Phospholane
Appearance

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Phospholane[1] | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| 605298 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.020.383 |
| EC Number |
|
| 323930 | |
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C4H9P | |
| Molar mass | 88.090 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | colorless liquid |
| Boiling point | 100–103 °C (212–217 °F; 373–376 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
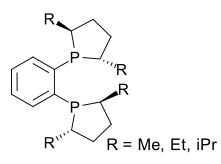
Phospholane is the organophosphorus compound with the formula (CH2)4PH. This colorless liquid is the parent member of a family of five-membered, saturated rings containing phosphorus. Although phospholane itself is only of minor academic interest, the class of C- and P-substituted phospholanes are valued ligands in asymmetric hydrogenation and related areas of homogeneous catalysis.[2] Phospholane is prepared by reduction of 1-chlorophospholane, which in turn is obtained by the reaction of 1-phenylphospholane and phosphorus trichloride.[3]
References
- ^ Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry : IUPAC Recommendations and Preferred Names 2013 (Blue Book). Cambridge: The Royal Society of Chemistry. 2014. pp. 392, 599. doi:10.1039/9781849733069. ISBN 978-0-85404-182-4.
- ^ "Recent developments in chiral phospholane chemistry". Tetrahedron: Asymmetry. 15: 2123–2137. 2004. doi:10.1016/j.tetasy.2004.06.025.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|authors=ignored (help) - ^ K. Sommer (1970). "Zur Spaltung tertiärer Phosphine. II". Zeitschrift fuer Anorganische und Allgemeine Chemie. 379: 56–62. doi:10.1002/zaac.19703790110.
