Retinoic acid receptor beta
Retinoic acid receptor beta (RAR-beta), also known as NR1B2 (nuclear receptor subfamily 1, group B, member 2) is a nuclear receptor that in humans is encoded by the RARB gene.[5][6]
Function
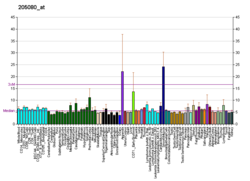
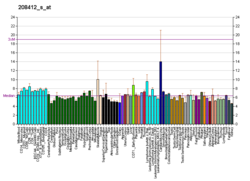
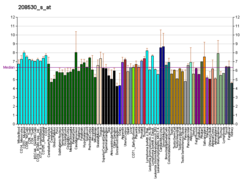
This gene encodes retinoic acid receptor beta, a member of the thyroid-steroid hormone receptor superfamily of nuclear transcriptional regulators. This receptor localizes to the cytoplasm and to subnuclear compartments. It binds retinoic acid, the biologically active form of vitamin A which mediates cellular signalling in embryonic morphogenesis, cell growth and differentiation. It is thought that this protein limits growth of many cell types by regulating gene expression. The gene was first identified in a hepatocellular carcinoma where it flanks a hepatitis B virus integration site. The gene expresses at least two transcript variants; one additional transcript has been described, but its full length nature has not been determined.[5]
Interactions
Retinoic acid receptor beta has been shown to interact with NR4A2.[7]
See also
References
- ^ a b c GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000077092 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ a b c GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000017491 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ a b "Entrez Gene: RARB retinoic acid receptor, beta".
- ^ Mattei MG, de Thé H, Mattei JF, Marchio A, Tiollais P, Dejean A (Oct 1988). "Assignment of the human hap retinoic acid receptor RAR beta gene to the p24 band of chromosome 3". Human Genetics. 80 (2): 189–90. doi:10.1007/BF00702867. PMID 2844650.
- ^ Perlmann T, Jansson L (Apr 1995). "A novel pathway for vitamin A signaling mediated by RXR heterodimerization with NGFI-B and NURR1". Genes & Development. 9 (7): 769–82. doi:10.1101/gad.9.7.769. PMID 7705655.
Further reading
- Dejean A, de Thé H (Jun 1990). "Hepatitis B virus as an insertional mutagene in a human hepatocellular carcinoma". Molecular Biology & Medicine. 7 (3): 213–22. PMID 2170809.
- Sun SY (Jan 2004). "Retinoic acid receptor beta and colon cancer". Cancer Biology & Therapy. 3 (1): 87–8. doi:10.4161/cbt.3.1.686. PMID 14726690.
- Saba N, Jain S, Khuri F (2004). "Chemoprevention in lung cancer". Current Problems in Cancer. 28 (5): 287–306. doi:10.1016/j.currproblcancer.2004.05.005. PMID 15375805.
- Klein O, Grignon Y, Civit T, Auque J, Marchal JC (Sep 2005). "[Methylation status of RARbeta gene promoter in low and high grade cerebral glioma. Comparison with normal tissue. Immuno-histochemical study of nuclear RARbeta expression in low and high grade cerebral glioma cells. Comparison with normal cells. 48 tumors]". Neuro-Chirurgie. 51 (3-4 Pt 1): 147–54. PMID 16389900.
- Katahira M, Knegtel RM, Boelens R, Eib D, Schilthuis JG, van der Saag PT, Kaptein R (Jul 1992). "Homo- and heteronuclear NMR studies of the human retinoic acid receptor beta DNA-binding domain: sequential assignments and identification of secondary structure elements". Biochemistry. 31 (28): 6474–80. doi:10.1021/bi00143a017. PMID 1321662.
- Berrodin TJ, Marks MS, Ozato K, Linney E, Lazar MA (Sep 1992). "Heterodimerization among thyroid hormone receptor, retinoic acid receptor, retinoid X receptor, chicken ovalbumin upstream promoter transcription factor, and an endogenous liver protein". Molecular Endocrinology. 6 (9): 1468–78. doi:10.1210/me.6.9.1468. PMID 1331778.
- van der Leede BJ, Folkers GE, Kruyt FA, van der Saag PT (Oct 1992). "Genomic organization of the human retinoic acid receptor beta 2". Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 188 (2): 695–702. doi:10.1016/0006-291X(92)91112-4. PMID 1332705.
- Prentice A, Matthews CJ, Thomas EJ, Redfern CP (May 1992). "The expression of retinoic acid receptors in cultured human endometrial stromal cells and effects of retinoic acid". Human Reproduction. 7 (5): 692–700. PMID 1379266.
- Shen S, Kruyt FA, den Hertog J, van der Saag PT, Kruijer W (1992). "Mouse and human retinoic acid receptor beta 2 promoters: sequence comparison and localization of retinoic acid responsiveness". DNA Sequence. 2 (2): 111–9. doi:10.3109/10425179109039679. PMID 1663808.
- de Thé H, Vivanco-Ruiz MM, Tiollais P, Stunnenberg H, Dejean A (Jan 1990). "Identification of a retinoic acid responsive element in the retinoic acid receptor beta gene". Nature. 343 (6254): 177–80. doi:10.1038/343177a0. PMID 2153268.
- Hoffmann B, Lehmann JM, Zhang XK, Hermann T, Husmann M, Graupner G, Pfahl M (Nov 1990). "A retinoic acid receptor-specific element controls the retinoic acid receptor-beta promoter". Molecular Endocrinology. 4 (11): 1727–36. doi:10.1210/mend-4-11-1727. PMID 2177841.
- de Thé H, Marchio A, Tiollais P, Dejean A (1988). "A novel steroid thyroid hormone receptor-related gene inappropriately expressed in human hepatocellular carcinoma". Nature. 330 (6149): 667–70. doi:10.1038/330667a0. PMID 2825037.
- Brand N, Petkovich M, Krust A, Chambon P, de Thé H, Marchio A, Tiollais P, Dejean A (Apr 1988). "Identification of a second human retinoic acid receptor". Nature. 332 (6167): 850–3. doi:10.1038/332850a0. PMID 2833708.
- Benbrook D, Lernhardt E, Pfahl M (Jun 1988). "A new retinoic acid receptor identified from a hepatocellular carcinoma". Nature. 333 (6174): 669–72. doi:10.1038/333669a0. PMID 2836738.
- Dejean A, Bougueleret L, Grzeschik KH, Tiollais P (1986). "Hepatitis B virus DNA integration in a sequence homologous to v-erb-A and steroid receptor genes in a hepatocellular carcinoma". Nature. 322 (6074): 70–2. doi:10.1038/322070a0. PMID 3014347.
- Si SP, Tsou HC, Lee X, Peacocke M (Jul 1995). "Effect of cellular senescence and retinoic acid on the expression of cellular retinoic acid binding proteins in skin fibroblasts". Experimental Cell Research. 219 (1): 243–8. doi:10.1006/excr.1995.1224. PMID 7628539.
- Houle B, Pelletier M, Wu J, Goodyer C, Bradley WE (Jan 1994). "Fetal isoform of human retinoic acid receptor beta expressed in small cell lung cancer lines". Cancer Research. 54 (2): 365–9. PMID 8275470.
- Knegtel RM, Katahira M, Schilthuis JG, Bonvin AM, Boelens R, Eib D, van der Saag PT, Kaptein R (Jan 1993). "The solution structure of the human retinoic acid receptor-beta DNA-binding domain". Journal of Biomolecular NMR. 3 (1): 1–17. doi:10.1007/BF00242472. PMID 8383553.
This article incorporates text from the United States National Library of Medicine, which is in the public domain.