Perfluorosulfonic acids
Perfluorosulfonic acids (PFSAs) are chemical compounds of the formula CnF(2n+1)SO3H and thus belong to the family of perfluorinated and polyfluorinated alkyl compounds (PFASs). The simplest example of a perfluorosulfonic acid is the trifluoromethanesulfonic acid. Perfluorosulfonic acids with six or more perfluorinated carbon atoms, i.e. from perfluorohexanesulfonic acid onwards, are referred to as long-chain.[1]
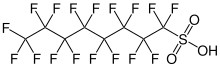

Properties
Perfluorosulfonic acids are organofluoroanalogues of conventional alkanesulfonic acids, but they are several pKA units stronger (and are therefore strong acids). Their perfluoroalkyl chain has a highly hydrophobic character.
Use
Perfluorooctanesulfonic acid, for example, has been used in hard chromium plating.
Regulation
Perfluorooctanesulfonic acid was included in Annex B of the Stockholm Convention in 2009 and subsequently in the EU POPs Regulation.[2]
Perfluorohexanesulfonic acid including its salts and related compounds was proposed for inclusion in the Stockholm Convention.[3]
