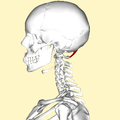
Rectus capitis posterior minor muscle
| Rectus capitis posterior minor muscle | |
|---|---|
 Human skull seen from back (rectus capitis posterior minor shown in red.) | |
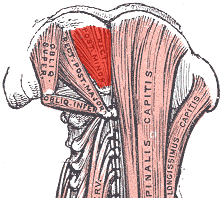 Deep muscles of the back. (rectus capitis posterior minor labeled at top center.) | |
| Details | |
| Origin | Tubercle on the posterior arch of the atlas |
| Insertion | Medial part of the inferior nuchal line of the occipital bone and the surface between it and the foramen magnum |
| Nerve | Branch of the dorsal primary division of the suboccipital nerve |
| Actions | extends the head at the neck, but is now considered to be more of a sensory organ than a muscle |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Musculus rectus capitis posterior minor |
| TA98 | A04.2.02.005 |
| TA2 | 2250 |
| FMA | 32526 |
| Anatomical terms of muscle | |
The rectus capitis posterior minor (or rectus capitis posticus minor, both being Latin for lesser posterior straight muscle of the head) arises by a narrow pointed tendon from the tubercle on the posterior arch of the atlas, and, widening as it ascends, is inserted into the medial part of the inferior nuchal line of the occipital bone and the surface between it and the foramen magnum, and also takes some attachment to the spinal dura mater.
The synergists are the rectus capitus posterior major and obliquus capitis.
Connective tissue bridges were noted at the atlanto-occipital joint between the rectus capitis posterior minor muscle and the dorsal spinal dura. Similar connective tissue connections of the rectus capitis posterior major have been reported recently as well.[1] The perpendicular arrangement of these fibers appears to restrict dural movement toward the spinal cord. The ligamentum nuchae was found to be continuous with the posterior cervical spinal dura and the lateral portion of the occipital bone. Anatomic structures innervated by cervical nerves C1-C3 have the potential to cause headache pain. Included are the joint complexes of the upper three cervical segments, the dura mater, and spinal cord.
The dura-muscular, dura-ligamentous connections in the upper cervical spine and occipital areas may provide anatomic and physiologic answers to the cause of the cervicogenic headache. This proposal would further explain manipulation's efficacy in the treatment of cervicogenic headache.[2]
Additional images
-
Position of rectus capitis posterior minor muscle (shown in red). Animation.
-
Lateral view of human skull (rectus capitis posterior minor shown in red.)
-
Occipital bone. Outer surface.
References
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 401 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 401 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
- ^ Anatomical Connection Between the Rectus Capitis Posterior Major and the Dura Mater. Scali F, Marsili ES, Pontell ME.http://journals.lww.com/spinejournal/Abstract/publishahead/Anatomical_Connection_Between_the_Rectus_Capitis.99006.aspx
- ^ Gary D. Hack, Peter Ratiu, John P. Kerr, Gwendolyn F. Dunn, Mi Young Toh. "Visualization of the Muscle-Dural Bridge in the Visible Human Female Data Set". The Visible Human Project, National Library of Medicine.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
See also
- Atlanto-occipital joint
- Rectus capitis lateralis
- Rectus capitis posterior major muscle
- Rectus capitis anterior muscle
External links
- . GPnotebook https://www.gpnotebook.co.uk/simplepage.cfm?ID=-1174011824.
{{cite web}}: Missing or empty|title=(help) - Anatomy figure: 01:07-01 at Human Anatomy Online, SUNY Downstate Medical Center
- Anatomy photo:01:10-0101 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center
- PTCentral