Ochre Coloured Pottery culture
 Ochre Coloured Pottery finds ( c.2600 - 1200 BCE ) | |
| Geographical range | North India |
|---|---|
| Period | Bronze Age |
| Dates | c. 2000–1500 BCE |
| Major sites | Ahichchhatra Bahadrabad Bargaon Bisauli Fatehgarh Hastinapur Hulas Jhinjhana Katpalon Kausambi Mitathal Red fort Sinauli |
| Characteristics | Extensive copper metallurgy Burials with pots and copper weapons |
| Preceded by | Neolithic |
| Followed by | Black and red ware Painted Grey Ware culture |
| History of South Asia |
|---|
 |
The Ochre Coloured Pottery culture (OCP) is a Bronze Age culture of the Indo-Gangetic Plain "generally dated 2000–1500 BCE,"[1][2] extending from eastern Punjab to northeastern Rajasthan and western Uttar Pradesh.[3][4]
Artefacts of this culture show similarities with both the Late Harappan culture and the Vedic culture.[5][6] Archaeologist Akinori Uesugi considers it as an archaeological continuity of the previous Harappan Bara style,[7] while according to Parpola, the find of carts in this culture may reflect an Indo-Iranian migration into the India subcontinent, in contact with Late Harappans.[6] The OCP marked the last stage of the North Indian Bronze Age and was succeeded by the Iron Age black and red ware culture and the Painted Grey Ware culture.
Geography and dating

The 'Ochre Coloured Pottery culture is "generally dated 2000-1500 BCE,"[1] Early specimens of the characteristic ceramics found near Jodhpura, Rajasthan, date from the 3rd millennium (this Jodhpura is located in the district of Jaipur and should not be confused with the city of Jodhpur). Several sites of culture flourish along the banks of Sahibi River and its tributaries such as Krishnavati river and Soti river, all originating from the Aravalli range and flowing from south to north-east direction towards Yamuna before disappearing in Mahendragarh district of Haryana.[8] The OCP sites of Atranjikhera, Lal Qila, Jhinjhana and Nasirpur are dated to from 2600 to 1200 BC.[9]

The culture reached the Gangetic plain in the early 2nd millennium. Recently, the Archaeological Survey of India discovered copper axes and some pieces of pottery in its excavation at the Saharanpur district of Uttar Pradesh.[10]
Pottery
The pottery had a red slip but gave off an ochre color on the fingers of archaeologists who excavated it, hence the name. It was sometimes decorated with black painted bands and incised patterns. It is often found in association with copper hoards, which are assemblages of copper weapons and other artifacts such as anthropomorphic figures.
Agriculture
OCP culture was rural and agricultural, characterized by cultivation of rice, barley, and legumes, and domestication of cattle, sheep, goats, pigs, horses, and dogs. Most sites were small villages in size, but densely distributed. Houses were typically made of wattle-and-daub. Other artifacts include animal and human figurines, and ornaments made of copper and terracotta.[11]
Copper hoards

The term copper hoards refers to different assemblages of copper-based artefacts in the northern areas of the Indian Subcontinent that are believed to date from the 2nd millennium BC. Few derive from controlled excavations and several different regional groups are identifiable: southern Haryana/northern Rajasthan, the Ganges-Yamuna plain, Chota Nagpur, and Madhya Pradesh, each with their characteristic artefact types. Initially, the copper hoards were known mostly from the Ganges-Yamuna doab and most characterizations dwell on this material.
Characteristic hoard artefacts from southern Haryana/northern Rajasthan include flat axes (celts), harpoons, double axes, and antenna-hilted swords. The doab has a related repertory. Artefacts from the Chota Nagpur area are very different; they seem to resemble ingots and are votive in character.


The raw material may have been derived from a variety of sources in Rajasthan (Khetri), Bihar, West Bengal, Odisha (especially Singhbhum), and Madhya Pradesh (Malanjkhand).
Relation with Harappan Civilization and Indo-Iranians
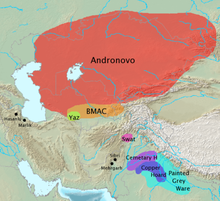
Artefacts of this culture show similarities with both the Late Harappan culture and the Vedic culture,[5][6] and the OCP may have been infiltrated by an Indo-Iranian migration into the India subcontinent coming into contact with Late Harappans.[6]
Various opinions exist on the origins of the OCP. There are relations with the Late Harappan phase, and some consider it as a token of this culture. Others regard it to be an independent cultural style.[12] Archaeologist Akinori Uesugi dates Ochre Coloured Pottery culture to c. 1900-1300 BCE, considering it as a Late Harappan expansion and archaeological continuity of the previous Bara style (c. 2300 and 1900 BCE), which was a regional culture of the Ghaggar valley rooted in the Indus Civilization, calling it the Bara-OCP cultural complex.[7]

Although the archaeologists conducting the investigation describe the chariots buried as horse drawn chariots,[14] one scholar rejects this claim. Similarities have been noted by Parpola between the use of carts, as attested in burial practices at Sinauli, and Indo-Iranian culture.[6][5] Reflecting on these finds, Parpola rejects the identification of these carts as horse-pulled chariots, instead considering them to be ox-pulled carts and part of an early wave of Indo-Iranian settlers, coming into contact with Late Harappan culture:
It seems, then, that the earliest Aryan-speaking immigrants to South Asia, the Copper Hoard people, came with bull-drawn carts (Sanauli and Daimabad) via the BMAC and had Proto-Indo-Iranian as their language. They were, however, soon followed (and probably at least partially absorbed) by early Indo-Aryans.[15]
According to Kumar, while the eastern OCP did not use Indus script, the whole of OCP had nearly the same material culture and likely spoke the same language throughout its expanse. OCP culture was a contemporary neighbor to Harappan civilization, and between 2500 BC and 2000 BC, the people of Upper Ganga valley were using Indus script.[16][12]
See also
References
- ^ a b Benedetti, Giacomo. "The Chronology of Puranic Kings and Rigvedic Rishis in Comparison with the Phases of the Sindhu–Sarasvati Civilization". p. 224.
- ^ Civilsdaily, (15 August 2017). "Case study | Pottery – Evolution and significance".
- ^ Singh 2008, p. 216.
- ^ Kumar 2017, pp. 83–85.
- ^ a b c Gupta & Mani 2017.
- ^ a b c d e Parpola 2020.
- ^ a b Uesugi, Akinori, (2018). "An Overview on the Iron Age in South Asia", in Abstracts for the International Symposium on the Iron Age in South Asia, 2 and 3 June 2018, at Kansai University, Osaka, p. 6: "...During the early second millennium BCE, the Bara-OCP (Ochre-Coloured pottery) cultural complex expanded from the Ghaggar valley to the western part of the Ganga valley. This cultural complex [...] has its origin rooted in the Indus Civilization in the preceding period, its eastward expansion indicates the colonization of the western Ganga valley probably giving great impetus to the Neolithic-Chalcolithic communities in the Ganga valley to transform into a more complex society..."
- ^ Cultural Contours of India: Dr. Satya Prakash Felicitation Volume, Vijai Shankar Śrivastava, 1981. ISBN 0391023586
- ^ Singh 2008, p. 218.
- ^ Ali, Mohammad (28 February 2017). "Copper axes point to an ancient culture story". Archived from the original on 25 April 2018. Retrieved 25 April 2018 – via www.thehindu.com.
- ^ Singh 2008, pp. 216–218.
- ^ a b Singh 2008, pp. 216–217.
- ^ Kumar, Vijay. "A note on Chariot Burials found at Sinauli district Baghpat U.P" (PDF). Indian Journal of Archaeology.
- ^ Kumar, Vijay. "A note on Chariot Burials found at Sinauli district Baghpat U.P" (PDF). Indian Journal of Archaeology.
- ^ Parpola 2020, p. 191.
- ^ Kumar 2017, p. 105.
Sources
- Gupta, S.P., ed. (1995), The lost Sarasvati and the Indus Civilization, Jodhpur: Kusumanjali Prakashan
- Gupta, Vinay; Mani, B.R. (2017). "Painted Grey Ware Culture: Changing Perspectives". Journal of Multidisciplinary Studies in Archaeology: 377–378.
- Kumar, Vijay (October 2017). "Archaeological Gazetteer of Aligarh & Hathras Districts with special reference to OCP & Other Proto-Historic Cultures of Indo-Gangetic Plains" (PDF). Indian Journal of Archaeology. 2 (4): 55–394. Archived from the original on 22 February 2021.
- Parpola, Asko (2020). "Royal "Chariot" burials of Sanauli near Delhi and Archaeological correlates of Prehistoric Indo-Iranian languages". Studia Orientalia Electronica. 8: 176. doi:10.23993/store.98032. S2CID 226331373.
- Sharma, Deo Prakash (2002), Newly Discovered Copper Hoard, Weapons of South Asia (C. 2800-1500 B.C.), Delhi: Bharatiya Kala Prakashan
- Singh, Upinder (2008), A History of Ancient and Early Medieval India From the Stone Age to the 12th Century, ISBN 9788131711200
- Yule, P. (1985), Metalwork of the Bronze Age in India, Munich: C.H. Beck, ISBN 3-406-30440-0
- Yule, P.; Hauptmann, A.; Hughes, M. (1992) [1989], "The Copper Hoards of the Indian Subcontinent: Preliminaries for an Interpretation", Jahrbuch des Römisch-Germanischen Zentralmuseums Mainz: 36, 193–275, ISSN 0076-2741
- Yule, Paul (2014), A New Prehistoric Anthropomorphic Figure from the Sharqiyah, Oman, in: 'My Life is like the Summer Rose' Maurizio Tosi e l'Archeologia come modo de vivere, Papers in Honour of Maurizio Tosi on his 70th Birthday, Oxford: BAR Intern. Series 2690
