Erebus Bay
| Erebus Bay | |
|---|---|
 Kirsten Carlson diving near Turtle Rock | |
| Location | Ross Island, Antarctica |
| Coordinates | 77°44′S 166°31′E / 77.733°S 166.517°E |
| Basin countries | Antarctica |
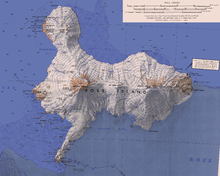
Erebus Bay (77°44′S 166°31′E / 77.733°S 166.517°E) is a bay about 13 nautical miles (24 km; 15 mi) wide between Cape Evans and Hut Point Peninsula, on the west side of Ross Island, Antarctica.
Exploration and naming[edit]
The bay was explored by the British National Antarctic Expedition (BrNAE) (1901–04) under Scott. It was named by Scott's second expedition, the British Antarctic Expedition (BrAE), 1910-13, which built its headquarters on Cape Evans. The feature is surmounted by Mount Erebus.[1]
Location[edit]
Erebus Bay extends from Cape Evans in the northwest to Hut Point on the Hut Point Peninsula to the southeast. It opens onto the Ross Sea to the west. Islands include the Dellbridge Islands and Turtle Rock. Features on the north shore include Tryggve Point and Turks Head, on either side of Turks Head Bay. The Erebus Glacier Tongue extends into the central part of the bay. Features on the east shore include Descent Cliff, Hutton Cliffs, Knob Point, Danger Slopes, Arrival Heights and Hut Point near McMurdo Station.[2]
Weddell seal population[edit]
Erebus Bay is home to the most southerly breeding population of Weddell seals in the world. They have been studied intensively since 1968. As of 2022 a database held data for 28,000 marked seals, and held detailed information on individual seals and on populations. The seals are easy to approach and tag while they are rearing their pups, and return to the same sites years after year.[3] They suffer a significant cost to personal survival when they breed, rather than conforming to the "prudent parent" reproductive strategy that life history theory predicts for long-lived mammals.[4]
Dellbridge Islands[edit]
77°40′S 166°25′E / 77.667°S 166.417°E. A group of small volcanic islands lying in McMurdo Sound, just south of Cape Evans. They were discovered by the British National Antarctic Expedition (BrNAE) (1901-04) under Robert Falcon Scott, who named them for James H. Dellbridge, second engineer with the expedition. [5]
-
L-R: Tent, Inaccessible, Big Razorback, Little Razorback
-
Inaccessible Island from southeast
-
Tent Island
-
Little Razorback, late season annual sea ice
-
Big Razorback
Inaccessible Island[edit]

77°39′S 166°21′E / 77.650°S 166.350°E. A small rocky island, the northernmost of the Dellbridge Islands, lying 1 nautical mile (1.9 km; 1.2 mi) southwest of Cape Evans. It is the most imposing of the group as it is nearly always bare of snow and rises to 95 meters. Discovered by the BrNAE (1901-04) under Scott, and so named because of the difficulty in reaching it.[6]
Tent Island[edit]
77°41′S 166°23′E / 77.683°S 166.383°E. The largest of the Dellbridge Islands, about 1 nautical mile (1.9 km; 1.2 mi) long and 135 metres (443 ft) high, lying south of Cape Evans. Discovered by the BrNAE (1901-04), which so named this island for its tentlike appearance.[7]
Little Razorback Island[edit]
77°40′S 166°31′E / 77.667°S 166.517°E. The smallest and easternmost of the Dellbridge Islands. Discovered by the BrNAE under Scott, 1901-04, and so named because of its size and similarity to nearby Big Razorback Island.[8]
Big Razorback Island[edit]
77°41′S 166°30′E / 77.683°S 166.500°E. The southeasternmost of the Dellbridge Islands. Discovered and named by the BrNAE, 1901-04, under Scott. The name is descriptive.[9]
Other features[edit]
Turks Head Bay[edit]
77°40′S 166°44′E / 77.667°S 166.733°E. A small bay between Tryggve Point and Turks Head. The bay name appears to be first used on a map of the British Antarctic Expedition (1910-13) and is in association with Turks Head.[10]
Descent Cliff[edit]
77°43′S 166°53′E / 77.717°S 166.883°E. Cliff on the west side of Hut Point Peninsula, between Hutton Cliffs and Erebus Glacier Tongue. Charted and so named by the British Antarctic Expedition under Scott, 1910-13, because it was here that a descent to the sea ice was made.[11]
Hutton Cliffs[edit]
77°44′S 166°51′E / 77.733°S 166.850°E. Cliffs on the west side of Hut Point Peninsula, about 2 nautical miles (3.7 km; 2.3 mi) north of Ford Rock. Discovered by the BrNAE (1901-04) and named for Captain Hutton of the Canterbury Museum, Christchurch, New Zealand.[12]
Turtle Rock[edit]
77°44′S 166°46′E / 77.733°S 166.767°E. Small island lying in Erebus Bay close west of Hut Point Peninsula. Discovered by the BrNAE, 1901-04, under Scott, and so named because of its low rounded appearance.[13]
References[edit]
- ^ Alberts 1995, p. 224.
- ^ Ross Island Map USGS.
- ^ Rotella 2022.
- ^ Hadley, Rotella & Garrott 2007, p. 448.
- ^ Alberts 1995, p. 181.
- ^ Alberts 1995, p. 359.
- ^ Alberts 1995, p. 738.
- ^ Alberts 1995, p. 438.
- ^ Alberts 1995, p. 66.
- ^ Alberts 1995, p. 764.
- ^ Alberts 1995, p. 185.
- ^ Alberts 1995, p. 357.
- ^ Alberts 1995, p. 765.
Sources[edit]
- Alberts, Fred G., ed. (1995), Geographic Names of the Antarctic (PDF) (2 ed.), United States Board on Geographic Names, retrieved 2024-01-30
 This article incorporates public domain material from websites or documents of the United States Board on Geographic Names.
This article incorporates public domain material from websites or documents of the United States Board on Geographic Names. - Hadley, Gillian L; Rotella, Jay J; Garrott, Robert A (May 2007), "Evaluation of reproductive costs for Weddell seals in Erebus Bay, Antarctica", J Anim Ecol, 76 (3): 448–58, doi:10.1111/j.1365-2656.2007.01219.x, retrieved 2024-02-05
- Ross Island Map, USGS: United States Geological Survey, 1972, retrieved 2024-02-05
- Rotella, Jay (2022), Weddell Seal Population Dynamics in Erebus Bay, Antarctica, Montana State University, retrieved 2024-02-05
![]() This article incorporates public domain material from websites or documents of the United States Geological Survey.
This article incorporates public domain material from websites or documents of the United States Geological Survey.






