Portal:World
Portal maintenance status: (No date set)
|
The World Portal

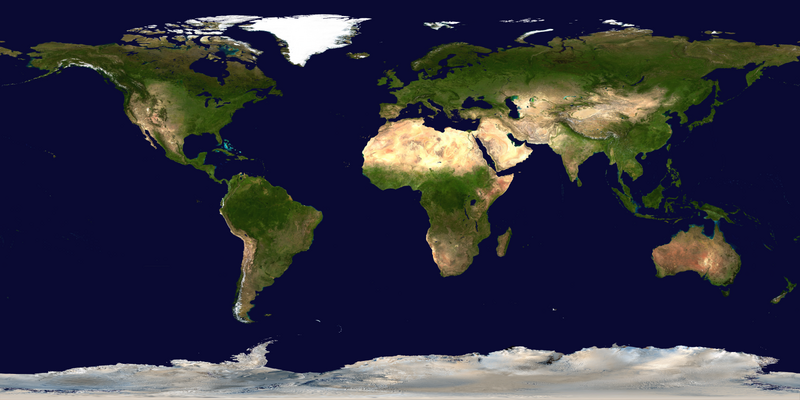
The world is the totality of entities, the whole of reality, or everything that exists. The nature of the world has been conceptualized differently in different fields. Some conceptions see the world as unique, while others talk of a "plurality of worlds". Some treat the world as one simple object, while others analyze the world as a complex made up of parts.
In scientific cosmology, the world or universe is commonly defined as "the totality of all space and time; all that is, has been, and will be". Theories of modality talk of possible worlds as complete and consistent ways how things could have been. Phenomenology, starting from the horizon of co-given objects present in the periphery of every experience, defines the world as the biggest horizon, or the "horizon of all horizons". In philosophy of mind, the world is contrasted with the mind as that which is represented by the mind.
Theology conceptualizes the world in relation to God, for example, as God's creation, as identical to God, or as the two being interdependent. In religions, there is a tendency to downgrade the material or sensory world in favor of a spiritual world to be sought through religious practice. A comprehensive representation of the world and our place in it, as is found in religions, is known as a worldview. Cosmogony is the field that studies the origin or creation of the world, while eschatology refers to the science or doctrine of the last things or of the end of the world.
In various contexts, the term "world" takes a more restricted meaning associated, for example, with the Earth and all life on it, with humanity as a whole, or with an international or intercontinental scope. In this sense, world history refers to the history of humanity as a whole, and world politics is the discipline of political science studying issues that transcend nations and continents. Other examples include terms such as "world religion", "world language", "world government", "world war", "world population", "world economy", or "world championship". (Full article...)
Selected articles - show another
-
Image 1

Gerardus Mercator 1512–1594
The Mercator world map of 1569 is titled Nova et Aucta Orbis Terrae Descriptio ad Usum Navigantium Emendate Accommodata (Renaissance Latin for "New and more complete representation of the terrestrial globe properly adapted for use in navigation"). The title shows that Gerardus Mercator aimed to present contemporary knowledge of the geography of the world and at the same time 'correct' the chart to be more useful to sailors. This 'correction', whereby constant bearing sailing courses on the sphere (rhumb lines) are mapped to straight lines on the plane map, characterizes the Mercator projection. While the map's geography has been superseded by modern knowledge, its projection proved to be one of the most significant advances in the history of cartography, inspiring the 19th century map historian Adolf Nordenskiöld to write "The master of Rupelmonde stands unsurpassed in the history of cartography since the time of Ptolemy." The projection heralded a new era in the evolution of navigation maps and charts and it is still their basis.The map is inscribed with a great deal of text. The framed map legends (or cartouches) cover a wide variety of topics: a dedication to his patron and a copyright statement; discussions of rhumb lines; great circles and distances; comments on some of the major rivers; accounts of fictitious geography of the north pole and the southern continent. The full Latin texts and English translations of all the legends are given below. Other minor texts are sprinkled about the map. They cover such topics as the magnetic poles, the prime meridian, navigational features, minor geographical details, the voyages of discovery and myths of giants and cannibals. These minor texts are also given below. (Full article...) -
Image 2Internationalism is a political principle that advocates greater political or economic cooperation among states and nations. It is associated with other political movements and ideologies, but can also reflect a doctrine, belief system, or movement in itself.
Supporters of internationalism are known as internationalists and generally believe that humans should unite across national, political, cultural, racial, or class boundaries to advance their common interests, or that governments should cooperate because their mutual long-term interests are of greater importance than their short-term disputes. (Full article...) -
Image 3

Blue light is scattered more than other wavelengths by the gases in the atmosphere, surrounding Earth in a visibly blue layer at the stratosphere, above the clouds of the troposphere, when seen from space on board the ISS at an altitude of 335 km (208 mi) (the Moon is visible as a crescent in the far background).
The atmosphere of Earth is composed of a layer of gas mixture that surrounds the Earth's planetary surface (both lands and oceans), known collectively as air, with variable quantities of suspended aerosols and particulates (which create weather features such as clouds and hazes), all retained by Earth's gravity. The atmosphere serves as a protective buffer between the Earth's surface and outer space, shields the surface from most meteoroids and ultraviolet solar radiation, keeps it warm and reduces diurnal temperature variation (temperature extremes between day and night) through heat retention (greenhouse effect), redistributes heat and moisture among different regions via air currents, and provides the chemical and climate conditions allowing life to exist and evolve on Earth.
By mole fraction (i.e., by quantity of molecules), dry air contains 78.08% nitrogen, 20.95% oxygen, 0.93% argon, 0.04% carbon dioxide, and small amounts of other trace gases. Air also contains a variable amount of water vapor, on average around 1% at sea level, and 0.4% over the entire atmosphere. Air composition, temperature and atmospheric pressure vary with altitude. Within the atmosphere, air suitable for use in photosynthesis by terrestrial plants and respiration of terrestrial animals is found only within 12 kilometres (7.5 mi) from the ground. (Full article...) -
Image 4
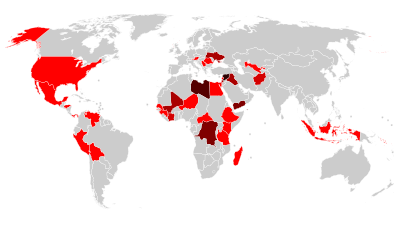
Countries with World Heritage Sites in danger. Number of sites indicated by colour: - Six or more sites
- Five sites
- Four sites
- Three sites
- Two sites
- One site
The List of World Heritage in Danger is compiled by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) through the World Heritage Committee according to Article 11.4 of the World Heritage Convention, which was established in 1972 to designate and manage World Heritage Sites. Entries in the list are threatened World Heritage Sites for the conservation of which major operations are required and for which "assistance has been requested". The list is intended to increase international awareness of the threats and to encourage counteractive measures. Threats to a site can be either proven imminent threats or potential dangers that could have adverse effects on a site.
In the case of natural sites, ascertained dangers include the serious decline in the population of an endangered or other valuable species or the deterioration of natural beauty or scientific value of a property caused by human activities such as logging, pollution, settlement, mining, agriculture and major public works. Ascertained dangers for cultural properties include serious deterioration of materials, structure, ornaments or architectural coherence and the loss of historical authenticity or cultural significance. Potential dangers for both cultural and natural sites include development projects, armed conflicts, insufficient management systems or changes in the legal protective status of the properties. In the case of cultural sites, gradual changes due to geology, climate or environment can also be potential dangers. (Full article...) -
Image 5Universal Time (UT or UT1) is a time standard based on Earth's rotation. While originally it was mean solar time at 0° longitude, precise measurements of the Sun are difficult. Therefore, UT1 is computed from a measure of the Earth's angle with respect to the International Celestial Reference Frame (ICRF), called the Earth Rotation Angle (ERA, which serves as the replacement for Greenwich Mean Sidereal Time). UT1 is the same everywhere on Earth. UT1 is required to follow the relationship
:ERA = 2π(0.7790572732640 + 1.00273781191135448 · Tu) radians
where Tu = (Julian UT1 date − 2451545.0). (Full article...) -
Image 6Post-Kyoto negotiations refers to high level talks attempting to address global warming by limiting greenhouse gas emissions. Generally part of the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC), these talks concern the period after the first "commitment period" of the Kyoto Protocol, which expired at the end of 2012. Negotiations have been mandated by the adoption of the Bali Road Map and Decision 1/CP.13 ("The Bali Action Plan").
UNFCCC negotiations are conducted within two subsidiary bodies, the Ad Hoc Working Group on Long-term Cooperative Action under the Convention (AWG-LCA) and the Ad Hoc Working Group on Further Commitments for Annex I Parties under the Kyoto Protocol (AWG-KP) and were expected to culminate in the United Nations Climate Change Conference taking place in December 2009 in Copenhagen (COP-15); negotiations are supported by a number of external processes, including the G8 process, a number of regional meetings and the Major Economies Forum on Energy and Climate that was launched by US President Barack Obama in March 2009. High level talks were held at the meeting of the G8+5 Climate Change Dialogue in February 2007 and at a number of subsequent G8 meetings, most recently leading to the adoption of the G8 leaders declaration "Responsible Leadership for a Sustainable Future" during the G8 summit in L´Aquila, Italy, in July 2009. (Full article...) -
Image 7A free trade area is the region encompassing a trade bloc whose member countries have signed a free trade agreement (FTA). Such agreements involve cooperation between at least two countries to reduce trade barriers, import quotas and tariffs, and to increase trade of goods and services with each other. If natural persons are also free to move between the countries, in addition to a free trade agreement, it would also be considered an open border. It can be considered the second stage of economic integration.
Customs unions are a special type of free trade area. All such areas have internal arrangements which parties conclude in order to liberalize and facilitate trade among themselves. The crucial difference between customs unions and free trade areas is their approach to third parties. While a customs union requires all parties to establish and maintain identical external tariffs with regard to trade with non-parties, parties to a free trade area are not subject to this requirement. Instead, they may establish and maintain whatever tariff regime applying to imports from non-parties as deemed necessary. In a free trade area without harmonized external tariffs, to eliminate the risk of trade deflection, parties will adopt a system of preferential rules of origin. (Full article...)
General images - load new batch
-
Image 1An artist's impression of the Archean, the eon after Earth's formation, featuring round stromatolites, which are early oxygen-producing forms of life from billions of years ago. After the Late Heavy Bombardment, Earth's crust had cooled, its water-rich barren surface is marked by continents and volcanoes, with the Moon still orbiting Earth half as far as it is today, appearing 2.8 times larger and producing strong tides. (from Earth)
-
Image 3Earth's land use for human agriculture in 2019 (from Earth)
-
Image 4Tracy Caldwell Dyson, a NASA astronaut, observing Earth from the Cupola module at the International Space Station on 11 September 2010 (from Earth)
-
Image 8"Lucy", the first Australopithecus afarensis skeleton found, was only 1.06 m (3 ft 6 in) tall.
-
Image 9Vitruvian Man by Leonardo da Vinci epitomizes the advances in art and science seen during the Renaissance. (from History of Earth)
-
Image 10Graph showing range of estimated partial pressure of atmospheric oxygen through geologic time (from History of Earth)
-
Image 11A 580 million year old fossil of Spriggina floundensi, an animal from the Ediacaran period. Such life forms could have been ancestors to the many new forms that originated in the Cambrian Explosion. (from History of Earth)
-
Image 12Empires of the world in 1898
-
Image 13Earth's axial tilt causing different angles of seasonal illumination at different orbital positions around the Sun (from Earth)
-
Image 17Obelisk of Axum, Ethiopia
-
Image 18A map of heat flow from Earth's interior to the surface of Earth's crust, mostly along the oceanic ridges (from Earth)
-
Image 19Change in average surface air temperature and drivers for that change. Human activity has caused increased temperatures, with natural forces adding some variability. (from Earth)
-
Image 20A view of Earth with different layers of its atmosphere visible: the troposphere with its clouds casting shadows, a band of stratospheric blue sky at the horizon, and a line of green airglow of the lower thermosphere around an altitude of 100 km, at the edge of space (from Earth)
-
Image 21Tiktaalik, a fish with limb-like fins and a predecessor of tetrapods. Reconstruction from fossils about 375 million years old. (from History of Earth)
-
Image 23Standing Buddha from Gandhara, 2nd century CE
-
Image 25Japanese depiction of a Portuguese carrack. European maritime innovations led to proto-globalization.
-
Image 27Artist's rendition of an oxinated fully-frozen Snowball Earth with no remaining liquid surface water. (from History of Earth)
-
Image 29Fall of the Berlin Wall, 1989
-
Image 31A schematic view of Earth's magnetosphere with solar wind flowing from left to right (from Earth)
-
Image 32Pale orange dot, an artist's impression of Early Earth, featuring its tinted orange methane-rich early atmosphere (from Earth)
-
Image 33Chloroplasts in the cells of a moss (from History of Earth)
-
Image 34Great Mosque of Kairouan, Tunisia, founded 670 CE
-
Image 35Last Moon landing: Apollo 17 (1972)
-
Image 36Peopling of the world, the Southern Dispersal scenario
-
Image 37Earth's history with time-spans of the eons to scale. Ma means "million years ago". (from History of Earth)
-
Image 38Cuneiform inscription, eastern Turkey
-
Image 41A banded iron formation from the 3.15 Ga Moodies Group, Barberton Greenstone Belt, South Africa. Red layers represent the times when oxygen was available; gray layers were formed in anoxic circumstances. (from History of Earth)
-
Image 44Yggdrasil, an attempt to reconstruct the Norse world tree which connects the heavens, the world, and the underworld. (from World)
-
Image 45First airplane, the Wright Flyer, flew on 17 December 1903.
-
Image 47Lithified stromatolites on the shores of Lake Thetis, Western Australia. Archean stromatolites are the first direct fossil traces of life on Earth. (from History of Earth)
-
Image 4813th-century French historiated initial with the three classes of medieval society: those who prayed (the clergy), those who fought (the knights), and those who worked (the peasantry) (from Human history)
-
Image 49Notre-Dame de Paris, France
-
Image 50An animation of the changing density of productive vegetation on land (low in brown; heavy in dark green) and phytoplankton at the ocean surface (low in purple; high in yellow) (from Earth)
-
Image 51Dinosaurs were the dominant terrestrial vertebrates throughout most of the Mesozoic (from History of Earth)
-
Image 53Artist's impression of the enormous collision that probably formed the Moon (from History of Earth)
-
Image 54Angkor Wat temple complex, Cambodia, early 12th century
-
Image 55Shanghai. China urbanized rapidly in the 21st century.
-
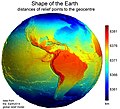
Image 56Earth's western hemisphere showing topography relative to Earth's center instead of to mean sea level, as in common topographic maps (from Earth)
-
Image 57One of the eleven Rock-hewn Churches of Lalibela constructed during the Zagwe dynasty in Ethiopia (from Human history)
-
Image 58A reconstruction of human history based on fossil data. (from History of Earth)
-
Image 61Earth's night-side upper atmosphere appearing from the bottom as bands of afterglow illuminating the troposphere in orange with silhouettes of clouds, and the stratosphere in white and blue. Next the mesosphere (pink area) extends to the orange and faintly green line of the lowest airglow, at about one hundred kilometers at the edge of space and the lower edge of the thermosphere (invisible). Continuing with green and red bands of aurorae stretching over several hundred kilometers. (from Earth)
-
Image 62Artist's conception of Hadean Eon Earth, when it was much hotter and inhospitable to all forms of life. (from History of Earth)
-
Image 63Olmec colossal head, now at the Museo de Antropología de Xalapa
-
Image 64Atomic bombing of Nagasaki, 1945
-
Image 65A reconstruction of Pannotia (550 Ma). (from History of Earth)
-
Image 66A 2012 artistic impression of the early Solar System's protoplanetary disk from which Earth and other Solar System bodies were formed (from Earth)
-
Image 67A pillar at Göbekli Tepe
-
Image 68An artist's impression of ice age Earth at glacial maximum. (from History of Earth)
-
Image 69A computer-generated image mapping the prevalence of artificial satellites and space debris around Earth in geosynchronous and low Earth orbit (from Earth)
-
Image 70A view of Earth with its global ocean and cloud cover, which dominate Earth's surface and hydrosphere; at Earth's polar regions, its hydrosphere forms larger areas of ice cover. (from Earth)
-
Image 71Benin Bronze head from Nigeria
-
Image 72Ajloun Castle, Jordan
-
Image 73The replicator in virtually all known life is deoxyribonucleic acid. DNA is far more complex than the original replicator and its replication systems are highly elaborate. (from History of Earth)
-
Image 74Great Pyramids of Giza, Egypt
-
Image 77A composite image of Earth, with its different types of surface discernible: Earth's surface dominating Ocean (blue), Africa with lush (green) to dry (brown) land and Earth's polar ice in the form of Antarctic sea ice (grey) covering the Antarctic or Southern Ocean and the Antarctic ice sheet (white) covering Antarctica. (from Earth)
-
Image 78Pangaea was a supercontinent that existed from about 300 to 180 Ma. The outlines of the modern continents and other landmasses are indicated on this map. (from History of Earth)
-
Image 79Artist's impression of a Hadean landscape with the relatively newly formed Moon still looming closely over Earth and both bodies sustaining strong volcanism. (from History of Earth)
-
Image 81Artist's impression of Earth during the later Archean, the largely cooled planetary crust and water-rich barren surface, marked by volcanoes and continents, features already round microbialites. The Moon, still orbiting Earth much closer than today and still dominating Earth's sky, produced strong tides. (from History of Earth)
-
Image 83The pale orange dot, an artist's impression of the early Earth which might have appeared orange through its hazy methane rich prebiotic second atmosphere. Earth's atmosphere at this stage was somewhat comparable to today's atmosphere of Titan. (from History of Earth)
-
Image 85Battle during the 1281 Mongol invasion of Japan
-
Image 87Geologic map of North America, color-coded by age. From most recent to oldest, age is indicated by yellow, green, blue, and red. The reds and pinks indicate rock from the Archean.
-
Image 88Trilobites first appeared during the Cambrian period and were among the most widespread and diverse groups of Paleozoic organisms. (from History of Earth)
Megacities of the world - show another
Tianjin is a direct-administered municipality in Northern China on the shore of the Bohai Sea. It is one of the nine national central cities, with a total population of 13,866,009 inhabitants at the time of the 2020 Chinese census. Its metropolitan area, which is made up of 12 central districts (other than Baodi, Jizhou, Jinghai and Ninghe), was home to 11,165,706 inhabitants and is also the world's 29th-largest agglomeration (between Chengdu and Rio de Janeiro) and 11th-most populous city proper.
Tianjin is governed as one of the four municipalities (alongside Beijing, Shanghai, and Chongqing) under the direct administration of the State Council of China. The city borders Hebei Province and Beijing Municipality, bounded to the east by the Bohai Gulf portion of the Yellow Sea. Part of the Bohai Economic Rim, it is the largest coastal city in Northern China and part of the Jing-Jin-Ji megapolis. (Full article...)
Did you know - load new batch

- ... that museum director Alena Aladava rebuilt the Belarusian national art collection in the aftermath of the Second World War?
- ... that the petunia carnage of 2017 led to worldwide economic losses?
- ... that the Cure's Shows of a Lost World has grossed $37.5 million and become their highest-grossing tour to date, despite the band's refusal to use Ticketmaster's dynamic pricing?
- ... that the Central Powers brought their armies under a supreme headquarters in September 1916, 18 months before the Allies did the same?
- ... that American Colossus is a biography of a man who was "the most famous sportsman in the world" and "the most forgotten great athlete in American history"?
- ... that Max Eisenbud helped make Maria Sharapova the world's highest-paid female athlete for more than a decade?
- ... that Hungarians Gyula Bajó and Endre Hevizi, who went on to design stained glass for the Debre Libanos monastery, worked as labourers in a British pottery after the Second World War?
- ... that a photograph of Chili Williams, known as the "Polka Dot Girl", was one of the "two most famous pin-up pictures" of World War II?
Countries of the world - show another

Iraq, officially the Republic of Iraq, is a country in West Asia and a core country in the geopolitical region known as the Middle East. With a population exceeding 46 million, it is the 35th-most populous country. It consists of 18 governorates. The country is bordered by Turkey to the north, Saudi Arabia to the south, Iran to the east, the Persian Gulf and Kuwait to the southeast, Jordan to the southwest, and Syria to the west. The capital and largest city is Baghdad. Iraqi people are diverse; mostly Arabs, as well as Kurds, Turkmen, Yazidis, Assyrians, Armenians, Mandaeans, Persians and Shabakis with similarly diverse geography and wildlife. Most Iraqis are Muslims – minority faiths include Christianity, Yazidism, Zoroastrianism, Mandaeism, Yarsanism and Judaism. The official languages of Iraq are Arabic and Kurdish; others also recognized in specific regions are Assyrian, Turkish, and Armenian.
Starting as early as the 6th millennium BC, the fertile alluvial plains between Iraq's Tigris and Euphrates Rivers, referred to as the region of Mesopotamia, gave rise to some of the world's earliest cities, civilizations, and empires. It was known as a "Cradle of Civilisation" that saw the inventions of a writing system, mathematics, timekeeping, a calendar, astrology, and a law code. Following the Muslim conquest, Baghdad became the capital and the largest city of the Abbasid Caliphate. During the time of the Islamic Golden Age, the city evolved into a significant cultural and intellectual center, and garnered a worldwide reputation for its academic institutions, including the House of Wisdom. It was largely destroyed at the hands of the Mongol Empire in 1258 during the siege of Baghdad, resulting in a decline that would linger through many centuries due to frequent plagues and multiple successive empires. (Full article...)

Related portals
Protected areas of the world - load new batch
-
Image 1

Cranes at Sevan National Park
This is a list of protected areas in Armenia that are categorized as follows: 4 national parks, 3 state reserves, 27 state sanctuaries and 5 botanical gardens. The percentage of protected land in Armenia is approximately 12.89% (2309.0853 km² 891.542819 sq mi). (Full article...) -
Image 2
-
Image 3

Redwood grove in Redwood National Park
According to the California Protected Areas Database (CPAD), in the state of California, United States, there are over 14,000 inventoried protected areas administered by public agencies and non-profits. In addition, there are private conservation areas and other easements. They include almost one-third of California's scenic coastline, including coastal wetlands, estuaries, beaches, and dune systems. The California State Parks system alone has 270 units and covers 1.3 million acres (5,300 km2), with over 280 miles (450 km) of coastline, 625 miles (1,006 km) of lake and river frontage, nearly 18,000 campsites, and 3,000 miles (5,000 km) of hiking, biking, and equestrian trails.
Obtaining an accurate total of all protected land in California and elsewhere is a complex task. Many parcels have inholdings, private lands within the protected areas, which may or may not be accounted for when calculating total area. Also, occasionally one parcel of land is included in two or more inventories. Over 90% of Yosemite National Park for example, is listed both as wilderness by the National Wilderness Preservation System, and as national park land by the National Park Service. The Cosumnes River Preserve is an extreme example, owned and managed by a handful of public agencies and private landowners, including the Bureau of Land Management, the County of Sacramento and The Nature Conservancy. Despite the difficulties, the CPAD gives the total area of protected land at 49,294,000 acres (199,490 km2), or 47.05% of the state (not including easements); a considerable amount for the most populous state in the country. (Full article...) -
Image 4Protected areas of Norway include:
About 17 percent of the mainland of Norway is protected. Of this, ca. 8.3 percent is national parks, 1.3 percent is nature reserves and 4.7 percent otherwise protected. (Full article...) -
Image 5
-
Image 6

Upolu Island, Samoa
This is a list of some protected areas of Samoa which include national parks, reservations, protected nature zones, marine reserves and other areas of significant biodiversity and conservation.
In 1994, Samoa ratified the international and legally binding treaty, the Convention on Biological Diversity to develop national strategies for conservation and sustainable use of biological diversity. In 2010, protected areas in the country cover 5% of land although the government aims to increase protected areas coverage to 15%. (Full article...) -
Image 7The following list of protected areas of British Columbia includes all federally and provincially protected areas within the Canadian province of British Columbia. As of 2015, approximately 15.46% of the province's land area and 3.17% of the province's waters are protected. (Full article...)
-
Image 8

Rock carvings at the Ewaninga Rock Carvings Conservation Reserve
The protected areas of the Northern Territory consists of protected areas managed by the governments of the Northern Territory and Australia and private organisations with a reported total area of 335,527 square kilometres (129,548 sq mi) being 24.8% of the total area of the Northern Territory of Australia. (Full article...) -
Image 9A National Biodiversity Conservation Area (NBCA) is an environmentally protected area in Laos. There are all together 21 different NBCAs in Laos, protecting 29,775 square kilometers. Another 10 NBCAs have been proposed, many of them being treated by authorities as though they were already officially protected. (Full article...)
-
Image 10Protected areas of Tasmania consist of protected areas located within Tasmania and its immediate onshore waters, including Macquarie Island. It includes areas of crown land (withheld land) managed by Tasmanian Government agencies as well as private reserves. As of 2016, 52% of Tasmania's land area has some form of reservation classification, the majority is managed by the Tasmania Parks & Wildlife Service (about 42% of total Tasmanian land area). Marine protected areas cover about 7.9% of state waters.
Within each classification of reserve there may be a variation of IUCN categories Australia is a signatory to the Convention of Biological Diversity and as such has obligations to report the status of its National Reserve System.IUCN provides on its website a prescription for activities consistent with the categorisation system. Changes made to the Nature Conservation Act 2002 in 2014 permit timber harvesting. These changes made in addition to the already established right to access minerals means that many of the IUCN categorisations assigned to individual reserves in Tasmania are no longer fit for purpose. In addition many reserves have had their reserve status downgraded from a class excluding timber harvesting and mineral extraction to ones where these activities are now permitted. This mis-application of the IUCN protected area categories needs to be remedied or the reserves protected land class under the Nature Conservation Act 2002 should be adjusted to reflect its currently assigned IUCN category. (Full article...) -
Image 11The protected areas of Nepal cover mainly forested land and are located at various altitudes in the Terai, in the foothills of the Himalayas and in the mountains, thus encompassing a multitude of landscapes and preserving a vast biodiversity in the Palearctic and Indomalayan realms.
Nepal covers 147,181 km2 (56,827 sq mi) in the central part of the Himalayas. Altitudes range from 67 m (220 ft) in the south-eastern Terai to 8,848 m (29,029 ft) at Mount Everest within a short horizontal span. This extreme altitudinal gradient has resulted in 11 bio-climatic zones ranging from lower tropical below 500 m (1,600 ft) to nival above 5,000 m (16,000 ft) in the High Himalayas, encompassing nine terrestrial ecoregions with 36 vegetation types.
Additionally, nine Ramsar sites were declared between 1988 and 2008. Two wildlife reserves were declared as national parks in 2017. (Full article...) -
Image 12

Bonampak is an ancient Maya archaeological site in the Mexican state of Chiapas, and is a natural monument.
There are currently 225 Protected Natural Areas in Mexico, covering 93.8 million hectares in total. They are protected and administered by the National Commission of Protected Natural Areas (Comisión Nacional de Áreas Naturales Protegidas, or 'CONANP'), a federal agency. CONANP administers:- 77 Mexican National Parks
- 48 biosphere reserves
- 54 flora and fauna protection areas
- 28 Mexican Nature Sanctuaries
- 13 natural resources protection areas
- 5 natural monuments
-
Image 13
Grand Canyon of Yellowstone
The protected areas of the United States are managed by an array of different federal, state, tribal and local level authorities and receive widely varying levels of protection. Some areas are managed as wilderness, while others are operated with acceptable commercial exploitation. As of 2022[update], the 42,826 protected areas covered 1,235,486 km2 (477,024 sq mi), or 13 percent of the land area of the United States. This is also one-tenth of the protected land area of the world. The U.S. also had a total of 871 National Marine Protected Areas, covering an additional 1,240,000 sq mi (3,200,000 km2), or 26 percent of the total marine area of the United States. (Full article...) -
Image 14This is a list of protected areas in Botswana. (Full article...)
-
Image 15

Viru bog in Lahemaa National Park
Protected areas in Estonia are national parks, nature reserves and landscape protection areas (nature parks).
Estonia has five national parks, 167 nature reserves and 152 landscape conservation areas. In addition, there are 116 (118) protected areas with an old (Soviet-era) protection regulation and 537 parks. In total, 18.1% of Estonia are protected nature areas, with Lääne County having the highest percentage (32%) and Põlva County the lowest percentage of protected areas, about 9%. (Full article...)
Selected world maps
-
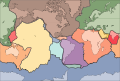
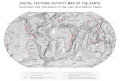
Image 1A plate tectonics map with volcano locations indicated with red circles
-
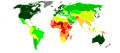
Image 2United Nations Human Development Index map by country (2016)
-
Image 3Time zones of the world
-
Image 41516 map of the world by Martin Waldseemüller
-
Image 5Only a few of the largest large igneous provinces appear (coloured dark purple) on this geological map, which depicts crustal geologic provinces as seen in seismic refraction data
-
Image 6The world map by Gerardus Mercator (1569), the first map in the well-known Mercator projection
-
Image 7Mollweide projection of the world
-
Image 8The Goode homolosine projection is a pseudocylindrical, equal-area, composite map projection used for world maps.
-
Image 9Index map from the International Map of the World (1:1,000,000 scale)
World records
- List of Olympic records in athletics
- List of world records in athletics
- List of junior world records in athletics
- List of world records in masters athletics
- List of world youth bests in athletics
- List of IPC world records in athletics
- List of world records in canoeing
- List of world records in chess
- List of cycling records
- List of world records in track cycling
- List of world records in finswimming
- List of world records in juggling
- List of world records in rowing
- List of world records in speed skating
- List of world records in swimming
- List of IPC world records in swimming
- List of world records in Olympic weightlifting
Topics
Continents of Earth | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||
| ||||||||
| ||||||||
| Cenozoic Era (present–66.0 Ma) |
| ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mesozoic Era (66.0–252 Ma) |
| ||||||||||||
| Paleozoic Era (252–539 Ma) |
| ||||||||||||
| Proterozoic Eon (539 Ma–2.5 Ga) |
| ||||||||||||
| Archean Eon (2.5–4 Ga) | |||||||||||||
| Hadean Eon (4–4.6 Ga) | |||||||||||||
ka = kiloannum (thousand years ago); Ma = megaannum (million years ago); Ga = gigaannum (billion years ago). See also: Geologic time scale • | |||||||||||||
| City proper | |
|---|---|
| Metropolitan area | |
| Urban area/agglomeration | |
| Historical | |
| Related articles | |
| Locations | ||
|---|---|---|
| Related | ||
| Retrospectively recognized expositions | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BIE-recognized Universal expositions | |||||||||||||
| BIE-recognized specialized expositions |
| ||||||||||||
| BIE-recognized horticultural exhibitions (AIPH) | |||||||||||||
| Not BIE- recognized |
| ||||||||||||
†Postponed to 2021 due to the COVID-19 pandemic | |||||||||||||
| Confederations | |
|---|---|
| World Championships | |
| World Cup | |
| Special events | |
| Presidents |
|
| Awards | |
| |||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||
Economic classification of countries | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Three-World Model | |||||
| Gross domestic product (GDP) |
| ||||
| Gross national income (GNI) | |||||
| Wages | |||||
| Wealth | |||||
| Other national accounts | |||||
| Human development | |||||
| Digital divide | |||||
| Net international investment position (NIIP) | |||||
| Technological |
| ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sociological | |||||
| Ecological |
| ||||
| Biological |
| ||||
| Astronomical | |||||
| Eschatological |
| ||||
| Others |
| ||||
| Fictional | |||||
| Organizations | |||||
| Theatres |
| ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Principal participants |
| ||||||||||||||||||
| Timeline |
| ||||||||||||||||||
| Aspects |
| ||||||||||||||||||
| General |
| ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Participants |
| ||||||||||||||||
| Timeline |
| ||||||||||||||||
Categories
Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikispecies
Directory of species -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wikivoyage
Free travel guide -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus
More portals
- Portals with undated maintenance templates
- Manually maintained portal pages with no date
- All manually maintained portal pages
- Portals with triaged subpages
- All portals with triaged subpages
- Portals with named maintainer
- Automated article-slideshow portals with 201–500 articles in article list
- Automated article-slideshow portals with 101–200 articles in article list
- Portals needing placement of incoming links