Chiraphos

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
* (2S,3S)-(–)-Bis(diphenylphosphino)butane
| |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.152.152 |
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C28H28P2 | |
| Molar mass | 426.47 g/mol |
| Appearance | White powder |
| Melting point | 104 to 109 °C (219 to 228 °F; 377 to 382 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Chiraphos is a chiral diphosphine employed as a ligand in organometallic chemistry. This bidentate ligand chelates metals via the two phosphine groups. Its name is derived from its description — being both chiral and a phosphine. Chiraphos is available in two enantiomeric forms, S,S and R,R, each with C2 symmetry.
Preparation
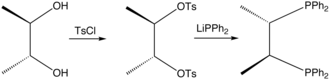
Chiraphos is prepared from S,S or R,R-2,3-butanediol, which are derived from commercially available S,S or R,R-tartaric acid; the technique of using cheaply available enantiopure starting materials is known as chiral pool synthesis. The diol is tosylated and then the ditosylate is treated with lithium diphenylphosphide.[1] The ligand was an important demonstration of how the conformation of the chelate ring can affect asymmetric induction by a metal catalyst. Prior to this work, in most chiral phosphines, e.g., DIPAMP, phosphorus was the stereogenic center.
References
- ^ M. D. Fryzuk, B. Bosnich (1977). "Asymmetric synthesis. Production of optically active amino acids by catalytic hydrogenation". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 99 (19): 6262–6267. doi:10.1021/ja00461a014. PMID 893889.