North American XA2J Super Savage
| XA2J "Super Savage" | |
|---|---|

| |
| The XA2J-1 Super Savage in flight in 1952 | |
| Role | Attack aircraft |
| National origin | United States |
| Manufacturer | North American Aviation |
| First flight | 4 January 1952 |
| Status | Cancelled |
| Produced | 1 |
| Developed from | North American AJ Savage |
The North American Aviation XA2J "Super Savage" was a prototype carrier-based attack aircraft built in the early 1950s. It was developed by North American Aviation (NAA) from the smaller AJ Savage.
Design and development[edit]
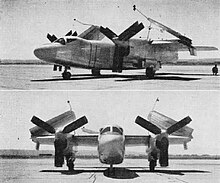
The XA2J was intended to be a turboprop-powered derivative of the AJ Savage, with the design as initially proposed in December 1947 a simple modification of the Savage, with extensive use of components of the earlier aircraft. The design gradually evolved, however, to improve performance and increase compatibility with operations from aircraft carriers,[1] as it was recognized that the AJ Savage was deficient in performance and was a less-than-satisfactory carrier aircraft.[2]

The A2J was essentially an enlarged AJ Savage with the two reciprocating engines replaced with two Allison T40 turboprop engines and removal of the tail-mounted turbojet. Like the AJ, it was a high-winged monoplane with unswept wings. The wings were fitted with leading edge slats and large trailing edge flaps, and folded outside of the engine nacelles to ease storage aboard ship. It had a crew of three: pilot, co-pilot/bombardier, and gunner who sat in a pressurised cabin in the nose of the aircraft. Up to 10,500 lb (4,800 kg) of bombs could be carried in a large enclosed bomb-bay in the center fuselage, while the planned defensive armament was a remotely controlled tail turret with two 20 mm cannon.[3]
Construction of two prototypes started 1 October 1948, but due to delays developing the engines, the first flight was not until 4 January 1952.[4] The competing Douglas XA3D, the prototypes of which were ordered the year after construction had begun on the XA2J prototypes, first flew in October 1952. The A3D had far superior performance, which doomed the XA2J.
The root cause for the failure of the XA2J was the protracted development and poor reliability of the Allison T40 engines. The T40 engine was an ambitious engine design with two power sections, (the T38 was developed from the T40 to assist in its development, by using a single power section with extension shaft and gearbox),[5] driving two large contra-rotating propellers through a combining gearbox. Both the engines and the gearbox proved to be unreliable. The T40 engine was also used in the developmental of other aircraft. After a number of engine-related mishaps, the XA2J project was abandoned and the second prototype was never flown.
Operators[edit]
Specifications (XA2J-1)[edit]

General characteristics
- Crew: 3
- Length: 70 ft 3 in (21.42 m)
- Wingspan: 71 ft 6 in (21.80 m)
- Height: 24 ft 2 in (7.37 m)
- Wing area: 836 sq ft (77.7 m2)
- Empty weight: 35,350 lb (16,035 kg)
- Gross weight: 46,890 lb (21,269 kg)
- Max takeoff weight: 61,200 lb (27,760 kg)
- Powerplant: 2 × Allison T40-A-6 turboprops, 5,035 hp (3,755 kW) each
Performance
- Maximum speed: 451 mph (726 km/h, 392 kn)
- Range: 2,180 mi (3,508 km, 1,890 nmi)
- Service ceiling: 37,500 ft (11,400 m)
- Rate of climb: 6,820 ft/min (34.7 m/s)
- Wing loading: 56 lb/sq ft (274 kg/m2)
- Power/mass: 0.21 hp/lb (350 W/kg)
Armament
- 10,500 lb (4,763 kg) of disposable stores
- 2 × 20 mm cannons in tail (never fitted)
See also[edit]
Related development
References[edit]
Notes[edit]
- ^ Air Pictorial December 1959, p. 453.
- ^ Miller 2001, pp. 90–9
- ^ Air Pictorial December 1959, p. 454.
- ^ Wagner 1982, pp. 389–490[page needed]
- ^ Nolan, D. J. (8 August 1952). "TURBO-LINER : Development of the Allison T-38 Engine in a Convair 240" (pdf). Flight. LXII (2272): 157–159. Retrieved 5 January 2019.
Bibliography[edit]
- Miller, Jerry (17 April 2001). Nuclear Weapons and Aircraft Carriers. Washington D.C.: Smithsonian institution Press, 2001. ISBN 1-56098-944-0.
- "They didn't quite: 5: Turbine-driven Savage". Air Pictorial. Vol. 21, no. 12. December 1959. pp. 453–454.
- Wagner, Ray (1982). American Combat Planes (3rd edition). Garden City, NY: Doubleday & Company, 1982. ISBN 0-385-13120-8.
External links[edit]
- "Navy Gets Turboprop Bomber." Popular Science, April 1952, p. 141.
