Clostridioides difficile infection: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
| binomial_authority = Hall & O'Toole, 1935 |
| binomial_authority = Hall & O'Toole, 1935 |
||
}} |
}} |
||
'''''Clostridium difficile''''' ([[Greek (language)|Greek]] ''kloster'' (κλωστήρ), spindle, and [[Latin]] ''difficile'',<ref>{{cite book | year = 2000 | title = American Heritage Dictionary | edition = Fourth | url = http://www.bartleby.com/61/67/D0216700.html | accessdate = 2009-02-15}}</ref> difficult), also known as "CDF/cdf", or "C. diff", is a species of [[Gram-positive]] [[bacteria]] of the genus ''[[Clostridium]]'' that causes diarrhea and other intestinal disease when competing bacteria are wiped out by antibiotics. |
'''''Clostridium difficile''''' ([[Greek (language)|Greek]] ''kloster'' (κλωστήρ), spindle, and [[Latin]] ''difficile'',<ref>{{cite book | year = 2000 | title = American Heritage Dictionary | edition = Fourth | url = http://www.bartleby.com/61/67/D0216700.html | accessdate = 2009-02-15}}</ref> difficult), also known as "CDF/cdf", or "C. diff", is a species of [[Gram-positive]] [[bacteria]] of the genus ''[[Clostridium]]'' that causes diarrhea and other intestinal disease when competing bacteria are wiped out by antibiotics. --[[Special:Contributions/70.232.5.178|70.232.5.178]] ([[User talk:70.232.5.178|talk]]) 17:28, 5 March 2010 (UTC) |
||
---- |
|||
#REDIRECT [[Target page name]] |
|||
Clostridia are [[Anaerobic organism|anaerobic]], [[endospore|spore]]-forming rods (bacilli).<ref name=Sherris>{{cite book | author = Ryan KJ, Ray CG (editors) | title = Sherris Medical Microbiology | edition = 4th | pages = 322–4 | publisher = McGraw Hill | year = 2004 | isbn= 0-8385-8529-9 }}</ref> ''C. difficile'' is the most serious cause of antibiotic-associated diarrhea (AAD) and can lead to [[pseudomembranous colitis]], a severe infection of the [[colon (anatomy)|colon]], often resulting from eradication of the normal [[gut flora]] by [[antibiotic]]s.<ref name=eMed1942>{{ cite web | url= http://www.emedicine.com/med/topic1942.htm#section~introduction | author=Curry J | title=Pseudomembranous Colitis | work=eMedicine | date=2007-07-20 | publisher=WebMD| accessdate=2008-11-17}}</ref> The ''C. difficile'' bacteria, which naturally reside in the body, become overpopulated: The overpopulation is harmful because the bacterium releases toxins that can cause [[bloating]], [[constipation]], and [[diarrhea]] with abdominal pain, which may become severe. Latent symptoms often mimic some [[flu-like symptoms]]. Often, it can be cured simply by discontinuing the antibiotics responsible.<ref name=Sherris /> In more serious cases, oral administration of [[metronidazole]] or [[vancomycin]] is the treatment of choice. Relapses of ''C. difficile'' AAD have been reported in up to 20% of cases.<ref name=Sherris /> |
Clostridia are [[Anaerobic organism|anaerobic]], [[endospore|spore]]-forming rods (bacilli).<ref name=Sherris>{{cite book | author = Ryan KJ, Ray CG (editors) | title = Sherris Medical Microbiology | edition = 4th | pages = 322–4 | publisher = McGraw Hill | year = 2004 | isbn= 0-8385-8529-9 }}</ref> ''C. difficile'' is the most serious cause of antibiotic-associated diarrhea (AAD) and can lead to [[pseudomembranous colitis]], a severe infection of the [[colon (anatomy)|colon]], often resulting from eradication of the normal [[gut flora]] by [[antibiotic]]s.<ref name=eMed1942>{{ cite web | url= http://www.emedicine.com/med/topic1942.htm#section~introduction | author=Curry J | title=Pseudomembranous Colitis | work=eMedicine | date=2007-07-20 | publisher=WebMD| accessdate=2008-11-17}}</ref> The ''C. difficile'' bacteria, which naturally reside in the body, become overpopulated: The overpopulation is harmful because the bacterium releases toxins that can cause [[bloating]], [[constipation]], and [[diarrhea]] with abdominal pain, which may become severe. Latent symptoms often mimic some [[flu-like symptoms]]. Often, it can be cured simply by discontinuing the antibiotics responsible.<ref name=Sherris /> In more serious cases, oral administration of [[metronidazole]] or [[vancomycin]] is the treatment of choice. Relapses of ''C. difficile'' AAD have been reported in up to 20% of cases.<ref name=Sherris /> |
||
Revision as of 17:28, 5 March 2010
| Clostridium difficile | |
|---|---|
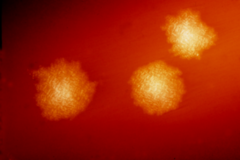
| |
| C. difficile colonies on a blood agar plate. | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| Phylum: | |
| Class: | |
| Order: | |
| Family: | |
| Genus: | |
| Species: | C. difficile
|
| Binomial name | |
| Clostridium difficile Hall & O'Toole, 1935
| |
Clostridium difficile (Greek kloster (κλωστήρ), spindle, and Latin difficile,[1] difficult), also known as "CDF/cdf", or "C. diff", is a species of Gram-positive bacteria of the genus Clostridium that causes diarrhea and other intestinal disease when competing bacteria are wiped out by antibiotics. --70.232.5.178 (talk) 17:28, 5 March 2010 (UTC)
- REDIRECT Target page name
Clostridia are anaerobic, spore-forming rods (bacilli).[2] C. difficile is the most serious cause of antibiotic-associated diarrhea (AAD) and can lead to pseudomembranous colitis, a severe infection of the colon, often resulting from eradication of the normal gut flora by antibiotics.[3] The C. difficile bacteria, which naturally reside in the body, become overpopulated: The overpopulation is harmful because the bacterium releases toxins that can cause bloating, constipation, and diarrhea with abdominal pain, which may become severe. Latent symptoms often mimic some flu-like symptoms. Often, it can be cured simply by discontinuing the antibiotics responsible.[2] In more serious cases, oral administration of metronidazole or vancomycin is the treatment of choice. Relapses of C. difficile AAD have been reported in up to 20% of cases.[2]
Bacteriology

Clostridia are motile bacteria that are ubiquitous in nature and are especially prevalent in soil. Under the microscope, clostridia appear as long, irregularly (often "drumstick" or "spindle") shaped cells with a bulge at their terminal ends. Under Gram staining, Clostridium difficile cells are Gram-positive and show optimum growth on blood agar at human body temperatures in the absence of oxygen. When stressed, the bacteria produce spores, which tolerate extreme conditions that the active bacteria cannot tolerate.[2]
C. difficile is a commensal bacterium of the human intestine in 2-5% of the population.[2] Long-term hospitalization or residence in a nursing home within the previous year are independent risk factors for increased colonization.[4] In small numbers, C. difficile does not result in significant disease. Antibiotics, especially those with a broad spectrum of activity, cause disruption of normal intestinal flora, leading to an overgrowth of C. difficile, which flourishes under these conditions. This can lead to pseudomembranous colitis (PMC), the generalized inflammation of the colon and the development of pseudomembrane, a viscous collection of inflammatory cells, fibrin, and necrotic cells.[2] Pathogenic C. difficile strains produce several known toxins. The most well-characterized are enterotoxin (toxin A) and cytotoxin (toxin B), both of which are responsible for the diarrhea and inflammation seen in infected patients, although their relative contributions have been debated.[2] Toxins A and B are glucosyltransferases that target and inactivate the Rho family of GTPases. Toxin A indcuses actin depolymerization by a mechanism correlated with a decrease in the ADP-ribosylation of the low molecular mass GTP-binding Rho proteins [5]. Another toxin, binary toxin, has also been described, but its role in disease is not yet fully understood.[6]
Antibiotic treatment of C. difficile infections can be difficult, due both to antibiotic resistance as well as physiological factors of the bacteria itself (spore formation, protective effects of the pseudomembrane).[2] C. difficile is transmitted from person to person by the fecal-oral route. Because the organism forms heat-resistant spores, it can remain in the hospital or nursing home environment for long periods of time. It can be cultured from almost any surface in the hospital. Once spores are ingested, they pass through the stomach unscathed because of their acid-resistance. They change to their active form in the colon and multiply. Pseudomembranous colitis caused by C. difficile is treated with specific antibiotics, for example, vancomycin (Vancocin®) or metronidazole (Flagyl®).
Several disinfectants commonly used in hospitals may be ineffective against C. difficile spores, and may actually promote spore formation. However, disinfectants containing bleach are effective in killing the organisms.[7]
Initially named bacillus difficilis by Hall and O'Toole in 1935 because it was resistant to early attempts at isolation and grew very slowly in culture, it was renamed in 1970.[8]
Cause
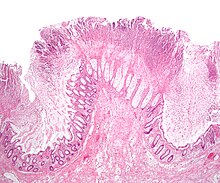
With the introduction of broad-spectrum antibiotics and chemotherapeutic antineoplastic drugs[citation needed] in the latter half of the twentieth century, antibiotic (and chemotherapy) associated diarrhea became more common. Pseudomembranous colitis was first described as a complication of C. difficile infection in 1978,[9] when a toxin was isolated from patients suffering from pseudomembranous colitis and Koch's postulates were met.
C. difficile infection (CDI) can range in severity from asymptomatic to severe and life-threatening, especially among the elderly. People are most often nosocomially infected in hospitals, nursing homes, or institutions, although C. difficile infection in the community, outpatient setting is increasing. The rate of C. difficile acquisition is estimated to be 13% in patients with hospital stays of up to 2 weeks, and 50% in those with hospital stays longer than 4 weeks.[citation needed] C. difficile-associated diarrhea (aka CDAD) is most strongly associated with fluoroquinolones. Fluoroquinolones are more strongly associated with C difficile infections than other antibiotics including clindamycin, 3rd generation cephalosporins and beta-lactamase inhibitors. One study found that fluoroquinolones were responsible for 55% of C difficile infections.[10] The European Center for Disease Prevention and Control recommend that fluoroquinolones and the antibiotic clindamycin be avoided in clinical practice due to their high association with clostridium difficile.[11] Frequency and severity of C. difficile colitis remains high and seems to be associated with increased death rates.[citation needed] Immunocompromised status and delayed diagnosis appear to result in elevated risk of death. Early intervention and aggressive management are key factors to recovery.
Increasing rates of community-acquired C. difficile-associated infection/disease have also been linked to the use of medication to suppress gastric acid production: H2-receptor antagonists increased the risk twofold, and proton pump inhibitors threefold, mainly in the elderly. It is presumed that increased gastric pH, (alkalinity), leads to decreased destruction of spores.[12]
The emergence of a new, highly toxic strain of C. difficile, resistant to fluoroquinolone antibiotics, such as ciprofloxacin (Cipro®) and levofloxacin (Levaquin®), said to be causing geographically dispersed outbreaks in North America was reported in 2005.[13] The Centers for Disease Control in Atlanta has also warned of the emergence of an epidemic strain with increased virulence, antibiotic resistance, or both.[14]
Diagnosis
Signs and Symptoms
In adults, a clinical prediction rule found the best signs to be: significant diarrhea ("new onset of > 3 partially formed or watery stools per 24 hour period"); recent antibiotic exposure; colitis (abdominal pain); and foul stool odour. The presence of any one of these findings has a sensitivity of 86% and a specificity of 45%.[15] In this study of hospitalized patients with a prevalence of positive cytotoxin assays of 14%, the positive predictive value was 20% and the negative predictive value was 95%.
Cytotoxicity assay
C. difficile toxins have a cytopathic effect in cell culture, and neutralized with specific anti-sera is the practical gold standard for studies investigating new CDAD diagnostic techniques.[2] Toxigenic culture, in which organisms are cultured on selective medium and tested for toxin production, remains the gold standard and is the most sensitive and specific test, although it is slow and labour-intensive.[16]
Toxin ELISA
Assessment of the A and B toxins by enzyme-linked immunoabsorbant assay (ELISA) for toxin A or B (or both) has a sensitivity of 63–99% and a specificity of 93–100%: at a prevalence of 15%, this leads to a positive predictive value (PPV) of 73% and a negative predictive value (NPV) of 96%.
Experts recommend sending as many as three samples to rule out disease if initial tests are negative. C. difficile toxin should clear from the stool of previously infected patients if treatment is effective. However, many hospitals test only for the prevalent toxin A. Strains that express only the B toxin are now present in many hospitals, and ordering both toxins should occur.[17] Not testing for both may contribute to a delay in obtaining laboratory results, which is often the cause of prolonged illness and poor outcomes.
Other stool tests
Stool leukocyte measurements and stool lactoferrin levels have also been proposed as diagnostic tests, but may have limited diagnostic accuracy.[18]
Computed tomography
In a recent study, a patient who received a diagnosis of CDC on the basis of computed tomography (CT scan) had an 88% probability of testing positive on stool assay.[19] Wall thickening is the key CT finding in this disease. Once colon wall thickening is identified as being >4 mm, the best ancillary findings were pericolonic stranding, ascites, and colon wall nodularity. The presence of wall thickness plus any one of these ancillary findings is 70% sensitive and 93% specific.
Using criteria of ≥10 mm or a wall thickness of >4 mm and any of the more-specific findings does not add significantly to the diagnosis but gives equally satisfactory results. In this study with a prevalence of positive C. difficile toxin of 54%, the PPV was 88%. Patients who have antibiotic-associated diarrhea who have CT findings diagnostic of CDC merit consideration for treatment on that basis. A weakness of this study was the lack of comparison with the accepted cytotoxicity assay.
Real-Time PCR
As the menu of molecular methods expands, more infectious diseases will be able to be quickly diagnosed with a high degree of accuracy. By the end of 2009, 3 different Real-Time PCR tests had achieved 510(k) clearance from the FDA. Cepheid's GeneXpert is by far the fastest and easiest of the three, but it is also the most expensive. Cepheid uses a cartridge based kit that is tailored for small hospitals or labs without the ability to batch large numbers of samples together. In fact, batching is not required since the extraction occurs in the same vial as amplification of the target, positive, and negative controls. The reported time from sample to result is ~45 minutes.
Prodesse offers another kit based IVD Real-Time PCR test (Pro-Gastro) which uses an external extraction and purification on the Roche MagnaPure. Prodesse (GeneProbe) tech support claims this external separation produces higher yields than the BD GeneOhm. The Prodesse technique is similar in price to the BD GeneOhm technique after one includes the price of the extraction and takes about three hours from sample to result.
The final IVD C. diff Real Time PCR test on the market since 2009 is from BD GeneOhm. The protocol uses a glass-bead lysis rather than an extraction, but results are reported to be good and the method shaves a little over an hour off the protocol time (about 1 hour 45 minutes from sample to result). Total costs for the Prodesse and BD GeneOhm tests are approximately the same. For each test, sensitivities are generally reported as 95-99% and specificities as 92-96%, depending on the tests and the size of the patient pool.
Prevention
The most effective method for preventing CDAD is proper antimicrobial prescribing. In the hospital setting, where CDAD is most common, nearly all patients that develop CDAD are exposed to antimicrobials. Although proper antimicrobial prescribing sounds easy to do, approximately 50% of antimicrobial use is considered inappropriate. This is consistent whether in the hospital, clinic, community, or academic setting. Several studies have demonstrated a decrease in CDAD by limiting antibiotics most strongly associated with CDAD or by limiting unnecessary antimicrobial prescribing in general, both in outbreak and non-outbreak settings. The testing of all hospital inpatients over the age of 65 with diarrhea for CDiff became a compulsory NHS practice in January 2008, when it became evident that many outbreaks were being disguised as Norovirus in the UK, by hospital Risk Managers, who can be sacked by the Department of Health if CDiff infection rates are too high, but cannot be dismissed as a result of a Norovirus outbreak.[citation needed] Patients most at risk are those with recent broad-spectrum antibiotic and proton-pump inhibitor treatments.
Infection control measures, such as wearing gloves when caring for patients with CDAD, have been proven to be effective at prevention. This works by limiting the spread of C. difficile in the hospital setting. In addition, washing with soap and water will eliminate the spores from contaminated hands, but alcohol-based hand rubs are ineffective.[20]Treatment with various oral supplements containing live bacteria has been studied in efforts to prevent Clostridium difficile-associated infection/disease. A randomized controlled trial using a probiotic drink containing Lactobacillus casei, L bulgaricus, and Streptococcus thermophilus was reported to have some efficacy. This study was sponsored by the company that produces the drink studied.[21] Although intriguing, several other studies have been unable to demonstrate any benefit of oral supplements of similar bacteria at preventing CDAD.[citation needed] Of note, patients on the antibiotics most strongly associated with CDAD were excluded from this study.
In a limited clinical trial, a C. difficile anti-toxoid vaccine was reported to improve patient outcomes. Further testing will be required to validate this trial.[22]
Treatment
Asymptomatic colonization with C. difficile is common. Treatment in asymptomatic patients is controversial, also leading into the debate of clinical surveillance and how it intersects with public health policy. Mild cases generally do not require specific treatment.[2][23]
Patients should be treated as soon as possible when the diagnosis of Clostridium difficile colitis (CDC) is made to avoid frank sepsis or bowel perforation. To reduce complications, physicians often begin treatment based on clinical presentation before definitive results are available. Knowledge of the local epidemiology of intestinal flora of a particular institution can guide therapy.
Saccharomyces boulardii Lyo is the only probiotic worldwide known to diminish levels of Clostridium difficile in the body. S. boulardii Lyo can be found under the brand name Florastor; clinically proven as effective treatment alongside traditional medications.[24]
Pharmacotherapy
Three antibiotics are specifically effective against C. difficile in vivo :
- Metronidazole (400–500 mg orally three times daily[25]) is the drug of choice, because of lower price and comparable efficacy.[26]
- Oral vancomycin (125 mg four times daily) is second-line therapy, but is often avoided due to concerns of converting intestinal flora into vancomycin-resistant organisms.[27][28] Vancomycin is the treatment of choice in the following cases: no response to oral metronidazole; the organism is resistant to metronidazole; the patient is allergic to metronidazole; the patient is either pregnant or younger than 10 years of age. Vancomycin must be administered orally because IV administration does not achieve gut lumen minimum therapeutic concentration.
- A more recent study by Zar and others[29] showed no difference between vancomycin and metronidazole in mild disease, but that vancomycin was superior to metronidazole for treating severe disease. In this study, severe disease was defined on a point score: One point each was given for age >60 years, temperature >38.3°C, albumin level <2.5 mg/dL, or peripheral WBC count >15,000 cells/mm3 within 48 h of enrollment. Two points were given for endoscopic evidence of pseudomembranous colitis or treatment in the intensive care unit. Severe disease was defined as 2 or more points on this score. The main criticism of this study is that a low, non-standard dose of metronidazole (250 mg) was used instead of (500 mg).
- The use of linezolid may be considered, too.
Newer drugs such as ramoplanin and fidaxomicin are in clinical development.
Drugs traditionally used to stop diarrhea frequently worsen the course of C. difficile-related pseudomembranous colitis. Loperamide, diphenoxylate and bismuth compounds are contraindicated: slowing of fecal transit time is thought to result in extended toxin-associated damage. Cholestyramine, a powder drink occasionally used to lower cholesterol, is effective in binding both Toxin A and B, and slows bowel motility and helps prevent dehydration.[30] The dosage can be 4 grams daily, to up to four doses a day: Caution should be exercised to prevent constipation, or drug interactions, most notably the binding of drugs by cholestyramine, preventing their absorption. Powdered banana flakes given twice daily is an alternative to cholestyramine and allow for stool bulking. Treatment with probiotics ("good" intestinal flora) has also been shown effective.[31] Provision of Saccharomyces boulardii (Florastor) or Lactobacillus acidophilus twice daily times 30 days along with antibiotics has been clinically shown to shorten the duration of diarrhoea. A last-resort treatment in immunosuppressed patients is intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG).[30]
Colectomy
In those patients that develop systemic symptoms of CDC, colectomy may improve the outcome if performed before the need for vasopressors.
Fecal bacteriotherapy
Fecal bacteriotherapy, a procedure related to probiotic research, has been suggested as a potential cure for the disease. It involves infusion of bacterial flora acquired from the feces of a healthy donor in an attempt to reverse bacterial imbalance responsible for the recurring nature of the infection. It has a success rate of nearly 95% according to some sources.[32][33][34]
Recurrence
The evolution of protocols for patients with recurrent C. difficile diarrhea also present a challenge: There is no known proper length of time or universally accepted alternative drugs with which one should be treated. However, re-treatment with metronidazole or vancomycin at the previous dose for 10 to 14 days is generally successful. The addition of rifampin to vancomycin also has been effective. Prophylaxis with competing, nonpathogenic organisms such as Lactobacillus spp. or Saccharomyces boulardii has been found to be helpful in preventing relapse in small numbers of patients (see, for example, Florastor, or Lactinex). It is thought that these organisms, also known as probiotics, help to restore the natural flora in the gut and make patients more resistant to colonization by C. difficile.[31]
Treatments in Development
- Fidaxomicin, previously known as OPT-80 and PAR-101, is the first of a new class of antibiotics, the macrocyclics. In clinical studies, fidaxomicin has demonstrated that it is narrow spectrum and minimally absorbed after oral administration.[35] It is currently being evaluated in double-blind, randomized, multicenter international Phase III clinical trials vs. oral vancomycin. Results from the first phase III North American trial were presented publicly in November 2008. Fidaxomicin has received fast track designation from the FDA and is being developed by Optimer Pharmaceuticals
- CDA-1 and CDB-1 (also known as MDX-066/MDX-1388 and MBL-CDA1/MBL-CDB1) is an investigational, monoclonal antibody combination co-developed by Medarex and Massachusetts Biologic Laboratories (MBL) to target and neutralize C. difficile toxins A and B, for the treatment of CDI. Merck & Co., Inc. gained worldwide rights to develop and commercialize CDA-1 and CDB-1 through an exclusive license agreement signed in April 2009. It is intended as an add-on therapy to one of the existing antibiotics to treat CDI.
- Nitazoxanide is a synthetic nitrothiazolyl-salicylamide derivative indicated as an antiprotozoal agent (FDA-approved for the treatment of infectious diarrhea caused by Cryptosporidium parvum and Giardia lamblia) and is also currently being studied in C. difficile infections vs. vancomycin.
- Rifaximin is a clinical-stage semi synthetic, rifamycin-based non-systemic antibiotic for CDI. It is FDA-approved for the treatment of infectious diarrhea and being developed by Salix Pharmaceuticals.
Prognosis
After a first treatment with metronidazole or vancomycin C. dif recurs in about 20% of people. This increase to 40% and 60% with subsequent recurrences.[36]
Society and culture
Pronunciation
Scientific names of organisms are Latin or Latinised Greek, in this case one of each. The anglicized pronunciation /klɒsˈtrɪdiəm dɨˈfɪsɨli/ is common, though a more Classical /dɨˈfɪkɨli/ is also used.
A common practice has developed of pronouncing difficile as /diːfiˈsiːl, as though it were French.
Notable outbreaks
- June 4, 2003, two outbreaks of a highly virulent strain of this bacterium were reported in Montreal, Quebec and Calgary, Alberta, in Canada. Sources put the death count as low as 36 and as high as 89, with approximately 1,400 cases in 2003 and within the first few months of 2004. C. difficile infections continued to be a problem in the Quebec health care system in late 2004. As of March 2005, it had spread into the Toronto, Ontario area, hospitalizing 10 people. One died while the others were being discharged.
- A similar outbreak took place at Stoke Mandeville Hospital in the United Kingdom between 2003 and 2005. The local epidemiology of C. difficile may offer clues on how its spread may relate to the amount of time a patient spends in hospital and/or a rehabilitation center. It also samples institutions' ability to detect increased rates, and their capacity to respond with more aggressive hand-washing campaigns, quarantine methods, and availability of yoghurt to patients at risk for infection.
- It has been suggested that both the Canadian and English outbreaks were related to the seemingly more virulent Strain NAP1/027 of bacterium. This novel strain, also known as Quebec strain, has also been implicated in an epidemic at two Dutch hospitals (Harderwijk and Amersfoort, both 2005). A theory for explaining the increased virulence of 027 is that it is a hyperproducer of both toxins A and B, and that certain antibiotics may actually stimulate the bacteria to hyperproduce.
- October 1, 2006, C.diff was said to have killed at least 49 people at hospitals in Leicester, England over eight months, according to a National Health Service investigation. Another 29 similar cases were investigated by coroners.[37] A UK Department of Health memo leaked shortly afterwards revealed significant concern in government about the bacterium, described as being "endemic throughout the health service"[38]
- October 27, 2006, 9 deaths were attributed to the bacterium in Quebec, Canada.[39]
- November 18, 2006, the bacterium was reported to have been responsible for 12 deaths in Quebec, Canada. This 12th reported death was only two days after the St. Hyacinthe's Honoré Mercier announced that the outbreak was under control. Thirty-one patients were diagnosed with Clostridium difficile and four (as of Sat. Nov 18th) were still under observation. Cleaning crews took measures in an attempt to clear the outbreak.[40]
- C. difficile was mentioned on 6,480 death certificates in 2006 in UK.[41]
- February 27, 2007, a new outbreak was identified at Trillium Health Centre in Mississauga, Ontario, where 14 people were diagnosed with the bacteria. The bacteria was of the same strain as the one in Quebec. Officials have not been able to determine whether C. difficile was responsible for deaths of four patients over the prior two months.[42]
- Between February and June 2007, three patients at Loughlinstown Hospital in Dublin, Ireland were found by the coroner to have died as a result of C.diff infection. In an inquest, the Coroner's Court found that the hospital had no designated infection control team or consultant microbiologist on staff.[43]
- October 2007, Maidstone and Tunbridge Wells NHS Trust was heavily criticized by the Healthcare Commission regarding its handling of a major outbreak of C. difficile in its hospitals in Kent from April 2004 to September 2006. In its report, the Commission estimated that about 90 patients "definitely or probably" died as a result of the infection.[44][45]
- November 2007, the 027 strain has spread into several hospitals in southern Finland, with ten deaths out of 115 infected patients reported on 2007-12-14.[46]
- November 2009, four deaths at Our Lady of Lourdes Hospital in Ireland, have possible links to Clostridium Difficile infection. A further 12 patients tested positive for infection, and another 20 show signs of infection, 10 November 2009.[47]
Research
Genome sequencing
The first complete genome sequence of a Clostridium difficile strain was first published in 2006 by Sanger Institute in the UK. This was of the C. difficile strain 630, a virulent and multidrug-resistant strain. Researchers at McGill University in Montreal, Quebec, sequenced the genome of the highly virulent Quebec strain of C. difficile in 2005 using ultra-high-throughput sequencing technology. The tests involved doing 400,000 DNA parallel sequencing reactions of the bacterium's genome which had been fragmented for sequencing. These sequences were assembled computationally to form a complete genome sequence.[13][48]
See also
- Contamination control
- Nosocomial infection
- Colitis-X (in horses)
References
- ^ American Heritage Dictionary (Fourth ed.). 2000. Retrieved 2009-02-15.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j Ryan KJ, Ray CG (editors) (2004). Sherris Medical Microbiology (4th ed.). McGraw Hill. pp. 322–4. ISBN 0-8385-8529-9.
{{cite book}}:|author=has generic name (help) - ^ Curry J (2007-07-20). "Pseudomembranous Colitis". eMedicine. WebMD. Retrieved 2008-11-17.
- ^ Halsey J (2008). "Current and future treatment modalities for Clostridium difficile-associated disease". Am J Health Syst Pharm. 65 (8): 705–15. doi:10.2146/ajhp070077. PMID 18387898.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ Just, I., Selzer, J., von Eichel-Streiber, C., and Aktories, K.(1995) J. Clin. Invest. 95, 1026-1031
- ^ Barth H, Aktories K, Popoff M, Stiles B (2004). "Binary bacterial toxins: biochemistry, biology, and applications of common Clostridium and Bacillus proteins". Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 68 (3): 373–402, table of contents. doi:10.1128/MMBR.68.3.373-402.2004. PMC 515256. PMID 15353562.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ "Cleaning agents 'make bug strong'". BBC News Online. 2006-04-03. Retrieved 2008-11-17.
- ^ Hall I, O'Toole E (1935). "Intestinal flora in newborn infants with a description of a new pathogenic anaerobe, Bacillus difficilis". Am J Dis Child. 49: 390.
- ^ Larson H, Price A, Honour P, Borriello S (1978). "Clostridium difficile and the aetiology of pseudomembranous colitis". Lancet. 1 (8073): 1063–6. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(78)90912-1. PMID 77366.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Pépin J, Saheb N, Coulombe MA; et al. (2005). "Emergence of fluoroquinolones as the predominant risk factor for Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea: a cohort study during an epidemic in Quebec". Clin. Infect. Dis. 41 (9): 1254–60. doi:10.1086/496986. PMID 16206099.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Dr Ralf-Peter Vonberg. "Clostridium difficile: a challenge for hospitals". European Center for Disease Prevention and Control. Institute for Medical Microbiology and Hospital Epidemiology: IHE. Retrieved 27 July 2009.
- ^ Dial S, Delaney J, Barkun A, Suissa S (2005). "Use of gastric acid-suppressive agents and the risk of community-acquired Clostridium difficile-associated disease". JAMA. 294 (23): 2989–95. doi:10.1001/jama.294.23.2989. PMID 16414946.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b Loo V, Poirier L, Miller M; et al. (2005). "A predominantly clonal multi-institutional outbreak of Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhoea with high morbidity and mortality". N Engl J Med. 353 (23): 2442–9. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa051639. PMID 16322602.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ McDonald L (2005). "Clostridium difficile: responding to a new threat from an old enemy" (PDF). Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 26 (8): 672–5. doi:10.1086/502600. PMID 16156321.
- ^ Katz DA, Lynch ME, Littenberg B (1996). "Clinical prediction rules to optimize cytotoxin testing for Clostridium difficile in hospitalized patients with diarrhea". Am. J. Med. 100 (5): 487–95. doi:10.1016/S0002-9343(95)00016-X. PMID 8644759.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Murray PR, Baron EJ, Pfaller EA, Tenover F, Yolken RH (editors) (2003). Manual of Clinical Microbiology (8th ed.). Washington DC: ASM Press. ISBN 1-55581-255-3.
{{cite book}}:|author=has generic name (help); Check|isbn=value: checksum (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Anna Salleh (2009-03-02). "Researchers knock down gastro bug myths". ABC Science Online. Retrieved 2009-03-02.
- ^ Kirkpatrick ID, Greenberg HM (2001). "Evaluating the CT diagnosis of Clostridium difficile colitis: should CT guide therapy?". AJR. American journal of roentgenology. 176 (3): 635–9. PMID 11222194.
- ^ http://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/563232
- ^ Hickson M, D'Souza AL, Muthu N; et al. (2007). "Use of probiotic Lactobacillus preparation to prevent diarrhoea associated with antibiotics: randomised double blind placebo controlled trial". BMJ. 335 (7610): 80. doi:10.1136/bmj.39231.599815.55. PMC 1914504. PMID 17604300.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Mattila E, Anttila VJ, Broas M; et al. (2008). "A randomized, double-blind study comparing Clostridium difficile immune whey and metronidazole for recurrent Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhoea: Efficacy and safety data of a prematurely interrupted trial". Scand. J. Infect. Dis. 40: 1–7. doi:10.1080/00365540801964960. PMID 18609231.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Nelson R; Nelson, Richard L (2007). "Antibiotic treatment for Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea in adults". Cochrane Database Syst Rev (3): CD004610. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD004610.pub3. PMID 17636768.
- ^ http://www.optibacprobiotics.co.uk/images/mcfarland_et_al_(1994)_randomised_placebo-controlled_trial_of_s.boulardii_with_antibiotics_for_clostridium_difficile_disease_
- ^ http://www.bnf.org/bnf/bnf/57/3932.htm?q=%22metronidazole%22
- ^ Teasley DG, Gerding DN, Olson MM; et al. (1983). "Prospective randomised trial of metronidazole versus vancomycin for Clostridium-difficile-associated diarrhoea and colitis". Lancet. 2 (8358): 1043–6. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(83)91036-X. PMID 6138597.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Morris JG Jr, Shay DK, Hebden JN; et al. (1995). "Ann Intern Med". 123: 250–9.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help); Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Rao GG, Ojo F, Kolokithas D (1997). "Vancomycin-resistant gram-positive cocci: risk factors for faecal carriage". J Hosp Infect. 35 (1): 63–9. doi:10.1016/S0195-6701(97)90169-9. PMID 9032637.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Zar FA, Bakkanagari SR, Moorthi KM, Davis MB (2007). "A comparison of vancomycin and metronidazole for the treatment of Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea, stratified by disease severity". Clin Infect Dis. 45 (3): 302–7. doi:10.1086/519265. PMID 17599306.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b Stroehlein J (2004). "Treatment of Clostridium difficile Infection". Curr Treat Options Gastroenterol. 7 (3): 235–239. doi:10.1007/s11938-004-0044-y. PMID 15149585.
- ^ a b "Inhibition of Clostridium difficile strains by intestinal Lactobacillus species". Society for General Microbiology. Retrieved 2008-09-17.
- ^ Schwan A, Sjölin S, Trottestam U, Aronsson B (1983). "Relapsing clostridium difficile enterocolitis cured by rectal infusion of homologous faeces". Lancet. 2 (8354): 845. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(83)90753-5. PMID 6137662.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Paterson D, Iredell J, Whitby M (1994). "Putting back the bugs: bacterial treatment relieves chronic diarrhoea". Med J Aust. 160 (4): 232–3. PMID 8309401.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Borody T (2000). ""Flora Power" - fecal bacteria cure chronic C. difficile diarrhea" (PDF). Am J Gastroenterol. 95 (11): 3028–9. doi:10.1111/j.1572-0241.2000.03277.x. PMID 11095314.
- ^ Louie, Thomas (2009-01). "OPT-80 Eliminates Clostridium difficile and Is Sparing of Bacteroides". Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy. 535 (1): 261–263. PMID 18955523.
{{cite journal}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help); Check date values in:|date=(help); Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Kelly CP, LaMont JT (2008). "Clostridium difficile--more difficult than ever". N. Engl. J. Med. 359 (18): 1932–40. doi:10.1056/NEJMra0707500. PMID 18971494.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ Trust confirms 49 superbug deaths - BBC News
- ^ Nigel Hawkes (2007-01-11). "Leaked memo reveals that targets to beat MRSA will not be met". The Times. London. Retrieved 2007-01-11.
- ^ "C. difficile blamed for 9 death in hospital near Montreal". cNews. 11th January 200. Retrieved 2007-01-11.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ 12th person dies of C. difficile at Quebec hospital - CBC News
- ^ Hospitals struck by new killer bugAn article by Manchester free newspaper 'Metro', May 7, 2008
- ^ CTV Toronto - C. difficile outbreak linked to fatal strain - CTV News, Shows and Sports - Canadian Television
- ^ Irish Independent, Superbug in hospitals linked to four deaths, 10 October 2007
- ^ Healthcare Commission press release: Healthcare watchdog finds significant failings in infection control at Maidstone and Tunbridge Wells NHS Trust, 11 October 2007
- ^ Daily Telegraph, Health Secretary intervenes in superbug row, 11 October 2007
- ^ Ärhäkkä suolistobakteeri on tappanut jo kymmenen potilasta - HS.fi - Kotimaa
- ^ Possible C Diff link to Drogheda deaths, RTE News, 10th November 2009
- ^ Scientists map C. difficile strain - Institute of Public Affairs, Montreal
Further reading
- Dallal R, Harbrecht B, Boujoukas A, Sirio C, Farkas L, Lee K, Simmons R (2002). "Fulminant Clostridium difficile: an underappreciated and increasing cause of death and complications". Ann Surg. 235 (3): 363–72. doi:10.1097/00000658-200203000-00008. PMC 1422442. PMID 11882758.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
- Martin S, Jung R (2005). Gastrointestinal infections and enterotoxigenic poisonings. In: Pharmacotherapy: A Pathophysiologic Approach (DiPiro JT, Talbert RL, Yee GC, Matzke GR, Wells BG, Posey LM, editors) (6th ed.). McGraw-Hill. pp. 2042–2043. ISBN.
- McDonald L, Killgore G, Thompson A, Owens R, Kazakova S, Sambol S, Johnson S, Gerding D (2005). "An epidemic, toxin gene-variant strain of Clostridium difficile". N Engl J Med. 353 (23): 2433–41. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa051590. PMID 16322603.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
- Yamada T; Alpers DH (editors) (2003). Textbook of Gastroenterology (4th ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 1870–1875. ISBN 0-7817-2861-4.
{{cite book}}:|author=has generic name (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
- van den Hof S, van der Kooi T, van den Berg R, Kuijper E, Notermans D (2006). "Clostridium difficile PCR ribotype 027 outbreaks in the Netherlands: recent surveillance data indicate that outbreaks are not easily controlled but interhospital transmission is limited". Euro Surveill. 11 (1): E060126.2. PMID 16801713.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
- Sunenshine R, McDonald L (2006). "Clostridium difficile-associated disease: New challenges from an established pathogen". Cleveland Clinic J. Med. 73: 187. doi:10.3949/ccjm.73.2.187.
External links
- Wins Story (The risks of C Diff infection and hospital neglect)
- Pseudomembranous colitis at Curlie
- "From hand to mouth" Article from The Economist discussing C. difficile (requires subscription)
- Pathema - Clostridium genomics resource
- US CDC Report on Severe Clostridium difficile--Associated Disease in Populations Previously at Low Risk--Four States, 2005
- from the UK Clostridium difficile Support Group (UK)
- MedscapeCME Healthcare-associated infections.
- "Sea Change Anticipated in the Management of C. difficile Infection" July 2009
