Educational management
The examples and perspective in this article may not represent a worldwide view of the subject. (November 2018) |
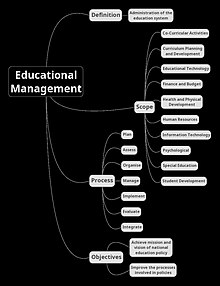
Educational management refers to the administration of the education system in which a group combines human and material resources to supervise, plan, strategise, and implement structures to execute an education system.[1][2] Education is the equipping of knowledge, skills, values, beliefs, habits, and attitudes with learning experiences. The education system is an ecosystem[citation needed] of professionals in educational institutions, such as government ministries, unions, statutory boards, agencies, and schools. The education system consists of political heads, principals, teaching staff, non-teaching staff, administrative personnel and other educational professionals working together to enrich and enhance.[3][4] At all levels of the educational ecosystem, management is required; management involves the planning, organising, implementation, review, evaluation, and integration of an institution. Research in educational management should explore the dynamic interplay among educational leaders, their followers, and the broader community to enhance the quality of teaching and learning outcomes.[5]
Scope[edit]
Co-curricular activities[edit]
Co-curricular activities help students maintain a holistic education, expressing their interests and talents. The activities help foster a sense of social integration, and add a sense of commitment and belonging to one's community and country. Co-curricular activities include science-oriented talent-development programmes, clubs and societies, sports, uniformed groups, and visual- and performing-arts groups. Co-curricular activities may also include advocacy, botany, personal-care, innovation, research-methodology and current-affairs groups.[6][7][8]
Curriculum planning and development[edit]
Curriculum planning and development involves "the design and development of integrated plans for learning, and the evaluation of plans, their implementation and the outcomes of the learning experience".[9] It designs and reviews curriculum, promotes teaching and assessment strategies aligned with curriculum, formulates special curriculum programmes, creates clear, observable objectives, and generates useful assessment rubrics.[10]
Curriculum development can be described as a three-stage process encompassing planned, delivered and experienced curriculum.[9] It may be shaped by pedagogical approaches contributed by theorists and researchers, such as John Dewey, Lev Vygotsky, Jean Piaget, Jerome Bruner, and Albert Bandura.[11]
Preschool[edit]
Curriculum development at the preschool level is based on several schools of thought. The Kindergarten was established by Friedrich Fröbel in Germany in 1837. Froebel described three forms of knowledge which he viewed as essential to all learning:[12] knowledge of life, which includes an appreciation of gardening, animals and domestic tasks; knowledge of mathematics, such as geometry; and knowledge of beauty, which includes colour and shape, harmony and movement.[12] The goals of Froebel's kindergarten are to awaken a child's physical senses through learning experiences and provide a common ground for individuals to advance.
Margaret and Rachel McMillan were social reformers in England who spent their lives trying to address poverty[13] and founded the Open-Air Nursery School and Training Centre in London. Their goals were to provide loving care, health support, nourishment and physical welfare to children.[14] Assistance was provided to parents to aid them in caring for, and interacting with, their children. Pedagogical models on how to engage and interact with young children were provided. The pedagogical principles of the Nursery School may be found in educational frameworks requiring teachers to nurture and teach a curriculum which covers an exploration of the world, aesthetics, music and movement, and literacy.[12]
John Dewey formulated the theory of progressive education.[15][16] His progressive-education philosophy embraces the idea that children should be taught how to think. Dewey was opposed to assessments, since they cannot measure whether or not a child is educated.[17] The school community should offer learning opportunities which are interesting and meaningful and prepare individuals to live in a democratic society. Children learn through doing, cooperation, problem-solving and collaboration, with the teacher acting as a guide. Projects in Dewey's curriculum encourage exploration, self-discovery and sensorial experiences which provide a holistic approach, focuses on the children's interests, and are developmentally appropriate.[18]
Montessori education was developed by Maria Montessori, who believed that children go through sensitive periods known as "windows of opportunity".[19] Everything in a Montessori classroom enhances and develops a child's growth. Materials address children's interests and the natural environment.[19] The learning environment is focused on the child. The curriculum trains children to be responsive, and promotes a desire for skills mastery.[20]
Waldorf education, created by the Austrian philosopher Rudolf Steiner, focuses on the whole child: body, mind, and spirit.[12] The curriculum is designed to provoke thought processes, develop sensitivity, and enhance creative and artistic fluency.[21][22] The Waldorf curriculum consists of storytelling, aesthetics (arts), practical work, imaginative play, and discovery of nature.[23] Modern schools adopting Waldorf education are independent and self-governing.[12]
The Reggio Emilia approach developed in the small north-Italian city of Reggio Emilia. Influenced by constructivist theories and the progressive-education movement, it is committed to uphold the rights of individuals.[24] Key concepts in a Reggio Emilia school include a child's right to education, the importance of interpersonal relationships amongst children, teachers and parents, and children's interactions in work and play.[25][26] Its curriculum emerges from the children's interest, and is developed through projects and inquiry.[27] Each individual plays an important role in the school, and parental involvement is a key aspect of the child's learning and development.[25]
Primary education[edit]
Curriculum development at the primary level focuses on the foundations of subjects, covering subject disciplines, knowledge skills and character development.[28] Subject disciplines are the cores and foundations of language, science, humanities, the arts, technology, and social studies.[29][30][31][32] Knowledge skills are personal skills and attributes such as communication, critical thinking, teamwork and judgement, which are developed through learning experiences based on the school's pedagogical practices.[33] Character development, according to Elliot Eisner, is the implicit curriculum: the school's hidden agenda.[34] Character traits and attributes include resilience, self-discipline, empathy and compassion, focusing on the social and emotional development of each student.[35] The curriculum development is a springboard towards personal and social capability, ethical and intercultural understanding, and sound moral judgement.[36]
Secondary education[edit]
Curriculum development varies at the secondary level, based on the course (or stream) in which a student is enrolled.[37] Curriculum focuses on core subjects such as language, mathematics, science and the humanities.[38][39][40] Learning experiences, strategic goals, national frameworks and school philosophy are also considered in curriculum development;[41] schools consider values and progressive skills in the development of a holistic curriculum.[42] Elective and vocational programmes are offered, which include social studies, art and music, design, and technology and computer studies.[38][39][40] Specialized schools integrate programmes with corporate partners in information and communication technology, entrepreneurship, art, design, media and Da Vinci Learning.[43][44] Enhanced programmes in sports, arts, and language are also offered.[45]
Tertiary education[edit]
Curriculum at the tertiary education level involves specific course design and development. Griffith University describes planning as based on previously-collected evidence; the process also involves assessment, technologically-informed learning and discipline-based capabilities.[46] The process aims to prepare students for the workforce while enhancing their understanding of a subject. Griffith University considers four key elements in curriculum development: learning analytics, external peer review, peer-based professional learning and professional learning workshops.[46]
Educational technology[edit]
Educational technology involves the integration, planning, implementation and management of information and communications technology (ICT) for effective learning and teaching.[47] The educational-technology branch of an education system conceptualizes and develops ICT in education, integrating it with curriculum frameworks, staff development and management.
The focus of educational technology has shifted to online and web-based applications, learning portals, flipped classrooms and a variety of social networks for teaching and learning.[48] Although educational technology includes ICT, it is not limited to hardware and educational theoretics. It encompasses several domains including collaborative learning, learning theory, linear learning, online portal learning, and (where mobile technologies are used) m-learning. These domains contribute to a personalized learning model and promote self-directed learning, as students take charge of their education.
Finances[edit]
This department oversees the financial policies of the educational institutes which provide administrative support to schools: financial assistance, revenue operations and school funds.[49] Financial assistance includes government subsidies, allowances and grants which are applied according to income levels and other factors, such as age or institution.[50] Scholarships and awards are distributed by merit or to categories of students.[51]
Health and physical development[edit]
This department's primary role is to develop safe and effective programmes to educate students on healthy living and physical education, and involves mastery of a sport and acquiring basic movement skills.[52] The department develops a curriculum based on sequential outcomes and the physical abilities of students.[52] An instructional model may be used as a plan which includes a theoretical foundation, learning outcomes, sequenced activities and task structures.[53] The department may promote parental involvement through partnerships with families and communities, and may rely on support from dieticians, physiotherapists, community health services and sports associations.[54]
Human resources[edit]
The primary goals of the human-resources department are attracting, developing, and retaining staff in the education ministry. It formulates operational policies and systems which directly affect staff performance and attitudes.[55] Departmental objectives include a review of organisational structures and procedures, staff skills development and enhancement, and leadership succession and transition.[56][57] These aim to foster greater staff involvement and expansion, eventually reaching the education system's overall goals.[58][59]
Information technology[edit]
Information technology harnesses technology to facilitate efficient administration, management and education.[60] This requires frequent staff training to ensure that educators at all levels are fully equipped with the needed skill set, and managers must identify and conceptualise relevant information for instruction.[61] IT systems must be reliable, accessible and assimilated by educators, and are vulnerable to hacking and malware. A period of close examination during integration may be necessary to ensure that educators are using new applications correctly.
Special education[edit]
Special education aims to facilitate a healthy learning environment for children with special needs or disabilities, giving all children an insightful and fruitful learning experience.[62][63] Special education may be provided in mainstream schools or specialised schools.[64][65] The appropriate choice of learning institution depends on the child's needs and the services available. Children may display learning difficulties or require additional materials for learning. Relevant courses are designed for children on the autism spectrum or with intellectual disabilities, visual impairment, hearing loss or cerebral palsy.[66] Additional assistance may be provided by social-service, non-governmental and voluntary welfare organisations and corporate partners.
The department tries to ensure that students with disabilities can participate in the school curriculum on the same basis as their peers.[67] It encompasses all education, including specialised schools and support classes;[67] this is key to ensuring student diversity. Special support services include accommodations, consultations, and personalised learning. Allied educators provide a high level of interaction with each child.[68] A multidisciplinary team of psychologists, special educators, and therapists fosters appropriate, meaningful learning.[69]
Student development[edit]
This department's primary role is to create curriculum and programmes which promote character, arts, citizenship, moral education, and global awareness.[70] Its mission is to promote individual student excellence, encourage collaboration and discovery and challenge students to take responsibility,[71] equipping students with future-ready qualities and competencies. Schools focus on values, collaboration, culture, and integration in approaching student-development programmes.[72][73] Overseas learning opportunities can be integrated to enable students to become aware of diverse cultures and backgrounds, with the goals of global connectivity and collaboration.[74][75]
Objectives[edit]
Educator level[edit]
Teachers plan and implement lessons based on pedagogical practices in an educational framework,[76] managing and updating student portfolios to recognise and assess diverse domains of development: social, emotional, intellectual, physical, moral and aesthetic. Pedagogical practices are supported by the curriculum philosophy, the goals and objectives of the subject matter, and individual student learning and developmental needs.[77] Although educational management at the educator level is similar to that of the education ministry,[78] its planning, development and monitoring focuses on individual students.[76] Teachers adopt classroom-management strategies and incorporate instructional approaches which promote independence, discipline, and a positive learning mindset. A teacher's classroom-management style influences many aspects of the learning environment. The four general styles of classroom management are authoritarian, authoritative, permissive and disengaged.[79][80][81] Teachers use a variety of positive guidance and disciplinary strategies to refocus a student's attention or manage conflicts.[82]
Ministerial-departmental level[edit]
Ministries and departments of education are responsible for the "design, implementation, monitoring and evaluation of educational legislation, policies, and programmes".[83] They provide structured support in strategic leadership, human resources, budgeting and administrative management to ensure that the educational system functions effectively and efficiently.[84][85]
Institutional level[edit]
The board of education and principals are responsible for managing an educational institution's daily operations. The school board formulates policies and has decision-making powers.[86] Their responsibilities include regulating the school budget, formulating its strategic vision and mission, and reviewing and enhancing school policies.[86] The board also monitors school performance, reporting to stakeholders (such as parents and the director-general) and collaborating with parents, government and non-governmental organisations.[87] The board of education can make legal decisions on behalf of the school, entering contracts and providing land.[87]
The principal has a professional and administrative role in the school.[88][89] With the school board, they chart the school's strategic goals reflecting its mission, vision, and philosophy. The principal supervises teaching and non-teaching staff, coordinating and managing day-to-day operations.[88] They are tasked with procuring resources for the school to achieve its strategic goals and ensuring that staff are trained and equipped with specialised skills, such as first aid. Principals are also required to engage with parents and community partners and provide performance indicators to the ministry (or department) of education.[90] Principals "build school culture", sustaining enhancement programmes and campaigns in the school.[91] Strategic goals for a school include excellence and engagement in learning, building character and leadership and developing staff competencies, collaborative partnerships, holistic education, quality student outcomes and lifelong, future-ready learners.[92][93][94][95]
National examples[edit]
Australia[edit]
Education in Australia is bureaucratic in nature. The national and state departments of education are responsible for the regulation of funding of education. Australia's educational system is governed by the Department of Education and Training, which is responsible for national policies and programmes. The department reports to two ministers; secretaries are responsible for the delivery of departmental services, which include corporate strategy, early-childhood education and childcare, higher education, research, and skills and training.[96] Each state is responsible for the delivery and coordination of its programmes and policies:
- Department of Education (New South Wales)
- Department of Education (Western Australia)
- Department of Education and Training (Queensland)
- Department for Education (South Australia)
- Department of Education and Training (Victoria)
- Department of Education (Tasmania)
Finland[edit]
Education in Finland is also bureaucratic in nature.[97] The Ministry of Education and Culture consists of departments of general education and early-childhood education; vocational education and training; higher education and science policy; art and cultural policy; youth and sport policy, and a unit for upper-secondary-school reform.[98] Common ministry functions are performed by administrative, finance and communications units and a secretariat for international relations.
Singapore[edit]
Education in Singapore is functional in structure, and is managed by the Ministry of Education (MOE).[99] Its organisational structure consists of:[90]
- Political leaders
- The Academy of Singapore Teachers, a professional organisation[90]
- The Communications and Engagement Group has two divisions: communications, and engagement and research. The communications division manages strategic messaging and promotes the communication of education policies and programmes to the media and the public.[100] The engagement and research division interacts with key MOE stakeholders.[90]
- The Curriculum Planning and Development Division's goal is to meet national, community and individual needs. Its responsibilities include syllabus design and review, teaching approaches and assessment, programmes, resources, library services, language centers, and consulting services.[101]
- The Curriculum Policy Office develops and reviews policies involved in the national curriculum and facilitates sound, balanced, purposeful and effective curriculum, pedagogy, and assessment practices.[102]
- The Educational Technology Division provides strategic direction, leadership, conceptualization and development of ICT integration into the educational master plan.[103]
- The Finance and Procurement division has two departments: finance and procurement. The finance department manages the ministry's budget and oversees and formulates policies. The procurement department manages contracts and tenders.
- The Higher Education Group formulates, implements and reviews policies relating to tertiary institutions, such as universities and polytechnics.
- The Human Resource Group "oversee recruitment and appointment, management of establishment matters for Education Officers, Executive & Administrative Staff, Allied Educators (EO/EAS/AED), employee engagement and HR partnerships with schools and HQ Divisions".[104]
- The Information Technology Branch integrates technology with different educational levels and includes administration and management.[105] They provide advice and support on the distribution of information and communication technologies for teaching and learning, and provide the MOE with the processes and procedures to implement IT strategically and effectively.
- Infrastructure and Facility Services has three branches.[106] The School Campus Department deals with infrastructure planning with building and upgrade programmes,[106] and monitors and reviews the Urban Redevelopment Authority's policies and plans for land use. The HQ Services Branch oversees policies and planning of physical infrastructure in the MOE HQ purview,[106] and provide administrative policy support for services in schools.[106] The Safety, Security and Emergency Branch oversees the emergency operations and procedures of schools and the MOE HQ, developing and implementing a "safety culture" in school programmes.[106]
- The Internal Audit Branch provides checks and balances in the educational system and ministry, independently monitoring and conducting financial and operational audits,[107] investigations and reviews.
- The Planning Department's main role is to "manage and analyse key MOE data to support MOE management in decision-making".[108] It has three divisions: the Education Policy Branch, the Corporate Planning Office, and the International Cooperation Branch.
- The Research and Management Information Department conducts research and analyses data essential for MOE strategic goals. It consists of the Management Information Branch, the Psychological Assessment Research Branch, the Research and Evaluation Branch, and the Corporate Management Branch.[109]
- The Schools Department ensures quality leadership in schools. It consists of the Schools Division; the School Branch North, South, East and West; the Pre-school Education Branch; the School Appraisal Branch, and the School Cockpit Administration Centre. The branches have management, administrative-support, implementation and consulting, and integration role.[110]
- Special Educational Needs serve and support students in inclusive environments and special-education institutions, charting the MOE's course in supporting students with special educational needs[111] and developing and reviewing curriculum.[111]
- The Student Placement and Services Division's primary role is the management and administration of admissions and scholarships. They also manage the MOE HQ's Customer Service Centre to "improve the quality of service delivery across all MOE public touch points".[112]
- Student Development Curriculum delivers a curriculum which meets the goals and vision of Singapore's education system.[113] They oversee the curriculum and co-curricular programme, collaborate with key stakeholders to review and revise curriculum, ensure the successful implementation of national programmes, and enhance student talent and development.[113]
See also[edit]
References[edit]
- ^ "Master of Arts (Educational Management) | National Institute of Education (NIE), Singapore". www.nie.edu.sg. Retrieved 2018-10-18.
- ^ Connolly, Michael; James, Chris; Fertig, Michael (2017-12-20). "The difference between educational management and educational leadership and the importance of educational responsibility". Educational Management Administration & Leadership. 47 (4): 504–519. doi:10.1177/1741143217745880. ISSN 1741-1432. S2CID 148809630.
- ^ "Educational Administration". www.rand.org. Retrieved 2018-11-09.
- ^ "What Is Educational Management?". Retrieved 2018-10-17.
- ^ Lemos, Monica; Liberali, Fernanda (2019-11-04). "The creative chain of activities towards educational management transformation: Findings from an intravention case study". International Journal of Educational Management. 33 (7): 1718–1732. doi:10.1108/IJEM-08-2017-0219. ISSN 0951-354X.
- ^ "Clubs & Societies". www.np.edu.sg. Archived from the original on 2019-11-04. Retrieved 2018-10-31.
- ^ "CCA". School of Science and Technology, Singapore. Archived from the original on 2018-07-22. Retrieved 2018-10-31.
- ^ "Achievements". www.mgs.moe.edu.sg. Archived from the original on 2016-11-12. Retrieved 2018-10-31.
- ^ a b "A Curriculum Development Process". www.flinders.edu.au. Archived from the original on 2010-10-12. Retrieved 2018-10-04.
- ^ Saphier, J; Haley, M; Gower; R (2008). The skilful teacher: Building your teaching skills. Acton, MA: Research For Better Teaching.
- ^ Nurturing Early Learners: A Curriculum Framework for Kindergartens in Singapore. Singapore: Ministry of Education, Singapore. 2012.
- ^ a b c d e Feeney, Stephanie; Moravcik, Eva; Nolte; Sherry (2013). Who Am I in the Lives of Children? An Introduction to Early Childhood Education. Singapore: Pearson Education. ISBN 978-981-45-2689-0.
- ^ "History of the McMillan Sisters". McMillan Nursery School. 2015-01-15. Retrieved 2018-10-17.
- ^ Betty, Liebovich (2014). "The Contributions of the McMIllan Sisters to Early Years Education in England". FORUM: For Promoting 3-19 Comprehensive Education. 56 (3): 529. doi:10.15730/forum.2014.56.3.529.
- ^ "John Dewey | American philosopher and educator". Encyclopedia Britannica. Retrieved 2018-10-17.
- ^ "John Dewey | American philosopher and educator". Encyclopedia Britannica. Retrieved 2018-10-18.
- ^ "Progressive Education - How Children Learn". ThoughtCo. Retrieved 2018-10-18.
- ^ "12 Principles of Child Development and Learning that Inform Practice | NAEYC". www.naeyc.org. Retrieved 2018-10-18.
- ^ a b "What is Montessori Education?". Montessori Northwest - Montessori Teacher Training & Professional Development in Portland, Oregon. Archived from the original on 2014-04-27. Retrieved 2018-11-08.
- ^ Marsh, C.; Willis, G (2007). Curriculum: Alternative approaches. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson/Merrill Prentice.
- ^ "Curriculum - Waldorf School of the Peninsula". Waldorf School of the Peninsula. Retrieved 2018-11-08.
- ^ "About Waldorf Education |". www.waldorfsingapore.com. Retrieved 2018-11-08.
- ^ "Early Childhood - Waldorf School of the Peninsula". Waldorf School of the Peninsula. Retrieved 2018-11-08.
- ^ Levine, Laura E. (2017-05-02). Child development: an active learning approach. Munsch, Joyce (Third ed.). Los Angeles; London; New Delhi; Singapore; Washington DC; Melbourne. ISBN 9781506386737. OCLC 992503617.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - ^ a b "The Reggio Emilia Philosophy of Learning | The Compass School". The Compass School. Archived from the original on 2018-11-08. Retrieved 2018-11-08.
- ^ "Reggio Emilia Approach | Reggio Children". Reggio Emilia Approach | Reggio Children. Archived from the original on 2013-07-25. Retrieved 2018-11-08.
- ^ "The Reggio Emilia Approach And Why It Works - Mulberry". Mulberry. 2016-05-16. Retrieved 2018-11-08.
- ^ "Primary School Curriculum". www.moe.gov.sg. Retrieved 2018-10-31.
- ^ "National curriculum in England: primary curriculum". GOV.UK. Retrieved 2018-10-31.
- ^ "Primary Curriculum - Primary School Curriculum". www.cambridgeschool.eu. Archived from the original on 2014-01-27. Retrieved 2018-10-31.
- ^ "Landsdale Primary School". www.australiancurriculum.edu.au. Retrieved 2018-10-31.
- ^ "Learning areas". www.australiancurriculum.edu.au. Retrieved 2018-10-31.
- ^ Primary School Education: Preparing Your Child For The Future. Singapore: Ministry of Education, Singapore. 2018.
- ^ Eisner, E. W.; Vance, E. (1974). Five conceptions of curriculum: Their roots and implications for curriculum planning. Berkeley, CA: McCutchan Publishing Company. pp. 1–14.
- ^ Department of Education (2017). Developing character skills in schools: Summary report. United Kingdom: Department of Education. ISBN 978-1-78105-759-9.
- ^ "General capabilities". www.australiancurriculum.edu.au. Retrieved 2018-10-31.
- ^ "Courses and subjects for secondary schools | Ministry of Education". beta.moe.gov.sg. Retrieved 2018-11-07.
- ^ a b "Express course for secondary school | Ministry of Education". beta.moe.gov.sg. Retrieved 2018-11-07.
- ^ a b "O Level Curriculum". National Curriculum Development Centre (NCDC). 2018. Archived from the original on 30 August 2018. Retrieved 7 November 2018.
- ^ a b "Ongoing Renewal of The School Curriculum". The Government of the Hong Kong Special Administration Region. Education Bureau. 2013. Retrieved 7 November 2018.
- ^ "How to choose secondary schools | Ministry of Education". beta.moe.gov.sg. Retrieved 2018-11-07.
- ^ The Government of The Hong Kong Administrative Region (2017). Learning Goals, School Curriculum Framework and Planning (PDF). Hong Kong: Education Bureau. p. 4. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2021-03-18. Retrieved 2018-11-07.
- ^ "Extended Curriculum". School of Science and Technology, Singapore. Archived from the original on 2018-10-31. Retrieved 2018-10-31.
- ^ "NUS High School Diploma". www.nushigh.edu.sg. Archived from the original on 2013-11-06. Retrieved 2018-10-31.
- ^ Ministry of Education, Singapore (2018). Secondary School Education: Shaping the Next Phase of your Child's Learning Journey. Singapore: Ministry of Education, Singapore.
- ^ a b Searles, Ainslie. "Curriculum development". www.griffith.edu.au. Archived from the original on 2018-04-01. Retrieved 2018-10-04.
- ^ "Educational Technology". edX. 2018-04-09. Retrieved 2018-11-09.
- ^ Ramey, Karehka (December 2, 2012). "6 Uses of Information Technology in Education". Useoftechnology.com. Retrieved 9 November 2018.
- ^ "Finance and Administration". www.education.go.ug. Archived from the original on 2013-05-07. Retrieved 2018-11-09.
- ^ "Finance Division | Ministry of Education, Youth and Information". moey.gov.jm. Retrieved 2018-11-09.
- ^ "Finance & Procurement". www.moe.gov.sg. Retrieved 2018-11-09.
- ^ a b "Curriculum in Physical Education: SHAPE America". Retrieved 2018-10-31.
- ^ "PE In School - 'The Solution'". www.phitamerica.org. Archived from the original on 2016-01-28. Retrieved 2018-10-31.
- ^ Guide to physical health and wellbeing: Resources for Queensland early childhood education and care services (PDF). Australia: Australian Early Development Census. 2018. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2018-03-18. Retrieved 2018-10-31.
- ^ Twomey, Stephen (12 January 2021). "Management & Main Branches of Management - Human Resource Management". Kennected. Archived from the original on 1 February 2021. Retrieved 28 January 2021.
- ^ "Human Resource Group". www.moe.gov.sg. Retrieved 2018-10-31.
- ^ "Ministry of Education". moe.gov.tt. Archived from the original on 2017-06-22. Retrieved 2018-10-31.
- ^ "Administrative branch". Opetus- ja kulttuuriministeriö. Retrieved 2018-10-31.
- ^ "Who We Are". www.edu.gov.on.ca. Retrieved 2018-10-31.
- ^ "Information Technology Branch". www.moe.gov.sg. Retrieved 2018-11-09.
- ^ Hamidi, Farideh; Meshkat, Maryam; Rezaee, Maryam; Jafari, Mehdi (2011). "Information technology in education". Procedia Computer Science. 3: 369–373. doi:10.1016/j.procs.2010.12.062. ISSN 1877-0509.
- ^ "About AASE - Australian Association of Special Education". Australian Association of Special Education. Retrieved 2018-11-07.
- ^ "Country information for Finland - Teacher education for inclusive education | European Agency for Special Needs and Inclusive Education". www.european-agency.org. Retrieved 2018-11-07.
- ^ "Special education". Encyclopedia Britannica. Retrieved 2018-11-07.
- ^ "Mainstream Education for Children with Special Needs". www.sgenable.sg. Retrieved 2018-11-07.
- ^ "Special Educational Needs". www.moe.gov.sg. Retrieved 2018-11-07.
- ^ a b "Students with disability". www.australiancurriculum.edu.au. Archived from the original on 2017-08-08. Retrieved 2018-10-31.
- ^ "Allied Educators". www.moe.gov.sg. Retrieved 2018-10-31.
- ^ Kirk, Samuel A.; Gallagher, James; Coleman, Mary Ruth (2014). Educating exceptional children (Fourteenth ed.). Australia. ISBN 9781473732063. OCLC 912318370.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - ^ The Australian Education System: Foundation Level (PDF). Australia: Department of Foreign Affairs and Trade (Australia). 2018.
- ^ "Elementary and Secondary Education". Just Landed. Retrieved 2018-11-07.
- ^ "Student Development". westwoodsec.moe.edu.sg. Retrieved 2018-11-07.
- ^ "Student Development". School of Science and Technology, Singapore. Archived from the original on 2018-11-07. Retrieved 2018-11-07.
- ^ "Overseas Learning Experience (OLE)". School of Science and Technology, Singapore. Archived from the original on 2019-12-29. Retrieved 2018-11-07.
- ^ "overseas_exposure_2016_2017". www.np.edu.sg. Archived from the original on 2018-11-07. Retrieved 2018-11-07.
- ^ a b Jon., Saphier (2008). The skillful teacher : building your teaching skills. Haley-Speca, Mary Ann., Gower, Robert R. (6th ed.). Acton, MA: Research for Better Teaching, Inc. ISBN 978-1886822108. OCLC 85019196.
- ^ "Teacher management". IIEP-UNESCO. 2014-11-20. Retrieved 2018-11-09.
- ^ Jensen, Ben (2010). What teachers want : better teacher management. Grattan Institute. [Carlton, Victoria]. ISBN 9781925015041. OCLC 861217361.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - ^ Djigic, Gordana; Stojiljkovic, Snezana (2011). "Classroom management styles, classroom climate and school achievement". Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences. 29: 819–828. doi:10.1016/j.sbspro.2011.11.310. ISSN 1877-0428.
- ^ "Classroom Management Definition". The Glossary of Education Reform. 2013-05-15. Retrieved 2018-11-09.
- ^ Marion, Marian (2014-03-12). Guidance of young children (Ninth ed.). Boston. ISBN 9780133427226. OCLC 867605709.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - ^ Daniel, Gartrell (2013). A Guidance Approach for the Encouraging Classroom (6th ed.). Belmont, CA: Wadsworth Cengage Learning. ISBN 9781133938934. OCLC 800031986.
- ^ "Roles and Responsibilities". www.education.gov.fj. Retrieved 2018-10-18.
- ^ "The role of the Ministry of Education". Education in New Zealand. 18 March 2014. Retrieved 2018-10-18.
- ^ "Responsibilities Of the Ministry of Education". old.moe.gov.cn. Retrieved 2018-10-18.
- ^ a b "School Board - Hillsborough County Public Schools". www.sdhc.k12.fl.us. Retrieved 2018-11-09.
- ^ a b "What School Boards Do | National School Boards Association". www.nsba.org. Retrieved 2018-11-09.
- ^ a b "19. The Key Roles of the Principal". www.is.vic.edu.au. Retrieved 2018-11-09.
- ^ "The School Principal as Leader: Guiding Schools to Better Teaching and Learning". Retrieved 2018-11-09.
- ^ a b c d "Organisational Structure". www.moe.gov.sg. Retrieved 2018-10-04.
- ^ Bush, Tony (November 2018). "SAGE Journals: Your gateway to world-class journal research". Educational Management Administration & Leadership. 46 (6): 883–887. doi:10.1177/1741143218795731.
- ^ "School Plan - Homebush Public School". www.homebushpublicschool.com.au. Retrieved 2018-10-17.
- ^ "Glebe Public School History - Glebe Public School". glebe-p.schools.nsw.gov.au. Retrieved 2018-10-17.
- ^ "School Information". fmsp.moe.edu.sg. Retrieved 2018-10-17.
- ^ "School strategy: A guide to meeting strategic goals and challenges in schools". ResourcEd. 2018-05-01. Retrieved 2018-10-17.
- ^ "Department of Education and Training - Organisation Chart" (PDF). Australian Government Department of Education and Training.
- ^ "Finnish National Agency for Education - Education system". www.oph.fi. Retrieved 2018-11-09.
- ^ "Finnish National Agency for Education - Tasks, services and organisation". www.oph.fi. Retrieved 2018-11-09.
- ^ "Home". www.moe.gov.sg. Retrieved 2018-10-18.
- ^ "Communications and Engagement Group". www.moe.gov.sg. Retrieved 2018-10-18.
- ^ "Curriculum Planning & Development". www.moe.gov.sg. Retrieved 2018-10-18.
- ^ "Curriculum Policy Office". www.moe.gov.sg. Retrieved 2018-10-18.
- ^ "Educational Technology". www.moe.gov.sg. Retrieved 2018-10-18.
- ^ "Human Resource Group". www.moe.gov.sg. Retrieved 2018-10-18.
- ^ "Information Technology Branch". www.moe.gov.sg. Retrieved 2018-11-06.
- ^ a b c d e "Infrastructure & Facility Services". www.moe.gov.sg. Retrieved 2018-11-06.
- ^ "Internal Audit Branch". www.moe.gov.sg. Retrieved 2018-11-06.
- ^ "Planning". www.moe.gov.sg. Retrieved 2018-11-06.
- ^ "Research & Management Information". www.moe.gov.sg. Retrieved 2018-11-06.
- ^ "Schools". www.moe.gov.sg. Retrieved 2018-11-06.
- ^ a b "Special Educational Needs". www.moe.gov.sg. Retrieved 2018-11-06.
- ^ "Student Placement & Services Division". www.moe.gov.sg. Retrieved 2018-11-06.
- ^ a b "Student Development Curriculum". www.moe.gov.sg. Retrieved 2018-11-06.
Further reading[edit]
- The Difference Between Educational Management and Educational Leadership and the Importance of Educational Responsibility in Educational Management Administration & Leadership by Michael Connolly, Chris James and Michael Fertig.
- Theories of Educational Management and Leadership: A Review by Majid Ghasemy and Sufean Hussin.
- What is Educational Management? by Learn.org
- Universal Concepts, Nature, and Basic Principles of Educational Management: Implication for Present Day School Management by Nwachukwu Prince Ololube, Erebagha Theophilus, Ingiabuna Ii, and Comfort N. Agbor.
