European Union Customs Union
European Union Customs Union | |
|---|---|
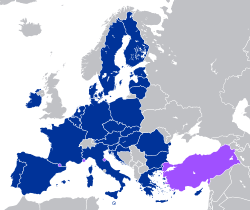 EU member states (including participating member state territories which are not part of the EU) Non-EU states which participate in the customs union, or are in bilateral customs unions with the EU | |
| Policy of | |
| Type | Customs union |
| Membership | 28 member states
4 states with bilateral agreements
|
| Establishment | 1958 |
| Area | |
• Total | 5,200,000 km2 (2,000,000 sq mi) |
| Population | |
• 2014 estimate | 585,000,000 |
| GDP (PPP) | 2014 estimate |
• Total | $19.6 trillion |
| GDP (nominal) | 2014 estimate |
• Total | $19.2 trillion |
| This article is part of a series on |
 |
|---|
|
|
The European Union Customs Union (EUCU) is a customs union which consists of all the member states of the European Union (EU), Monaco, and some territories of the United Kingdom which are not part of the EU (Akrotiri and Dhekelia, Bailiwick of Guernsey, Bailiwick of Jersey, and the Isle of Man).[1] Some territories within the EU do not participate in the customs union, usually as a result of their geographic circumstances. Besides the EUCU, the EU, through separate agreements, is in customs unions with Andorra, San Marino, and Turkey, with the exceptions of certain goods.[2]
The customs union is a principal component of the European Economic Community, established in 1958, and now succeeded by the European Union. No customs duties are levied on goods travelling within the customs union and – unlike a free trade area – members of the customs union impose a common external tariff on all goods entering the union.
A precondition of the customs union is that the European Commission negotiates for and on behalf of the Union as a whole in international trade deals such as the World Trade Organisation, rather than each member state negotiating individually.
Non-EU participants
Monaco and the British territories of Akrotiri and Dhekelia, Guernsey, the Isle of Man and Jersey are integral parts of the EU's customs territory.[2]
| State / territory | Agreement | Entry into force | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Franco-Monegasque Customs Convention[3][4] | 1963 | ||
|
Act concerning the conditions of accession of the Czech Republic, the Republic of Estonia, the Republic of Cyprus, the Republic of Latvia, the Republic of Lithuania, the Republic of Hungary, the Republic of Malta, the Republic of Poland, the Republic of Slovenia and the Slovak Republic and the adjustments to the Treaties on which the European Union is founded Protocol No 3 on the sovereign base areas of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland in Cyprus[5] |
1 May 2004 | |
|
Documents concerning the accession to the European Communities of the Kingdom of Denmark, Ireland, the Kingdom of Norway and the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland Protocol No 3 on the Channel Islands and the Isle of Man[6] |
1 January 1973 |
Bilateral customs unions
Andorra, San Marino and Turkey, a candidate for EU membership, are each in a customs union with the EU.[2]
| State | Agreement | Entry into force | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Agreement in the form of an Exchange of Letters between the European Economic Community and the Principality of Andorra – Joint Declarations[7] | 1 January 1991 | Excludes agricultural products | |
| Agreement on Cooperation and Customs Union between the European Economic Community and the Republic of San Marino[8] | 16 December 1991 | ||
| Decision No 1/95 of the EC-Turkey Association Council of 22 December 1995 on implementing the final phase of the European Union–Turkey Customs Union[9] | 31 December 1995 | Excludes agricultural products |
EU territories with an opt-out
While all EU member states are part of the customs union, not all of their respective territories participate. Territories of member states which have remained outside of the EU (overseas countries and territories of the European Union) generally do not participate in the customs union.
However, there are seven territories that are within the EU which do not participate in the customs union:
- Büsingen am Hochrhein (a German exclave within Switzerland, part of the Switzerland–Liechtenstein customs area)[10]
- Campione d'Italia and the adjacent Italian waters of Lake Lugano (an Italian exclave within Switzerland, part of the Switzerland–Liechtenstein customs area)[10]
- Livigno[10]
- Ceuta[10]
- Melilla[10]
- Gibraltar[11]
- Heligoland[10]
- Canary Islands
- Madeira
- Azores
Union Customs Code
The Union Customs Code (UCC), intended to modernise customs procedures, entered into force on 1 May 2016.[12] Implementation will take place over a period of time and full implementation is anticipated by 31 December 2020 at the latest.[13] The European Commission has stated that the aims of the UCC are simplicity, service and speed.
Common external tariffs
The EU Customs Union sets the tariff rates for imports to the EU from other countries. These rates are detailed and depend on the specific type of product imported, and can also vary by the time of year.[14] The full WTO Most Favoured Nation tariff rates apply only to those countries that do not have a Free Trade Agreement with the EU, or are not on a WTO recognised exemption scheme such as Everything but Arms (an EU support arrangement for Least Developed Countries).
See also
- European Customs Information Portal
- European integration
- European Single Market
- European Free Trade Association
- European Economic Area (EU and EFTA except Switzerland)
- European Union–Turkey Customs Union
- Free trade areas in Europe
- Non-tariff barriers to trade
External links
- TARIC database enquiry system, gives current tariff rates applicable by exporting country and season – European Commission: Communication and Information Resource Centre for Administrations, Businesses and Citizens.
- TARIC and Quota Data & Information: user guides for the TARIC database above – European Commission: Communication and Information Resource Centre for Administrations, Businesses and Citizens.
- Turkey border gridlock hints at pain to come for Brexit Britain The Financial Times, February 16, 2017
References
- ^ FAQ: Customs, Taxation and Customs Union, European Commission. Retrieved 20 August 2016.
- ^ a b c Customs unions, Taxation and Customs Union, European Commission. Retrieved 20 August 2016.
- ^ "Taxation and Customs – FAQ". European Commission. Archived from the original on 8 June 2012. Retrieved 12 September 2012.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Council Regulation (EEC) No 2913/92 of 12 October 1992 establishing the Community Customs Code". Official Journal of the European Union. 19 October 1992. Retrieved 12 September 2012.
- ^ "EUR-Lex – 12003T/PRO/03 – Act concerning the conditions of accession of the Czech Republic, the Republic of Estonia, the Republic of Cyprus, the Republic of Latvia, the Republic of Lithuania, the Republic of Hungary, the Republic of Malta, the Republic of Poland, the Republic of Slovenia and the Slovak Republic and the adjustments to the Treaties on which the European Union is founded – Protocol No 3 on the sovereign base areas of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland on Cyprus". eur-lex.europa.eu.
- ^ "EUR-Lex – 11972B/PRO/03 – DOCUMENTS CONCERNING THE ACCESSION TO THE EUROPEAN COMMUNITIES OF THE KINGDOM OF DENMARK, IRELAND, THE KINGDOM OF NORWAY AND THE UNITED KINGDOM OF GREAT BRITAIN AND NORTHERN IRELAND, PROTOCOL NO 3 ON THE CHANNEL ISLANDS AND THE ISLE OF MAN". eur-lex.europa.eu.
- ^ "Andorra : Customs Unions and preferential arrangements". European Commission. Archived from the original on 26 October 2012. Retrieved 12 September 2012.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Agreement on Cooperation and Customs Union between the European Economic Community and the Republic of San Marino".
- ^ "Decision No 1/95 of the EC-Turkey Association Council of 22 December 1995 on implementing the final phase of the Customs Union" (PDF).
- ^ a b c d e f Article 6 of Council Directive 2006/112/EC, 28 November 2006
- ^ Article 28 of the Act concerning the conditions of Accession and the Adjustments to the Treaties, 22 January 1972
- ^ "Union Customs Code – Taxation and customs union – European Commission". Taxation and customs union.
- ^ UCC: an Introduction, accessed 29 January 2017
- ^ Taric and Quota Data & Information – European Commission Communication and Information Resource Centre for Administrations, Businesses and Citizens.




