Differentiable curve
- This article considers only curves in Euclidean space. Most of the notions presented here have analogues for curves in Riemannian and pseudo-Riemannian manifolds. For a discussion of curves in an arbitrary topological space, see the main article on curves.
Differential geometry of curves is the branch of geometry that deals with smooth curves in the plane and the Euclidean space by methods of differential and integral calculus.
Many specific curves have been thoroughly investigated using the synthetic approach. Differential geometry takes another path: curves are represented in a parametrized form, and their geometric properties and various quantities associated with them, such as the curvature and the arc length, are expressed via derivatives and integrals using vector calculus. One of the most important tools used to analyze a curve is the Frenet frame, a moving frame that provides a coordinate system at each point of the curve that is "best adapted" to the curve near that point.
The theory of curves is much simpler and narrower in scope than the theory of surfaces and its higher-dimensional generalizations because a regular curve in a Euclidean space has no intrinsic geometry. Any regular curve may be parametrized by the arc length (the natural parametrization). From the point of view of a theoretical point particle on the curve that does not know anything about the ambient space, all curves would appear the same. Different space curves are only distinguished by how they bend and twist. Quantitatively, this is measured by the differential-geometric invariants called the curvature and the torsion of a curve. The fundamental theorem of curves asserts that the knowledge of these invariants completely determines the curve.
Definitions
Let (i) , (ii) , and (iii) be a non-empty interval of real numbers. Then a vector-valued function
of class (i.e., the component functions of are -times continuously differentiable) is called a parametric -curve or a -parametrization. Note that is called the image of the parametric curve. It is important to distinguish between a parametric curve and its image because a given subset of can be the image of several distinct parametric curves. The parameter in can be thought of as representing time, and the trajectory of a moving particle in space. When is a closed interval , is called the starting point and is the endpoint of . If the starting and the end points coincide, i.e. , then is called a closed or a loop. Furthermore, is called a closed parametric -curve if and only if for all .
If is injective, then is simple.
If each component function of can be expressed as a power series, then is analytic (i.e. being of class ).
is written for the parametric curve that is traversed in the direction opposite to that of .
is regular of order (where ) if and only if for any ,
is a linearly independent subset of .
In particular, a parametric -curve is regular if and only if for any .
Re-parametrization and equivalence relation
Given the image of a parametric curve, there are several different parametrizations of the parametric curve. Differential geometry aims to describe the properties of parametric curves that are invariant under certain re-parametrizations. A suitable equivalence relation on the set of all parametric curves must be defined. The differential-geometric properties of a parametric curve (e.g., its length, its Frenet frame, and its generalized curvature) are invariant under re-parametrization and therefore properties of the equivalence class itself. The equivalence classes are called -curves and are central objects studied in the differential geometry of curves.
Two parametric -curves, and , are said to be equivalent if and only if there exists a bijective -map such that
and
is then said to be a re-parametrization of .
Re-parametrization defines an equivalence relation on the set of all parametric -curves of class . The equivalence class of this relation simply a -curve.
An even finer equivalence relation of oriented parametric -curves can be defined by requiring to satisfy .
Equivalent parametric -curves have the same image, and equivalent oriented parametric -curves even traverse the image in the same direction.
Length and natural parametrization
The length of a parametric -curve is defined as
The length of a parametric curve is invariant under re-parametrization and is therefore a differential-geometric property of the parametric curve.
For each regular parametric -curve , where , the function is defined
Writing , where is the inverse function of , This is a re-parametrization of that is called a arc-length parametrization, natural parametrization, unit-speed parametrization. The parameter is called the natural parameter of .
This parametrization is preferred because the natural parameter traverses the image of at unit speed, so that
In practice, it is often very difficult to calculate the natural parametrization of a parametric curve, but it is useful for theoretical arguments.
For a given parametric curve , the natural parametrization is unique up to a shift of parameter.
The quantity
is sometimes called the energy or action of the curve; this name is justified because the geodesic equations are the Euler–Lagrange equations of motion for this action.
Frenet frame
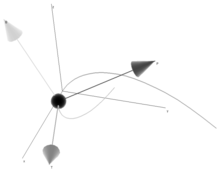
A Frenet frame is a moving reference frame of n orthonormal vectors ei(t) which are used to describe a curve locally at each point γ(t). It is the main tool in the differential geometric treatment of curves because it is far easier and more natural to describe local properties (e.g. curvature, torsion) in terms of a local reference system than using a global one such as Euclidean coordinates.
Given a Cn + 1-curve γ in Rn which is regular of order n the Frenet frame for the curve is the set of orthonormal vectors
called Frenet vectors. They are constructed from the derivatives of γ(t) using the Gram–Schmidt orthogonalization algorithm with
The real-valued functions χi(t) are called generalized curvatures and are defined as
The Frenet frame and the generalized curvatures are invariant under reparametrization and are therefore differential geometric properties of the curve.
Bertrand curve
A Bertrand curve is a Frenet curve in with the additional property that there is a second curve in such that the principal normal vectors to these two curves are identical at each corresponding point. In other words, if and are two curves in such that for any , , then and are Bertrand curves. For this reason it is common to speak of a Bertrand pair of curves (like and in the previous example). According to problem 25 in Kühnel's "Differential Geometry Curves – Surfaces – Manifolds", it is also true that two Bertrand curves that do not lie in the same 2-dimensional plane are characterized by the existence of a linear relation where are real constants and .[1] Furthermore, the product of torsions of Bertrand pairs of curves are constant.[2]
Special Frenet vectors and generalized curvatures
The first three Frenet vectors and generalized curvatures can be visualized in three-dimensional space. They have additional names and more semantic information attached to them.
Tangent vector
If a curve γ represents the path of a particle, then the instantaneous velocity of the particle at a given point P is expressed by a vector, called the tangent vector to the curve at P. Mathematically, given a parametrized C1 curve γ = γ(t), for every value t = t0 of the parameter, the vector
- at
is the tangent vector at the point P = γ(t0). Generally speaking, the tangent vector may be zero. The tangent vector's magnitude
is the speed at the time t0.
The first Frenet vector e1(t) is the unit tangent vector in the same direction, defined at each regular point of γ:
- .
If t = s is the natural parameter, then the tangent vector has unit length. The formula simplifies:
- .
The unit tangent vector determines the orientation of the curve, or the forward direction, corresponding to the increasing values of the parameter. The unit tangent vector taken as a curve traces the spherical image of the original curve.
Normal or curvature vector
The normal vector, sometimes called the curvature vector, indicates the deviance of the curve from being a straight line.
It is defined as
- .
Its normalized form, the unit normal vector, is the second Frenet vector e2(t) and is defined as
- .
The tangent and the normal vector at point t define the osculating plane at point t.
It can be shown that . Therefore, .
Curvature
The first generalized curvature χ1(t) is called curvature and measures the deviance of γ from being a straight line relative to the osculating plane. It is defined as
and is called the curvature of γ at point t. It can be shown that .
The reciprocal of the curvature
is called the radius of curvature.
A circle with radius r has a constant curvature of
whereas a line has a curvature of 0.
Binormal vector
The unit binormal vector is the third Frenet vector e3(t). It is always orthogonal to the unit tangent and normal vectors at t. It is defined as
In 3-dimensional space, the equation simplifies to
or to
- .
That either sign may occur is illustrated by the examples of a right-handed helix and a left-handed helix.
Torsion
The second generalized curvature χ2(t) is called torsion and measures the deviance of γ from being a plane curve. In other words, if the torsion is zero, the curve lies completely in the same osculating plane (there is only one osculating plane for every point t). It is defined as
and is called the torsion of γ at point t.
Main theorem of curve theory
Given n − 1 functions:
then there exists a unique (up to transformations using the Euclidean group) Cn + 1-curve γ which is regular of order n and has the following properties:
where the set
is the Frenet frame for the curve.
By additionally providing a start t0 in I, a starting point p0 in Rn and an initial positive orthonormal Frenet frame {e1, …, en − 1} with
The Euclidean transformations are eliminated to obtain unique curve γ.
Frenet–Serret formulas
The Frenet–Serret formulas are a set of ordinary differential equations of first order. The solution is the set of Frenet vectors describing the curve specified by the generalized curvature functions χi.
2 dimensions
3 dimensions
n dimensions (general formula)
See also
References
- ^ Kühnel, Wolfgang (2005). Differential Geometry: Curves, Surfaces, Manifolds. Providence: AMS. p. 53. ISBN 0-8218-3988-8.
- ^ http://mathworld.wolfram.com/BertrandCurves.html
Further reading
- Kreyszig, Erwin (1991). Differential Geometry. New York: Dover Publications. ISBN 0-486-66721-9. Chapter II is a classical treatment of Theory of Curves in 3-dimensions.








![{\displaystyle \gamma [I]\subseteq \mathbb {R} ^{n}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/27a675bd019e880d10ce7c4e1f744884fa8afab8)
![{\displaystyle \gamma [I]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/15372c4642fd421ba9fbb1c8bbc8ea17f4f6accc)



![{\displaystyle [a,b]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/9c4b788fc5c637e26ee98b45f89a5c08c85f7935)
























![{\displaystyle \gamma :[a,b]\to \mathbb {R} ^{n}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/cac70dec799b73a718bdc3431587a65f829bf03b)


![{\displaystyle \forall t\in [a,b]:\quad s(t)~{\stackrel {\text{df}}{=}}~\int _{a}^{t}\left\|\gamma '(x)\right\|~\mathrm {d} {x}.}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/e25b42b45a73c2e117edb8209c19e38276205af1)



































![{\displaystyle \chi _{i}\in C^{n-i}([a,b],\mathbb {R} ^{n}){\mbox{, }}\chi _{i}(t)>0,\,1\leq i\leq n-1}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/612b295bafb7e5d21ce721743e663a3af490aae3)
![{\displaystyle \|\gamma '(t)\|=1\qquad (t\in [a,b])}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/7839ccad0be696587f4508e9e4cfb5ccb5f3b8f9)





