modern and Contemporary Culture – IMCC the Institute for Modern and Contemporary Culture". Archived from the original on 14 January 2013. Retrieved 23 October 2012.
- ^ "Listed Buildings in Harrow". britishlistedbuildings.co.uk. Retrieved 27 October 2022.
- ^ Bruce Thain (16 December 2013). "Kodak: 123 years of history in Harrow". Harrow Times. Retrieved 30 March 2014.
After more than a century in the borough Kodak has announced it is set to stay.... Kodak has sold off large parts of the Harrow site for development.
- ^ Draft Core Strategy Retrieved on 20 October 2013.
- ^ "Police web site download in Excel format". Archived from the original on 25 April 2012.
- ^ "Which London boroughs are the most dangerous? | Metro News". Metro.co.uk. 31 July 2018. Retrieved 4 May 2020.
- ^ Robin De Peyer (23 June 2018). "Revealed: The boroughs with the highest (and lowest) murder rates in London | London Evening Standard". Standard.co.uk. Retrieved 4 May 2020.
- ^ "Ward Profiles and Atlas". Retrieved 4 May 2020.
- ^ "Harrow Council election results".
- ^ "LGBCE | Harrow | LGBCE Site". www.lgbce.org.uk. Retrieved 11 January 2022.
- ^ Boothroyd, David. "Greater London Council Election results: Harrow". United Kingdom Election Results. Archived from the original on 24 March 2016. Retrieved 28 August 2023.
- ^ "Revolution is about to start", Pinner Observer, p. 10, 10 September 1987
- ^ "Tertiary starts", Pinner Observer, p. 3, 3 September 1987
- ^ :"Harrow Sixth Form College: Decision Makers' Guidance" (PDF). Harrow Council. Archived (PDF) from the original on 11 September 2012.
- ^ "School reorganisation to change the ages of transfer". London borough of Harrow. 2009. Archived from the original on 17 April 2009. Retrieved 24 April 2009.
- ^ "Harrow Music Service". Harrow Music Service. Retrieved 19 April 2018.
- ^ "Search for schools and colleges to compare - GOV.UK". Find and compare schools in England.
- ^ "2011 Census: QS701EW Method of travel to work, local authorities in England and Wales". Office for National Statistics. Retrieved 23 November 2013. Percentages are of all residents aged 16-74 including those not in employment. Respondents could only pick one mode, specified as the journey’s longest part by distance.
- ^ Pathé, British. "Churchill At Harrow". www.britishpathe.com.
- ^ "Sir Roger recalls the run of his life". Harrow Times.
- ^ "Former mayor granted freedom of Harrow". Harrow Times.
- ^ "Further info – Freedoms granted by Harrow – Harrow Council". www.harrow.gov.uk. Archived from the original on 23 August 2015. Retrieved 20 August 2015.



