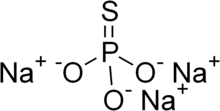
Sodium monothiophosphate
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Sodium monothiophosphate
| |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.030.224 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Na3PO3S | |
| Molar mass | 180.030 g/mol |
| Appearance | White solid |
| Density | 1.58 g/cm3 (dodecahydrate), 2.40 g/cm3 for anhydrous |
| Melting point | 120 to 125 °C (248 to 257 °F; 393 to 398 K) (decomposition) |
| soluble | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Sodium monothiophosphate, or sodium phosphorothioate, is an inorganic compound with the molecular formula Na3PO3S(H2O)x. All are white solids. The anhydrous material (x = 0) decomposes without melting at 120-125 °C. More common is the dodecahydrate. A nonahydrate is also known.
Related salts are the dithiophosphate Na3PS2O2.11H2O, trithiophosphate Na3PS3O.11H2O, and tetrathiophosphate Na3PS4.8H2O.[1]
Preparation
Sodium monothiophosphate is prepared by the base hydrolysis of thiophosphoryl chloride using aqueous sodium hydroxide:[2][3]
- PSCl3 + 6 NaOH + 9 H2O → Na3PO3S.(H2O)12 + 3 NaCl
This reaction affords the dodecahydrate, which is easily dehydrated.
Partial dehydration over 6.5 M H2SO4 gives the nonahydrate. Under flowing N2, the anhydrous salt is formed.[4]
Sodium phosphorothiolate decomposes at neutral pH. Silicone grease catalyses the hydrolysis of the phosphorothioate ion, so it is recommended that it is not used in the glass joints.[5]
In the anhydrous material, the P-S bond is 211 pm and the three equivalent P-O bonds are short at 151 pm. These disparate values suggest that the P-S bond is single.[6]
References
- ^ Elias, D. P. (1957). "Crystallographic Data on Some Sodium Phosphorothioates". Acta Crystallographica. 10: 600. doi:10.1107/S0365110X57002108.
- ^ "Sodium Monothiophosphate". Inorganic Syntheses. 5: 102–104. 1957. doi:10.1002/9780470132364.ch28.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|authors=ignored (help) - ^ "Importance of Excess Base in the Synthesis of Sodium Monothiophosphate: (Sodium Phosphorothioate)". Inorganic Syntheses. 17: 193–4. 1977. doi:10.1002/9780470132487.ch53.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|authors=ignored (help) - ^ Palazzi, Marcel (1973). "Trisodium monothiophosphate. Radiocrystallographic study". Bulletin de la Société Chimique de France. 12: 3246–8.
- ^ Lucian C. Pop and M. Saito (2015). "Serendipitous Reactions Involving a Silicone Grease". Coordination Chemistry Reviews. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2015.07.005.
- ^ "Natriummonothiophosphat(V): Kristallstruktur und Natriumionenleitfähigkeit" [Sodium monothiophosphate(V). Crystal structure and sodium ionic conductivity]. Zeitschrift fuer Anorganische und Allgemeine Chemie. 628: 641–646. 2002. doi:10.1002/1521-3749(200203)628:3<641::AID-ZAAC641>3.0.CO;2-8.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|authors=ignored (help)
