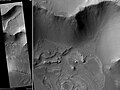
Juventae Chasma
Template:MarsGeo-Valley Juventae Chasma is an enormous box canyon (250 km × 100 km) on Mars which opens to the north and forms the outflow channel Maja Valles.[1]
Juventae Chasma is located north of Valles Marineris in the Coprates quadrangle and cuts more than 5 km into the plains of Lunae Planum. The floor of Juventae Chasma is partly covered by sand dunes. There is also a 2.5 km high mountain inside Juventae, 59 km long and 23 km wide, that was confirmed by Mars Express to be composed of sulfate deposits.[2] MRO discovered sulfates, hydrated sulfates, and iron oxides in Juventae Chasma.[3] Juventae Chasma has four bright mounds or light-toned interior layered deposits (IlD's), as they are often called. Researchers have found that monohydrated sulfates were first deposited on the floor. And then polyhydrated sulfates were laid down. Kieserite, a magnesium sulfate, was also found in Juventae Chasma.[4]
-
Light toned sedimentary outcrops on the floor of Juventae Chasma.
-
Juventae Chasma Troughs, as seen by HiRISE.
-
Inverted Streams near Juventae Chasma, as seen by Mars Global Surveyor. These streams begin at the top of a ridge then run together.
-
Inverted Channels near Juventae Chasma, as seen by HiRISE. Channels were once regular stream channels. Scale bar is 500 meters long.
-
Layers west of Juventae Chasma, as seen by HiRISE. Scale bar is 500 meters long.
-
Plateau near Juventae Chasma.
References
- ^ PIA03818: Floor of Juventae Chasma
- ^ Sulphate deposits in Juventae Chasma
- ^ Murchie, S. et al. 2009. A synthesis of Martian aqueous mineralogy after 1 Mars year of observations from the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter. Journal of Geophysical Research: 114.
- ^ Noel, A., J. Bishop, M. Al-Samir, C. Gross, J. Flahaut, P. McGuire, C. Weitz, F. Seelos, S. Murchie. 2015. Mineralogy, morphology and stratigraphy of the light-toned interior layered deposits at Juventae Chasma. Icarus: 251, 315–331