Battle of Chains
| Battle of Chains | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of Muslim conquest of the Persian Empire | |||||||
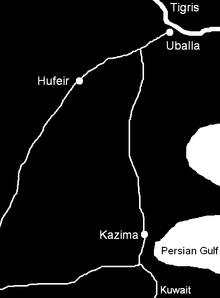 Map showing the location of Kazima, Uballa and Hufeir in present Kuwait and Iraq respectively. | |||||||
| |||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
| Rashidun Caliphate |
Sassanid Persian Empire Christian Arab allies[citation needed] . | ||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||
| Khalid ibn al-Walid |
Hormozd †[3] Qubad Anoshagan | ||||||
| Strength | |||||||
| 18,000 | 20,000(primary sources) 17,000 (modern sources) | ||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||
| Low | Heavy | ||||||
The Battle of Sallasil (Dhat al-Salasil)[4] or the Battle of Chains was the first battle fought between the Rashidun Caliphate and the Sassanid Persian Empire. The battle was fought in Kuwait (Kazima) soon after the Ridda Wars were over and Eastern Arabia was united under the authority of Caliph Abu Bakr. It was also the first battle of the Rashidun Caliphate in which the Muslim army sought to extend its frontiers.[citation needed]
Background
Muthana ibn Haritha Shaybani was a tribal chief in north Eastern Arabia, residing close to the Persian border. After the wars of apostasy, Muthana raided the Persian towns in Iraq. The raids were successful, with a considerable amount of booty being won. Muthana ibn Haritha went to Madinah to inform Caliph Abu Bakr about his success, and Abu Bakr appointed him as the commander of his people; after this he began deeper raids into Iraq. Using the mobility of his Light cavalry he could easily raid any town near the desert and disappear again in to the desert, leaving the Sassanid army unable to chase him. Muthana’s actions made Abu Bakr decide to conquer Iraq and liberate it from the Sassanids. To make certain of victory, Abu Bakr decided on two measures: the army would consist entirely of volunteers, and it would be commanded by his best general, Khalid ibn Walid. After defeating the self-proclaimed prophet Musailima in the Battle of Yamama, Khalid was still in the Yamama district when Abu Bakr sent him orders to fight the Sassanid Persian Empire. Making Al-Hirah (an area in Iraq) the objective of Khalid's mission, Abu Bakr sent reinforcements and ordered the tribal chiefs of northeastern Arabia Muthana ibn Haritha, Mazhur bin Adi, Harmala and Sulma to operate under the command of Khalid. In approximately the third week of March 633 AD (first week of Muharram 12th Hijrah) Khalid set out from Yamama with an army of 10,000 men. But before doing so he wrote to Hormozd, the Persian governor of the frontier district of Dast Meisan:
Submit to Islam and be safe. Or agree to the payment of the Jizya, and you and your people will be under our protection, else you will have only yourself to blame for the consequences, for I bring the men who desire death as ardently as you desire life.[5]
The tribal chiefs and their warriors (2,000 each) joined Khalid in his quest. Thus Khalid entered the Persian Empire with 18,000 troops.[5] The Persian commander informed the emperor about the threat from Arabia and concentrated an army for the battle, consisting of a large number of Christian Arab auxiliaries.
Khalid’s strategy
The Sassanid army was one of the most powerful and best equipped armies of the time, and was an ideal force for a set-piece, head-on confrontation. The only weakness of the Persian army was in its lack of mobility: the heavily armed Persians were not able to move fast, and any prolonged movement would tire them. On the other hand, Khalid's troops were mobile; they were mounted on camels with horses at the ready for cavalry attacks. Khalid's strategy was to use his own speed to exploit the lack in mobility of the Sassanid army. He planned to force the Persians to carry out marches and counter-marches until they were worn out, and then strike when the Persians were exhausted. Geography would help Khalid ibn Walid to carry out this strategy successfully. There were two routes to Uballa, via Kazima or via Hufair, so Khalid wrote a letter to the Persian leader Hormozd from Yamama so that he would expect Khalid to arrive via the direct route from Yamama to Kazima and then to Uballa.
The battle
Expecting Khalid ibn Walid to come though Kazima, Hormozd marched from Uballa to Kazima. At Kazima there were no signs of the Muslim army. Soon information was given by scouts that Khalid ibn Walid was moving towards Hufeir. As Hufeir was only 21 miles from Uballa, this endangered Hormozd’s base. Uballa which was an important port of the Sassanid Empire, situated near modern-day Basra. Hormozd immediately ordered a move to Hufeir, 50 miles away. Khalid waited at Hufeir until his scouts informed him about the hurried approach of Hormozd. Passing though the desert, Khalid moved towards Kazima. On his arrival at Hufeir, Hormozd was informed about Khalid’s march towards Kazima. Because Hormozd could not leave the Kazima route to the Muslims, the heavily armed Sassanid army was once again ordered to set off for Kazima. The Persians arrived at Kazima in a state of exhaustion.[citation needed]

Movement of Khalid ibn Walid's army and the Sassanid army before the battle. Khalid's strategy was to wear out the Sassanid army.
Hormozd at once deployed the army for battle in the normal formation of a centre and wings. The generals commanding his wings were Qubaz and Anoshagan. The men linked themselves together with chains as a sign to the enemy that they were ready to die than to run away from the battle field in case of defeat. This lessened the danger of a breakthrough by enemy cavalry, as with the men linked together in chains it was not easy for cavalry groups to knock down a few men and create a gap for penetration. Since the Sassanid army was organized and trained for the set-piece battle, this tactic enabled it to stand like a rock in the face of an enemy assault. But the chains had one major drawback: in case of defeat the men were incapable of withdrawal, for then the chains acted as fetters. It was the use of chains that gave this battle its name.[6] Hormozd had deployed his army just forward of the western edge of Kazima, keeping the city covered by his dispositions. Khalid deployed his army with the desert behind them, so that they could retreat there in case of defeat. The exhausted Persian army was unable to stand the attack for long and the Muslims successfully penetrated the Persian front in many places. Sensing defeat, the Persian generals commanding the wings, Qubaz and Anoshagan, ordered a withdrawal, which led to a general retreat. Most of the Persians who were not chained managed to escape, but those who were chained together were unable to move fast, and thousands of them were slain.
Aftermath
After the Battle of Chains, Khalid defeated the Persian armies in three more battles and captured his objective: Al-Hirah. The first Muslim conquest of Iraq was completed within four months. Abu Bakr did not direct Khalid to move deeper into the Sassanid territory,as the Sassanids had ordered reinforcements which could have easily routed and defeated the worn out Muslim armies and Khalid's orders were now to set out to win over the Persian population of Hira. After nine months he sent him to command the Muslim conquest of Syria.
References
- ^ Parvaneh Pourshariati, The Decline and Fall of the Sasanian Empire, (I.B. Tauris, 2011), 193.
- ^ "Chapter 19: The Battle of Chains".
- ^ Parvaneh Pourshariati, The Decline and Fall of the Sasanian Empire, 193.
- ^ Parvaneh Pourshariati, The Decline and Fall of the Sasanian Empire, 192.
- ^ a b Tabari: Vol. 2, p. 554.
- ^ Tabari: Vol. 3, p. 206.
Online resources
