October 1968 lunar eclipse
Appearance
| Total lunar eclipse October 6, 1968 | |
|---|---|
| (No photo) | |
 The moon passes west to east (right to left) across the Earth's umbral shadow, shown in hourly intervals. | |
| Series | 136 (17 of 72) |
| Gamma | 0.36054 |
| Magnitude | 1.16913 |
| Duration (hr:mn:sc) | |
| Totality | 01h02m58.1s |
| Partial | 03h33m57.9s |
| Penumbral | 05h52m07.1s |
| Contacts (UTC) | |
| P1 | 08:45:55.0 |
| U1 | 09:54:55.4 |
| U2 | 11:10:25.7 |
| Greatest | 11:41:56.0 |
| U3 | 12:13:23.8 |
| U4 | 13:28:53.3 |
| P4 | 14:38:02.1 |
A total lunar eclipse took place on Sunday, October 6, 1968, the second of two total eclipses in 1968, the first was on April 13, 1968. The tables below contain detailed predictions and additional information on the total lunar eclipse of October 6, 1968.
| Eclipse characteristics | |
| Parameter | Value |
| Penumbral magnitude | 2.22423 |
| Umbral magnitude | 1.16913 |
| Gamma | 0.36054 |
| Epilson | 0.3345º |
| Opposition times | ||
| Event | Calendar date & time | Julian date |
| Greatest eclipse | 1968 Oct 06 at 11:42:35.0 TD (11:41:56.0 UT1) | 2440135.987453 |
| Ecliptic opposition | 1968 Oct 06 at 11:46:44.1 TD (11:46:05.2 UT1) | 2440135.990337 |
| Equatorial opposition | 1968 Oct 06 at 12:05:11.4 TD (12:04:32.4 UT1) | 2440136.003153 |
| Geocentric coordinates of Sun and Moon | ||
| 1968 Oct 06 at 11:42:35.0 TD (11:41:56.0 UT1) | ||
| Coordinate | Sun | Moon |
| Right ascension | 12h48m51.9s | 00h48m13.3s |
| Declination | -05°14'36.0" | +05°32'13.0" |
| Semi-diameter | 16'00.2" | 15'10.1" |
| Eq. hor. parallax | 08.8" | 0°55'39.9" |
| Geocentric libration of Moon | |
| Angle | Value |
| l | 4.6° |
| b | -0.4° |
| c | -21.4° |
| Earth's shadows | |
| Parameter | Value |
| Penumbral radius | 1.2062° |
| Umbral radius | 0.6728° |
| Prediction parameters | |
| Parameter | Value |
| Ephemerides | JPL DE406 |
| ΔT | 39.0 s |
| Shadow rule | Danjon |
| Shadow enlargement | 1.010 |
| Saros series | 136 (17/72) |
Visibility
[edit]It was completely visible over Asia, Australia, and North America, seen rising over central Asia, and setting over central North America.
Related lunar eclipses
[edit]Lunar year series
[edit]| Lunar eclipse series sets from 1966–1969 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Descending node | Ascending node | |||||||
| Saros | Date Viewing |
Type Chart |
Gamma | Saros | Date Viewing |
Type Chart |
Gamma | |
| 111 | 1966 May 4
|
Penumbral
|
1.05536 | 116 | 1966 Oct 29
|
Penumbral
|
−1.05999 | |
| 121 | 1967 Apr 24
|
Total
|
0.29722 | 126 | 1967 Oct 18
|
Total
|
−0.36529 | |
| 131 | 1968 Apr 13
|
Total
|
−0.41732 | 136 | 1968 Oct 6
|
Total
|
0.36054 | |
| 141 | 1969 Apr 2
|
Penumbral
|
−1.17648 | 146 | 1969 Sep 25
|
Penumbral
|
1.06558 | |
| Last set | 1965 Jun 14 | Last set | 1965 Dec 8 | |||||
| Next set | 1970 Feb 21 | Next set | 1969 Aug 27 | |||||
Saros series
[edit]It was part of Saros series 136.
Tritos series
[edit]- Preceded: Lunar eclipse of November 7, 1957
- Followed: Lunar eclipse of September 9, 1979
Tzolkinex
[edit]- Preceded: Lunar eclipse of August 26, 1961
- Followed: Lunar eclipse of November 18, 1975
Half-Saros cycle
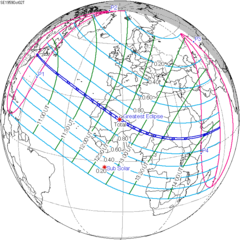
[edit]A lunar eclipse will be preceded and followed by solar eclipses by 9 years and 5.5 days (a half saros).[1] This lunar eclipse is related to two total solar eclipses of Solar Saros 143.
| October 2, 1959 | October 12, 1977 |
|---|---|
|

|
See also
[edit]Notes
[edit]- ^ Mathematical Astronomy Morsels, Jean Meeus, p.110, Chapter 18, The half-saros
External links
[edit]- 1968 Oct 06 chart Eclipse Predictions by Fred Espenak, NASA/GSFC




