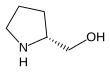
Prolinol
Appearance
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(R/S) 2-pyrrolidinemethanol
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
| |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
| ||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.157.355 | ||
PubChem CID
|
|||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C5H11NO | |||
| Molar mass | 101.15 g/mol | ||
| Appearance | Liquid | ||
| Density | 1.036 g/mL liquid | ||
| Boiling point | 74 to 76 °C (165 to 169 °F; 347 to 349 K) at 2 mmHg | ||
| Hazards | |||
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |||
Main hazards
|
Irritant | ||
| Flash point | 86 °C (187 °F; 359 K) | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
- This article is about a compound used in synthesis of certain stimulants and should not be confused with a stimulant in that class the brand name of which is propalin
Prolinol is a chiral amino-alcohol that is used as a chiral building block in organic synthesis. It exists as two enantiomers: the D and L forms.
Preparation
Prolinol is obtained by reduction of the amino acid proline using lithium aluminium hydride.[1][2] Because proline is cheaply available in high optical purity, enantiomerically pure prolinol is also widely available.
Use
Prolinol is used in broad variety of chemical reactions as chiral ligand, chiral catalyst or chiral auxiliary reagent in the Hajos-Parrish-Eder-Sauer-Wiechert reaction, the Baylis-Hillman reaction, Noyori type reaction and the Michael reaction. [3][4]
See also
References
- ^ Dickman, D. A.; Meyers, A. I.; Smith, G. A.; Gawley, R. E. Reduction of α-Amino Acids: L-Valinol Organic Syntheses, Collected Volume 7, p.530 (1990).
- ^ Enders D.; Fey P.; Kipphardt, H. [1] Organic Syntheses, Collected Volume 8, p.26 (1993).
- ^ Benjamin List (2002). "Proline-catalyzed asymmetric reactions". Tetrahedron. 58 (28): 5573–5590. doi:10.1016/S0040-4020(02)00516-1.
- ^ Shinichi Itsuno, Koichi Ito, Akira Hirao and Seiichi Nakahama (1984). "Asymmetric synthesis using chirally modified borohydrides. Part 2. Enantioselective reduction of ketones with polymeric (S)-prolinol–borane reagent". J. Chem. Soc., Perkin Trans. 1 (12): 2887–2895. doi:10.1039/P19840002887.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)