Common cold
| Common cold | |
|---|---|
| Specialty | Family medicine, infectious diseases, otorhinolaryngology |
Acute viral nasopharyngitis, often known as the common cold, is a viral infectious disease of the upper respiratory system (nose and throat).[1] Symptoms include sneezing, sniffling, stomach aches, runny nose, nasal congestion; scratchy, sore, or phlegmy throat; coughing; headache; and tiredness. Those affected may also feel achy. Colds typically last three to five days, with residual coughing and/or catarrh lasting up to three weeks. The common cold is the most common of all human diseases infecting adults at an average rate of 2–4 infections per year, and school-aged children as many as 12 times per year. Children and their parents or caretakers are at a higher risk, possibly due to the high population density of schools and because transmission to family members is highly efficient.
The common cold belongs to the upper respiratory tract infections. It is different from influenza, a more severe viral infection of the respiratory tract that shows the additional symptoms of rapidly rising fever, chills, and body and muscle aches. While the common cold itself is rarely life-threatening, its complications, such as pneumonia, can be.
Pathology
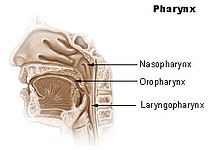
The common cold is caused by numerous viruses (mainly rhinoviruses, coronaviruses, and also certain echoviruses, paramyxoviruses, and coxsackieviruses) infecting the upper inspiratory system. Several hundred cold-causing viruses have been described, and a virus can evolve to survive, ensuring that any cure is still a long time from being developed. The nasopharynx is the central area infected.[2] The reasons that the virus concentrates in the nasopharynx rather than the throat may be the low temperature and high concentration of cells with receptors needed for the virus. [citation needed]
The viruses are transmitted from person to person in two ways. The most effective is by physical contact: a cold sufferer wipes his or her nose, shakes hands with someone who then rubs his or her eyes or nose. There is a lesser but significant level of infection from inhaling droplets from coughs or sneezes (Tyrrell DA, Ann. Rev Microbiology 1988 42 35–47). Infective cold viruses can also persist on objects that have been handled, such as doorknobs and shopping carts, with a half-life of about one hour.[citation needed]
The virus takes advantage of both the copious flow of nasal fluid and sneezes and coughs to infect the next person before it is defeated by the body's immune system. Sneezes expel a significantly larger concentration of virus "cloud" than coughing. The "cloud" is partly invisible and falls at a rate slow enough to last for hours—with part of the droplet nuclei evaporating and leaving much smaller and invisible "droplet nuclei" in the air. Droplets from turbulent sneezing or coughing or hand contact also can last for hours on surfaces, although less virus can be recovered from porous surfaces such as wood or paper towel than non-porous surfaces such as a metal bar. A sufferer is most infectious within the first three days of the illness. Symptoms, however, are not necessary for viral shedding or transmission, as a percentage of asymptomatic subjects exhibit viruses in nasal swabs, likely controlling the virus at concentrations too low for them to have symptoms.
Mechanism of infection
The virus enters the cells of the lining of the nasopharynx (the area between the nose and throat), and rapidly multiplies. The major entry point is normally the nose, but can also be the eyes (in this case drainage into the nasopharynx would occur through the Nasolacrimal duct). The mouth is not a major point of entry and transmission does not usually occur with kissing or swallowing.
The virus enters the cell by binding to ICAM-1 receptors in these cells. The presence of ICAM-1 affects whether a cell will be infected. Its concentration also can be affected by various other factors, including allergic rhinitis and some other irritants including rhinoviruses themselves. ICAM-1 has been a major focal point in drug research into cold treatments.
Symptoms
Between a third and a half of people exposed to a cold virus become infected (Jackson GG et al, AMA Arch Intern. Med 1958 101 267); 75% show symptoms, which start 1–2 days after infection. Generally, a cold starts with a sore throat with no respiratory blockage. Later symptoms are a result of the body's defense mechanisms—sneezes, runny nose, and coughs. Coughs expel the invader while inflammation attracts and activates immune cells. Severe colds can even lead to a slightly stiff neck and mild to severe headaches with a slight fever for some.
Often confused with influenza (or the flu), the common cold is caused by a different type of virus and usually does not result in a significantly higher body temperature—a high fever is a very reliable indicator of the flu.
After a common cold, a sufferer develops immunity to the particular virus. This immunity offers only limited protection against the many other cold viruses. The person, therefore, can easily be infected by a different cold virus.
Complications
Bacteria that are normally present in the respiratory tract can take advantage of the weakened immune system during a common cold and produce a coinfection. Middle ear infection (in children) and bacterial sinusitis are common coinfections. A possible explanation for these coinfections is that strong blowing of the nose drives nasal fluids into those areas.
The best way to blow the nose is keeping both nasal openings open when blowing and wiping rather than fully covering them, permitting pressure to partially dissipate. Doing so will reduce the pressure that would otherwise drive into the ears or sinuses.
Prevention
The best way to avoid a cold is to avoid close contact with existing sufferers; to wash hands thoroughly and regularly; and to avoid touching the face. Anti-bacterial soaps have no effect on the cold virus — it is the mechanical action of hand washing that removes the virus particles.[3][4]
In 2002, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommended alcohol-based hand gels as an effective method for reducing infectious viruses on the hands.[citation needed] However, as with standard handwashing, alcohol gels provide no residual protection from re-infection. Tobacco smoking has also been linked with the weakening of the immune system; non-smokers are known on average to take fewer days off sick than the smoking population.[citation needed].
The common cold is caused by a large variety of viruses, which mutate quite frequently during reproduction, resulting in constantly changing virus strands. Thus, successful immunization is highly improbable.
Treatment
As there is no medically proven and accepted medication directly targeting the causative agent, there is no cure for the common cold. Treatment is limited to symptomatic supportive options, maximizing the comfort of the patient, and limiting complications and harmful sequelae. The most reliable treatment is a combination of fluids and plenty of rest.
The common cold is self-limited, and is effectively dealt with by the host's immune system. Within a few days, the body's humoral immune response begins producing specific antibodies that can prevent the virus from infecting cells. Additionally, as part of the cell-mediated immune response, leukocytes destroy the virus through phagocytosis and destroy infected cells to prevent further viral replication. In healthy, immunocompetent individuals, the common cold resolves in seven days on average.[1]
Antibiotics
Antibiotics are pharmaceutical agents active against bacteria. They have no value in cases of viral infection, and thus are ineffective against the common cold. Treatment of colds with antibiotics can be counterproductive, as it can promote the evolution of drug resistant bacteria, and can result in side effects including allergic reactions to the antibiotic or diarrhea caused by disruption of the normal balance of intestinal flora.[5]
Steam inhalation
Some people have reported that inhaling warm air or steam for five to 15 minutes can cure or substantially limit the symptoms of a cold. In some parts of the world this remedy (Italian: suffumigio) has been used for centuries and is commonly considered very effective, although scientific studies have concluded that there is insufficient evidence in the literature to support the use of steam inhalation as a treatment.[6][7][8] The alleged effectiveness of this remedy may be based on the fact that rhinovirus cannot survive at elevated temperatures for more than a few minutes.[9] Because of this weakness, rhinovirus infects the outer membranes of the throat and sinuses, where it is not exposed to normal human body temperature.[9] Breathing hot air may expose much of the virus to excessive heat.[9] Some doctors also advise that breathing steam helps to loosen the mucus in your nose and lungs so that it can be removed by coughing.[10]
This remedy is commonly undertaken by bringing tap water to a boil in a large, low pot, then turning off the heat source, dissolving balsamic substances in the hot water (commonly used are a combination of Eucalyptol and Baking soda) and immediately placing a bath towel over one's head to form an enclosed space between the face and the water, slowly inhaling the hot air/steam. The steam should feel very hot, but not scalding. In fact, care should be taken to avoid burning the sinuses and throat. The remedy is concluded by going straight to bed after the inhalation.
Echinacea
Although there have been scientific studies done on echinacea, its effectiveness has not been demonstrated. A peer-reviewed clinical study published in the New England Journal of Medicine concluded that …extracts of E. angustifolia root, either alone or in combination, do not have clinically significant effects on rhinovirus infection or on the clinical illness that results from it. Use of echinacea should not exceed two weeks, and it may adversely interact with other medications.[11]
Antivirals
ViroPharma Incorporated and Schering-Plough have been developing an anti-viral drug that targets picornaviruses, the viruses that cause the majority of common colds. Pleconaril has been shown to be effective in an oral form.[12][13] Schering-Plough is developing an intra-nasal formulation that may have fewer adverse effects.[14]
Interferons
Interferons, natural proteins produced by the cells of the immune system, can be administered intranasally in low doses. In Eastern Europe, Russia, and Japan this is used as a method to prevent and treat viral respiratory diseases such as cold and flu, though its effectiveness has not been proven. Interferon-containing lozenges are currently being investigated as an alternative method of delivery.
Vitamin C
Publications in the 1960s and 1970s suggested that large doses of vitamin C could both prevent as well as reduce the effects of the common cold.[15] A well known supporter of this theory was Nobel Prize winner Linus Pauling, who publicly advocated the intake of large doses of vitamin C to prevent infection.[16] In 1970 he wrote the bestseller Vitamin C and the Common Cold. A meta-analysis published in 2005 found that vitamin C reduced the incidence of colds by 50% in six trials with physically stressed participants, but that 200+mg daily had no effect on the incidence of colds in ordinary people.[17] Regular vitamin C supplementation shortened the duration of colds in children by 14% and in adults by 8%.[17]
Findings from therapeutic trials of dosages under 6 grams per day and single doses[1] have been conflicting. It is worth noting that none of the recent conventional therapeutic trials carried out so far have examined the effect of vitamin C on children, although the regular supplementation trials have shown a substantially greater effect on episode duration in children.[citation needed]
The Vitamin C Foundation recommends an initial usage of up to 8 grams of vitamin C every 20–30 minutes[18] in order to show an effect on the symptoms of a cold infection that is in progress. Most of the studies showing little or no effect employ doses of ascorbate such as 100 mg to 500 mg per day, considered "small" by vitamin C advocates. Equally important, the plasma half life of high dose ascorbate above the baseline, controlled by renal resorption, is approximately 30 minutes,[19][20] which implies that most high dose studies have been methodologically defective and would be expected to show a minimum benefit. Clinical studies of divided dose supplementation, predicted on pharmacological grounds to be effective, have only rarely been reported in the literature.
Because vitamin C is metabolized to oxalic acid in the body, some scientists have long speculated that high doses may contribute to the development of kidney stones. Such hypotheses have so far proven inconclusive with other aggravating and mitigating factors being better identified.[21]
The United States Department of Agriculture recommends a minimum daily requirement of 75mg to 90mg Vitamin C for adults and 120mg for lactating females,[22] while the European Commission Health and Consumer Protection DG recommends a minimum of 60mg for all adults.[23]
Zinc preparations
Zinc-containing lozenges were first claimed to be effective in the treatment of cold infections by Eby, Davis and Halcomb.[24] There have been a number of clinical studies of the efficacy of zinc, some of which have shown an effect and some of which have shown no effect.[25]
A 1997 meta-analysis of six clinical studies concluded that Despite numerous randomized trials, the evidence for effectiveness of zinc salts lozenges in reducing the duration of common colds is still lacking.[26] A 1999 scientific review of published data concluded: Overall, the results suggest that treatment with zinc lozenges did not reduce the duration of cold symptoms. Evidence of the effects of zinc lozenges for treating the common cold is inconclusive. Given the potential for treatment to produce side effects, the use of zinc lozenges to treat cold symptoms deserves further study.[27] Another scientific review by George Eby in 2004, one that considered the solution chemistry of all zinc lozenge formulations tested from 1984 through 2004, showed a statistically significant dose response when the amount of ionic zinc, rather than total zinc, was considered.[28] However, Eby and Halcomb failed to show any efficacy from zinc gluconate nasal sprays in 2006, and suggested why some throat lozenges are effective, while nasal application is not effective.[2]
There are concerns regarding the safety of long-term use of cold preparations in an estimated 25 million persons who are haemochromatosis heterozygotes.[29] Another concern with use of very high-dose zinc for more than two weeks is copper depletion, which leads to anemia.
Although widely available and advertised in the United States, the safety and efficacy of zinc preparations have not been evaluated or approved by the Food and Drug Administration, and they are not likely to have any utility against colds due to removal of ionic zinc through additive food acids (citric acid, ascorbic acid and glycine). Consequently, a "cure for the common cold" using zinc acetate lozenges without additive food acids[30] is not available due to marketing, rather than scientific, considerations. In the United Kingdom, the National Health Service includes zinc lozenges in a list of not-recommended treatments.[3]
Treatments
There are a number of effective treatments which, rather than treat the viral infection, focus on relieving the symptoms. For some people, colds are relatively minor inconveniences and they can go on with their daily activities with tolerable discomfort. This discomfort has to be weighed against the price and possible side effects of the remedies, and the possibility, though not scientifically proven, that by suppressing responses evolved to fight the cold, the symptom suppressants may prolong the illness.
Common treatments include: analgesics such as aspirin or paracetamol, as well as localised versions targeting the throat (often delivered in lozenge form), nasal decongestants such as phenylephrine which reduce the inflammation in the nasal passages by constricting local blood vessels, cough suppressants (which work to suppress the cough reflex of the brain or by diluting the mucus in the lungs), and first-generation anti-histamines such as brompheniramine, chlorpheniramine, diphenhydramine and clemastine (which reduce mucus gland secretion and thus combat blocked/runny noses but also may make the user drowsy). Second generation anti-histamines do not have a useful effect on colds.
A warm and humid environment and high fluid intake, especially hot liquids, can alleviate symptoms somewhat. Common home remedies include chamomile, lemon or ginger root tisanes and soup, (these probably work in part by soothing the irritated respiratory passages with their steam and sore throats with their liquid heat, though intake of nutritious food is of course usually beneficial to health in general), nebulized medicinal mixtures, hot compresses, mustard plasters, hot toddies, tamagozake, licorice and echinacea. Eating spicy food can help alleviate congestion, although it may also irritate the already-tender throat. Coffee, or its active component, caffeine, has also been shown to improve mood and mental performance during rhinovirus infection.
Chicken soup in particular has long been considered an acceptable remedy for the symptoms of the common cold (and in ancient times, for various other minor ailments); recently, however, scientific experimentation lent credence to this belief, finding that the particular blend of nutrients and vitamins in traditional chicken soup can slow the activity of certain white blood cells. This may have an anti-inflammatory effect that could hypothetically lead to temporary ease from symptoms of illness. This research was published in 2000 in the scientific journal Chest (see chicken soup for more information and direct citation).
Other home remedies include gargling and flushing the nose with salt water. A strong salt solution reduces swelling in the throat and nasal tissue through osmosis. The high saline concentration draws fluids out of the cells through the cell membranes. This helps reduce the irritations in the throat and can clear the nasal passages and restore easy breathing without the use of medication. It is better to use iodine-free salt. Iodine has a bitter taste and may irritate the nasal tissues. A common technique for flushing the sinus is to use a Jala neti pot. However a flexible cup or commercial sinus squirt bottle also works very well.
Societal impact
Common colds interfere with school attendance and can cause lost days on the job, resulting in considerable costs to the economy. In addition, a large sum of money is spent on over-the-counter drugs and home remedies.
Arguably the most common communicable disorder that humans can be afflicted with, the cold is considered something of a common cultural point of reference. Thus, catching a cold is often used as a plot device in various stories, movies, and television series.[31]
Many companies offer a number of paid sick days per year to avoid errors during work and transmission to co-workers. In many countries this is mandated by law.
University of Michigan researcher Dr. A. Mark Fendrick published a 2003 study on effects of the common cold in the United States. The study found that the common cold leads to more than 100 million physician visits annually at a conservative cost estimate of $7.7 billion per year. More than one-third of patients who saw a doctor received an antibiotic prescription, which Fendrick says not only contributes to unnecessary costs, but also has implications for antibiotic resistance from overuse of such drugs.
The study found that Americans spend $2.9 billion on over-the-counter drugs and another $400 million on prescription medicines for symptomatic relief. Additionally, cold sufferers spend $1.1 billion annually on an estimated 41 million antibiotic prescriptions, even though the drugs have no effect on a viral illness.
The study reports that an estimated 189 million school days are missed annually due to a cold. As a result, parents missed 126 million workdays to stay home to care for their children. When added to the workdays missed by employees suffering from a cold, the total economic impact of cold-related work loss exceeds $20 billion. In the UK, £67,692,708.08 were lost in the cause of workdays lost due to rhinovirus.
Recent UK studies have shown that men take longer to recover from the common colds than women, leading to the introduction of the term Man Flu. While such so-called Man Flu is no different than the common cold, the differences in symptoms and recovery between males and females has puzzled many researchers.[citation needed] The term Man Flu is also sometimes used when a person is exaggerating their cold for personal reasons, i.e to allow them more time off work/school.
History
Colds have existed since ancient times, being known in ancient Egypt; where there were hieroglyphs representing the cough and the common cold. The Greek physician Hippocrates gave a description of the disease in the 5th century BC. The common cold was also known among the ancient American Indian Aztec and Maya civilizations. A mixture of chili pepper, honey, and tobacco was one common Aztec treatment for colds.
In the 18th century, John Wesley wrote a book about curing diseases; it advised against cold baths, stating that chilling causes the common cold. The work was widely reprinted in the 19th century. Another book by William Buchan in the 18th century also gave wet feet and clothes as the cause of the common cold.
The idea that microscopic infectious agents cause disease only arose in the second half of the 19th century. Initially, bacteria were suspected to be the cause of the common cold, and vaccines were produced based on this theory; these were still prescribed in the 1950s.
Viruses had been described beginning in the 1890s: infectious agents so small that they could pass through all filters and could not be seen under a microscope. In 1914, Walter Kruse, a professor in Leipzig, Germany, showed that viruses caused the common cold: nose secretions of a cold sufferer were diluted, filtered, and introduced into the noses of volunteers, producing colds in about half of the cases. These findings were not widely accepted, until they were repeated in the 1920s by Alphonse Dochez, first in chimpanzees, and then in human volunteers using a double-blind setup. Nevertheless, in 1932 a major textbook on the common cold by David Thomson still presented bacteria as the most likely cause.
In the United Kingdom, the Common Cold Unit was set up by the civilian Medical Research Council in 1946. The unit worked with volunteers who were infected with various viruses. The rhinovirus was discovered there. In the late 1950s, researchers were able to grow one of these cold viruses in a tissue culture, as it would not grow in fertilized chicken eggs, the method used for many other viruses. In the 1970s, the CCU demonstrated that treatment with interferon during the incubation phase of rhinovirus infection protects somewhat against the disease, but no practical treatment could be developed. The unit was closed in 1989, just two years after it demonstrated the benefit of zinc gluconate lozenges in the prophylaxis and treatment of rhinovirus colds. [4]
"Cold" as a misnomer
Originally, the term "cold" may have referred to a "cold condition" such as the hot, cold, dry, and wet "conditions" described by the ancient Anatolian physician Galen, but the climate is only an enabler and not the cause. Colds are somewhat more common in winter, and cold climate may affect transmission by causing people to stay indoors where ventilation is reduced and proximity to infected persons is increased, but the cause of the infection remains viral. Some allergies, bacterial respiratory infections, and even climate changes can also cause common-cold-like symptoms that can last for days.
Infection with a cold virus affects thermogenesis. This makes people associate post-infection shivering with situations in which they were exposed to cold that intensifies shivering (e.g. wet hair, draft, long wait on a bus stop, etc.). This association helps propagate the myth.
If cold weather were directly linked to the spread of the common cold, then it could possibly be demonstrated by comparing the infection rates of people who live in colder climates (such as Iceland or Greenland) with people who live in warmer climates (such as countries close to the equator). Studies done in the 1960s found no significant increase in infection rates in people who live in colder climates.[32]
It is not known conclusively whether cold weather or a humid climate can affect transmission by other means, such as by affecting the immune system, or ICAM-1 receptor concentration, or simply increasing the amount and frequency of nasal secretions and frequency of hand to face contact. A person can best avoid colds by avoiding those who are ill and the objects that they touch, as well as by keeping their immune system in top form by getting enough sleep, reducing stress, eating nutritious foods, and avoiding excess alcohol consumption.
In a widely-publicized experiment, researchers at the Common Cold Centre at the Cardiff University attempted to demonstrate that cold temperatures can lead to a greater susceptibility to viral infection.[33] In the experiment, 29% of a group of 90 people who sat with their feet in ice-cold water for 20 minutes a day for five days developed cold symptoms during the five days, while 9% of a control group of 90 people who were not similarly exposed developed symptoms. But there's a flaw in the Cardiff study, says the University of Virginia's Dr. Ronald Turner: The researchers didn't check to see if a virus was ever present. "They measured symptoms," says Turner, a pediatrician who investigates the effectiveness of cold remedies, like echinacea. "They didn't do any virology, so that study has nothing to do with becoming infected," he says.[34]
See also
References
- ^ a b What a common cold is.
- ^ Henry V. Huang. "Conservation by Coupled Evolution". Washington University School of Medicine, Department of Molecular Microbiology.
- ^ Canadian Health Network - The importance of handwashing for your health
- ^ Integrative Healthcare Studies Archive, 04 Oct 2006
- ^ University of Michigan Health System: Antibiotic-Associated Diarrhea, November 26, 2006
- ^ MA Akhavani (1 July 2005). "Steam inhalation treatment for children". British Journal of General Practice. 55. Retrieved 2007-03-29.
{{cite journal}}: Check date values in:|date=(help); Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help); Unknown parameter|quotes=ignored (help) - ^ M Singh (19 April 2004). "Heated, humidified air for the common cold". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (2). Retrieved 2007-03-29.
{{cite journal}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ "Effect of inhaling heated vapor on symptoms of the common cold". Journal of the American medical Association (JAMA). 271 (14). 13 April 1994. Retrieved 2007-03-29.
{{cite journal}}: Check date values in:|date=(help); Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - ^ a b c Ford, Norman D. (1 January 1990). "Beating the common cold". Highbeam encyclopedia - from Mothering. Retrieved 2007-03-29.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help); Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|publisher=(help) - ^ Ray Sahelian, M.D. "Common Cold Cure? A step by step guide". Retrieved 2007-03-29.
- ^
Turner, Ronald B., M.D. (2005-07-28). "An Evaluation of Echinacea angustifolia in Experimental Rhinovirus Infections". New England Journal of Medicine. 353 (4): 341–348. Retrieved 2007-02-12.
{{cite journal}}: Check date values in:|date=(help); Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Pevear, Daniel C. (1999). "Activity of Pleconaril against Enteroviruses". Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy. 43 (9): 2109–2115.
{{cite journal}}: Check date values in:|year=(help); Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ McConnell, J. (2 October 1999). "Enteroviruses succumb to new drug". The Lancet. 354 (9185): 1185.
{{cite journal}}: Check date values in:|date=(help); Cite has empty unknown parameter:|quotes=(help) - ^ "Effects of Pleconaril Nasal Spray on Common Cold Symptoms and Asthma Exacerbations Following Rhinovirus Exposure (Study P04295AM2)". ClinicalTrials.gov. U.S. National Institutes of Health. 2007. Retrieved 2007-04-10.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ Irwin Stone, The Healing Factor: Vitamin C Against Disease, Chapter 12
- ^ Pauling L, The Significance of the Evidence about Ascorbic Acid and the Common Cold, Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 November; 68(11): 2678–2681.
- ^ a b Douglas RM, Hemila H (2005). "Vitamin C for preventing and treating the common cold". PLoS Med. 2 (6): e168, quiz e217. PMID 15971944.
- ^ Vitamin C as a cold cure Vitamin C Foundation, accessed June 2006
- ^ Padayatty SL et al, "Vitamin C Pharmacokinetics: Implications for Oral and Intravenous Use," Ann Intern Med. 2004 Apr 6;140(7):533-7.
- ^ Researchers Question Government Recommended Daily Allowance (RDA) for vitamin C, PR Web, July 7, 2004
- ^ What About Vitamin C and Kidney Stones?
- ^ http://www.iom.edu/Object.File/Master/21/372/0.pdf
- ^ http://www.food.gov.uk/multimedia/pdfs/vitaminc.pdf
- ^ Eby GA, Davis DR, Halcomb WW (1984). "Reduction in duration of common colds by zinc gluconate lozenges in a double-blind study". Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 25 (1): 20–4. PMID 6367635.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Hulisz, D.T. Zinc and the Common Cold: What Pharmacists Need to Know (accessed 2005-01-31)
- ^ Jackson JL, Peterson C, Lesho E (1997). "A meta-analysis of zinc salts lozenges and the common cold". Arch Intern Med. 157 (20): 2373–6. PMID 9361579.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Marshall I. 1999. Zinc for the common cold. The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (accessed 2005-01-31)
- ^ Eby GA (2004). "Zinc lozenges: cold cure or candy? Solution chemistry determinations". Biosci Rep. 24 (1): 23–39. PMID 15499830.
- ^ Barton JC, Bertoli LF (1997). "Zinc gluconate lozenges for treating the common cold". Ann Intern Med. 126 (9): 738–9. PMID 9139564.
- ^ U.S. patent 5,409,905, Cure for Common Cold, G.A. Eby, 1995
- ^ Love Hina, see Love Hina plot summaries
The Beverly Hillbillies, episode "The Common Cold" - ^ "Catching a Cold" citing H.F. Dowling in American Journal of Hygiene, 1958, (Vol. 68, pp. 659–65) and R.G. Douglas, Jr. in New England Journal of Medicine, 1968, article by Gabe Mirkin, M.D., August, 2005, URL accessed August 13, 2006
- ^ Crop tops 'harming girls' health' BBC News, 21 December 2005
- ^ Why Kids Hate to Wear Coats, National Public Radio, 2006-02-02
External links
- US Food and Drug Administration, May 2000. What to Do for Colds and Flu
- Commoncold.org edited by MDs
- Common Cold Links to health information from MedlinePlus
- Common Cold syllabus from Infectious Diseases, Medical Microbiology, by Neal Chamberlain, PhD. Kirksville College of Osteopathic Medicine
- "Falling ill to a chill" (Milwaukee Journal Sentinel, 17 Mar 2003)
- Merck Manual on Respiratory Viral Diseases: Common cold
- Basic Common Cold Information
- Natural Remedies for Common Cold
- The first common cold experiments (1946) with film clip
- Acute cooling of the feet and the onset of common cold symptoms Johnson and Eccles Fam. Pract..2005; 0: 721
- Common Cold Centre at Cardiff University
- What's the lifespan of a germ?
