Crotalus basiliscus
| Crotalus basiliscus | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| Phylum: | |
| Subphylum: | |
| Class: | |
| Order: | |
| Suborder: | |
| Family: | |
| Subfamily: | |
| Genus: | |
| Species: | C. basiliscus
|
| Binomial name | |
| Crotalus basiliscus (Cope, 1864)
| |
| |
| Synonyms | |
Crotalus basiliscus is a venomous pit viper species found in western Mexico. The specific name is derived from the Greek word for king, basiliskos, and alludes to this snake's large size and potent venom.[2] No subspecies is currently recognized.[4]
Description

This is one of the largest rattlesnake species. Specimens exceeding 150 cm (4.9 ft) are not uncommon, while the maximum size reported is 204.5 cm (6.71 ft) (Klauber, 1972).[2] The body is moderately stout and rather rectangular in cross section.[5]
At midbody, 25-29 rows of strongly keeled dorsal scales occur. The ventral scales number 174-206 and the subcaudals 18-36.[5]
The color pattern consists of brown or grayish ground color overlaid with 26-41 dark, rhombus-shaped (diamond) blotches with light edges. The head is a uniform grayish-brown except for its lighter labial scales and dark postorbital bar. No distinct pattern is found on the crown or neck areas. The tail may be gray, with darker bands, or almost uniform in color without any distinct markings. The belly is white or cream-colored.[5] The young are mostly red, but adults eventually become an olive green.[3] Within its range, this is the only rattlesnake with diamond-shaped dorsal markings.[5]
This snake often occurs in the same areas as C. molossus, where the two appear to hybridize freely. While these two species are easily distinguished, identifying the hybrid specimens is problematic.[2]
Common names
Mexican west coast rattlesnake,[2] Mexican green rattler,[3] Mexican west coast green rattlesnake.[6]
Geographic range
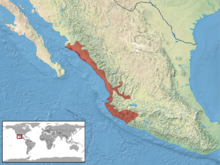
This rattler is found in western Mexico from southern Sonora to Michoacán,[1] where it is mostly restricted to the coastal plain.[3] The type locality given is "Near Colima, Mexico".[1]
Habitat
Around Colima, where it is (or was at one point) particularly plentiful, the area has been described as mostly treeless and covered with short grass with scattered clumps of mesquite, acacias, and other thorny bushes, as well as plenty of large cacti. The habitat of C. basiliscus is mostly tropical thorn forest, with an extension into tropical deciduous forest.[3]
Conservation status
This species is classified as Least Concern on the IUCN Red List (v3.1, 2001).[7] Species are listed as such due to their wide distribution, presumed large population, or because they are unlikely to be declining fast enough to qualify for listing in a more threatened category. The trend for this species was stable when assessed in 2007.[8]
Behavior
In the lowlands, these snakes are primarily active during the rainy summer months and most are found crossing the roads at night. However, a few have been seen basking early in the morning.[2] It has been reported to tame quickly in captivity.[3]
Feeding
Klauber reported seven specimens contained mammal hair, probably belonging to rodents.[3]
Venom
C. basilicus is known to produce large amounts of highly toxic venom, and large specimens should be regarded as very dangerous.[5]
Brown (1973) mentioned an average venom yield of 297 mg (dried venom), as well as LD50 values of 11.1 mg/kg IV and 4.0 and 12.9 mg/kg IP.[9]
In some populations, the venom may contain a component structurally related to Mojave toxin. The venom also contains proteases.[10] Antivenin is produced by the Instituto Nacional de Higiene in Mexico.[5] In the US, Protherics in Brentwood, Tennessee, produces an antivenin called "Crotalidae Polyvalent Immune Fab (Ovine)" containing a paraspecific antibody that protects against bites from this snake.[11]
Taxonomy
Before 1989, two subspecies were recognized: C. b. basiliscus and C. b. oaxacus. In that year, the latter was transfererred to C. molossus by Campbell and Lamar.[1] Occasionally, one may also encounter references to another subspecies, C. b. totonacus (Gloyd & Kauffeld, 1940), found in northeastern Mexico. It was more commonly considered to be a subspecies of C. durissus,[1] until recently, when it was elevated to a full species by Campbell and Lamar (2004): Crotalus totonacus.[2][12]
See also
- List of crotaline species and subspecies
- Crotalus by common name
- Crotalus by taxonomic synonyms
- Crotalinae by common name
- Crotalinae by taxonomic synonyms
- Snakebite
References
- ^ a b c d e McDiarmid RW, Campbell JA, Touré T. 1999. Snake Species of the World: A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference, vol. 1. Herpetologists' League. 511 pp. ISBN 1-893777-00-6 (series). ISBN 1-893777-01-4 (volume).
- ^ a b c d e f g Campbell JA, Lamar WW. 2004. The Venomous Reptiles of the Western Hemisphere. Comstock Publishing Associates, Ithaca and London. 870 pp. 1500 plates. ISBN 0-8014-4141-2.
- ^ a b c d e f g Klauber LM. 1997. Rattlesnakes: Their Habitats, Life Histories, and Influence on Mankind. Second Edition. First published in 1956, 1972. University of California Press, Berkeley. ISBN 0-520-21056-5.
- ^ "Crotalus basiliscus". Integrated Taxonomic Information System. Retrieved 4 February 2007.
- ^ a b c d e f U.S. Navy. 1991. Poisonous Snakes of the World. US Govt. New York: Dover Publications Inc. 203 pp. ISBN 0-486-26629-X.
- ^ Mehrtens JM. 1987. Living Snakes of the World in Color. New York: Sterling Publishers. 480 pp. ISBN 0-8069-6460-X.
- ^ C 3 September {{{species}}} at the IUCN Red List
- ^ 2001 Categories & Criteria (version 3.1) at the IUCN Red List. Accessed 13 September 2007.
- ^ Brown JH. 1973. Toxicology and Pharmacology of Venoms from Poisonous Snakes. Springfield, Illinois: Charles C. Thomas. 184 pp. LCCCN 73-229. ISBN 0-398-02808-7.
- ^ Norris R. 2004. Venom Poisoning in North American Reptiles. In Campbell JA, Lamar WW. 2004. The Venomous Reptiles of the Western Hemisphere. Comstock Publishing Associates, Ithaca and London. 870 pp. 1500 plates. ISBN 0-8014-4141-2.
- ^ Crotalus basiliscus at Munich AntiVenom INdex. Accessed 4 February 2007.
- ^ "Crotalus totonacus". Integrated Taxonomic Information System. Retrieved 27 August 2007.
Further reading
- Cope, E.D. 1864. Contributions to the Herpetology of Tropical America. Proc. Acad. Nat. Sci. Philadelphia 16: 166-181. (Caudisona basilisca, p. 166.)
External links
- Crotalus basiliscus at the Reptarium.cz Reptile Database. Accessed 9 August 2007.
- Crotalus basiliscus at Biodiversity of Mexico. Accessed 4 February 2007.
- Longevity record for Crotalus basiliscus basiliscus at Max Planck Institute for Demographic Research. Accessed 4 February 2007.

