Federated States of Micronesia
6°55′N 158°15′E / 6.917°N 158.250°E
Federated States of Micronesia | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Motto: "Peace, Unity, Liberty" | |||||||
| Anthem: "Patriots of Micronesia" | |||||||
 | |||||||
| Capital | Palikir 6°55′N 158°11′E / 6.917°N 158.183°E | ||||||
| Largest town | Weno[1] | ||||||
| Official language | English | ||||||
| Recognized regional languages | |||||||
| Ethnic groups (2000) |
| ||||||
| Religion (2016)[2] |
| ||||||
| Demonym(s) | Micronesian | ||||||
| Government | Federal assembly-independent republic under non-partisan democracy | ||||||
| David Panuelo | |||||||
| Yosiwo George | |||||||
| Legislature | Congress | ||||||
| Independence from the United States | |||||||
• Republic proclaimed | May 10, 1979 | ||||||
| November 3, 1986 | |||||||
| Area | |||||||
• Total | 702 km2 (271 sq mi) (177th) | ||||||
• Water (%) | negligible | ||||||
| Population | |||||||
• 2019 estimate | 104,468 [3] (198th) | ||||||
• Density | 158.1/km2 (409.5/sq mi) (75th) | ||||||
| GDP (PPP) | 2019 estimate | ||||||
• Total | $367 million | ||||||
• Per capita | $3,584[4] | ||||||
| GDP (nominal) | 2019 estimate | ||||||
• Total | $383 million | ||||||
• Per capita | $3,735[4] | ||||||
| Gini (2013) | 40.1[5] medium | ||||||
| HDI (2019) | medium (136th) | ||||||
| Currency | United States dollar (USD) | ||||||
| Time zone | UTC+10 and +11 | ||||||
• Summer (DST) | not observed | ||||||
| Date format | MM/DD/YYYY | ||||||
| Driving side | right | ||||||
| Calling code | +691 | ||||||
| ISO 3166 code | FM | ||||||
| Internet TLD | .fm | ||||||
| |||||||
| |||||||
The Federated States of Micronesia (/ˌmaɪkroʊˈniːʒə/ ⓘ; abbreviated FSM) or simply Micronesia, is an island country in Oceania. It consists of four states – from west to east, Yap, Chuuk, Pohnpei and Kosrae – that are spread across the western Pacific. Together, the states comprise around 607 islands (a combined land area of approximately 702 km2 or 271 sq mi) that cover a longitudinal distance of almost 2,700 km (1,678 mi) just north of the equator. They lie northeast of Indonesia and Papua New Guinea, south of Guam and the Marianas, west of Nauru and the Marshall Islands, east of Palau and the Philippines, about 2,900 km (1,802 mi) north of eastern Australia, 3,400 km (2,133 mi) southeast of Japan, and some 4,000 km (2,485 mi) southwest of the main islands of the Hawaiian Islands.
While the FSM's total land area is quite small, it occupies more than 2,600,000 km2 (1,003,866 sq mi) of the Pacific Ocean, giving the country the 14th-largest exclusive economic zone in the world.[7] The sovereign island nation's capital is Palikir, located on Pohnpei Island, while the largest city is Weno, located in the Chuuk Atoll.
Each of its four states is centered on one or more main high islands, and all but Kosrae include numerous outlying atolls. The Federated States of Micronesia is spread across part of the Caroline Islands in the wider region of Micronesia, which consists of thousands of small islands divided among several countries. The term Micronesia may refer to the Federated States or to the region as a whole.
The FSM was formerly a part of the Trust Territory of the Pacific Islands (TTPI), a United Nations Trust Territory under U.S. administration, but it formed its own constitutional government on May 10, 1979, becoming a sovereign state after independence was attained on November 3, 1986, under a Compact of Free Association with the United States. Other neighboring island entities, and also former members of the TTPI, formulated their own constitutional governments and became the Republic of the Marshall Islands (RMI) and the Republic of Palau (ROP). The FSM has a seat in the United Nations and has been a member of the Pacific Community since 1983.
History
This section needs additional citations for verification. (October 2019) |
Captaincy General of the Philippines 1574–1899
German New Guinea 1899–1914
Imperial Japanese Navy occupation 1914–1919
South Seas Mandate 1919–1947
Trust Territory of the Pacific Islands 1947–1979
Federated States of Micronesia 1979–present
The ancestors of the Micronesians settled over four thousand years ago. A decentralized chieftain-based system eventually evolved into a more centralized economic and religious culture centered on Yap Island.

Nan Madol, a UNESCO World Heritage site, consisting of a series of small artificial islands linked by a network of canals, is often called the Venice of the Pacific. It is located on the eastern periphery of the island of Pohnpei and used to be the ceremonial and political seat of the Saudeleur dynasty that united Pohnpei's estimated 25,000 people from about AD 500 until 1500, when the centralized system collapsed.
European explorers—first the Portuguese in search of the Spice Islands (Indonesia) and then the Spanish—reached the Carolines in the sixteenth century. The Treaty of Tordesillas gave these lands to Spain and the Spanish incorporated the archipelago to the Spanish East Indies through the capital, Manila, and in the 19th century established a number of outposts and missions. In 1887, they founded the town of Santiago de la Ascensión in what today is Kolonia on the island of Pohnpei.
Following defeat in the Spanish–American War, the Spanish sold the archipelago to Germany in 1899 under the German–Spanish Treaty of 1899. Germany incorporated it into German New Guinea.
During World War I, it was captured by Japan. Following the war, the League of Nations awarded a mandate for Japan to administer the islands as part of the South Seas Mandate.
During World War II, a significant portion of the Japanese fleet was based in Truk Lagoon. In February 1944, Operation Hailstone, one of the most important naval battles of the war, took place at Truk, in which many Japanese support vessels and aircraft were destroyed.
Following World War II, it was administered by the United States under United Nations auspices in 1947 as part of the Trust Territory of the Pacific Islands pursuant to Security Council Resolution 21.
On May 10, 1979, four of the Trust Territory districts ratified a new constitution to become the Federated States of Micronesia. Palau, the Marshall Islands, and the Northern Mariana Islands chose not to participate. The FSM signed a Compact of Free Association with the United States, which entered into force on November 3, 1986, marking Micronesia's emergence from trusteeship to independence. Independence was formally concluded under international law in 1990, when the United Nations officially ended the Trusteeship status pursuant to Security Council Resolution 683. The Compact was renewed in 2004.[8]
Politics
The Federated States of Micronesia is governed by the 1979 constitution, which guarantees fundamental human rights and establishes a separation of governmental powers. This constitution constructs the national government to be similar to - but not exactly alike - that of the United States. The unicameral Congress has fourteen members elected by popular vote. Four senators—one from each state—serve four-year terms; the remaining ten senators represent single-member districts based on population and serve two-year terms. Congress elects the President and Vice President from among the four state-based senators to serve four-year terms in the executive branch. Their congressional seats are then filled by special elections.
An appointed cabinet supports the president and vice president. There are no formal political parties.
Defense and foreign affairs

In international politics, the Federated States of Micronesia has often voted with the United States with respect to United Nations General Assembly resolutions.[9]
The FSM is a sovereign, self-governing state in free association with the United States of America, which is wholly responsible for its defense. The Division of Maritime Surveillance operates a paramilitary Maritime Wing and a small Maritime Police Unit. The Compact of Free Association allows FSM citizens to join the U.S. military without having to obtain U.S. permanent residency or citizenship,[10] allows for immigration and employment for Micronesians in the U.S., and establishes economic and technical aid programs.
FSM has foreign relations with 56 countries, including the Holy See. FSM was admitted to the United Nations based on the Security Council's recommendation on August 9, 1991 in Resolution 703 and the General Assembly's approval on September 17, 1991 in Resolution 46/2.[11] The FSM was an active member of the Pacific Islands Forum.[12] However, in February 2021, FSM announced it would be formally withdrawing from the Forum in a joint statement with Marshall Islands, Kiribati and Nauru after a dispute regarding Henry Puna's election as the Forum's secretary-general.[13][14]
Administrative divisions
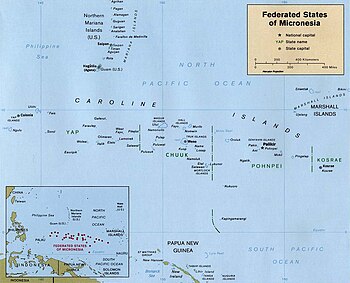
The four states in the federation are, from west to east:
| Flag | States[15] | Capital | Current Governor | Land | Population[16] | Population density | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| km2 | sq mi[17] | per km2[16] | per sq mi | |||||
| Yap | Colonia | Henry Falan[18] | 118.1 | 45.6 | 16,436 | 94 | 243 | |
| Chuuk | Weno | Johnson Elimo | 127.4 | 49.2 | 54,595 | 420 | 1088 | |
| Pohnpei | Kolonia | Marcelo Peterson | 345.5 | 133.4 | 34,685 | 98 | 255 | |
| Kosrae | Tofol | Carson K. Sigrah | 109.6 | 42.3 | 7,686 | 66 | 170 | |
These states are further divided into municipalities.
Disputed sovereignty
Spain has a claim to sovereignty over a few islands including Kapingamarangi in Pohnpei State. A commission of cardinals under Pope Leo XIII arbitrated a dispute for the Caroline Islands and others extending from the equator to 11°N latitude and from 133°E to 164°E longitude. Germany and Spain on 17 December 1885 agreed in a treaty that they were a part of the Spanish East Indies. In 1899, Spain sold "las Carolinas" to Germany. Kapingamarangi is far south of the Carolines and the people are racially and culturally Polynesian, not Micronesian or Carolinian. In 1948, Emilio Pastor Santos of the Spanish National Research Council found that the charts and maps up to 1899 had shown that Kapingamarangi and a few other islands had never been considered part of the Carolines, were not included in the description of the territory transferred to Germany and were never ceded by Spain; therefore, Spain retained sovereignty. In 1949, the Cabinet of Diplomatic Information of the Spanish Ministry of Foreign Affairs issued the following declaration:
... The Ministry recognises that it is a certain fact and historic truth due to Article 3 of the Treaty of July 1, 1899, that Spain reserved a series of rights in Micronesia and for another thing, the specifications of the territories which Spain ceded in 1899 leaves apart certain groups of islands in the same zone.[19]
Successive Spanish governments have not abandoned Spain's sovereignty, or insisted on enforcing it, or recognized the sovereignty of the Federated States of Micronesia over Kapingamarangi.[20][21] The Federated States of Micronesia claims sovereignty and has de facto control of the island.
Geography

The Federated States of Micronesia consists of 607 islands extending 2,900 km (1,802 mi) across the archipelago of the Caroline Islands east of the Philippines. The islands have a combined area of 702 km2 (271 sq mi).[15]
The islands are grouped into four states, which are Yap, Chuuk (called Truk until January 1990), Pohnpei (known as "Ponape" until November 1984), and Kosrae (formerly Kusaie).[22][23] These four states are each represented by a white star on the national flag. The capital is Palikir, on Pohnpei.
Two terrestrial ecoregions lie within the country's borders: Carolines tropical moist forests and Yap tropical dry forests.[24] It had a 2019 Forest Landscape Integrity Index mean score of 7.55/10, ranking it 37th globally out of 172 countries.[25]
Biodiversity
The major coastal communities are mangrove forests, seagrass beds, lagoons and coral reefs, biologically and physically linked. About 300 species of coral, 1000 species of fish and 1200 species of mollusks are recognized in Micronesia. In the mangrove forests there are shrimps, crabs and fish, as well as birds that feed on them. Seagrass meadows appear offshore following the mangroves. The lagoons provide food for the reef inhabitants and contain various kinds of plankton. The biodiversity and complexity of the coral reefs increases markedly from east to west, with 150 species of hard coral at Kosrae, 200 at Pohnpei and 300 at Chuuk. Coral productivity in this area is among the highest in the world, absorbing about 2500 grams of carbon per square meter per year, against 2200 grams in the tropical forest and 125 grams in the open sea.
Inland, from the tidal zone to the top of the mountains there is a varied range of vegetation, cloud forest, upland, palm, plantation, areas dominated by climbers of the genus Merremia, savannas, native secondary forest, fragments of introduced trees, cultivated areas, freshwater swamps, swamps of the palm Nypa fruticans, atoll forests, forests in rocky areas and beaches. There are about 1230 species of ferns and flowering plants, of which 782 are native, including 145 native fern species. On Pohnpei Island, there are about 750 plant species, of which 110 are endemic. Another 457 species have been introduced.
Climate

The climate of the Federated States of Micronesia is equatorial, warm, humid and rainy all year round. The islands are located north of the equator and are affected by constant trade winds, which temper the climate. Minimum temperatures range all year round between 22 and 25°C, and maximum temperatures between 30 and 32°C. The abundant precipitations oscillate between 2500 and 5000 mm per year, although in the faces oriented to the wind they can surpass 6000 mm. Mount Nahnalaud, only 750 m high, on the island of Pohnpei, receives an average of 10,160 mm, being one of the rainiest places on earth, with almost always overcast skies. In general, the rains are produced by showers and storms of short duration but very intense. The driest places are the flat atolls, where rainfall can drop below 3000 mm. The driest months are January and February, with no less than 250 mm and 20 days of rain.
Transportation
The Federated States of Micronesia is served by four international airports.
- Pohnpei International Airport, on the main island of Pohnpei State.[26]
- Chuuk International Airport, located on the main island of Chuuk State.[27]
- Kosrae International Airport, located on the main island of Kosrae State.[28]
- Yap International Airport, located on the main island of Yap State.[29]
Economy
Economic activity in the Federated States of Micronesia consists primarily of subsistence farming and fishing. The islands have few mineral deposits worth exploiting, except for high-grade phosphate. Long line fishing of tuna is also viable with foreign vessels from China that operated in the 1990s. The potential for a tourist industry exists, but the remoteness of the location and a lack of adequate facilities hinder development. Financial assistance from the U.S. is the primary source of revenue, with the U.S. pledged to spend $1.3 billion in the islands in 1986–2001; when the Compact was amended in 2004, the United States committed to providing $110 million in development aid through 2023.[30] The CIA World Factbook lists high dependence on U.S. aid as one of the main concerns of the FSM.[15] Geographical isolation and a poorly developed infrastructure are major impediments to long-term growth.[31]
Society
Demographics

The indigenous population of the nation, which is predominantly Micronesian, consists of various ethnolinguistic groups. It has a nearly 100% Pacific Islander and Asian population: Chuukese 48.8%, Pohnpeian 24.2%, Kosraean 6.2%, Yapese 5.2%, Yap outer islands 4.5%, Asian 1.8%, Polynesian 1.5%, other 6.4%, unknown 1.4%. A sizable minority also have some Japanese ancestry, which is a result of intermarriages between Japanese settlers and Micronesians during the Japanese colonial period.[32]
There is also a growing expatriate population of Americans, Australians, Europeans, and residents from China and the Philippines since the 1990s. English has become the common language of the government, and for secondary and tertiary education. Outside of the main capital towns of the four FSM states, the local languages are primarily spoken. Population growth remains high at more than 3% annually, offset somewhat by net emigration.
Languages
English is the official and common language. Beside it the following Austronesian languages are spoken:[15][33]
| Rank | Language | Language family | Number of speakers |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Chuukese | Micronesian | 45,900 |
| 2 | Pohnpeian | Micronesian | 30,000 |
| 3 | Kosraean | Micronesian | 8,000 |
| 4 | Mortlockese | Micronesian | 5,900 |
| 5 | Yapese | Admiralty Islands? | 5,130 |
| 6 | Ulithian | Micronesian | 3,000 |
| 7 | Kapingamarangi | Polynesian | 3,000 |
| 8 | Pingelapese | Micronesian | 3,000 |
| 9 | Woleaian | Micronesian | 1,700 |
| 10 | Mokilese | Micronesian | 1,500 |
| 11 | Puluwat | Micronesian | 1,400 |
| 12 | Pááfang | Micronesian | 1,300 |
| 13 | Namonuito | Micronesian | 940 |
| 14 | Nukuoro | Polynesian | 700 |
| 15 | Ngatikese | Micronesian | 700 |
| 16 | Satawalese | Micronesian | 500 |
| 17 | Nguluwan | Admiralty Islands? | 50 |
| 18 | Ngatikese Creole | Creole | 30 |
Religion

Most Micronesians are Christian. Several Protestant denominations, as well as the Roman Catholic Church, are present in every Micronesian state.[34] Most Protestant groups trace their roots to American Congregationalist missionaries.[34] On the island of Kosrae, the population is approximately 7,800; 95 percent are Protestants.[34] On Pohnpei, the population of 35,000 is evenly divided between Protestants and Catholics. Most immigrants are Filipino Catholics who have joined local Catholic churches, e.g. Our Lady of Mercy Catholic Church in Pohnpei.[34]
On Chuuk and Yap, an estimated 60 percent are Catholic and 40 percent are Protestant.[34] Religious groups with small followings include Baptists, Assemblies of God, Salvation Army, Seventh-day Adventists, Jehovah's Witnesses, The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints (Mormons), and the Baháʼí Faith.[34] There is a small group of Buddhists on Pohnpei,[34] and a small group of Ahmadiyya Muslims in Kosrae. Attendance at religious services is generally high; churches are well supported by their congregations and play a significant role in civil society.[34]
In the 1890s, on the island of Pohnpei, intermissionary conflicts and the conversion of clan leaders resulted in religious divisions along clan lines which persist today.[34] More Protestants live on the western side of the island, while more Catholics live on the eastern side.[34] Missionaries of many religious traditions are present and operate freely.[34] The Constitution provides for freedom of religion, and the Government generally respects this right in practice.[34] The US government received no reports of societal abuses or discrimination based on religious belief or practice in 2007.[34]
Health
Life expectancy was 66 for men and 69 for women in 2018.[35][36]
Pingelap in Pohnpei State is notable for the prevalence of an extreme form of color blindness called Achromatopsia, and known locally as maskun.[37][38] Approximately 5% of the atoll's 3000 inhabitants are afflicted.[37][38]
Sport
Baseball
Baseball is very popular in FSM.[39]
Association football
The sport of association football in the Federated States of Micronesia is run by the Federated States of Micronesia Football Association. They control the Micronesian Games, the nation's football championship and the Micronesia national football team.
FSMAA
The Federated States of Micronesia Athletic Association is the governing body for the country's sports and athletics.[40][41]
Culture

Each of the four states has its own culture and traditions, but there are also common cultural and economic bonds that are centuries old. Cultural similarities include the importance of the traditional extended family and clan systems and are found on all the islands.
The island of Yap is notable for its "stone money" (Rai stones), large disks usually of calcite, up to 4 metres (13 ft) in diameter, with a hole in the middle. The islanders, aware of the owner of a piece, do not necessarily move them when ownership changes. There are five major types: Mmbul, Gaw, Ray, Yar, and Reng, the last being only 30 cm (12 in) in diameter. Their value is based on both size and history, many of them having been brought from other islands, as far as New Guinea, but most coming in ancient times from Palau. Approximately 6,500 of them are scattered around the island.
Pohnpei is home to Nan Madol: Ceremonial Centre of Eastern Micronesia, a UNESCO World Heritage Site, but the site is currently listed as In Danger due to natural causes.[42] The government is working on the conservation of the site.
Music
Traditional dances on the main islands includes "stick dancing" on Pohnpei, Chuuk and Yap, standing dances on Chuuk and sitting dances on Yap[43] and Chuuk. The Yapese are particularly known for their skills in dancing. The Yapese stick dance is performed by men, women and children together, while standing dances are performed either by women or men and boys, but never both together. The men participate in various dancing competitions, which are segregated by caste; the lower castes have some distinct dances, such as a woman's standing dance, but can only dance when authorized by a person of a higher caste.[44]
Newspapers
The following papers have been published in the FSM:
- Pohnpei[45]
- The Kaselehlie Press — from 2001. English. Published biweekly.
- Senyavin Times — from 1967 to the 1970s. Bilingual (Pohnpeian and English).
- Chuuk[46]
- Truk Chronicle — from 1979 to the 1980s. Published biweekly in English, with some articles in Carolinian.
- Kosrae[47]
- Kosrae State Newsletter — from 1983 to 2004. Published monthly in Kosraean.
- Yap[48]
- The Yap Networker — from 1999 to 2005. Published weekly in English.
Literature
There have been very few published literary writers from the Federated States of Micronesia.[49] In 2008, Emelihter Kihleng became the first ever Micronesian to publish a collection of poetry in the English language.[50]
See also
- Outline of the Federated States of Micronesia
- Index of Federated States of Micronesia–related articles
References
- ^ Summary Analysis of Key Indicators: from the FSM 2010 Census of Population and Housing (PDF). Palikir: Division of Statistics, Office of SBOC. p. 8. Retrieved March 16, 2018 – via Prism (SPC).
- ^ "Religions in Federated States Of Micronesia | PEW-GRF". www.globalreligiousfutures.org.
- ^ "NA – FSM Statistics".
- ^ a b "Report for Selected Countries and Subjects". www.imf.org.
- ^ "GINI index". World Bank. Retrieved July 26, 2013.
- ^ Human Development Report 2020 The Next Frontier: Human Development and the Anthropocene (PDF). United Nations Development Programme. December 15, 2020. pp. 343–346. ISBN 978-92-1-126442-5. Retrieved December 16, 2020.
- ^ "Drops in the ocean: France's marine territories". The Economist. January 13, 2016.
- ^ "Compact of Free Association". Archived from the original on January 26, 2016. Retrieved January 2, 2016.
- ^ General Assembly - Overall Votes - Comparison with U.S. vote lists Micronesia as in the country with the fourth high coincidence of votes. Micronesia has always been in the top four.
- ^ "U.S. Military Enlistment Standards" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on October 1, 2008.
- ^ "United Nations Official Document". www.un.org. Archived from the original on September 3, 2015.
- ^ "Federated States of Micronesia". U.S. Department of the Interior. June 11, 2015. Archived from the original on October 23, 2016. Retrieved December 2, 2016.
- ^ "Five Micronesian countries leave Pacific Islands Forum". RNZ. February 9, 2021. Retrieved February 9, 2021.
- ^ "Pacific Islands Forum in crisis as one-third of member nations quit". The Guardian. February 8, 2021. Retrieved February 9, 2021.
- ^ a b c d "The World Factbook -- Central Intelligence Agency". Cia World Factbook. Retrieved August 8, 2018.
- ^ a b "FSM government website - Population". Archived from the original on June 29, 2012.
- ^ "FSM government website - Geography". Archived from the original on March 4, 2016.
- ^ "Marianas Variety - New Yap governor, other elected officials sworn in". www.mvariety.com. Retrieved July 10, 2019.
- ^ Pastor y Santos 1950, p. 21.
- ^ Pastor y Santos 1950.
- ^ Weaver, Zay Territories under Spanish Sovereignty in Oceania (partial translation of Pastor y Santos 1950), Palau Museum, Koror, 1967
- ^ Keesing, Roger M. (1988). Melanesian Pidgin and the oceanic substrate. Stanford, Calif.: Stanford University Press. p. 15. ISBN 0-8047-1450-9. OCLC 17383715.
- ^ The Europa world year book 2004. London: Europa. 2004. ISBN 1-85743-253-3. OCLC 55795909.
- ^ Dinerstein, Eric; et al. (2017). "An Ecoregion-Based Approach to Protecting Half the Terrestrial Realm". BioScience. 67 (6): 534–545. doi:10.1093/biosci/bix014. ISSN 0006-3568. PMC 5451287. PMID 28608869.
- ^ Grantham, H. S.; et al. (2020). "Anthropogenic modification of forests means only 40% of remaining forests have high ecosystem integrity - Supplementary Material". Nature Communications. 11 (1): 5978. doi:10.1038/s41467-020-19493-3. ISSN 2041-1723. PMC 7723057. PMID 33293507.
- ^ "Federated States Of Micronesia (FSM) Division of Civil Aviation l Pohnpei International Airport (PNI) (PTPN), Pohnpei Island, Micronesia". Federated States of Micronesia Division of Civil Aviation. August 7, 2018. Archived from the original on August 8, 2018. Retrieved August 7, 2018.
- ^ "Federated States of Micronesia (FSM) Division of Civil Aviation l Chuuk International Airport (TKK) (PTKK) Weno Island, Micronesia". Federated States of Micronesia Division of Civil Aviation. August 7, 2018. Archived from the original on August 8, 2018. Retrieved August 7, 2018.
- ^ "Federated States of Micronesia (FSM) Division of Civil Aviation l Kosrae International Airport (KSA) (PTSA), Kosrae Island, Micronesia". Federated States of Micronesia Division of Civil Aviation. August 7, 2018. Archived from the original on August 8, 2018. Retrieved August 7, 2018.
- ^ "Federated States of Micronesia (FSM) Division of Civil Aviation l Yap International Airport (YAP) (PTYA), Wa'ab, Micronesia". Federated States of Micronesia Department of Civil Aviation. August 7, 2018. Archived from the original on August 8, 2018. Retrieved August 7, 2018.
- ^ "US Relations with the Federated States of Micronesia". United States Department of State.
- ^ "Federated States of Micronesia". United Nations. Archived from the original on November 30, 2012. Retrieved November 17, 2012.
- ^ President Emanuel Mori Meets With Japan Prime Minister Yasuo Fukuda Archived September 24, 2015, at the Wayback Machine; AESonline.org Archived June 16, 2007, at archive.today Government of the Federated States of Micronesia, December 12, 2007
- ^ "Micronesia". Ethnologue. Retrieved February 1, 2019.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m International Religious Freedom Report 2007: Micronesia, Federated States of . United States Bureau of Democracy, Human Rights and Labor (September 14, 2007). This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ^ "Life expectancy at birth, male (years) - Micronesia, Fed. Sts. | Data". The World Bank. Retrieved February 27, 2021.
- ^ "Life expectancy at birth, female (years) - Micronesia, Fed. Sts. | Data". The World Bank. Retrieved February 27, 2021.
- ^ a b Brody JA, Hussels I, Brink E, Torres J (1970). "Hereditary blindness among Pingelapese people of Eastern Caroline Islands". Lancet. 1 (7659): 1253–7. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(70)91740-X. PMID 4192495.
- ^ a b Hussels IE, Morton NE (1972). "Pingelap and Mokil Atolls: achromatopsia". Am. J. Hum. Genet. 24 (3): 304–9. PMC 1762260. PMID 4555088.
- ^ Wood, Robert (2014). "Sport in Micronesia". Topend Sports Website. Retrieved February 27, 2021.
- ^ "Federated States of Micronesia Athletic Association". IAAF. Retrieved January 28, 2014.
- ^ "FEDERATED STATES OF MICRONESIA ATHLETIC ASSOCIATION". Oceania Athletics Association. Retrieved January 28, 2014.
- ^ "Nan Madol: Ceremonial Centre of Eastern Micronesia - UNESCO World Heritage Centre". UNESCO World Heritage Centre. August 7, 2018. Archived from the original on August 7, 2018. Retrieved August 7, 2018.
- ^ "Micronesia Music Anthology". Jane's Oceania Page. Archived from the original on January 1, 2006. Retrieved September 27, 2005.
- ^ "Aspects of Yap". Jane's Oceania Page. Archived from the original on February 27, 2005. Retrieved September 27, 2005.
- ^ "Pacific Islands Newspapers : Pohnpei State (FSM)". University of Hawaii at Manoa. Retrieved September 7, 2020.
- ^ "Pacific Islands Newspapers : Chuuk State (FSM)". University of Hawaii at Manoa. Retrieved September 7, 2020.
- ^ "Pacific Islands Newspapers : Kosrae State (FSM)". University of Hawaii at Manoa. Retrieved September 7, 2020.
- ^ "Pacific Islands Newspapers : Yap State (FSM)". University of Hawaii at Manoa. Retrieved September 7, 2020.
- ^ "Seeking Micronesian literary writers", Marianas Variety, February 18, 2009 Archived September 28, 2014, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "Micronesian Poet Publishes Collection of Poems", Office of Insular Affairs, May 12, 2008 Archived February 29, 2012, at the Wayback Machine
Sources
- Arnold, Bruce Makoto (2011). "Conflicted Childhoods in the South Seas: The Failure of Racial Assiimilation in the Nan'yo". Tufts Historical Review. 4 (11): 79–96.
- Brower, Kenneth; Harri Peccinotti (1981). Micronesia: The Land, the People, and the Sea. Baton Rouge: Louisiana State University Press. ISBN 978-0-8071-0992-2.
- Darrach, Brad; David Doubilet (1995). "Treasured Islands". Life (August 1995): 46–53.
- Falgout, Suzanne (1995). "Americans in Paradise: Anthropologists, Custom, and Democracy in Postwar Micronesia". Ethnology. 34 (Spring 1995): 99–111. doi:10.2307/3774100. JSTOR 3774100.
- Friedman, Hal M. (1993). "The Beast in Paradise: The United States Navy in Micronesia, 1943–1947". Pacific Historical Review. 62 (May 1993): 173–195. doi:10.2307/3639910. JSTOR 3639910.
- Friedman, Hal M. (1994). "Arguing over Empire: American Interservice and Interdepartmental Rivalry over Micronesia, 1943-1947". Journal of Pacific History. 29 (1): 36–48. doi:10.1080/00223349408572757.
- Hanlon, David (1998). Remaking Micronesia: Discourses over Development in a Pacific Territory, 1944–1982. Honolulu: University of Hawaii Press. ISBN 978-0-8248-1894-4.
- Hezel, Francis X. (1995). "The Church in Micronesia". America. 18 (February 1995): 23–24.
- Kluge, P. F. (1991). The Edge of Paradise: America in Micronesia. New York: Random House. ISBN 978-0-394-58178-1.
- Malcomson, S. L. (1989). "Stranger than Paradise". Mother Jones. 14 (January 1989): 19–25.
- "Micronesia: A New Nation". U.S. News & World Report (October 15, 1984): 80–81.
- Parfit, Michael (2003). "Islands of the Pacific". National Geographic. 203 (March 2003): 106–125.
- Pastor y Santos, Emilio (1950). Territorios de soberanía española en Oceanía (in Spanish). Madrid: Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Científicas, Instituto de Estudios Africanos. OCLC 912692168.
- Patterson, Carolyn Bennett (1986). "In the Far Pacific: At the Birth of Nations". National Geographic. 170 (October 1986): 460–500.
- Peoples, James G. (1993). "Political Evolution in Micronesia". Ethnology. 32 (Winter 1993): 1–17. doi:10.2307/3773542. JSTOR 3773542.
- Rainbird, Paul (2003). "Taking the Tapu: Defining Micronesia by Absence". Journal of Pacific History. 38 (2): 237–250. doi:10.1080/0022334032000120558. S2CID 162140479.
- Schwalbenberg, Henry M.; Hatcher, Thomas (1994). "Micronesian Trade and Foreign Assistance: Contrasting the Japanese and American Colonial Periods". Journal of Pacific History. 29 (1): 95–104. doi:10.1080/00223349408572762.
External links
Government
General information
- Federated States of Micronesia. The World Factbook. Central Intelligence Agency.
- Federated States of Micronesia from UCB Libraries GovPubs
- Federated States of Micronesia at Curlie
- Micronesia from the BBC News
- Jane's Federated States of Micronesia Home Page
- Trust Territory of the Pacific Archives at the University of Hawaii
- Pacific Islands Legal Information Institute - Federated States of Micronesia
- Nature.org - Micronesia environmental conservation
- myMicronesia.com Online resource center about the islands of Micronesia. Provides free listings and links to all Micronesian businesses, as well as civic, cultural, health and educational organizations.
- Habele.org - Outer Islands Information about the remote islands and atolls outside the four state capitals of Micronesia from an educational nonprofit.
- Development Forecasts for Federated States of Micronesia
News media
- The Kaselehlie Press – The Kaselehlie Press is a Pohnpei-based newspaper that covers stories throughout the FSM.
- Pohnpei (Spanish)
Maps
 Wikimedia Atlas of the Federated States of Micronesia
Wikimedia Atlas of the Federated States of Micronesia- Nan Madol islet complex Provides computer based reconstruction of the main islets and features
Travel
Weather
- Federated States of Micronesia
- 1986 establishments in Oceania
- Associated states of the United States
- Caroline Islands
- Countries in Micronesia
- Countries in Oceania
- English-speaking countries and territories
- Federal constitutional republics
- Former German colonies
- Former Japanese colonies
- Former Spanish colonies
- Island countries
- Member states of the United Nations
- Small Island Developing States
- Spanish East Indies
- States and territories established in 1986